Abstract
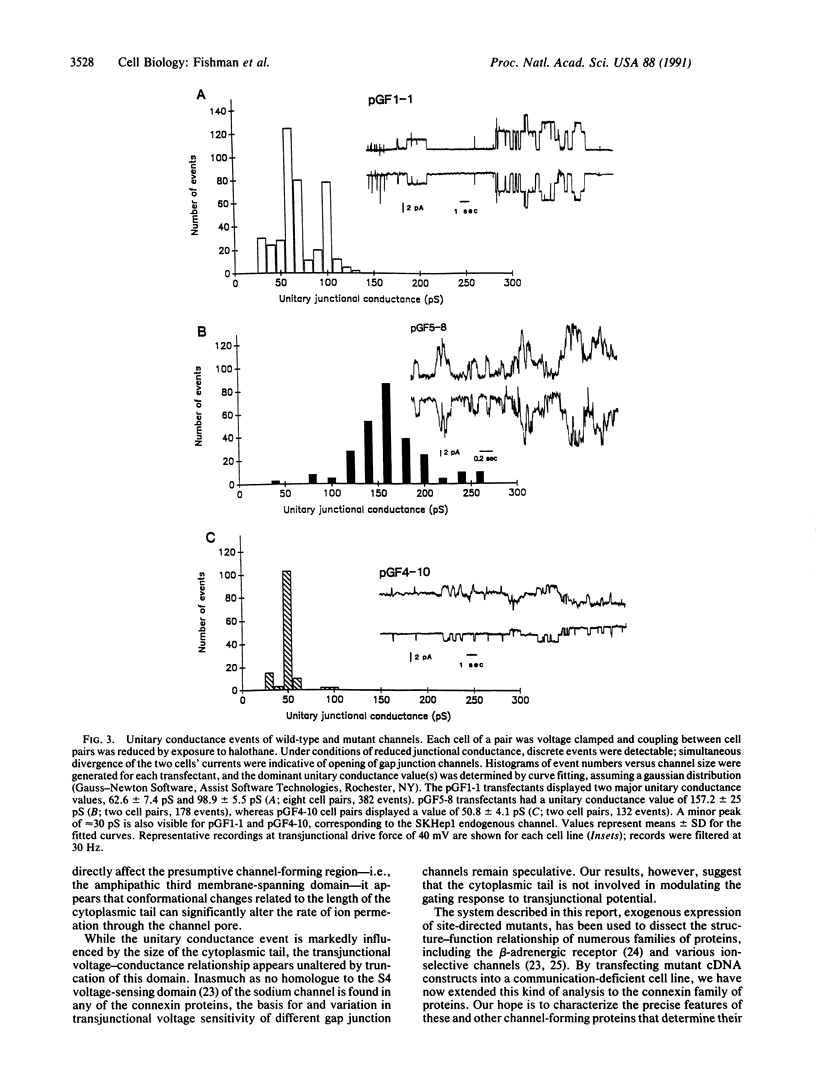
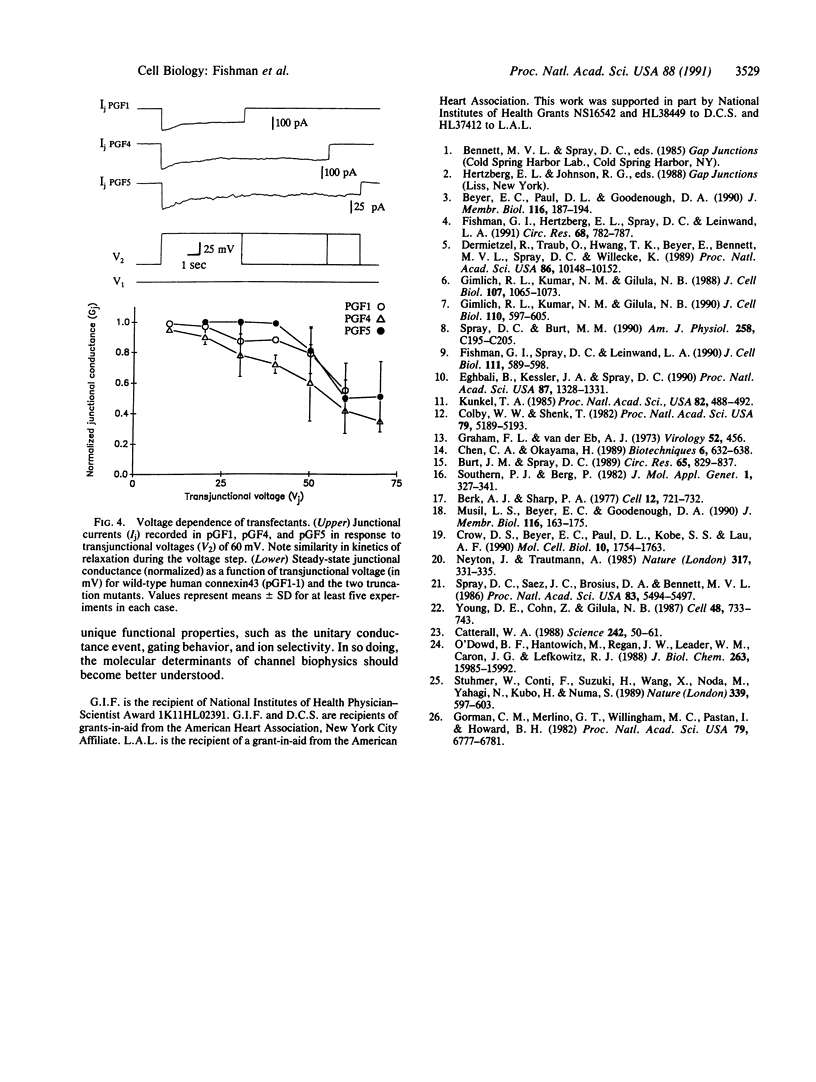
The connexins form a family of membrane spanning proteins that assemble into gap junction channels. The biophysical properties of these channels are dependent upon the constituent connexin isoform. To begin identifying the molecular basis for gap junction channel behavior in the human heart, a tissue that expresses connexin43, we used site-directed mutagenesis to generate mutant cDNAs of human connexin43 with shortened cytoplasmic tail domains. Premature stop codons were inserted, resulting in proteins corresponding in length to the mammalian isoforms connexin32 and connexin26, which are expressed primarily in liver. All constructs restore intercellular coupling when they are transfected into SKHep1 cells, a human hepatoma line that is communication deficient. Whereas wild-type connexin43 transfectants display two distinct unitary conductance values of about 60 and 100 pS, transfectants expressing the mutant proteins, from which 80 and 138 amino acids have been deleted, exhibit markedly different single-channel properties, with unitary conductance values of about 160 and 50 pS, respectively. Junctional conductance of channels composed of wild-type connexin43 is less voltage-sensitive compared with transfectants expressing wild-type connexin32. However, neither of the connexin43 truncation mutants alters this relative voltage insensitivity. These results suggest that the cytoplasmic tail domain is an important determinant of the unitary conductance event of gap junction channels but not their voltage dependence. Furthermore, since the mutant connexins are missing several consensus phosphorylation sites, modification of these particular sites may not be required for membrane insertion or assembly of human connexin43 into functional channels.
Full text
PDF

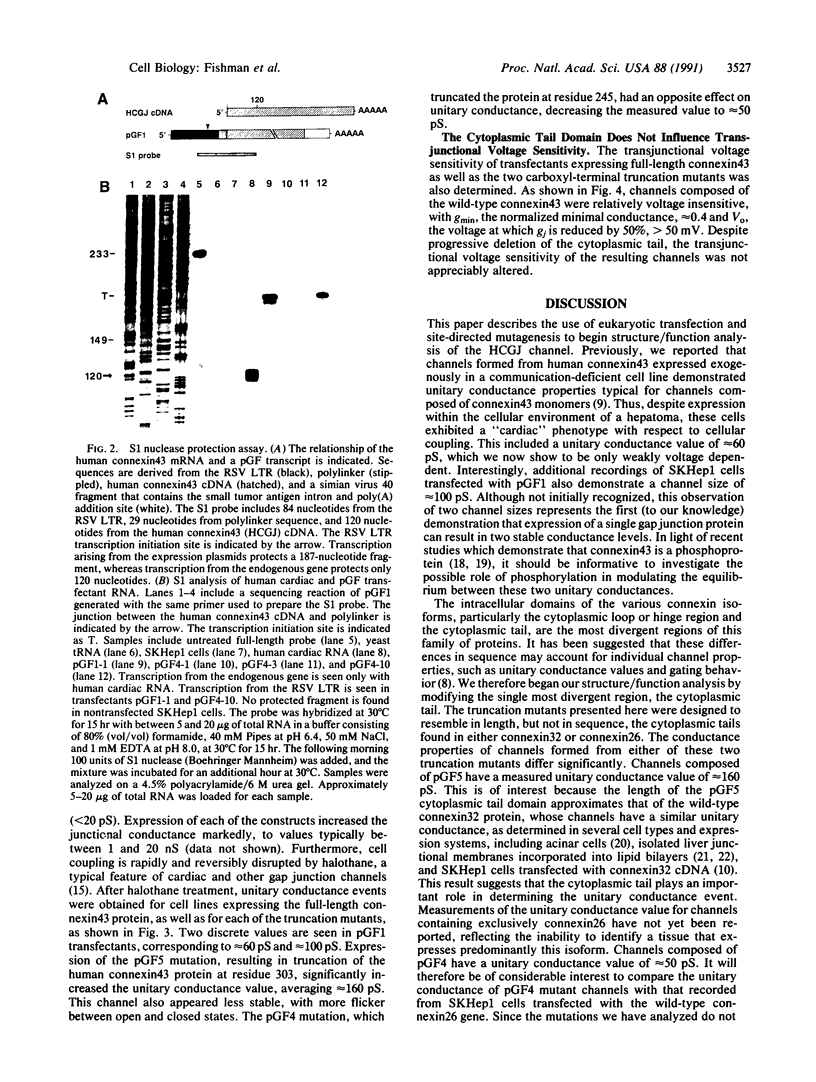
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer E. C., Paul D. L., Goodenough D. A. Connexin family of gap junction proteins. J Membr Biol. 1990 Jul;116(3):187–194. doi: 10.1007/BF01868459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burt J. M., Spray D. C. Volatile anesthetics block intercellular communication between neonatal rat myocardial cells. Circ Res. 1989 Sep;65(3):829–837. doi: 10.1161/01.res.65.3.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Structure and function of voltage-sensitive ion channels. Science. 1988 Oct 7;242(4875):50–61. doi: 10.1126/science.2459775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. A., Okayama H. Calcium phosphate-mediated gene transfer: a highly efficient transfection system for stably transforming cells with plasmid DNA. Biotechniques. 1988 Jul-Aug;6(7):632–638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby W. W., Shenk T. Fragments of the simian virus 40 transforming gene facilitate transformation of rat embryo cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5189–5193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crow D. S., Beyer E. C., Paul D. L., Kobe S. S., Lau A. F. Phosphorylation of connexin43 gap junction protein in uninfected and Rous sarcoma virus-transformed mammalian fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1754–1763. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dermietzel R., Traub O., Hwang T. K., Beyer E., Bennett M. V., Spray D. C., Willecke K. Differential expression of three gap junction proteins in developing and mature brain tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):10148–10152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.10148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eghbali B., Kessler J. A., Spray D. C. Expression of gap junction channels in communication-incompetent cells after stable transfection with cDNA encoding connexin 32. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1328–1331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman G. I., Hertzberg E. L., Spray D. C., Leinwand L. A. Expression of connexin43 in the developing rat heart. Circ Res. 1991 Mar;68(3):782–787. doi: 10.1161/01.res.68.3.782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman G. I., Spray D. C., Leinwand L. A. Molecular characterization and functional expression of the human cardiac gap junction channel. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):589–598. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimlich R. L., Kumar N. M., Gilula N. B. Differential regulation of the levels of three gap junction mRNAs in Xenopus embryos. J Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;110(3):597–605. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.3.597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimlich R. L., Kumar N. M., Gilula N. B. Sequence and developmental expression of mRNA coding for a gap junction protein in Xenopus. J Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;107(3):1065–1073. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.3.1065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musil L. S., Beyer E. C., Goodenough D. A. Expression of the gap junction protein connexin43 in embryonic chick lens: molecular cloning, ultrastructural localization, and post-translational phosphorylation. J Membr Biol. 1990 Jun;116(2):163–175. doi: 10.1007/BF01868674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neyton J., Trautmann A. Single-channel currents of an intercellular junction. 1985 Sep 26-Oct 2Nature. 317(6035):331–335. doi: 10.1038/317331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dowd B. F., Hnatowich M., Regan J. W., Leader W. M., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Site-directed mutagenesis of the cytoplasmic domains of the human beta 2-adrenergic receptor. Localization of regions involved in G protein-receptor coupling. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):15985–15992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spray D. C., Burt J. M. Structure-activity relations of the cardiac gap junction channel. Am J Physiol. 1990 Feb;258(2 Pt 1):C195–C205. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.2.C195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spray D. C., Saez J. C., Brosius D., Bennett M. V., Hertzberg E. L. Isolated liver gap junctions: gating of transjunctional currents is similar to that in intact pairs of rat hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5494–5497. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stühmer W., Conti F., Suzuki H., Wang X. D., Noda M., Yahagi N., Kubo H., Numa S. Structural parts involved in activation and inactivation of the sodium channel. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):597–603. doi: 10.1038/339597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Cohn Z. A., Gilula N. B. Functional assembly of gap junction conductance in lipid bilayers: demonstration that the major 27 kd protein forms the junctional channel. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):733–743. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90071-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]