Figure 1.
Crystallographic Structure of HD-PTPCC
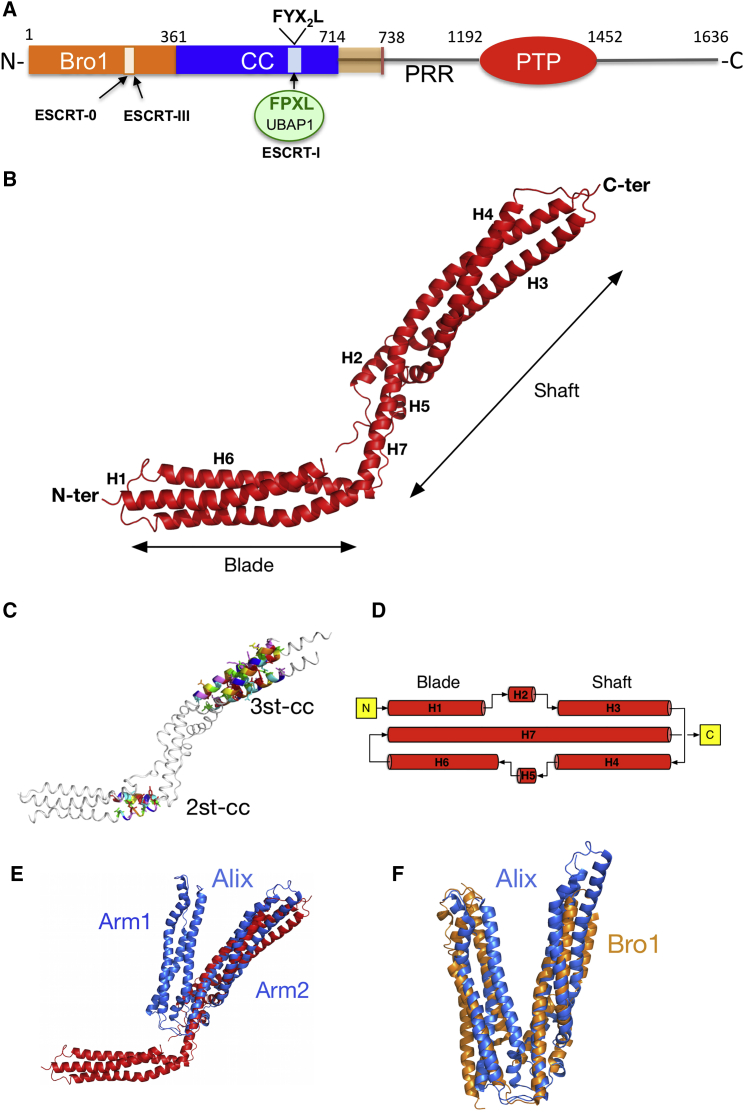
(A) Diagram of HD-PTP domain structure indicating domain boundaries and sites of interaction for ESCRT partners. The position of the conserved FYX2L motif in the CC domain is shown, as well as the FPXL motif in UBAP1.
(B) Cartoon diagram of the HD-PTPCC crystal structure. HD-PTPCC resembles an ice hockey stick, where the N-terminal region represents the blade and the C-terminal region is the shaft. The seven α helices are labeled H1 to H7, with H7 being the central and longest helix extending the whole length of the structure.
(C) Coiled-coil motifs in the HD-PTPCC structure after analysis with SOCKET (Walshaw and Woolfson, 2001). HD-PTPCC contains two canonical coiled coils: one two-stranded coiled coil (2st-cc) in the blade and one three-stranded coiled coil (3st-cc) in the shaft.
(D) Topology diagram of the structure of HD-PTPCC showing the arrangement of the seven α helices.
(E) Superimposition of the HD-PTPCC (red) and AlixV (blue) structures. The AlixV crystal structure (PDB: 2OJQ) shows a V-shaped helical protein in a closed conformation, in contrast to the open and extended conformation of HD-PTPCC. The two arms in AlixV are labeled.
(F) Superposition of the structures of AlixV (blue) and yeast Bro1V (orange, PDB: 4JIO). Both structures contain two arms joined by flexible loops.