Abstract
Chromobacterium violaceum is a gram negative saprophytic bacterium, prevalent in tropical and subtropical climates. Infections caused by C. violaceum are very uncommon, yet it can cause severe systemic infections with higher mortality when entered into the bloodstream through open wound. A case of symptomatic bacteremia in a woman caused by C. violaceum was identified recently at a tertiary care teaching hospital in Nepal. Timely diagnosis by microbiological methods and rapid administration of antimicrobials led to a successful treatment of this life-threatening infection in this case. From this experience, we suggest to include this bacterium in the differential diagnosis of sepsis, especially when abraded skin is exposed to soil or stagnant water in tropical areas. The precise antimicrobial selection and timely administration should be considered when this infection is suspected.
Keywords: Chromobacterium violaceum, case report, bacteremia, Nepal
Introduction
Chromobacterium violaceum is a gram negative, rod shaped, nonsporing, and motile bacteria that can utilize carbohydrate fermentatively and grows readily on the ordinary laboratory culture media at 35°C–37°C.1 It naturally resides in soil and stagnant water of tropical and subtropical regions as saprophyte2 and produces a chemical antioxidant compound called violacein (violet non-diffusible pigment).3 Although first identified in 1881, its pathogenic potential was illustrated only in 1905 by Woolley from a fatal case of a buffalo in Philippines.4 Human case of infection caused by this pathogen was first established by Lessler from Malaysia in 1927.4 This organism is usually considered as nonpathogenic, but it is an opportunistic pathogen of extreme virulence for humans and animals when inoculated into bloodstream via open wound.5 Several reports of serious and fatal infections have been reported worldwide, especially from Asian and American countries. In majority of these cases, bacteria entered through the breached or abraded skins subsequently after exposure to contaminated soil or water.6 Clinical disease caused by this organism ranges from a localized skin lesion to multiple abscesses in the vital organs and fatal septicemia.7,8 Here we report a new case of bacteremia caused by C. violaceum at Manmohan Memorial Medical College Teaching Hospital (MMTH), Kathmandu, Nepal. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case of culture-proven bacteremia caused by C. violaceum from Nepal.
Written informed consent was taken from the patient for necessary investigations and case publication in scientific journal.
Case report
A 36-year-old immunocompetent female presented at midnight of 24 August 2016 to the emergency department of MMTH, a tertiary care referral hospital in Kathmandu, the capital of Nepal, with the clinical symptoms of fever, headache, chills, excessive sweating, burning sensation over epigastric region, and shortness of breath for the past 12 hours. There was no nausea, no vomiting, and normal bowel. She denied any previous illness, but her husband recalled that she had previously been diagnosed with pulmonary tuberculosis and treated with isoniazid and ethambutol as a directly observed therapy 6 years back. She lived in Sitapaila, a nearby village, and spent her life as an active housewife until 3 days ago when she plucked her left toe while working in the paddy farmland. Thereafter, her left toe became inflamed and swollen with edematous ulceration.
On examination, the patient was conscious and alert, but ill-looking. Local examination showed indurations above the toe region that was edematous, but not discharging pus or any serous fluid. Furthermore, she had blood pressure of 110/70 mmHg, pulse rate of 110 beats per minute, temperature of 39.6°C, and respiratory rate of 22 breaths per minute. The patient was provisionally diagnosed as a case of acute febrile illness with a suspicion of wound-related sepsis and immediate management was started. After necessary physical examination, blood and urine samples were collected aseptically for laboratory investigations viz blood culture, urine culture, hematology parameters, widal test, and blood chemistry tests. Paracetamol (500 mg) and Ibuprofen (400 mg) were administered by parenteral route along with electrolyte fluids. After specimen collection for laboratory investigations, the patient was admitted to the medical unit for further treatment. Antimicrobial regimen of 400 mg/24-hour of ciprofloxacin and 2 g/24-hour of ceftriaxone were initiated as empiric therapy for gram negative sepsis immediately after admission.
Hematological findings
The hematological investigations showed a normal (unremarkable) level of total leukocyte count with adequate cellular distribution, but low hemoglobin concentration (Table 1). Other blood cell parameters and indices were found in the acceptable range.
Table 1.
Hematological findings of the case on admission
| Tests (reference range) | Results/findings |
|---|---|
| Hemoglobin (12–16 g/dL) | 10.2 g/dL |
| Total leucocytes (4,000–10,000 cells/mm3) | 7,100/mm3 |
| Differential leucocytes count | |
| Polymorphs (40%–70%) | 70% |
| Lymphocytes (20%–45%) | 25% |
| Eosinophils (1%–6%) | 03% |
| Monocytes (2%–10%) | 02% |
| Basophils (0%–2%) | 00% |
| PCV (37%–48%) | 37% |
| Total red cell count (4.2–5.4 million/mm3) | 4.2 million/mm3 |
| MCV (80–100 fL) | 82 fL |
| MCH (27–32 pg) | 29.9 pg |
| MCHC (32%–36%) | 35.1% |
| Total platelet count (1.5–4.5 lakhs/mm3) | 275,000/mm3 |
Abbreviations: MCV, mean corpuscular volume; MCH, mean corpuscular hemoglobin; MCHC, mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration; PCV, packed cell volume.
Blood chemistry findings
The clinical parameters of blood glucose, urea, electrolytes, and common liver enzymes were found normal (Table 2). Widal test titer, serological test for enteric fever, was also insignificant in validating that there was no such infectious cause in the disease. C-reactive protein by latex agglutination was also negative. Urine microscopy and chemical findings were normal. Abdominal ultrasonography was also unremarkable.
Table 2.
Blood chemistry results of case on admission
| Tests (reference range) | Results/findings |
|---|---|
| Glucose, random (70–140 mg/dL) | 118 mg/dL |
| Blood urea (15–45 mg/dL) | 27 mg/dL |
| Serum creatinine (0.6–1.1 mg/dL) | 0.7 mg/dL |
| Sodium (135–146 mEq/L) | 143 mEq/L |
| Potassium (3.5–5.2 mEq/L) | 3.9 mEq/L |
| SGOT (AST) (<40 IU/L) | 33 IU/L |
| SGPT (ALT) (<37 IU/L) | 30 IU/L |
| ALP (90–460 IU/L) | 144 IU/L |
| Serum amylase (25–115 IU/L) | 66 IU/L |
Abbreviations: ALT, alanine aminotransferase; ALP, alkaline phosphatase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; SGOT, serum glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase; SGPT, serum glutamate pyruvate transaminase.
Microbiological findings
Blood and urine samples were subjected for bacteriological cultivation. Ten milliliters of blood sample was aseptically inoculated into brain heart infusion broth and incubated in aerobic atmosphere for 24 hours. Urine sample was inoculated into blood agar and MacConkey agar plates semi-quantitatively and incubated aerobically for 24 hours at 37°C. Blood culture broth was inspected next day, and blind subculture was made on blood agar, chocolate agar, and MacConkey agar and incubated for next 24 hours. Urine culture plates were found with no growth of any bacterial species and reported as sterile.
After overnight incubation of subcultured plates from blood culture, the agar plates demonstrated numerous small colonies with a faint violet metallic pigmentation (which later became dark violet on incubation) with no hemolysis (Figure 1). For better demonstration of pigment, we transferred the colonies to fresh nutrient agar plate (Figure 2) and incubated aerobically for next 24 hours. Some colonies on the nutrient agar were initially nonpigmented, but later converted to dark violet on prolonged incubation (72 hours) at room temperature.
Figure 1.
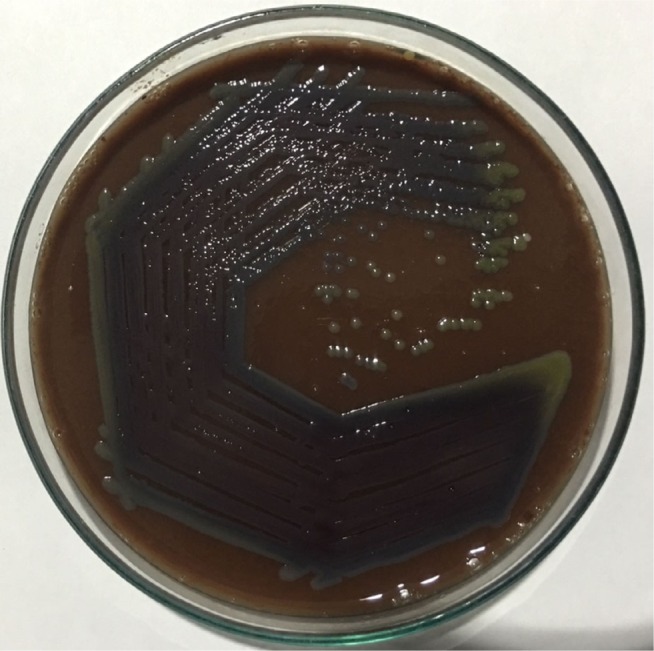

Chromobacterium violaceum growing on chocolate agar.
Figure 2.
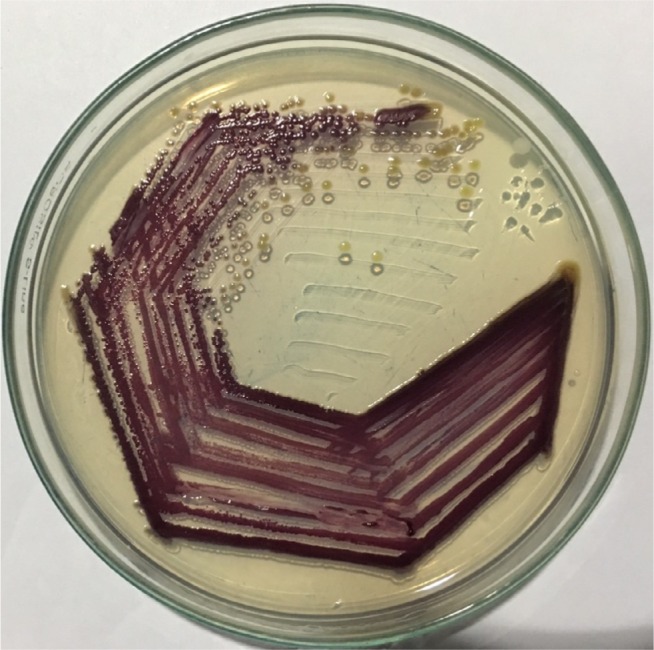
Chromobacterium violaceum growing on nutrient agar.
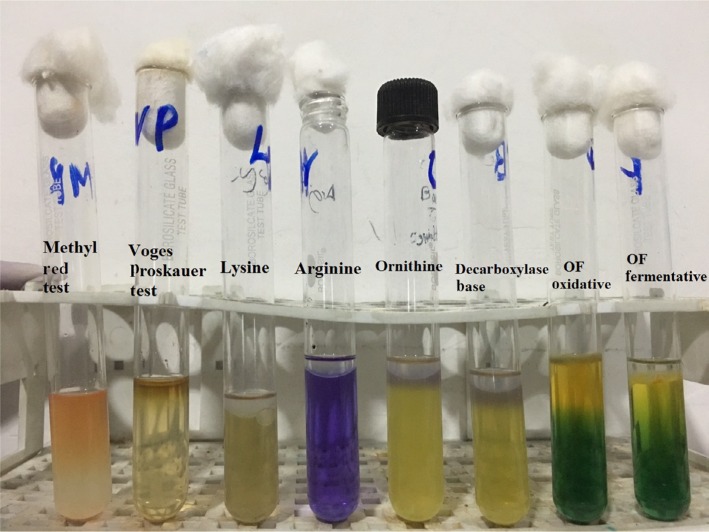
Biochemical characterization of the bacteria was carried out by conventional biochemical tests such as catalase test, oxidase test, triple sugar iron agar test, citrate utilization, urea hydrolysis, sulfide indole motility, oxidation–fermentation test, methyl red-Voges–Proskauer test, decarboxylase tests (lysine, arginine, and ornithine). The oxidase test was performed by picking the single isolated colony with the sterile bamboo stick and rubbing over the surface of the filter paper disk impregnated with 1% tetra methyl paraphenylene diamine dihydrochloride reagent. Citrate utilization test was done by using Simmons citrate agar. All the results of biochemical tests are summarized in Figure 3 and Table 3. Simultaneously, antimicrobial susceptibility test was performed by Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion method on Mueller-Hinton agar using commercially available antibiotic disks (Figures 4; 5) and the result of the susceptibility test was interpreted according to the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute guidelines for non-fermenting gram negatives.9
Figure 3.
Biochemical test results of Chromobacterium violaceum.
Abbreviation: OF, oxidation–fermentation.
Table 3.
Biochemical findings of the bacterial isolate from case
| Biochemical tests performed | Results |
|---|---|
| Gram stain | Gram negative bacilli |
| Catalase test | Positive |
| Oxidase test | Positive |
| TSI agar | |
| Acid production in slant | Negative |
| Acid production in butt | Positive |
| Hydrogen sulfide production | Negative |
| Gas production | Negative |
| Glucose fermentation | Positive |
| Lactose and/or sucrose fermentation | Negative |
| Alkali production in slant | Positive |
| SIM | |
| Motility | Positive |
| Hydrogen sulfide production | Negative |
| Indole | Negative |
| Urea hydrolysis test | Negative |
| Citrate utilization test | Positive |
| Methyl red test | Negative |
| Voges–Proskauer test | Negative |
| OF test | Fermentative |
| Decarboxylase tests | |
| Lysine decarboxylase | Negative |
| Arginine dihydrolase | Positive |
| Ornithine decarboxylase | Negative |
| DNAse test | Positive |
| Pigment | Violet (violacein) |
Abbreviations: DNAse, deoxyribonuclease; OF, oxidation–fermentation; SIM, sulfide indole motility; TSI, triple sugar iron.
Figure 4.
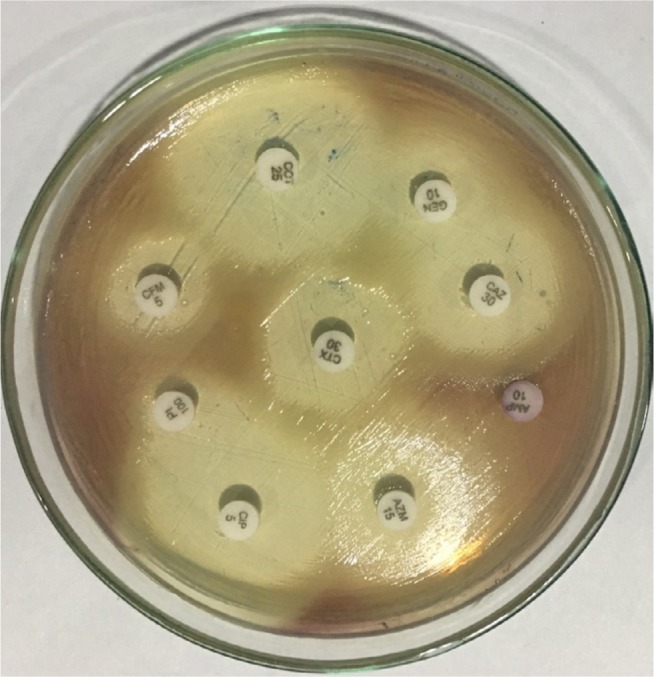
Antimicrobial susceptibility test of Chromobacterium violaceum.
Figure 5.
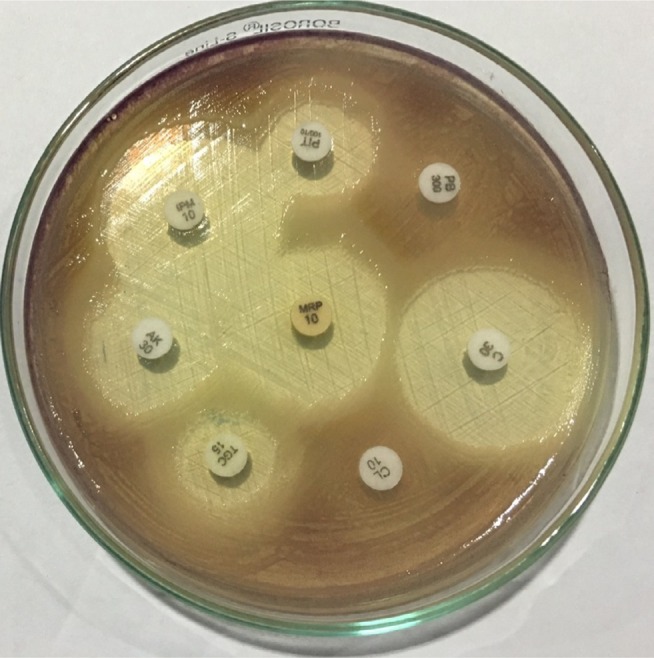
Antimicrobial susceptibility test of Chromobacterium violaceum.
The patient was responding better after initial antimicrobial therapy, and fever subsidized after 8 hours. Empirical antibiotic therapy was continued until the complete laboratory reports were available. Based on the biochemical findings and microscopic observation (Gram staining, motility), the organism was confirmed as C. violaceum. Antimicrobial susceptibility test indicated that it is resistant to polymixin group of antibiotics, but susceptible to other therapeutic antibiotics (Table 4).
Table 4.
Antibiogram of Chromobacterium violaceum clinical isolate from the case
| Antibiotics | Results |
|---|---|
| Ampicillin | Resistant |
| Cotrimoxazole | Sensitive |
| Ceftazidime | Sensitive |
| Cefixime | Sensitive |
| Ciprofloxacin | Sensitive |
| Levofloxacin | Sensitive |
| Gentamycin | Sensitive |
| Amikacin | Sensitive |
| Piperacillin tazobactam | Sensitive |
| Ampicillin sulbactam | Resistant |
| Cefoperazone sulbactam | Sensitive |
| Imipenem | Sensitive |
| Meropenem | Sensitive |
| Polymixin B | Resistant |
| Colistin sulfate | Resistant |
The initial antimicrobial regime was found susceptible and continued for 14 days. Additional blood culture was performed on day 6 to confirm the prognosis, but was negative for bacterial growth. She was discharged on day 7 on oral ciprofloxacin (1,000 mg/24 hours) and cefixime (500 mg/24 hours) for next 9 days (total 14 days). On followup visit, the wound appeared dry, crusty, and membranous without any serous fluid. After completion of the therapy, she made absolute recovery without any complications and the antibiotics were discontinued.
Discussion
C. violaceum is the single species of the genus responsible for human infections.10 Most clinicians are unaware of this rare bacterium despite its ubiquitous distribution.6 In the published literature, common clinical features in majority of the cases with fatal outcome appear to be sepsis, multiple liver abscesses, and diffuse pustular dermatitis.4 Bacteremia associated with C. violaceum has been reported by Chen et al and Yang et al from Taiwan,7,11 Campbell et al from Vietnam,5 Ray et al from India,4 Nanayakkara et al from Sri Lanka,12 and others. Most of the reported cases had the fatal outcome but successful therapeutic experience with the use of timely therapy has also been reported.5
Although C. violaceum is confined to tropical countries, especially in South and Southeast Asia, there are only two previously reported cases from Nepal. Of the two cases, the wound sepsis case by Ansari et al has demonstrated the fatality of the case while another asymptomatic bacteriuria by Pant et al was self-limiting.13,14 Blood culture confirmed bacteremia associated with this rare pathogen has not been reported from Nepal yet. In this case, clinical features of the febrile woman appear to be similar to that of common enteric fever, but skin lesion and isolated bacterial strain helped in timely identification of the rare case of bacteremia. Besides, previous studies suggested that the common predisposing factors for C. violaceum associated bacteremia were immunocompromised state, chronic granulomatous disease, steroid therapy, diabetes, and other systemic illnesses,6,10 but in this report there were no such factors to be noted.
Consumption of contaminated water or food or through exposure of damaged skin to stagnant water or soil is a common route for transmission of this pathogen to healthy individuals. Moreover, severe infections after swimming in contaminated water, recreational or stagnant muddy water, and post-surgical cases have also been reported.6 In this case, too, there was sufficient evidence of inoculation of the pathogen and symptoms were also promising although undifferentiated. The ability of the organism to produce a peculiar metabolite violacein giving the colonies their distinctive purple color helped in proper identification of the bacteria. Nevertheless, nonpigmented strains of C. violaceum have also been involved in human infections.11,15
Chromobacterium is usually susceptible to therapeutic antimicrobials, however genes associated with intrinsic resistance toward penicillins and early cephalosporins have been described.16 Isolates have been found susceptible to common therapeutic antimicrobials like chloramphenicol, trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole, tetracyclines, ciprofloxacin, cefepime, and imipenem.17 Therefore, broad-spectrum cephalosporins, carbapenems or fluoroquinolones can be used as an appropriate initial choice for C. violaceum infections due to the unavailability of recommended therapeutic guidelines. Timely diagnosis and aggressive antimicrobial therapy would be a critical factor for an effective management of C. violaceum and reduce the high mortality associated with these infections.5,7 In our case, timely intervention with administration of broad-spectrum antibiotics to which the organism was sensitive, assisted in proper management of the illness, and the infection did not progress to septicemia and other complications.
Conclusion
Although human infections with C. violaceum are rare, they are often associated with higher morbidity and mortality. Nevertheless, the clinical symptoms and presentation of the infection are not distinctive, it should be included in differential diagnosis of sepsis, especially if exposure to stagnant water and skin breaching is involved. Early clinical detection and administration of the appropriate systemic antimicrobial therapy is highly recommended.
Footnotes
Authors’ contributions
NPP identified the case, performed necessary laboratory tests, and prepared the manuscript, AB performed laboratory tests and prepared the manuscript, SG performed laboratory tests, AM performed laboratory tests, SS performed laboratory tests, DS performed laboratory tests, RP identified the case and followed the treatment, and PRK performed laboratory tests and prepared the manuscript. All authors contributed toward data analysis, drafting and revising the paper, gave final approval of the version to be published and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
- 1.Martin W, Martin S. Calymmatobacterium, cardiobacterium, chromo-bacterium and streptobacillus. In: Collier Leslie BA, Max S, editors. Topley and Wilson’s Microbiology and Microbial Infections. 9th ed. London, England: Arnold; 1998. pp. 1217–1227. distributed by Oxford University Press, New York. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lima-Bittencourt CI, Astolfi-Filho S, Chartone-Souza E, Santos FR, Nascimento AM. Analysis of chromobacterium sp. natural isolates from different Brazilian ecosystems. BMC Microbiol. 2007;7:58. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-7-58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Duran N, Menck CF. Chromobacterium violaceum: a review of pharmacological and industrial perspectives. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2001;27(3):201–222. doi: 10.1080/20014091096747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ray P, Sharma J, Marak RS, Singhi S, Taneja N, Garg RK, Sharma M. Chromobacterium violaceum septicaemia from north India. Indian J Med Res. 2004;120(6):523–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Campbell JI, Lan NP, Qui PT, Dung le T, Farrar JJ, Baker S. A successful antimicrobial regime for Chromobacterium violaceum induced bacteremia. BMC Infect Dis. 2013;13:4. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-13-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Yang CH, Li YH. Chromobacterium violaceum infection: a clinical review of an important but neglected infection. J Chin Med Assoc. 2011;74(10):435–441. doi: 10.1016/j.jcma.2011.08.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Chen CH, Lin LC, Liu CE, Young TG. Chromobacterium violaceum bacteremia: a case report. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2003;36(2):141–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Manjunath M. Fatal septicaemia due to Chromobacterium violaceum. West Indian Med J. 2007;56(4):380–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute . Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk Susceptibility Tests. 11th Ed. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute; 2012. pp. M02–A11. Approved Standard. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Jitmuang A. Human Chromobacterium violaceum infection in Southeast Asia: case reports and literature review. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2008;39(3):452–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Yang CH. Nonpigmented Chromobacterium violaceum bacteremic cellulitis after fish bite. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2011;44(5):401–405. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2010.04.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Nanayakkara GM, Pethiyagoda P, Jayasinghe PN, Premachandra U. Chromobacterium violaceum infection in a provincial hospital in Sri Lanka. Ceylon Med J. 2008;53(4):156–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ansari S, Paudel P, Gautam K, et al. Chromobacterium violaceum isolated from a wound sepsis: a case study from Nepal. Case Rep Infect Dis. 2015;2015:181946. doi: 10.1155/2015/181946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Pant ND, Sharma M, Khatiwada S. Asymptomatic bacteriuria caused by Chromobacterium violaceum in an immunocompetent adult. Case Rep Med. 2015;2015:652036. doi: 10.1155/2015/652036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Grier DD, Qiu J, Rand K, Donnelly WH. Pathologic quiz case: a 13-year-old boy with a 2-day history of fever, vomiting, and mental status changes. Chromobacterium violaceum bacteremia. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2004;128(10):e131–e132. doi: 10.5858/2004-128-e131-PQCAYB. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Fantinatti-Garboggini F, Almeida R, Portillo Vdo A, et al. Drug resistance in Chromobacterium violaceum. Genet Mol Res. 2004;3(1):134–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Aldridge KE, Valainis GT, Sanders CV. Comparison of the in vitro activity of ciprofloxacin and 24 other antimicrobial agents against clinical strains of Chromobacterium violaceum. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988;10(1):31–39. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(88)90124-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



