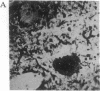
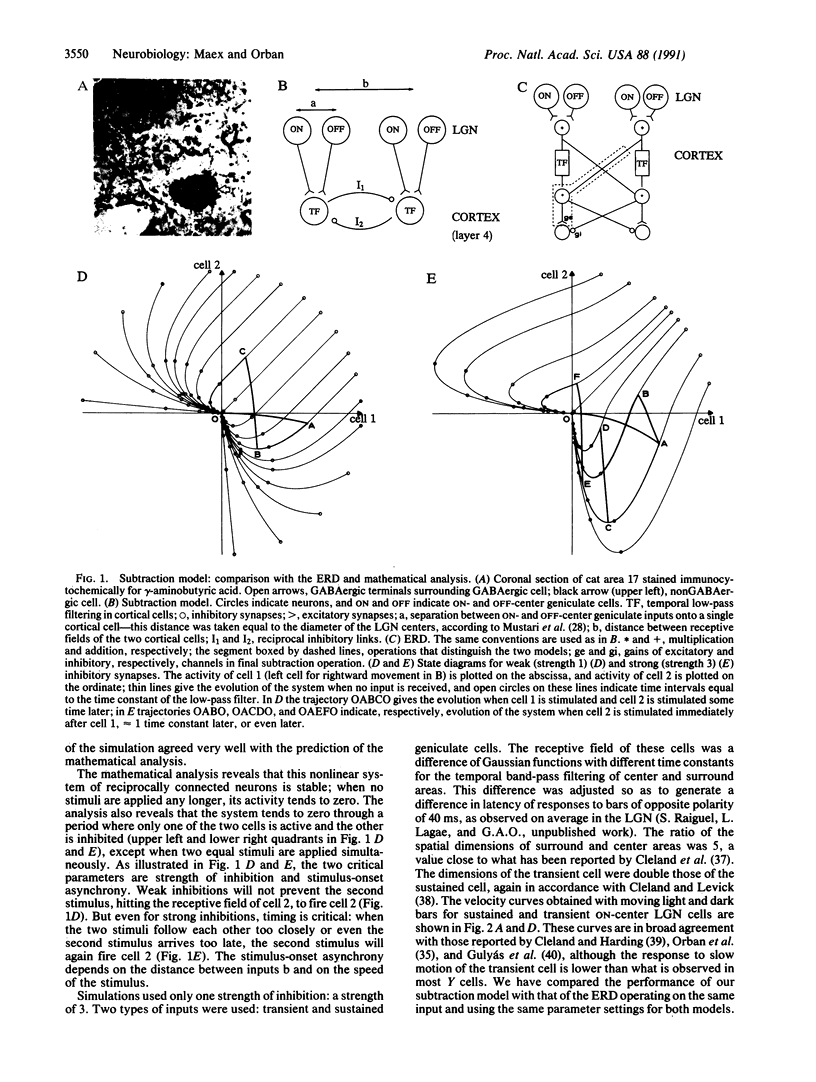
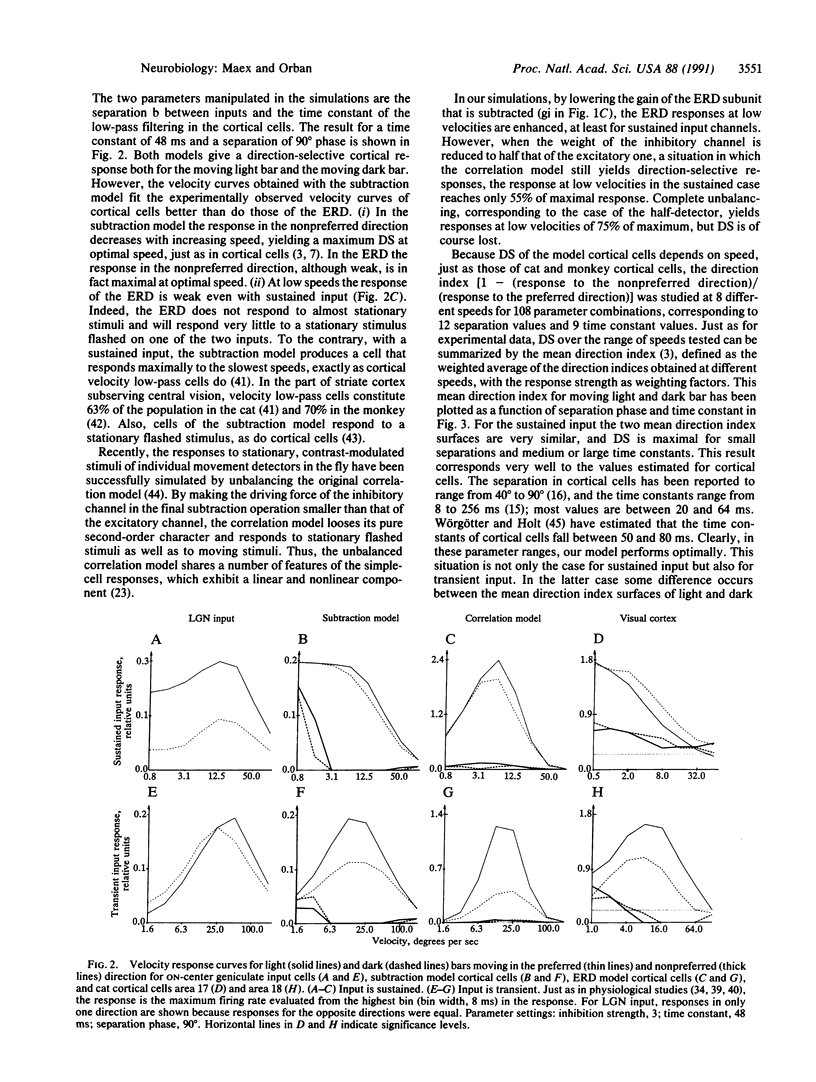
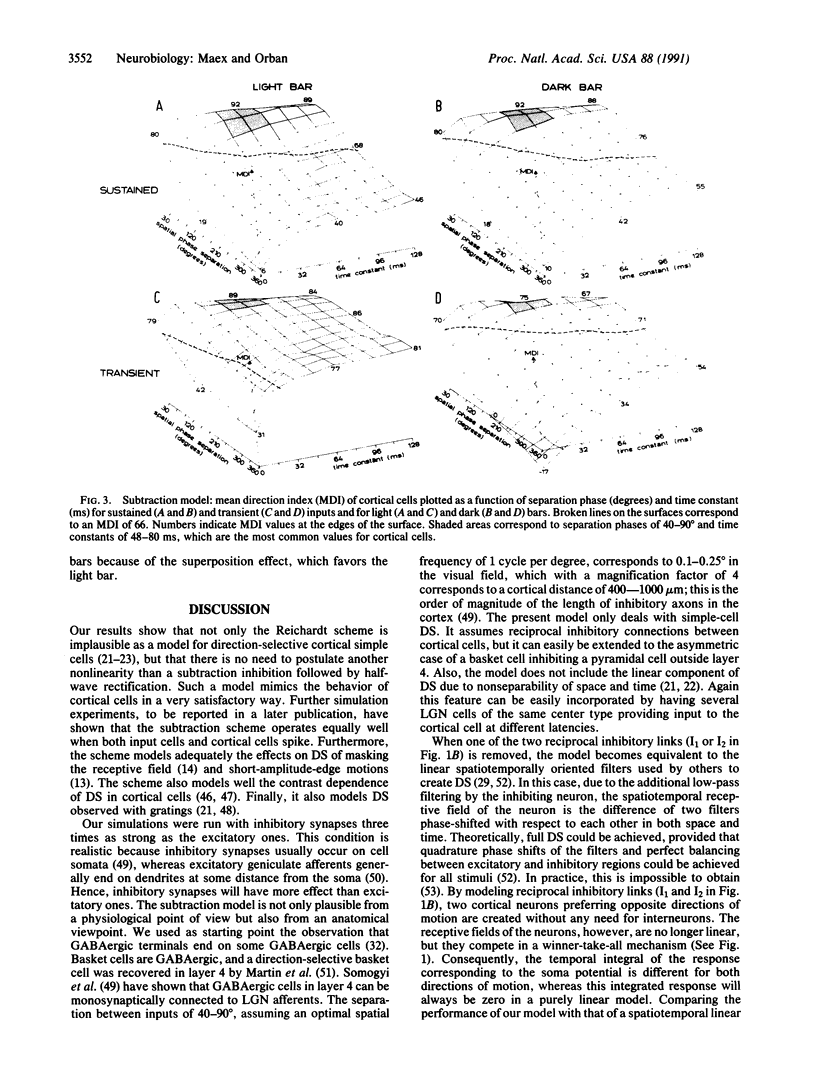
Abstract
We have modeled simple-cell direction selectivity by a nonlinearity consisting of a subtraction inhibition followed by half-wave rectification and compared the performance of this model to that of different versions of the elaborated Reichardt detector for similar inputs and parameter settings. Not only does the subtraction model fit the experimental data more closely than the elaborated Reichardt detector, but the subtraction model also is more plausible from a physiological and anatomical point of view. Moreover, the subtraction model operates optimally at plausible spatiotemporal parameter settings. Therefore, we conclude that there is no need to invoke specific synaptic interactions, such as implied in the Reichardt detector, to account for simple-cell direction selectivity.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelson E. H., Bergen J. R. Spatiotemporal energy models for the perception of motion. J Opt Soc Am A. 1985 Feb;2(2):284–299. doi: 10.1364/josaa.2.000284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albus K. The detection of movement direction and effects of contrast reversal in the cat's striate cortex. Vision Res. 1980;20(4):289–293. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(80)90015-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. L., Jr, Cynader M. S. Spatial receptive-field properties of direction-selective neurons in cat striate cortex. J Neurophysiol. 1986 Jun;55(6):1136–1152. doi: 10.1152/jn.1986.55.6.1136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. L., Jr Spatial and temporal determinants of directionally selective velocity preference in cat striate cortex neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1988 May;59(5):1557–1574. doi: 10.1152/jn.1988.59.5.1557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullier J., Henry G. H. Ordinal position of neurons in cat striate cortex. J Neurophysiol. 1979 Sep;42(5):1251–1263. doi: 10.1152/jn.1979.42.5.1251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullier J., Mustari M. J., Henry G. H. Receptive-field transformations between LGN neurons and S-cells of cat-striate cortex. J Neurophysiol. 1982 Mar;47(3):417–438. doi: 10.1152/jn.1982.47.3.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland B. G., Dubin M. W., Levick W. R. Sustained and transient neurones in the cat's retina and lateral geniculate nucleus. J Physiol. 1971 Sep;217(2):473–496. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland B. G., Harding T. H. Response to the velocity of moving visual stimuli of the brisk classes of ganglion cells in the cat retina. J Physiol. 1983 Dec;345:47–63. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland B. G., Levick W. R. Brisk and sluggish concentrically organized ganglion cells in the cat's retina. J Physiol. 1974 Jul;240(2):421–456. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas R. J., Martin K. A., Whitteridge D. Selective responses of visual cortical cells do not depend on shunting inhibition. Nature. 1988 Apr 14;332(6165):642–644. doi: 10.1038/332642a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duysens J., Maes H., Orban G. A. The velocity dependence of direction selectivity of visual cortical neurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1987 Jun;387:95–113. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duysens J., Orban G. A., Cremieux J. Velocity selectivity in the cat visual system. II. Independence from interactions between different loci. J Neurophysiol. 1985 Oct;54(4):1050–1067. doi: 10.1152/jn.1985.54.4.1050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duysens J., Orban G. A. Is stimulus movement of particular importance in the functioning of cat visual cortex? Brain Res. 1981 Sep 7;220(1):184–187. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90223-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egelhaaf M., Borst A., Reichardt W. Computational structure of a biological motion-detection system as revealed by local detector analysis in the fly's nervous system. J Opt Soc Am A. 1989 Jul;6(7):1070–1087. doi: 10.1364/josaa.6.001070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson R. C., Citron M. C., Vaughn W. J., Klein S. A. Nonlinear directionally selective subunits in complex cells of cat striate cortex. J Neurophysiol. 1987 Jul;58(1):33–65. doi: 10.1152/jn.1987.58.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eysel U. T., Muche T., Wörgötter F. Lateral interactions at direction-selective striate neurones in the cat demonstrated by local cortical inactivation. J Physiol. 1988 May;399:657–675. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund T. F., Martin K. A., Smith A. D., Somogyi P. Glutamate decarboxylase-immunoreactive terminals of Golgi-impregnated axoaxonic cells and of presumed basket cells in synaptic contact with pyramidal neurons of the cat's visual cortex. J Comp Neurol. 1983 Dec 10;221(3):263–278. doi: 10.1002/cne.902210303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin A. W., Henry G. H., Bishop P. O. Direction selectivity of simple striate cells: properties and mechanism. J Neurophysiol. 1975 Nov;38(6):1500–1523. doi: 10.1152/jn.1975.38.6.1500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grzywacz N. M., Koch C. Functional properties of models for direction selectivity in the retina. Synapse. 1987;1(5):417–434. doi: 10.1002/syn.890010506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulyás B., Lagae L., Eysel U., Orban G. A. Corticofugal feedback influences the responses of geniculate neurons to moving stimuli. Exp Brain Res. 1990;79(2):441–446. doi: 10.1007/BF00608257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulyás B., Spileers W., Orban G. A. Modulation by a moving texture of cat area 18 neuron responses to moving bars. J Neurophysiol. 1990 Mar;63(3):404–423. doi: 10.1152/jn.1990.63.3.404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBEL D. H., WIESEL T. N. Receptive fields, binocular interaction and functional architecture in the cat's visual cortex. J Physiol. 1962 Jan;160:106–154. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holub R. A., Morton-Gibson M. Response of Visual Cortical Neurons of the cat to moving sinusoidal gratings: response-contrast functions and spatiotemporal interactions. J Neurophysiol. 1981 Dec;46(6):1244–1259. doi: 10.1152/jn.1981.46.6.1244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B. B., Elepfandt A., Virsu V. Phase of responses to sinusoidal gratings of simple cells in cat striate cortex. J Neurophysiol. 1981 May;45(5):818–828. doi: 10.1152/jn.1981.45.5.818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini M., Madden B. C., Emerson R. C. White noise analysis of temporal properties in simple receptive fields of cat cortex. Biol Cybern. 1990;63(3):209–219. doi: 10.1007/BF00195860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin K. A., Somogyi P., Whitteridge D. Physiological and morphological properties of identified basket cells in the cat's visual cortex. Exp Brain Res. 1983;50(2-3):193–200. doi: 10.1007/BF00239183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin K. A. The Wellcome Prize lecture. From single cells to simple circuits in the cerebral cortex. Q J Exp Physiol. 1988 Sep;73(5):637–702. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1988.sp003190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maunsell J. H., Van Essen D. C. Functional properties of neurons in middle temporal visual area of the macaque monkey. I. Selectivity for stimulus direction, speed, and orientation. J Neurophysiol. 1983 May;49(5):1127–1147. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.49.5.1127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean J., Palmer L. A. Contribution of linear spatiotemporal receptive field structure to velocity selectivity of simple cells in area 17 of cat. Vision Res. 1989;29(6):675–679. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(89)90029-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movshon J. A. The velocity tuning of single units in cat striate cortex. J Physiol. 1975 Aug;249(3):445–468. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustari M. J., Bullier J., Henry G. H. Comparison of response of properties of three types of monosynaptic S-cell in cat striate cortex. J Neurophysiol. 1982 Mar;47(3):439–454. doi: 10.1152/jn.1982.47.3.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orban G. A., Gulyás B., Spileers W., Maes H. Responses of cat striate neurons to moving light and dark bars: changes with eccentricity. J Opt Soc Am A. 1987 Aug;4(8):1653–1665. doi: 10.1364/josaa.4.001653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orban G. A., Hoffmann K. P., Duysens J. Velocity selectivity in the cat visual system. I. Responses of LGN cells to moving bar stimuli: a comparison with cortical areas 17 and 18. J Neurophysiol. 1985 Oct;54(4):1026–1049. doi: 10.1152/jn.1985.54.4.1026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orban G. A., Kennedy H., Bullier J. Velocity sensitivity and direction selectivity of neurons in areas V1 and V2 of the monkey: influence of eccentricity. J Neurophysiol. 1986 Aug;56(2):462–480. doi: 10.1152/jn.1986.56.2.462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orban G. A., Kennedy H., Maes H. Response to movement of neurons in areas 17 and 18 of the cat: direction selectivity. J Neurophysiol. 1981 Jun;45(6):1059–1073. doi: 10.1152/jn.1981.45.6.1059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orban G. A., Kennedy H., Maes H. Response to movement of neurons in areas 17 and 18 of the cat: velocity sensitivity. J Neurophysiol. 1981 Jun;45(6):1043–1058. doi: 10.1152/jn.1981.45.6.1043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid R. C., Soodak R. E., Shapley R. M. Linear mechanisms of directional selectivity in simple cells of cat striate cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8740–8744. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller P. H. Central connections of the retinal ON and OFF pathways. Nature. 1982 Jun 17;297(5867):580–583. doi: 10.1038/297580a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller P. H., Finlay B. L., Volman S. F. Quantitative studies of single-cell properties in monkey striate cortex. I. Spatiotemporal organization of receptive fields. J Neurophysiol. 1976 Nov;39(6):1288–1319. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.6.1288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherk H., Horton J. C. Receptive field properties in the cat's area 17 in the absence of on-center geniculate input. J Neurosci. 1984 Feb;4(2):381–393. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-02-00381.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillito A. M. Inhibitory processes underlying the directional specificity of simple, complex and hypercomplex cells in the cat's visual cortex. J Physiol. 1977 Oct;271(3):699–720. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somogyi P., Kisvárday Z. F., Martin K. A., Whitteridge D. Synaptic connections of morphologically identified and physiologically characterized large basket cells in the striate cortex of cat. Neuroscience. 1983 Oct;10(2):261–294. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90133-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson A. B., Ahumada A. J., Jr Model of human visual-motion sensing. J Opt Soc Am A. 1985 Feb;2(2):322–341. doi: 10.1364/josaa.2.000322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wörgötter F., Holt G. Spatiotemporal mechanisms in receptive fields of visual cortical simple cells: a model. J Neurophysiol. 1991 Mar;65(3):494–510. doi: 10.1152/jn.1991.65.3.494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamane S., Maske R., Bishop P. O. Direction selectivity of simple cells in cat striate cortex to moving light bars. II. Relation to moving dark bar responses. Exp Brain Res. 1985;57(3):523–536. doi: 10.1007/BF00237839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Santen J. P., Sperling G. Elaborated Reichardt detectors. J Opt Soc Am A. 1985 Feb;2(2):300–321. doi: 10.1364/josaa.2.000300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Santen J. P., Sperling G. Temporal covariance model of human motion perception. J Opt Soc Am A. 1984 May;1(5):451–473. doi: 10.1364/josaa.1.000451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]