Abstract
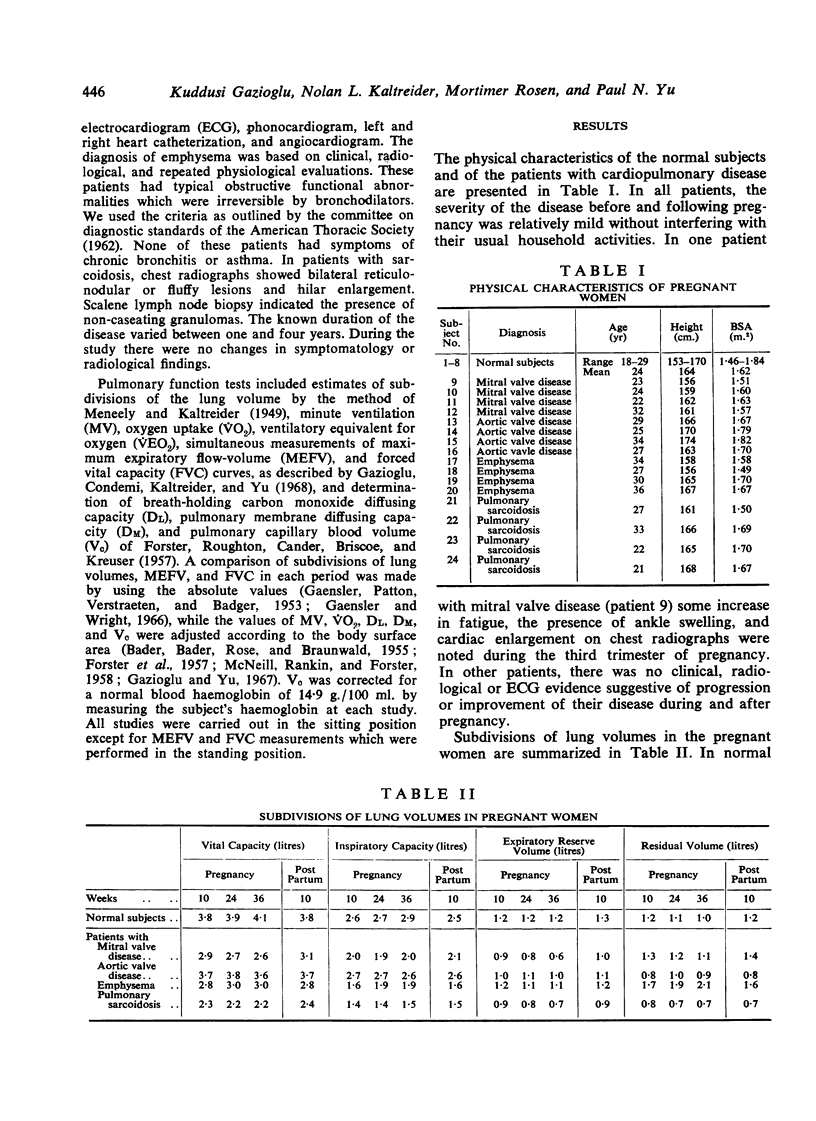
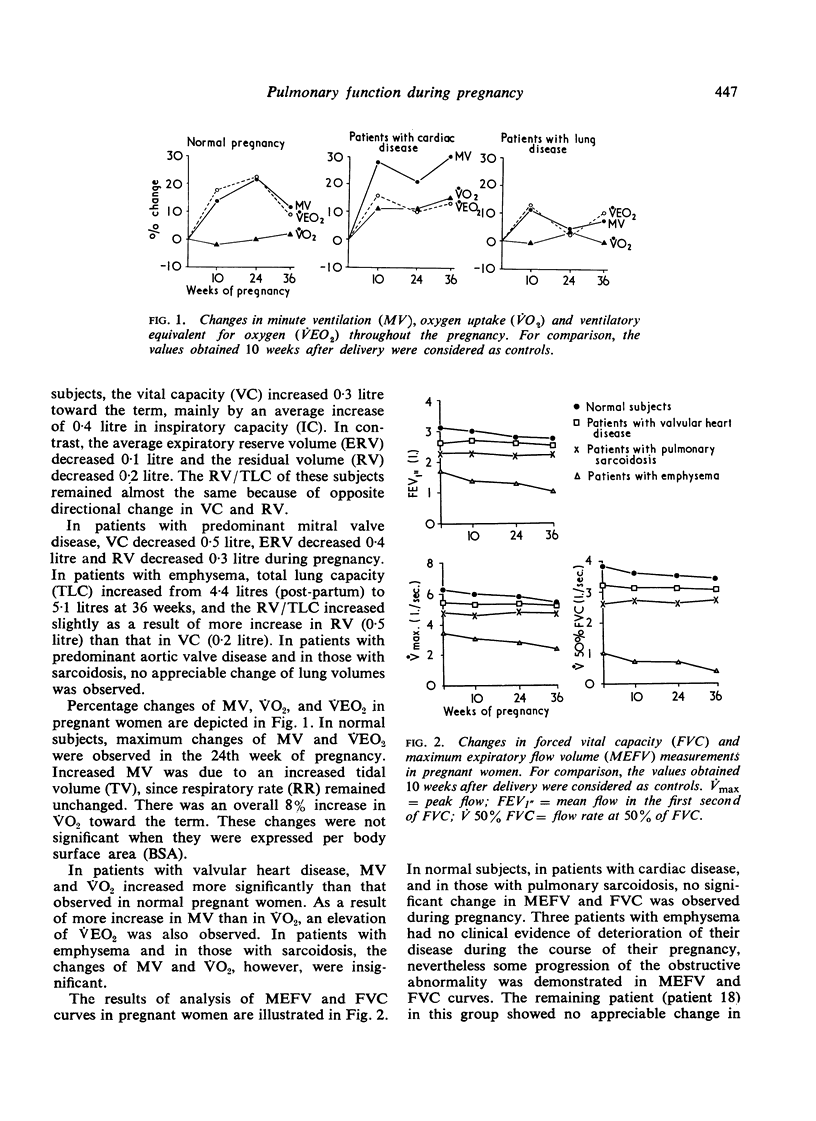
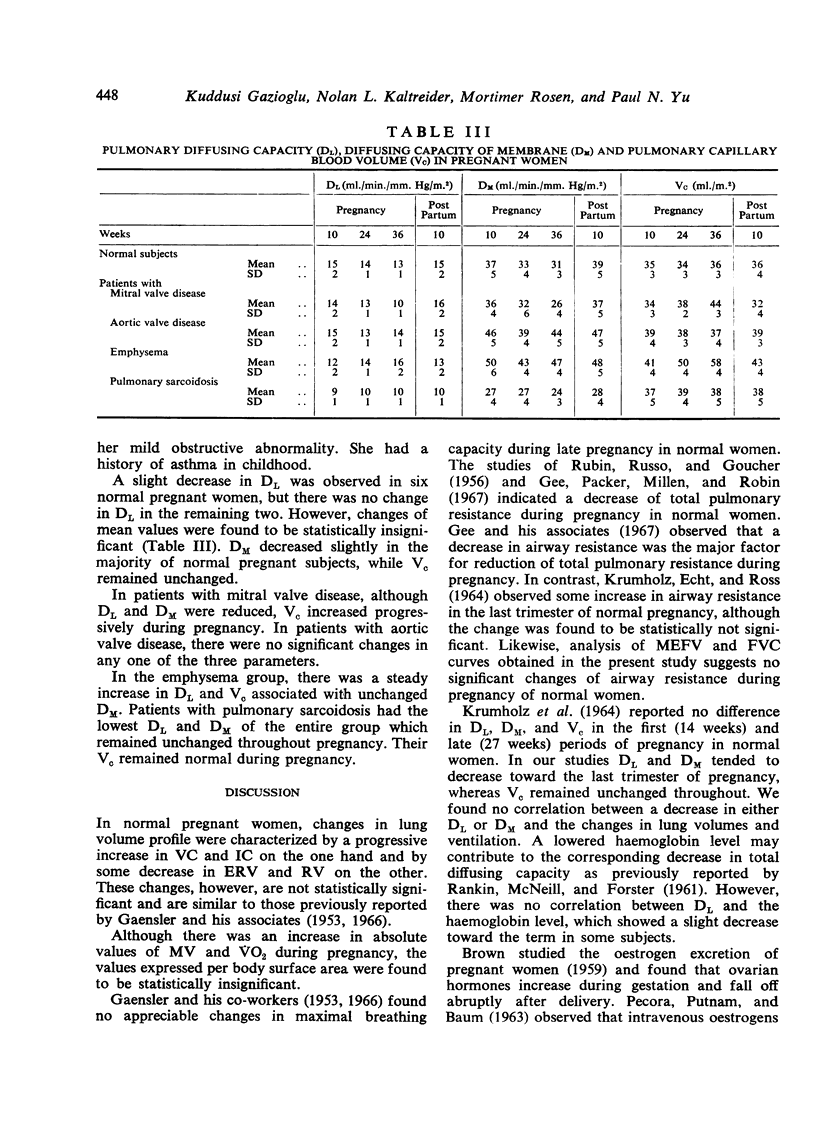
Pulmonary function studies were carried out during pregnancy in 8 normal women, in 8 patients with valvular (either mitral or aortic) heart disease, and in 8 patients with chronic pulmonary disease (either emphysema or sarcoidosis). In healthy pregnant women, changes in lung volumes and maximal expiratory flow rates were not significant. Diffusing capacity tended to decrease associated with unchanged pulmonary capillary blood volume. In patients with valvular heart disease, ventilation and oxygen consumption increased toward the term. The patients with mitral valve lesions showed a significant decrease in diffusing capacity with an increase in pulmonary capillary blood volume. In patients wth emphysema, characteristic changes were increasing obstructive functional abnormalities associated with an increase in pulmonary diffusing capacity and pulmonary capillary blood volume. None of these patients, however, had clinical evidence of deterioration of their disease. Patients with sarcoidosis had no appreciable alteration in pulmonary function tests.
The influence of various factors, such as increased ovarian hormones, ventilation-perfusion relationships, intra-abdominal distension, and cardiac haemodynamics, are discussed in relation to the change in pulmonary diffusing capacity and pulmonary capillary blood volume. From the standpoint of pulmonary function studies we think that patients with mitral heart disease and those with pulmonary emphysema tolerate pregnancy less favourably than normal subjects and patients with sarcoidosis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- APTHORP G. H., MARSHALL R. Pulmonary diffusing capacity: a comparison of breath-holding and steady state methods using carbon monoxide. J Clin Invest. 1961 Sep;40:1775–1784. doi: 10.1172/JCI104401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BADER R. A., BADER M. E., ROSE D. F., BRAUNWALD E. Hemodynamics at rest and during exercise in normal pregnancy as studies by cardiac catheterization. J Clin Invest. 1955 Oct;34(10):1524–1536. doi: 10.1172/JCI103205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CADIGAN J. B., MARKS A., ELLICOTT M. F., JONES R. H., GAENSLER E. A. An analysis of factors affecting the measurement of pulmonary diffusing capacity by the single breath method. J Clin Invest. 1961 Aug;40:1495–1514. doi: 10.1172/JCI104380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORSTER R. E., ROUGHTON F. J., CANDER L., BRISCOE W. A., KREUZER F. Apparent pulmonary diffusing capacity for CO at varying alveolar O2 tensions. J Appl Physiol. 1957 Sep;11(2):277–289. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1957.11.2.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAENSLER E. A., PATTON W. E., VERSTRAETEN J. M., BADGER T. L. Pulmonary function in pregnancy. III. Serial observations in patients with pulmonary insufficiency. Am Rev Tuberc. 1953 Jun;67(6):779–797. doi: 10.1164/art.1953.67.6.779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOUCHER D., RUBIN A., RUSSO N. The effect of pregnancy upon pulmonary function in normal women. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1956 Nov;72(5):963–969. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(56)90058-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaensler E. A., Wright G. W. Evaluation of respiratory impairment. Arch Environ Health. 1966 Feb;12(2):146–189. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1966.10664355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazioglu K., Condemi J., Kaltreider N. L., Yu P. N. Study of forced vital capacity and maximal expiratory flow-volume curves in obstructive lung disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1968 Nov;98(5):857–867. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1968.98.5.857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazioglu K., Yu P. N. Pulmonary blood volume and pulmonary capillary blood volume in valvular heart disease. Circulation. 1967 Apr;35(4):701–709. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.35.4.701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gee J. B., Packer B. S., Millen J. E., Robin E. D. Pulmonary mechanics during pregnancy. J Clin Invest. 1967 Jun;46(6):945–952. doi: 10.1172/JCI105600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatzfeld C., Wiener F., Briscoe W. A. Effects of uneven ventilation-diffusion ratios on pulmonary diffusing capacity in disease. J Appl Physiol. 1967 Jul;23(1):1–10. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1967.23.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holley H. S., Milic-Emili J., Becklake M. R., Bates D. V. Regional distribution of pulmonary ventilation and perfusion in obesity. J Clin Invest. 1967 Apr;46(4):475–481. doi: 10.1172/JCI105549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRUMHOLZ R. A., ECHT C. R., ROSS J. C. PULMONARY DIFFUSING CAPACITY, CAPILLARY BLOOD VOLUME, LUNG VOLUMES, AND MECHANICS OF VENTILATION IN EARLY AND LATE PREGNANCY. J Lab Clin Med. 1964 Apr;63:648–655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNEILL R. S., RANKIN J., FORSTER R. F. The diffusing capacity of the pulmonary membrane and the pulmonary capillary blood volume in cardiopulmonary disease. Clin Sci. 1958 Aug;17(3):465–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meneely G. R., Kaltreider N. L. THE VOLUME OF THE LUNG DETERMINED BY HELIUM DILUTION. DESCRIPTION OF THE METHOD AND COMPARISON WITH OTHER PROCEDURES. J Clin Invest. 1949 Jan;28(1):129–139. doi: 10.1172/JCI102041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALMER W. H., GEE J. B., BATES D. V. DISTURBANCES OF PULMONARY FUNCTION IN MITRAL VALVE DISEASE. Can Med Assoc J. 1963 Oct 12;89:744–750. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PECORA L. J., PUTNAM L. R., BAUM G. L. EFFECTS OF INTRAVENOUS ESTROGENS ON PULMONARY DIFFUSING CAPACITY. Am J Med Sci. 1963 Jul;246:48–52. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196307000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PROWSE C. M., GAENSLER E. A. RESPIRATORY AND ACID-BASE CHANGES DURING PREGNANCY. Anesthesiology. 1965 Jul-Aug;26:381–392. doi: 10.1097/00000542-196507000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANKIN J., McNEILL R. S., FORSTER R. E. Influence of increased alveolar carbon dioxide tension on pulmonary diffusing capacity for CO in man. J Appl Physiol. 1960 Jul;15:543–549. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1960.15.4.543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



