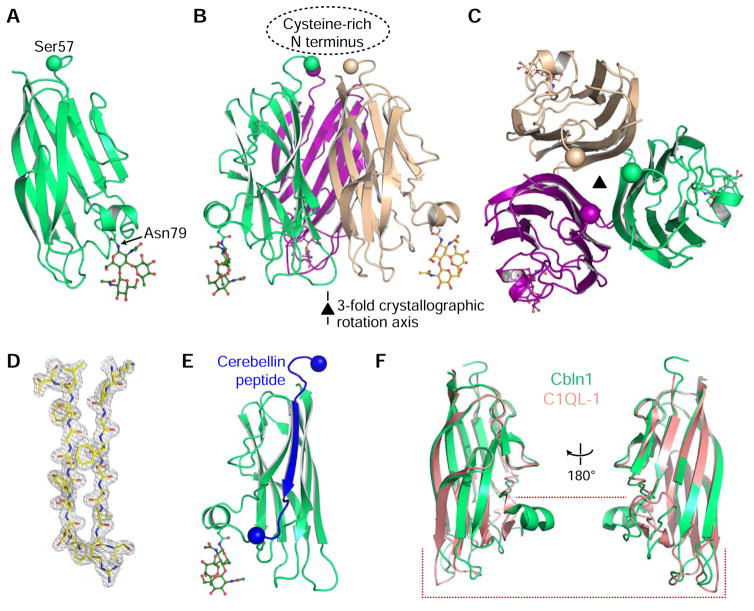
Figure 3. Crystal structure of Cbln1.
A. Cartoon model of the Cerebellin-1 C1q monomer. N-linked glycan attached to Asn79 side chain is shown in stick representation. The Cα atom of the last residue visible in the electron density is shown as a ball.
B. Cbln1 trimer can be formed by applying the crystallographic three-fold symmetry operation. The location of the missing Cysteine-rich N-terminal (CRN) domain is highlighted.
C. Looking at the Cbln1 trimer along the symmetry axis from the top, where CRN would be positioned.
D. Representative 2mFo-DFc electron density electron density.
E. Source of the Cerebellin peptide within the Cbln1 protein. Balls highlight Cα atoms of the first and last residues of the peptide.
F. Comparison of Cbln1 C1q domain to the C1q domain of C1QL-1 (PDB: 4D7Y), where most differences are towards the “bottom half” of the domain. For comparisons with other C1q domains, see Figure S2.