Abstract
Thyroid cancer is the most common endocrine malignancy and is predicted to be the 4th most commonly diagnosed cancer by 2030. Approximately one-half of follicular thyroid carcinomas (FTC) contain genetic alterations in RAS family members. Furthermore, Cowden's disease, which is characterized by loss of PTEN, predisposes for the development of FTC in humans. We have shown that thyroid specific expression of HrasG12V at endogenous levels and Pten inactivation (HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-cre mice) leads to the development of FTCs that closely recapitulate human disease, with complete penetrance at one year. In patients, FTCs metastasize via the bloodstream to distant sites, frequently the lungs, bones and brain. The first objective of the study was to determine if these mice developed de novo metastasis to relevant sites. Indeed, spontaneous metastasis to the lungs was observed in 56% of HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-cre mice. We next sought to identify the cellular components within the tumor microenvironment (TME) of FTC that contribute to tumor progression and metastasis via FACS analysis. Surprisingly, a large amount of immune infiltrate was observed. HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre thyroid tumors were comprised of 68.5 ± 11.79% CD45+ cells, in stark contrast to wild-type (WT) thyroids which were comprised of 17.6% CD45+ cells. Further, 53.1 ± 10.9% of the CD45+ cells from HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre thyroid tumors were of myeloid-lineage (CD11b+), consisting of macrophages (F4/80+Gr-1−) and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (F4/80−Gr-1+). Further, HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-cre tumors contained Arginase-1 positive cells as determined by immunohistochemical analysis, supporting an immunosuppressive TME in HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre thyroid tumors. We next evaluated whether or not cytotoxic (CD8+) or helper T cells (CD4+) were recruited to HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre tumors. The majority of T cells in these tumors were double positive for CD4 and CD25, markers of immune suppressive regulatory T cells (Treg). Additionally, we identified Foxp3 positive cells by immunohistochemical analysis of tumor sections, indicating a functional suppressive Treg phenotype in vivo. HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre tumor cell lines displayed increased secretion of SDF-1, I-TAC, CCL9/10, and MCP5, cytokines that have been reported to play a direct role in the chemotaxis of immune cells and thus could contribute to the increased recruitment of myeloid and lymphoid derived cells in HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre tumors. These studies are the first to identify and implicate the interaction between tumor cells and immune cells in Ras-driven thyroid cancer progression, which we hope will lead to the development of more effective therapeutic approaches for aggressive forms of thyroid cancer that target the TME.
Keywords: Hras, Thyroid cancer, Tumor microenvironment, Immunosuppression, Immune cells
Introduction
Thyroid cancer is the most common endocrine malignancy and is predicted to be the 4th most commonly diagnosed cancer by 2030 [1]. Follicular thyroid carcinoma (FTC) is the second most commonly diagnosed form of thyroid cancer. Approximately one-half of FTCs contain genetic alterations in RAS family members, most notably NRAS and HRAS, and these mutations are also frequently found in adenomas, suggesting MAPK activation is an early event in thyroid carcinogenesis [2]. In addition to MAPK signaling, the importance of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in thyroid tumorigenesis has also been acknowledged [3]. Germline mutations that result in loss of PTEN, a negative regulator of PI3K signaling, predisposes for the development of FTC in humans [4]. Further, in addition to activation of the MAPK signaling pathway, RAS can also activate the PI3K pathway. Mutations that lead to MAPK and PI3K activation commonly co-occur in more advanced thyroid cancers, such as poorly differentiated thyroid cancer (PDTC), however these mutations occur throughout the spectrum of disease from benign tumors to FTC to PDTC [5]. Therefore, it has been suggested that activation of MAPK signaling via oncogenic RAS and PI3K signaling cooperate to promote FTC initiation and progression to PDTC.
Despite its well differentiated characteristics, FTCs are often invasive, growing into vascular structures within the thyroid gland and the neck [6] and FTC metastasis most commonly occurs through blood vessels to distant sites in the body including the lungs, bone, and brain [7-9]. Unlike papillary thyroid cancers, metastasis to the lymph nodes is very uncommon in FTC [10,11]. Further, PDTC patients with distant metastasis are more likely to succumb to disease than those with locoregional spread to the lymph nodes [12]. The mechanisms that dictate the spread of FTC/PDTC to distant sites in the body are currently unknown. This observation, along with the decreased responsiveness of these tumor types to standard therapies for thyroid cancer, underscores the need for development of novel treatment strategies for PDTC and the identification of biomarkers that are predictive of disease progression toward a poorly differentiated state.
The bidirectional communication established between tumor cells and their microenvironment is essential for tumor progression. In addition to tumor cells, the tumor microenvironment (TME) is comprised of stromal cells and non-cellular components such as extracellular matrix proteins and growth factors [13]. It is now widely accepted that the interactions between tumor cells and the cellular and non-cellular components of the TME has a profound effect on all aspects of tumorigenesis and can contribute to therapeutic resistance, further complicating the already challenging task of treating cancer [14]. However, our knowledge regarding how oncogenic signals derived from tumor cells changes the TME to promote progression and metastasis of thyroid cancer is minimal.
Tumor infiltrating leukocytes are a hallmark of many different types of cancers and have been shown to directly impact various aspects of tumorigenesis including metastasis and immunosuppression [15-17]. Innate and adaptive immune cells including myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), tumor associated macrophages (TAMs) and regulatory T cells (Tregs) have all been shown to contribute to tumor induced immune suppression and angiogenesis in the TME of breast, head and neck, pancreatic cancers and melanoma [18-21]. While it has been well established that these types of immune cells play a pivotal role in tumorigenesis and resistance to therapy in several cancer types, it is largely unknown as to whether this is the case in thyroid cancer progression.
To identify potential mechanisms of FTC progression in the context of the TME, a novel model of thyroid cancer progression (HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre) was created and the TME dissected to identify factors that influence thyroid tumorigenesis. Activation of Hras and Pten loss cooperate in the development of FTCs that progress to PDTC and metastasize to the lungs in 56% of animals by one year of age. The TME of this model is characterized by an immune-rich tumor stroma comprised of MDSCs, M2-like TAMs, and Foxp3+Tregs. Further, stable tumor cell lines isolated from HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre tumors (Hras1, H245T, H340T) display increased secretion of cytokines that play a direct role in promoting immune suppression and angiogenesis in the TME, including TGFβ1 and MCSF. Unlike Braf driven thyroid tumors [22], the tumor stroma of HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre is not enriched with fibroblasts, type 1 collagen, or lysyl-oxidase, suggesting that activation of closely related MAPK effectors leads to distinct remodeling of the TME in thyroid cancer. Based on these observations, we hypothesize that activation of Ras and loss of Pten in the TME leads to the robust recruitment of immune cells that in turn, directly augment FTC metastasis and immune escape. These findings suggest that novel immunotherapies that have shown promise in other cancer types may provide a viable therapeutic option for advanced thyroid cancers for which current treatment strategies are unfortunately limited.
Materials and Methods
Experimental animals
All animal experiments were performed at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences and approved by the IACUC. The FR-HrasG12V, Ptenfl/fl, and thyroid peroxidase promoter (TPO)-Cre strains have been previously described [23-25]. Mice were on pure 129SVJ genetic backgrounds. Genotypes were determined by PCR as previously described [23-25].
Histology and immunohistochemistry
Thyroid tissues were fixed in 10% formalin buffered acetate and embedded in paraffin. Five-micrometer sections were prepared and histological diagnosis performed by a thyroid pathologist. Paraffin-embedded tissues were dewaxed in xylene and rehydrated in alcohol. Following citrate antigen retrieval (Thermo Scientific), tissue sections were blocked with 12% BSA fraction V for immunofluorescence (Pierce, Rockford, IL, USA) or goat serum for DAB staining and incubated overnight at 4°C with the following antibodies at the specified dilutions: CD45-FITC (BioLegend, 1:200), F4/80 (Abcam, 1:200), Arginase-1 (Santa Cruz, 1:200), and Foxp3 (Abcam, 1:100). For immunofluorescence staining, primary and secondary antibodies were diluted in 12% Fraction V BSA. Immunofluorecence slides were mounted in SlowFade mounting medium containing 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (Invitrogen) and imaged using the EVOS FL Auto Cell Imaging System. Staining with Diaminobenzidine (DAB) was performed using the Elite ABC KIT (Vector Labs) according to the manufacturer's protocol and visualized on a an Olympus DP73 microscope equipped with a Nikon eclipse 8400 camera. Images were acquired using Cell Sens Entry software (Olympus).
Cell lines
Hras1, H340T and H245T tumor cell lines were establish from thyroid tumors from HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre mice. Thyroid tumors were dissected and minced, followed by digestion in a solution of 1 mg/ml collagenase Type I (Sigma) and dispase (Gibco) in Hank's Balanced Salt Solution at 37°C with gentle shaking for 1.5 hours. Following digestion, samples were centrifuged at 1200 rpm for 3 minutes and resuspended in F12 medium (Gibco) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, Gibco), 2 mM L-Glutamine (Gibco), and Penicillin/Streptomycin/Fungizone (Sigma). The samples were then plated into tissue culture flasks and maintained at 37°C in 5% CO2. To ensure removal of contaminating stromal cells and purity of the tumor cell lines, all cell lines were genotyped using primers specific for Pten and Pten recombination [24].
TGFβ ELISA analysis
Hras1 and WT primary thyrocytes were seeded in six-well tissue culture plates in 10% FBS. Once the cells had reached 85% confluency, they were serum-starved for 18 hours. The conditioned medium was collected, briefly centrifuged at 5000 rpm to remove any contaminating debris, and immediately assayed using the Quantikine TGF β1 ELISA (R and D Systems) according to the manufacturer's protocol.
RT-PCR analysis
Total RNA was extracted using the RNeasy Plus Mini Kit (Qiagen). Equal amounts of RNA template were reverse transcribed using the Verso cDNA synthesis kit (Thermo Scientific). Mcsf and 18s mRNA expression was measured using TaqMan Mastermix and pre-designed Taqman assays (Applied Biosystems). Four μl of cDNA from tumor samples and independent passages of each cell line were run in triplicate on a Bio-Rad CFX96. Q-Gene software [26] was used to determine relative normalized expression to 18s. Data analysis was based on the Ct method.
FACS analysis
Tumors from HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre mice were dissected, minced and digested in a solution of serum free DMEM (Gibco) containing 1 mg/ml Collagenase I (Sigma) and 1 mg/ml Dispase (Sigma) for 1.5 hours at 37°C with gentle shaking. The digested samples were then filtered through 70 μm nylon strainers (Fisher Scientific) into 10 cm tissue culture dishes containing 10 mL of PBS. The samples were then treated with 100 ug/mL DNAse I (Sigma) for 5 minutes at room temperature, centrifuged for 5 minutes at 1400 rpm, and resuspended in 1 mL red-cell lysis buffer. The cell suspensions were filtered again through 70 μm nylon strainers, centrifuged, and resuspended in FACS buffer containing 2 mM EDTA. Before incubation with antibodies specific for immune populations, the cell suspensions were treated with Fc receptor blocking antibody (BD biosciences) for 20 minutes on ice in order to block unspecific binding of the constant region (Fc) of primary antibodies to Fc receptors expressed on immune cells within the cell suspensions. After Fc receptor blocking, antibodies specific for the following immune cell populations were added to the cell suspensions and incubated for 25 minutes at 4°C in the dark: CD45-PECy7, Gr-1-APC, F4/80-FITC, CD11B-PE, CD8-FITC, Foxp3-PE, PerCP-Cy5.5 CD25, APC-CD4, and APC-CY7 CD3 (all from Biolegend). The samples were then washed with FACS buffer, centrifuged, and resuspended in FACS buffer containing Zombie Aqua viability dye (Biolegend) and immediately run on a FACS Aria (BD) cell sorter. The data were analyzed using Flow Jo V.10 (Tree Star, INC).
Cytokine secretion analysis
Equal numbers of Braf1, B297T, H340T and Hras1 cells were seeded at a high density in six-well tissue culture plates in 10% FBS. After 24 hours of incubation, the cell lines were at equal densities in the wells at 85% confluency. The cells were then serum-starved for 18 hours to allow for secretion of cytokines for the analysis. The conditioned medium was collected, briefly centrifuged at 5000 rpm to remove any contaminating debris, and immediately assayed using the Proteome Profiler Mouse Chemokine Array (R and D Systems) according to the manufacturer's protocol.
Statistical analysis
All data were analyzed using Prism 6 software (GraphPad). Differences with P values of ≤ 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
HrasG12V and Pten cooperate in the development of FTCs that progress to PDTC in HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre mice
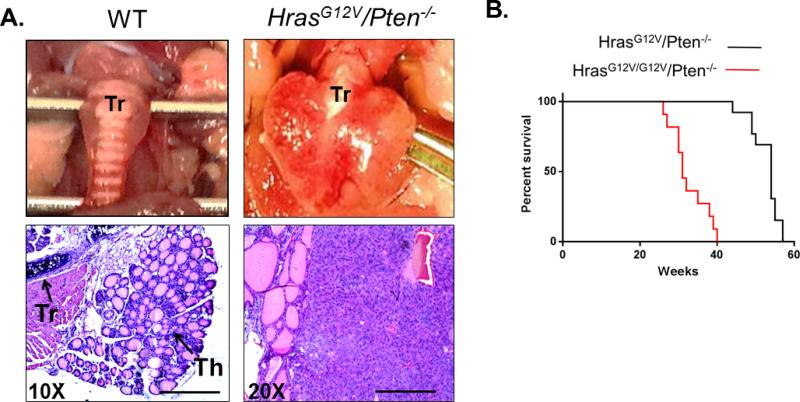
Approximately one-half of FTCs contain genetic alterations in RAS family members [27]. Furthermore, Cowden's disease, which is characterized by loss of PTEN, predisposes for the development of FTC in humans [28]. Given that PTEN is a negative regulator of PI3K signaling, we hypothesized that simultaneous MAPK activation via HrasG12V and PI3K activation via Pten loss would cooperate in FTC initiation and progression to advanced disease. To determine whether HrasG12V and PI3K signaling could cooperate in thyroid cancer development in vivo, FR-HrasG12V mice were crossed with Ptenflox/flox/TPO-Cre mice to generate mice in which HrasG12V is conditionally activated and Pten is homozygously inactivated through thyroidspecific Cre recombinase activation (HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre). The majority of HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre mice (13/16) developed well-differentiated FTC or FTC that had progressed to PDTC by one year of age (Figure 1A). Survival of HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre mice is 100% at the time of sacrifice; however homozygous activation of HrasG12V leads to FTC that progresses to PDTC and is lethal by 40 weeks of age in HrasG12V/G12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre mice (Figure 1B).
Figure 1.
HrasG12V and Pten loss leads to FTCs that progress to PDTC in HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre mice. (A) Top panel: Gross histology of wild-type (WT, left) and HrasG12V/Pten−/− (right) thyroid at 50 weeks of age. Tr=Trachea. HrasG12V/Pten−/− thyroid is significantly enlarged. (A) Bottom panel: H and E staining of 5 μm thick tissue sections from WT (left) and HrasG12V/Pten−/− (right) thyroid tissue. Th=Thyroid tissue, Tr=Trachea. WT thyroid contains organized follicles filled with colloid, in contrast to HrasG12V/Pten−/− thyroids, in which the normal follicular architecture is disrupted. 20X magnification, scale bar is 100 μM. (B) Survival of mice with heterozygous activation of HrasG12V (black line) is 100% at one year of age, while homozygous activation of HrasG12V (red line) is lethal by 40 weeks of age, with no mice surviving past this time point.
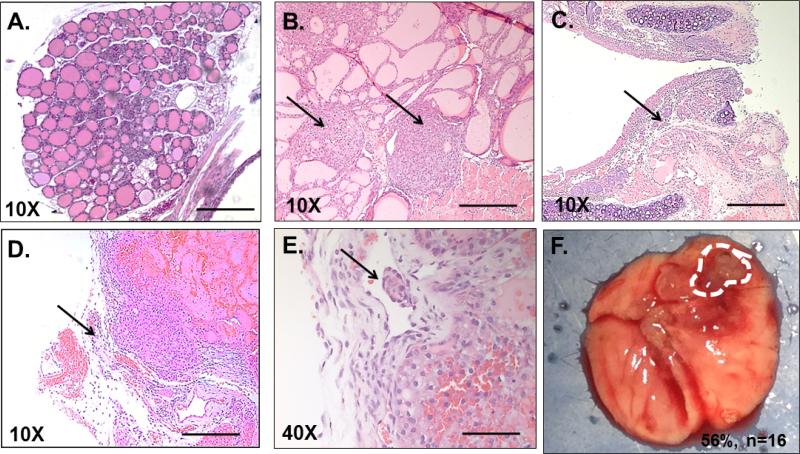
HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre tumors are multifocal (Figure 2B) and display many of the classical hallmarks of high grade human FTC and PDTC including extrathyroidal extension and invasion into surrounding tracheal cartilage and soft tissue (Figures 2C and 2D), as well as lymphovascular invasion (Figure 2E). In patients, FTCs metastasize primarily via the bloodstream to distant sites, frequently the lungs, bones and brain [7,8]. Our next objective was to determine if HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre mice developed de novo metastasis to relevant sites. Although there was no detection of macro-metastases to the bones and/or brain, spontaneous metastasis to the lungs was observed in 56% (n=9/16) of HrasG12V/Ptenhom/TPO-Cre mice at one year of age (Figure 2F).
Figure 2.
HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre mice develop tumors with features of classical and aggressive FTC that metastasize to the lungs. H and E stained 5 μm thick tumor sections from wild type and HrasG12V/Pten−/− thyroid sections. (A) 10X image of wild type thyroid. Scale bar=200 μM. (B) 10X image of HrasG12V/Pten−/− tumor tissue with multiple foci (arrows). (C) 10X image of tumor tissue invading into tracheal cartilage (arrow). (D). 10X image of tumor displaying extrathyroidal extension into surrounding soft tissue (arrow). (E) 40X image showing invasion of tumor tissue into lymph vessel (arrow). Scale bar=50 μM. (F) Gross histological image of lungs from a HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre mouse, dashed line highlights the perimeter of metastatic nodule. By one year of age, 56% of HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre mice (n=16) with FTC develop metastasis to the lungs.
Immune cells are recruited to HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre tumors
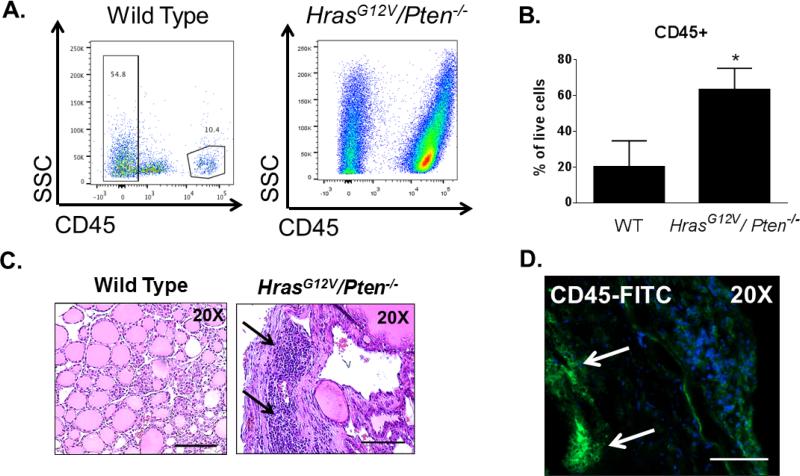
We next sought to identify the cellular components within the tumor microenvironment (TME) of FTC that contribute to tumor progression and metastasis. In order to quantify the overall number of immune cells within the TME, FACS analysis was performed on whole HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre thyroid tumors. Strikingly, a large quantity of immune infiltrate was observed. HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre thyroid tumors were comprised of 68.5 ± 11.79% CD45+ cells, in stark contrast to wild-type (WT) thyroids which were comprised of 20.2 ± 14.5% CD45+ cells (Figures 3A and 3B). Histological analysis of H & E stained tumor sections from HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre mice revealed populations of cells with similar morphology to leukocytes (Figure 3C, arrows). We further confirmed immune recruitment to HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre tumors via immunostaining with CD45 (Figure 3D, arrows), a cell surface marker expressed on all immune cells [29].
Figure 3.
Robust recruitment of immune cells to HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre tumors. (A) Representative FACS analysis of CD45+ (immune) cells in pooled wild type thyroids (left) and a HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre tumor (right). (B) Quantification of the percentage of CD45+ cells detected out of all live, single cells analyzed from 2 separate pools of 10 wild-type (WT) thyroids and 8 HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre tumors. (C) 20X images of H and E stained sections from WT (left) or HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre tumor tissue (right). Arrows point to immune infiltration. Scale bar=100 μm. (D) 20X image of HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre tumor section immunostained with CD45-FITC antibody (green). Arrows point to clusters of CD45+ cells. Nuclei are counterstained with DAPI. Scale bar=100 μm.
Myeloid derived suppressor cells and macrophages are recruited to HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre tumors
Immune infiltration into the TME has been well documented in many different solid tumor types and can play a pivotal role in dictating tumor progression. Further, recent studies suggest the involvement of myeloid and lymphoid derived cell types in thyroid cancer pathogenesis [30-32]. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) and macrophages are myeloid derived cell types that have been shown to promote angiogenesis, provide key growth factors for tumor cells, and suppress the tumor killing capacity of innate and adaptive immune cells [33,34].
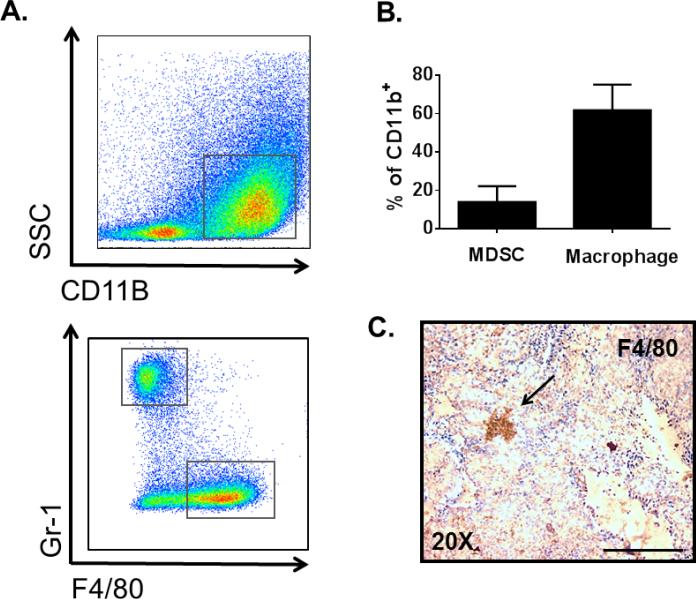
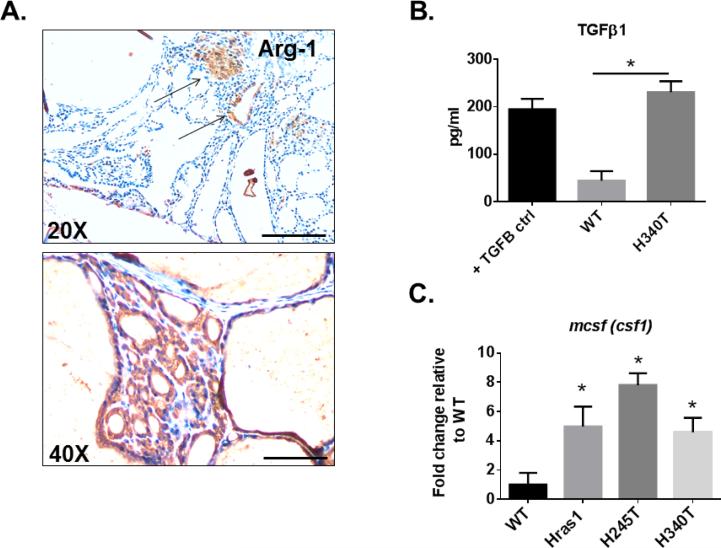
Using FACS analysis with cell-surface specific antibodies, we first characterized the myeloid compartment (MDSCs and macrophages) of HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre thyroid tumors (Figures 4A and 4B). Of all CD45+ cells, 53.1 ± 10.9% were of myeloid-lineage (CD11b+), consisting of 60.1 ± 16.8% non-classical macrophages (F4/80+Gr-1−) and 19 ± 7.6% MDSCs (F4/80−Gr-1+). The presence of macrophages and their tumor location was further validated in HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre via immunohistochemical analysis of tumor sections with F4/80 antibody (Figure 4C), which revealed macrophage infiltration into the tumor. We next determined whether the macrophages in HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre tumors were polarized toward a tumor promoting M2 phenotype in the TME. Immunohistochemical analysis of HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre tumor sections with anti-Arginase-1 (Arg-1), a marker expressed by M2 macrophages, revealed positive cells within the tumors (Figure 5A). Further, stable tumor cell lines isolated from HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre tumors (Hras1, H245T, H340T) displayed increased secretion of TGFβ1 and expression of Mcsf, cytokines that can induce polarization of macrophages toward a tumor-promoting M2 phenotype (Figures 5B and 5C).
Figure 4.
Macrophages and MDSCs are recruited to HrasG12V/Pten−/− tumors. (A) Top: Representative FACS analysis of myeloid (CD11b+) cells within a HrasG12V/Pten−/− thyroid tumor. Bottom: Representative FACS analysis of macrophage (F4/80+Gr-1-) and MDSC (F4/80−Gr-1+) populations within a HrasG12V/Pten−/− thyroid tumor. (B) Average percentages of MDSCs and Macrophages out of all myeloid derived cells (CD11b+) in HrasG12V/Pten−/− thyroid tumors (N=8). (C) 20X image of 5 μm thick HrasG12V/Pten−/− tumor section immunostained with F4/80 to confirm presence of macrophages (arrow) Scale bar=100 μm.
Figure 5.
HrasG12V/Pten−/− tumors are positive for Arginase-1 and express cytokines that induce M2 polarization. (A) 20X (top) and 40X (bottom) images of 5 μm thick HrasG12V/Pten−/− tumor sections immunostained with Arginase-1, a marker of M2 polarization. Scale bar=100 μm for 20X image, 200 μm for 40X. (B) Elisa analysis of TGFβ1 secretion from primary wild-type (WT) thyrocytes and tumor cells isolated from a HrasG12V/Pten−/− tumor (H340T). (C) RT-PCR analysis of mcsf expression in primary WT thyrocytes and three independent tumor cell lines isolated from HrasG12V/Pten−/− tumors (Hras1, H245T, and H340T).
HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre tumors contain significant numbers of CD4+ T cells, but very few CD8+ T cells
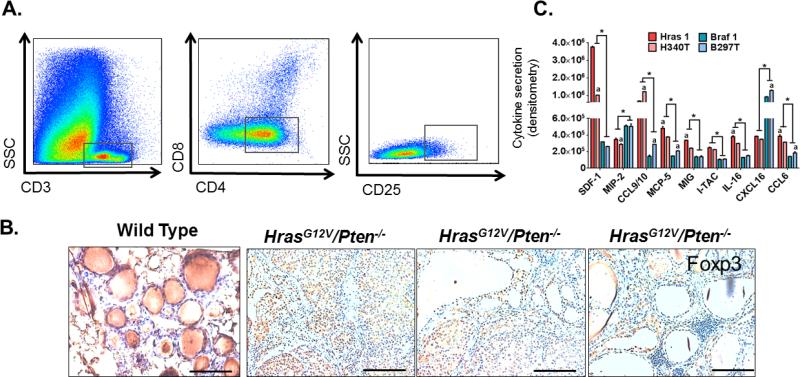
Cytotoxic T cells (CD11b-CD3+CD8+) and T helper cells (CD11b−CD3+CD4+) are lymphoid derived immune cells that can aid directly and indirectly in the destruction of tumor cells. However, in the TME these cells types are often induced into a state of anergy by tumor cells, MDSCs, and macrophages, allowing the tumor to avoid detection and destruction by the immune system [35,36]. Using FACS analysis, the populations of cytotoxic (CD8+) or helper T cells (CD4+) recruited to HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre tumors were evaluated. The majority of T cells in HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre tumors were identified as CD4+ T cells, with very few CD8+ T cells identified by FACS analysis (Figure 6A). Due to the large proportion of CD4+ T cells in the lymphoid compartment, we sought to determine whether these cells were anti-tumorigenic effector (Teff) or pro-tumorigenic, immunosuppressive regulatory (Treg) T cells. FACS analysis revealed a double positive CD4+ CD25+ T cell population, indicating the presence of Tregs (versus Teffs) within HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre tumors (Figure 6A). Tumor sections were then immunostained for Foxp3, a transcription factor specifically expressed by Tregs. Foxp3 nuclear staining was present within HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre tumors, indicating active immunosuppression [37] within the TME (Figure 6B). Although we did detect a significant amount of background DAB staining in wild-type thyroid tissue (Figure 6B, far left), this is non-specific staining due to the presence of colloid within the thyroid follicles and no nuclear staining of Foxp3 was detected. Cytokine analysis of conditioned medium from independently isolated HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre tumor cell lines (Hras1 and H340T) revealed significant differences in secretions in comparison to cell lines isolated from BrafV600E/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre tumors (Braf1 and B297T) (Figure 6C). Despite the variability in cytokine secretions of SDF-1, ITAC, CCL9/10, and IL-16 observed between the two independently isolated Hras tumor-derived cell lines, the overall secretion of these cytokines in both cell lines was significantly higher than that of both Braf tumor-derived cell lines. In contrast, MIP-2 and CXCL16 secretion levels were significantly higher in both Braf-driven cell lines in comparison to both Hras-driven cell lines. These factors have been reported to play a direct role in the chemotaxis of immune cells and thus could contribute to the differential recruitment of myeloid and lymphoid derived cell types observed between these two tumor subtypes.
Figure 6.
Recruitment of immunosuppressive Tregs to HrasG12V/Pten−/− thyroid tumors. (A) Representative image of FACS analysis showing gating used to identify T cell populations. CD3+ cells (T-cells) were gated out of all CD45+CD11b− immune cells and further classified according to CD8 expression (cytotoxic T cells) and CD4 expression (T helper cells). CD4 T cells were classified as regulatory T cells (Treg) based on expression of CD25. (B) 20X images of 5 μm thick WT or HrasG12V/Pten−/− tumor tissue sections immunostained with Foxp3, a transcription factor exclusively expressed by immunosuppressive regulatory T cells. In WT thyroid, non-specific DAB staining occurs in thyroid follicles due to presence of colloid, however there no observed Foxp3 nuclear staining in thyrocytes or T-cell populations. Scale bar=100 μm. (C) Cytokine densitometry analysis from conditioned medium isolated from independent tumor cell lines derived from BrafV600E/Pten−/− (Braf1, B297T) and HrasG12V/Pten−/− (Hras1, H340T) thyroid tumors. *, P<0.01, significant difference observed between genotypes (Hras1 versus Braf 1, H340T versus B297T); a, P<0.05, significant difference between values obtained from cell lines of the same genotype (Hras1 versus H340T, Braf1 versus B297T) based on two-way ANOVA with post-hoc analysis (Tukey).
Discussion
Solid tumors are not just a homogenous mass of tumor cells, but instead a complex ecosystem to which many different cell types are recruited and corrupted by tumor cells to serve as accessories to the crime. The TME is formed by communication networks that are established between transformed cells and non-malignant immune and non-immune derived cells, which often function to promote all aspects of tumorigenesis [38]. In the last decade, there has been an exponential increase in studies that address the effect of the TME on tumor progression, yet most focus on one cell type or matrix component versus the cross-talk between multiple components. In this study, we dissected the immune-derived cellular components within the TME of thyroid cancer in order to understand how the presence of these cell types contributes to thyroid cancer progression.
After BRAFV600E, RAS mutations are the second most common mutation in thyroid cancer and are found with increased frequency in FTC and PDTC as opposed to other thyroid tumor subtypes [27]. Our data demonstrate that thyroid specific activation of HrasG12V and PI3K in mice leads to the development of FTC/PDTCs that metastasize to the lungs by one year of age. Recent studies have demonstrated that mutations in RAS not only alter intracellular signaling in tumor cells, but also modulate the tumor microenvironment by inducing various pro-tumorigenic factors such as TGFβ1 [39,40]. Further, oncogenic RAS is heavily implicated in the recruitment and immunosuppression of immune cells in the TME [41-44]. In agreement with these observations, our data demonstrate that activation of Hras and PI3K signaling in thyrocytes results in the development of an immune rich tumor stroma in HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre tumors, characterized by robust recruitment of macrophages, MDSCs, and Foxp3+Tregs (Figure 7). In this model, we propose that activation of HrasG12V and loss of Pten in thyroid tumor cells leads to upregulation and secretion of factors that recruit both myeloid and lymphoid derived cells to the TME. Via the action of tumor and stromal derived cytokines, macrophages, MDSCs, and Tregs are induced toward a protumorigenic phenotype. We hypothesize that these cells in turn secrete factors that support tumor cell growth, immune suppression, and angiogenesis-ultimately leading to tumor progression and metastasis.
Figure 7.
Proposed model of HrasG12V driven remodeling of the TME that contributes to progression of thyroid cancer. Activation of HrasG12V and loss of Pten in thyroid cells leads to transformation of thyroid epithelial cells and development of FTCs that progress to PDTC. HrasG12V/Pten−/− tumor cells stimulate the recruitment of myeloid and lymphoid derived immune cells, including macrophages, CD4+ Tregs, and MDSCs, to the TME via secretion of key cytokines that are chemotactic for these cell types. HrasG12V/Pten−/− tumor cell derived TGFβ1 and MCSF induces macrophages, CD4+ T cells, and MDSCs to upregulate immune suppressive molecules including IL-10, TGFβ, and CTLA4, as well as pro-angiogenic factors such as VEGFA. This results in further immune suppression and angiogenesis in the TME, promoting thyroid cancer progression.
HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre tumors contained a striking amount of immune infiltration in comparison to WT thyroids, which contain at most 20% CD45+ cells. Both myeloid and lymphoid derived immune cells are prevalent in HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre tumors, including macrophages, MDSCs, and Treg cells, however cytotoxic CD8+ T cell numbers are very rare. Unlike BrafV600E/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre tumors [22], activation of HrasG12V in the thyroid did not result in enhanced fibroblast recruitment or remodeling of the tumor matrix via increased collagen deposition (data not shown). These data indicate that in the context of Pten loss, activation of Hras, but not Braf, results in a robust recruitment of immune cells to the TME of thyroid cancer, which promotes tumor progression and potentially metastasis. We are intrigued that the activation of closely associated MAPK pathway effectors in the same tissue type results in the development of drastically different tumor landscapes. Although our results are consistent with mounting evidence demonstrating that activation of RAS in tumor cells leads to recruitment of immune cells to the TME [40,45], future studies are needed to unravel the molecular basis by which RAS and RAF activation results in the differential recruitment of distinct cell types to the TME of thyroid cancer. Cytokine arrays indicate that HrasG12V/Pten−/− tumor cells display increased secretion of factors that are chemotactic for MDSCs, T-cells, and macrophages in comparison to BrafV600E/Pten−/− tumor cells, and more careful molecular analysis is needed to determine how these MAPK effectors differentially regulate cytokine and chemokine production and secretion.
Eighty percent of all myeloid cells in HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre tumors were identified as macrophages or MDSCs (60% and 20%, respectively). These cell types promote angiogenesis, provide key growth factors for tumor cells, and suppress the tumor killing capacity of innate and adaptive immune cells-including T cells [36]. Tregs suppress the anti-tumor effects of antigen presenting cells and cytotoxic T cells in the TME. A high ratio of Tregs versus CD8+ T cells in the TME is predictive of a poor prognosis in breast cancer [46]. The majority of all T cells in HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre tumors were identified as Tregs while less than 1% were CD8+. We hypothesize that the known pro-tumorigenic effects exerted by Tregs are exacerbated by the lack of CD8+ T cells in the TME, which collectively contributes to a more aggressive tumor phenotype. In addition, Tregs were Foxp3+, indicating that these cells are actively functioning as immune suppressors in the TME of HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre tumors.
We found that tumor cells derived from HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre tumors secrete high levels of TGFβ1 and M-CSF, which are cytokines that induce recruitment of proliferation of MDSCs, macrophages, and also inhibit the cytotoxic function of CD8+ T cells and CD4+ T cells [47-50]. Further, these cytokines also induce the polarization of macrophages toward an M2 phenotype [51]. It is therefore likely that these cytokines contribute to macrophage recruitment and polarization in the TME of HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre tumors, and future studies will test this hypothesis as well as identify additional tumor-promoting roles of these cytokines in this model.
Arginase-1 metabolizes L-arginine, which is necessary for the function of T cells [51]. Immunohistochemical analysis of HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre tumors revealed Arginase-1 positive cells in the TME. Arginase-1 is expressed by M2 macrophages in mice and is routinely used as a marker of macrophage polarization [52-54], however its expression is not exclusive to M2 macrophages [55]. It is possible that macrophages and/or other cell types including tumor cells and MDSCs express Arginase-1 in the TME of HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre tumors; however regardless of the source of Arginase-1, its presence is highly suggestive of active immunesuppression within the TME. Future studies will identify the cell type(s) that express Arginase-1 in HrasG12V/Pten−/−/TPO-Cre tumors to better understand their roles in promoting tumor progression.
Much emphasis has been placed on the development of treatments for thyroid cancers that target common oncogenic mutations seen in this disease. However, the use of MAPK pathway inhibitors in advanced disease has been modest, suggesting that in addition to the oncogenic mutations in the tumor cells, there are other factors within the TME that contribute to therapeutic resistance. In recent years, immune checkpoint inhibitors such as CTLA-4 and PD-1 antibodies, which work to activate the immune cells in the TME to attack tumor cells, have shown great promise in treating human melanoma, bladder, and lung cancers [56,57]. Our data suggests that thyroid cancer patients harboring RAS mutations may benefit from these treatments as well, and futures studies are needed to validate our findings in human thyroid tumors.
The TME is essential for tumorigenesis; however, few studies address the effects of tumor cell on the surrounding stroma and the reciprocal effects of the stroma on tumor cell behavior. In order to unravel the molecular mechanisms by which thyroid tumors escape immune surveillance and are resistant to targeted therapies, we must acquire a global perspective of the TME and acknowledge its complexity. This study is the first to identify and implicate the interaction between tumor cells and immune cells in Ras-driven thyroid cancer progression, opening the door to more effective therapeutic approaches for aggressive forms of thyroid cancer that target multiple components of the TME.
Acknowledgments
Financial Support
This work was supported by the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences CTSA grant NID UL1TR000039; The National Institute of General Medical Sciences supported this work through the Center for Microbial Pathogenesis and Host Inflammatory Responses at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences COBRE Grant 1P20GM103625-02; The American Thyroid Association/Thyca research grant (A. Franco); UAMS Envoys Seeds of Science Award (A. Franco).
Footnotes
Conflicts of Interest
The authors disclose no potential conflicts of interest.
References
- 1.Rahib L, Smith BD, Aizenberg R, Rosenzweig AB, Fleshman JM, et al. Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: the unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res. 2014;74:2913–2921. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-0155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gupta N, Dasyam AK, Carty SE, Nikiforova MN, Ohori NP, et al. RAS mutations in thyroid FNA specimens are highly predictive of predominantly low-risk follicular-pattern cancers. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98:E914–922. doi: 10.1210/jc.2012-3396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Saji M, Ringel MD. The PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway in initiation and progression of thyroid tumors. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010;321:20–28. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2009.10.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Son EJ, Nosé V. Familial follicular cell-derived thyroid carcinoma. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2012;3:61. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2012.00061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hou P, Liu D, Shan Y, Hu S, Studeman K, et al. Genetic alterations and their relationship in the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway in thyroid cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:1161–1170. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-1125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.McHenry CR, Phitayakorn R. Follicular adenoma and carcinoma of the thyroid gland. Oncologist. 2011;16:585–593. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2010-0405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Muresan MM, Olivier P, Leclere J, Sirveaux F, Brunaud L, et al. Bone metastases from differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Endocrine Relat Cancer. 2008;15:37–49. doi: 10.1677/ERC-07-0229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lin JD, Chao TC, Hsueh C. Follicular thyroid carcinomas with lung metastases: a 23-year retrospective study. Endocr J. 2004;51:219–225. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.51.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sevinc A, Buyukberber S, Sari R, Baysal T, Mizrak B. Follicular thyroid cancer presenting initially with soft tissue metastasis. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2000;30:27–29. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyd007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Schmid KW. Lymph node and distant metastases of thyroid gland cancer : Metastases in the thyroid glands. Pathologe. 2015;36:171–175. doi: 10.1007/s00292-015-0071-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kim HJ, Sung JY, Oh YL, Kim JH, Son YI, et al. Association of vascular invasion with increased mortality in patients with minimally invasive follicular thyroid carcinoma but not widely invasive follicular thyroid carcinoma. Head Neck. 2014;36:1695–1700. doi: 10.1002/hed.23511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ibrahimpasic T, Ghossein R, Carlson DL, Nixon I, Palmer FL, et al. Outcomes in patients with poorly differentiated thyroid carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99:1245–1252. doi: 10.1210/jc.2013-3842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Joyce JA, Pollard JW. Microenvironmental regulation of metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:239–252. doi: 10.1038/nrc2618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Trédan O, Galmarini CM, Patel K, Tannock IF. Drug resistance and the solid tumor microenvironment. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2007;99:1441–1454. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djm135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kitamura T, Qian BZ, Pollard JW. Immune cell promotion of metastasis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015;15:73–86. doi: 10.1038/nri3789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gajewski TF, Schreiber H, Fu YX. Innate and adaptive immune cells in the tumor microenvironment. Nat Immunol. 2013;14:1014–1022. doi: 10.1038/ni.2703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ghirelli C, Hagemann T. Targeting immunosuppression for cancer therapy. J Clin Invest. 2013;123:2355–2357. doi: 10.1172/JCI69999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Cannarile MA, Ries CH, Hoves S, Ruttinger D. Targeting tumor-associated macrophages in cancer therapy and understanding their complexity. Oncoimmunology. 2014;3:e955356. doi: 10.4161/21624011.2014.955356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kurahara H, Shinchi H, Mataki Y, Maemura K, Noma H, et al. Significance of M2-polarized tumor-associated macrophage in pancreatic cancer. J Surg Res. 2011;167:e211–219. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2009.05.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Pak AS, Wright MA, Matthews JP, Collins SL, Petruzzelli GJ, et al. Mechanisms of immune suppression in patients with head and neck cancer: presence of CD34(+) cells which suppress immune functions within cancers that secrete granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Clin Cancer Res. 1995;1:95–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Chattopadhyay S, Chakraborty NG, Mukherji B. Regulatory T cells and tumor immunity. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2005;54:1153–1161. doi: 10.1007/s00262-005-0699-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Jolly LA, Novitskiy SV, Owens P, Massoll N, Cheng N, et al. Fibroblast-mediated collagen remodeling within the tumor microenvironment facilitates progression of thyroid cancers driven by BrafV600E and Pten loss. Cancer Res. 2016;76:1804–1813. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-2351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Franco AT, Malaguarnera R, Refetoff S, Liao XH, Lundsmith E, et al. Thyrotrophin receptor signaling dependence of Braf-induced thyroid tumor initiation in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;108:1615–1620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1015557108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Miller KA, Yeager N, Baker K, Liao XH, Refetoff S, et al. Oncogenic Kras requires simultaneous PI3K signaling to induce ERK activation and transform thyroid epithelial cells in vivo. Cancer Res. 2009;69:3689–3694. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-0024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Chen X, Mitsutake N, LaPerle K, Akeno N, Zanzonico P, et al. Endogenous expression of Hras(G12V) induces developmental defects and neoplasms with copy number imbalances of the oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:7979–7984. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0900343106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Muller PY, Janovjak H, Miserez AR, Dobbie Z. Processing of gene expression data generated by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Biotechniques. 2002;32:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Fukahori M, Yoshida A, Hayashi H, Yoshihara M, Matsukuma S, et al. The associations between RAS mutations and clinical characteristics in follicular thyroid tumors: new insights from a single center and a large patient cohort. Thyroid. 2012;22:683–689. doi: 10.1089/thy.2011.0261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ngeow J, Mester J, Rybicki LA, Ni Y, Milas M, et al. Incidence and clinical characteristics of thyroid cancer in prospective series of individuals with Cowden and Cowden-like syndrome characterized by germline PTEN, SDH, or KLLN alterations. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96:2063–2071. doi: 10.1210/jc.2011-1616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Donovan JA, Koretzky GA. CD45 and the immune response. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1993;4:976–985. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V44976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Imam S, Paparodis R, Sharma D, Jaume JC. Lymphocytic profiling in thyroid cancer provides clues for failure of tumor immunity. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2014;21:505–516. doi: 10.1530/ERC-13-0436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Bastman JJ, Serracino HS, Zhu Y, Koenig MR, Mateescu V, et al. Tumor-Infiltrating T Cells and the PD-1 Checkpoint Pathway in Advanced Differentiated and Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016;101:2863–2873. doi: 10.1210/jc.2015-4227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ryder M, Gild M, Hohl TM, Pamer E, Knauf J, et al. Genetic and pharmacological targeting of CSF-1/CSF-1R inhibits tumor-associated macrophages and impairs BRAF-induced thyroid cancer progression. PloS one. 2013;8:e54302. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lindau D, Gielen P, Kroesen M, Wesseling P, Adema GJ. The immunosuppressive tumour network: myeloid-derived suppressor cells, regulatory T cells and natural killer T cells. Immunology. 2013;138:105–115. doi: 10.1111/imm.12036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Noy R, Pollard JW. Tumor-associated macrophages: from mechanisms to therapy. Immunity. 2014;41:49–61. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.06.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.McGray AJ, Hallett R, Bernard D, Swift SL, Zhu Z, et al. Immunotherapy-induced CD8+ T cells instigate immune suppression in the tumor. Mol Ther. 2014;22:206–218. doi: 10.1038/mt.2013.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Croci DO, Zacarias Fluck MF, Rico MJ, Matar P, Rabinovich GA, et al. Dynamic cross-talk between tumor and immune cells in orchestrating the immunosuppressive network at the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2007;56:1687–1700. doi: 10.1007/s00262-007-0343-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Mercer F, Unutmaz D. The biology of FoxP3: a key player in immune suppression during infections, autoimmune diseases and cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2009;665:47–59. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-1599-3_4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Quail DF, Joyce JA. Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat Med. 2013;19:1423–1437. doi: 10.1038/nm.3394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Wang SE, Yu Y, Criswell TL, DeBusk LM, Lin PC, et al. Oncogenic mutations regulate tumor microenvironment through induction of growth factors and angiogenic mediators. Oncogene. 2010;29:3335–3348. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Ji H, Houghton AM, Mariani TJ, Perera S, Kim CB, et al. K-ras activation generates an inflammatory response in lung tumors. Oncogene. 2006;25:2105–2112. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Sparmann A, Bar-Sagi D. Ras-induced interleukin-8 expression plays a critical role in tumor growth and angiogenesis. Cancer Cell. 2004;6:447–458. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2004.09.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Maudsley DJ, Bateman WJ, Morris AG. Reduced stimulation of helper T cells by Ki-ras transformed cells. Immunol. 1991;72:277–281. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Testorelli C, Bussini S, De Filippi R, Marelli O, Orlando L, et al. Dacarbazine-induced immunogenicity of a murine leukemia is attenuated in cells transfected with mutated K-ras gene. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 1997;16:15–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Clark CE, Beatty GL, Vonderheide RH. Immunosurveillance of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: insights from genetically engineered mouse models of cancer. Cancer Lett. 2009;279:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2008.09.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Bayne LJ, Beatty GL, Jhala N, Clark CE, Rhim AD, et al. Tumor-derived granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor regulates myeloid inflammation and T cell immunity in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Cell. 2012;21:822–835. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.04.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Ruffell B, Au A, Rugo HS, Esserman LJ, Hwang ES, et al. Leukocyte composition of human breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109:2796–2801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1104303108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Chitu V, Stanley ER. Colony-stimulating factor-1 in immunity and inflammation. Curr Opin Immunol. 2006;18:39–48. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2005.11.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Oh SA, Li MO. TGF-β: guardian of T cell function. J Immunol. 2013;191:3973–3979. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1301843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Ng TH, Britton GJ, Hill EV, Verhagen J, Burton BR, et al. Regulation of adaptive immunity; the role of interleukin-10. Front Immunol. 2013;4:129. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Cao Q, Wang Y, Zheng D, Sun Y, Lee VW, et al. IL-10/TGF-beta-modified macrophages induce regulatory T cells and protect against adriamycin nephrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010;21:933–942. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2009060592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Rodriguez PC, Zea AH, DeSalvo J, Culotta KS, Zabaleta J, et al. L-arginine consumption by macrophages modulates the expression of CD3 zeta chain in T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 2003;171:1232–1239. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.3.1232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Doedens AL, Stockmann C, Rubinstein MP, Liao D, Zhang N, et al. Macrophage expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha suppresses T-cell function and promotes tumor progression. Cancer Res. 2010;70:7465–7475. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Sharda DR, Yu S, Ray M, Squadrito ML, De Palma M, et al. Regulation of macrophage arginase expression and tumor growth by the Ron receptor tyrosine kinase. J Immunol. 2011;187:2181–2192. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Sica A, Mantovani A. Macrophage plasticity and polarization: in vivo veritas. J Clin Invest. 2012;122:787–795. doi: 10.1172/JCI59643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Bronte V, Zanovello P. Regulation of immune responses by L-arginine metabolism. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:641–654. doi: 10.1038/nri1668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Kvistborg P, Philips D, Kelderman S, Hageman L, Ottensmeier C, et al. Anti-CTLA-4 therapy broadens the melanoma-reactive CD8+ T cell response. Sci Transl Med. 2014;6:254ra128. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3008918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Ascierto PA, Marincola FM. 2015: The Year of Anti-PD-1/PD-L1s Against Melanoma and Beyond. EBioMedicine. 2015;2:92–93. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2015.01.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]