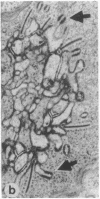
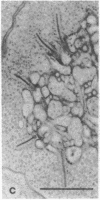
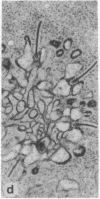
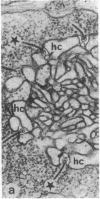
Abstract
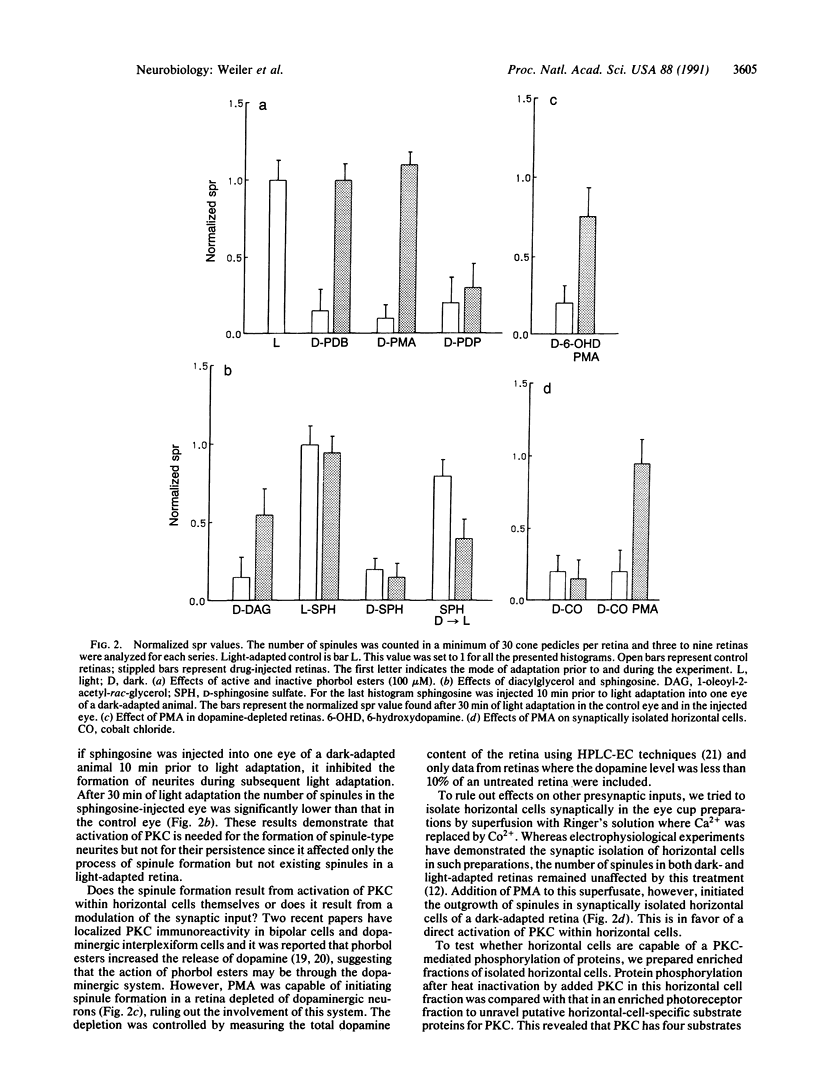
Light and dark adaptation of the teleost retina is accompanied by a remarkable morphological rearrangement of the synaptic connections between photoreceptors and second-order neurons: during light adaptation, numerous new neurites, the so-called spinules, arise from the terminal dendrites of horizontal cells invaginating the cone pedicle, and during dark adaptation, these spinules are retracted. The formation of these spinules is paralleled by the appearance of color opponency in horizontal and ganglion cells, which led to the suggestion that these spinules are the site of the inhibitory synapses in the negative feedback loop between cones and horizontal cells. The formation of the spinules in the light and their disappearance in darkness have a time course of minutes and are modulated by the neurotransmitters dopamine and glutamate, respectively. Neurotransmitters can modulate neuronal processing through a variety of second messengers that activate protein kinases, resulting most commonly in protein phosphorylation. Herein we report that activation of protein kinase C by phorbol esters promotes the formation of new horizontal-cell spinules in animals kept in the dark. Partial inhibition of protein kinase C activation with sphingosines prevents the formation of new spinules during light adaptation but does not affect established spinules. The spinule-forming effect of phorbol esters is not mediated by dopaminergic neurons, since the effect is also seen in retinas depleted of dopaminergic neurons. Phorbol esters also initiate the formation of spinules in synaptically isolated horizontal cells, demonstrating that they have a direct action on these cells. In addition, isolated horizontal cells have substrate proteins that are phosphorylated in a protein kinase C-dependent manner.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. E., Maude M. B., Kelleher P. A., Rayborn M. E., Hollyfield J. G. Phosphoinositide metabolism in the retina: localization to horizontal cells and regulation by light and divalent cations. J Neurochem. 1983 Sep;41(3):764–771. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb04806.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudry M., Evans J., Lynch G. Excitatory amino acids inhibit stimulation of phosphatidylinositol metabolism by aminergic agonists in hippocampus. Nature. 1986 Jan 23;319(6051):329–331. doi: 10.1038/319329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor D. A., Fuortes M. G., O'Bryan P. M. Receptive fields of cones in the retina of the turtle. J Physiol. 1971 Apr;214(2):265–294. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djamgoz M. B., Downing J. E., Kirsch M., Prince D. J., Wagner H. J. Plasticity of cone horizontal cell functioning in cyprinid fish retina: effects of background illumination of moderate intensity. J Neurocytol. 1988 Oct;17(5):701–710. doi: 10.1007/BF01260997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hama T., Huang K. P., Guroff G. Protein kinase C as a component of a nerve growth factor-sensitive phosphorylation system in PC12 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2353–2357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannun Y. A., Loomis C. R., Merrill A. H., Jr, Bell R. M. Sphingosine inhibition of protein kinase C activity and of phorbol dibutyrate binding in vitro and in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12604–12609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato S., Ishita S., Mawatari K., Matsukawa T., Negishi K. Dopamine release via protein kinase C activation in the fish retina. J Neurochem. 1990 Jun;54(6):2082–2090. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb04914.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Takai Y., Minakuchi R., Inohara S., Nishizuka Y. Calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase from rat brain. Subcellular distribution, purification, and properties. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13341–13348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp A. G., Dowling J. E. Dopamine enhances excitatory amino acid-gated conductances in cultured retinal horizontal cells. 1987 Jan 29-Feb 4Nature. 325(6103):437–439. doi: 10.1038/325437a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler Konrad, Weiler Reto. Dopaminergic Modulation of Transient Neurite Outgrowth from Horizontal Cells of the Fish Retina is not Mediated by cAMP. Eur J Neurosci. 1990;2(9):788–794. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1990.tb00470.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolbinger W., Kohler K., Oetting H., Weiler R. Endogenous dopamine and cyclic events in the fish retina, I: HPLC assay of total content, release, and metabolic turnover during different light/dark cycles. Vis Neurosci. 1990 Aug;5(2):143–149. doi: 10.1017/s0952523800000183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malenka R. C., Madison D. V., Nicoll R. A. Potentiation of synaptic transmission in the hippocampus by phorbol esters. Nature. 1986 May 8;321(6066):175–177. doi: 10.1038/321175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malinow R., Madison D. V., Tsien R. W. Persistent protein kinase activity underlying long-term potentiation. Nature. 1988 Oct 27;335(6193):820–824. doi: 10.1038/335820a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malinow R., Schulman H., Tsien R. W. Inhibition of postsynaptic PKC or CaMKII blocks induction but not expression of LTP. Science. 1989 Aug 25;245(4920):862–866. doi: 10.1126/science.2549638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negishi K., Kato S., Teranishi T. Dopamine cells and rod bipolar cells contain protein kinase C-like immunoreactivity in some vertebrate retinas. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Dec 5;94(3):247–252. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90025-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):661–665. doi: 10.1038/334661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raynauld J. P., Laviolette J. R., Wagner H. J. Goldfish retina: a correlate between cone activity and morphology of the horizontal cell in clone pedicules. Science. 1979 Jun 29;204(4400):1436–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.451577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladeczek F., Récasens M., Bockaert J. A new mechanism for glutamate receptor action: phosphoinositide hydrolysis. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Dec;11(12):545–549. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90183-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stell W. K., Lightfoot D. O. Color-specific interconnections of cones and horizontal cells in the retina of the goldfish. J Comp Neurol. 1975 Feb 15;159(4):473–502. doi: 10.1002/cne.901590404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Buskirk R., Dowling J. E. Isolated horizontal cells from carp retina demonstrate dopamine-dependent accumulation of cyclic AMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7825–7829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner H. J. Light-dependent plasticity of the morphology of horizontal cell terminals in cone pedicles of fish retinas. J Neurocytol. 1980 Oct;9(5):573–590. doi: 10.1007/BF01205026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watling K. J., Dowling J. E., Iversen L. L. Dopamine receptors in the retina may all be linked to adenylate cyclase. Nature. 1979 Oct 18;281(5732):578–580. doi: 10.1038/281578a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiler R., Kohler K., Kirsch M., Wagner H. J. Glutamate and dopamine modulate synaptic plasticity in horizontal cell dendrites of fish retina. Neurosci Lett. 1988 May 3;87(3):205–209. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90449-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiler R., Kohler K., Kolbinger W., Wolburg H., Kurz-Isler G., Wagner H. J. Dopaminergic neuromodulation in the retinas of lower vertebrates. Neurosci Res Suppl. 1988;8:S183–S196. doi: 10.1016/0921-8696(88)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiler R., Wagner H. J. Light-dependent change of cone-horizontal cell interactions in carp retina. Brain Res. 1984 Apr 23;298(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91141-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkovsky P., Stone S., Tranchina D. Photoreceptor to horizontal cell synaptic transfer in the Xenopus retina: modulation by dopamine ligands and a circuit model for interactions of rod and cone inputs. J Neurophysiol. 1989 Oct;62(4):864–881. doi: 10.1152/jn.1989.62.4.864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]