Abstract
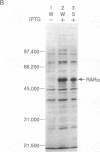
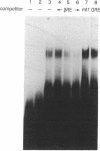
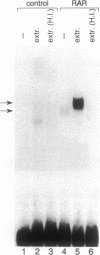
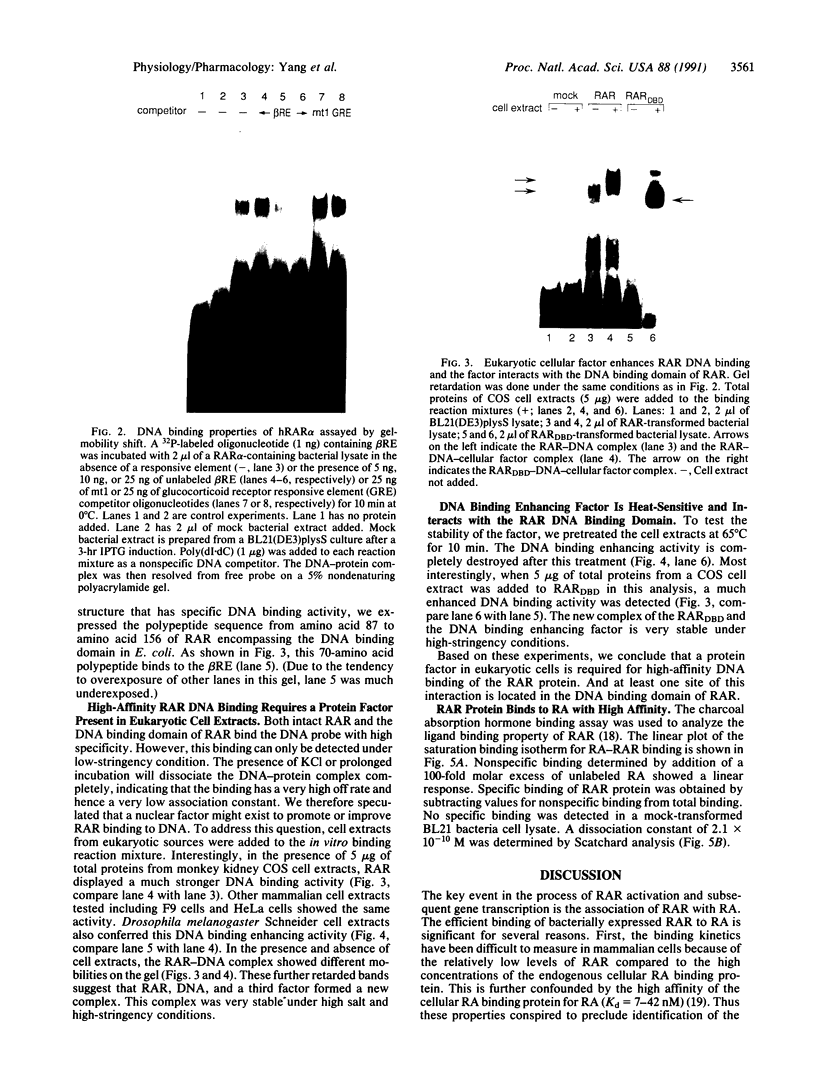
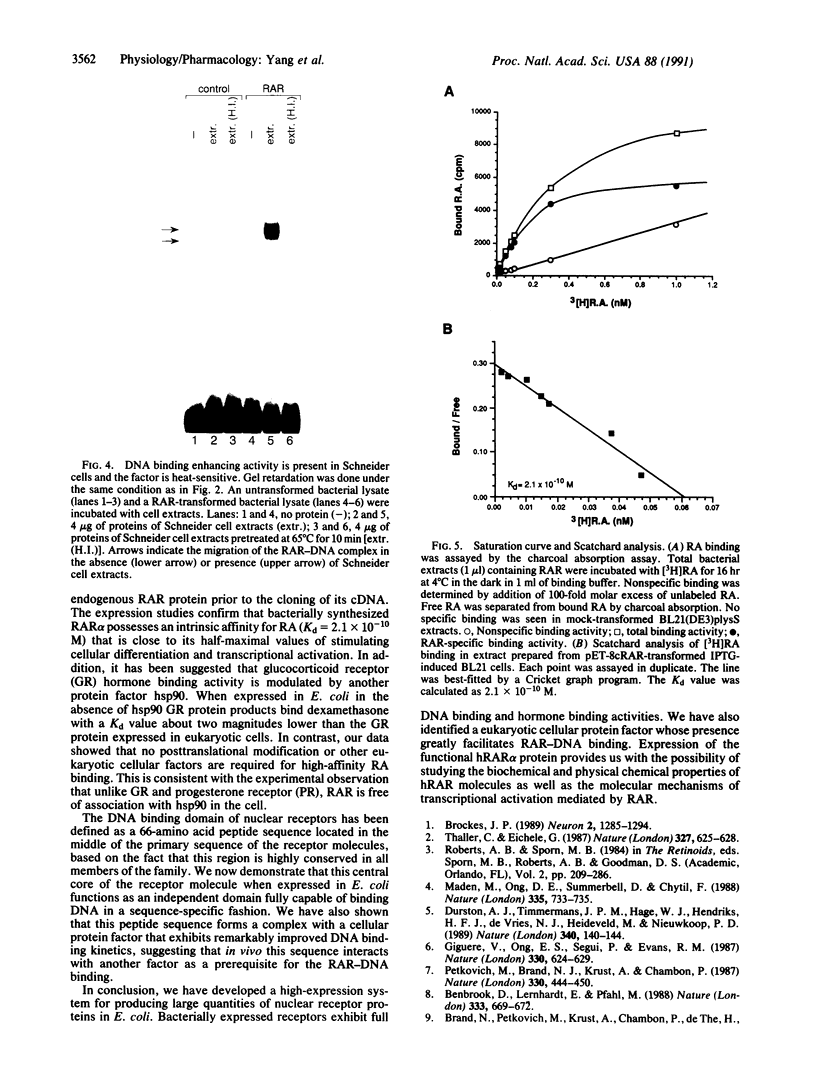
High-level expression of the full-length human retinoic acid receptor (RAR) alpha and the DNA binding domain of the RAR in Escherichia coli was achieved by using a T7 RNA polymerase-directed expression system. After induction, full-length RAR protein was produced at an estimated level of 20% of the total bacterial proteins. Both intact RAR molecules and the DNA binding domain bind to the cognate DNA response element with high specificity in the absence of retinoic acid. However, this binding is enhanced to a great extent upon the addition of eukaryotic cell extracts. The factor responsible for this enhancement is heat-sensitive and forms a complex with RAR that binds to DNA and exhibits a distinct migration pattern in the gel-mobility-shift assay. The interaction site of the factor with RAR is localized in the 70-amino acid DNA binding region of RAR. The hormone binding ability of the RAR alpha protein was assayed by a charcoal absorption assay and the RAR protein was found to bind to retinoic acid with a Kd of 2.1 x 10(-10) M.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benbrook D., Lernhardt E., Pfahl M. A new retinoic acid receptor identified from a hepatocellular carcinoma. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):669–672. doi: 10.1038/333669a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand N., Petkovich M., Krust A., Chambon P., de Thé H., Marchio A., Tiollais P., Dejean A. Identification of a second human retinoic acid receptor. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):850–853. doi: 10.1038/332850a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockes J. P. Retinoids, homeobox genes, and limb morphogenesis. Neuron. 1989 Apr;2(4):1285–1294. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90066-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damm K., Thompson C. C., Evans R. M. Protein encoded by v-erbA functions as a thyroid-hormone receptor antagonist. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):593–597. doi: 10.1038/339593a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dokoh S., Pike J. W., Chandler J. S., Mancini J. M., Haussler M. R. An improved radioreceptor assay for 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D in human plasma. Anal Biochem. 1981 Sep 1;116(1):211–222. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90346-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durston A. J., Timmermans J. P., Hage W. J., Hendriks H. F., de Vries N. J., Heideveld M., Nieuwkoop P. D. Retinoic acid causes an anteroposterior transformation in the developing central nervous system. Nature. 1989 Jul 13;340(6229):140–144. doi: 10.1038/340140a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguere V., Ong E. S., Segui P., Evans R. M. Identification of a receptor for the morphogen retinoic acid. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):624–629. doi: 10.1038/330624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haussler M. R., Donaldson C. A., Kelly M. A., Mangelsdorf D. J., Bowden G. T., Meinke W. J., Meyskens F. L., Sidell N. Identification and quantitation of intracellular retinol and retinoic acid binding proteins in cultured cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Feb 17;803(1-2):54–62. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(84)90054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krust A., Kastner P., Petkovich M., Zelent A., Chambon P. A third human retinoic acid receptor, hRAR-gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5310–5314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maden M., Ong D. E., Summerbell D., Chytil F. Spatial distribution of cellular protein binding to retinoic acid in the chick limb bud. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):733–735. doi: 10.1038/335733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petkovich M., Brand N. J., Krust A., Chambon P. A human retinoic acid receptor which belongs to the family of nuclear receptors. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):444–450. doi: 10.1038/330444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Umesono K., Mangelsdorf D. J., Bolado J., Pike J. W., Evans R. M. Jun-Fos and receptors for vitamins A and D recognize a common response element in the human osteocalcin gene. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):497–504. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90531-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sucov H. M., Murakami K. K., Evans R. M. Characterization of an autoregulated response element in the mouse retinoic acid receptor type beta gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5392–5396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thaller C., Eichele G. Identification and spatial distribution of retinoids in the developing chick limb bud. Nature. 1987 Jun 18;327(6123):625–628. doi: 10.1038/327625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasios G. W., Gold J. D., Petkovich M., Chambon P., Gudas L. J. A retinoic acid-responsive element is present in the 5' flanking region of the laminin B1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9099–9103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Thé H., Vivanco-Ruiz M. M., Tiollais P., Stunnenberg H., Dejean A. Identification of a retinoic acid responsive element in the retinoic acid receptor beta gene. Nature. 1990 Jan 11;343(6254):177–180. doi: 10.1038/343177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]