Abstract
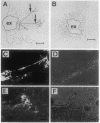
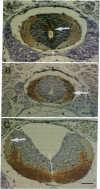
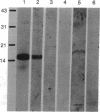
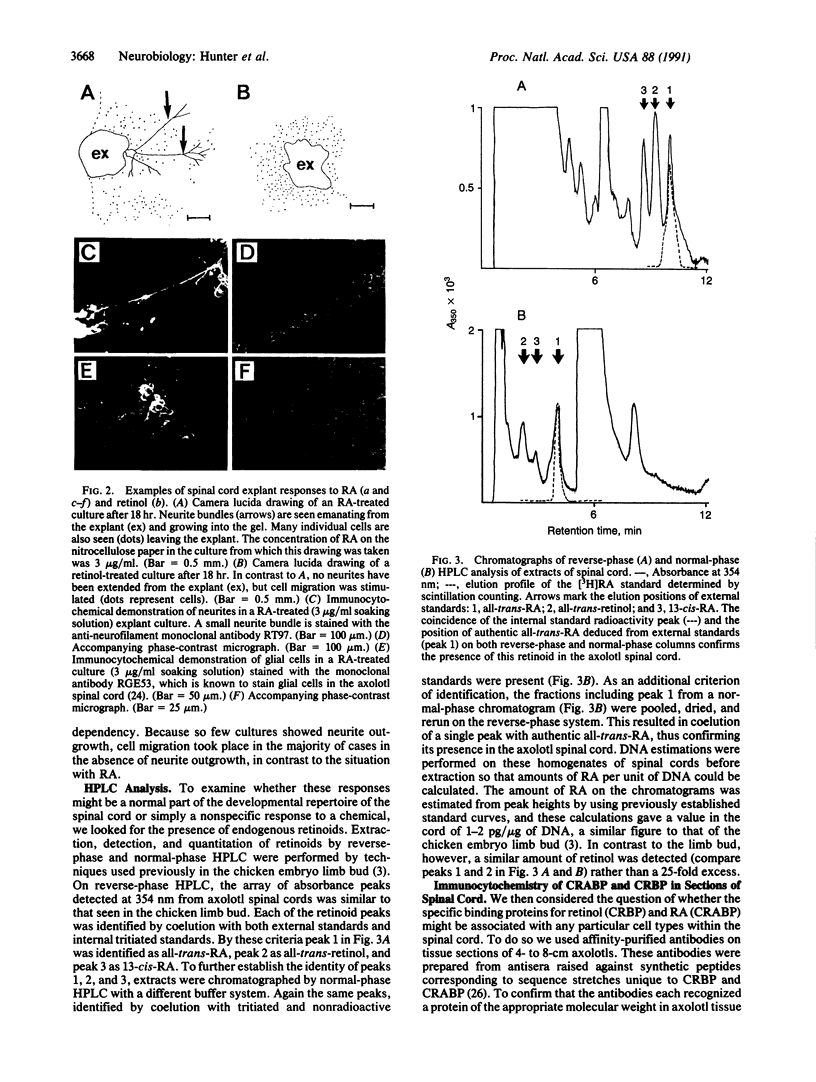
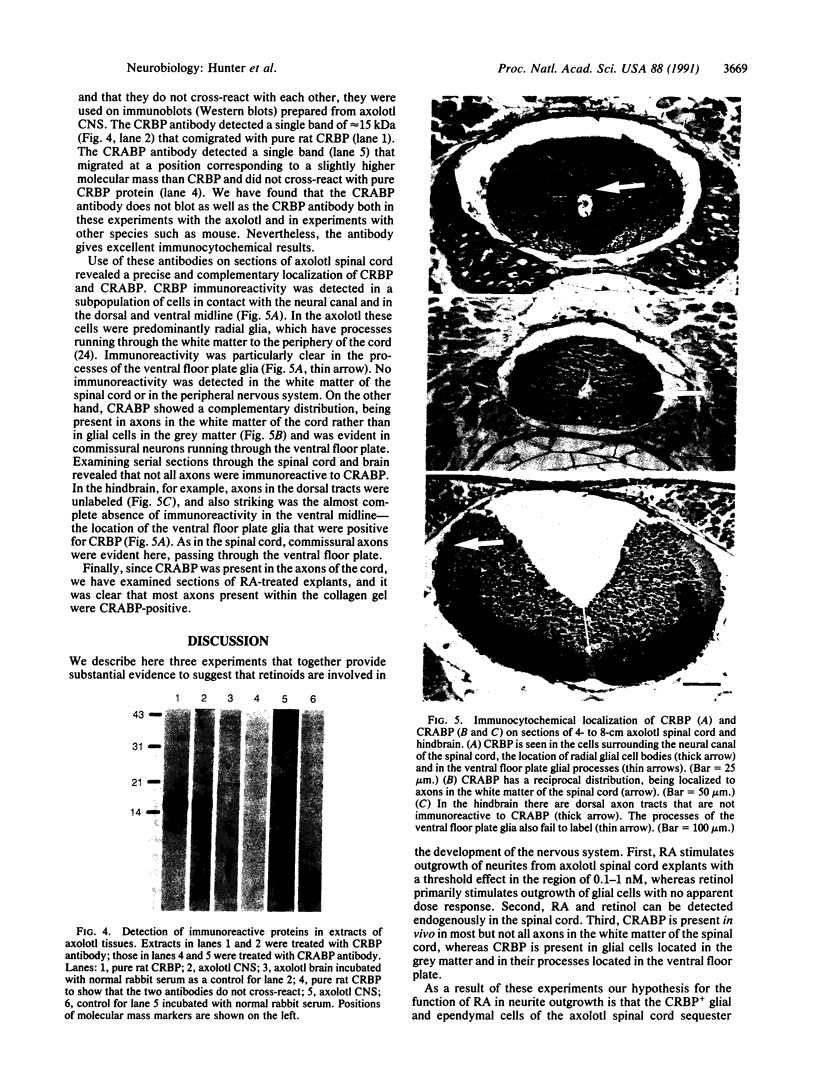
There is increasing evidence that retinoic acid (RA), a vitamin A metabolite, plays a role in the development of the nervous system. Here we specifically test this notion by examining the effect of RA on neurite outgrowth from explanted segments of the axolotl spinal cord. We show that there is a threshold concentration in the region of 0.1-1 nM above which neurite outgrowth is stimulated 4-5 fold. Retinol, by contrast, only stimulated the migration of glial cells from the explants. Using HPLC we demonstrate that RA and retinol are present endogenously in the axolotl spinal cord. In addition, we have identified by immunocytochemistry with antipeptide antibodies the cells of the spinal cord that contain the binding proteins for RA (cellular RA-binding protein; CRABP) and retinol (cellular retinol-binding protein; CRBP). CRABP is found in the axons and CRBP is found in the ependyma and glial cells. These results provide strong evidence for a role for RA in the developing nervous system, and we propose a specific hypothesis involving CRBP, CRABP, retinol, and RA in the control of axon outgrowth in the spinal cord.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. W. Retinoic acid induces neuronal differentiation of a cloned human embryonal carcinoma cell line in vitro. Dev Biol. 1984 Jun;103(2):285–293. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90316-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey J. S., Siu C. H. Purification and partial characterization of a novel binding protein for retinoic acid from neonatal rat. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9326–9332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dencker L., Annerwall E., Busch C., Eriksson U. Localization of specific retinoid-binding sites and expression of cellular retinoic-acid-binding protein (CRABP) in the early mouse embryo. Development. 1990 Oct;110(2):343–352. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.2.343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dollé P., Ruberte E., Leroy P., Morriss-Kay G., Chambon P. Retinoic acid receptors and cellular retinoid binding proteins. I. A systematic study of their differential pattern of transcription during mouse organogenesis. Development. 1990 Dec;110(4):1133–1151. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.4.1133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durston A. J., Timmermans J. P., Hage W. J., Hendriks H. F., de Vries N. J., Heideveld M., Nieuwkoop P. D. Retinoic acid causes an anteroposterior transformation in the developing central nervous system. Nature. 1989 Jul 13;340(6229):140–144. doi: 10.1038/340140a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebendal T., Jacobson C. O. Tissue explants affecting extension and orientation of axons in cultured chick embryo ganglia. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Mar 15;105(2):379–387. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90135-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards M. K., McBurney M. W. The concentration of retinoic acid determines the differentiated cell types formed by a teratocarcinoma cell line. Dev Biol. 1983 Jul;98(1):187–191. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90348-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson U., Hansson E., Nordlinder H., Busch C., Sundelin J., Peterson P. A. Quantitation and tissue localization of the cellular retinoic acid-binding protein. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Dec;133(3):482–490. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041330308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguere V., Ong E. S., Segui P., Evans R. M. Identification of a receptor for the morphogen retinoic acid. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):624–629. doi: 10.1038/330624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguère V., Lyn S., Yip P., Siu C. H., Amin S. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding a second cellular retinoic acid-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6233–6237. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath J. P., Hedlund K. O. Locomotion and cell surface movements of fibroblasts in fibrillar collagen gels. Scan Electron Microsc. 1984;(Pt 4):2031–2043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holder N., Clarke J. D., Kamalati T., Lane E. B. Heterogeneity in spinal radial glia demonstrated by intermediate filament expression and HRP labelling. J Neurocytol. 1990 Dec;19(6):915–928. doi: 10.1007/BF01186819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holder N., Clarke J. D., Stephens N., Wilson S. W., Orsi C., Bloomer T., Tonge D. A. Continuous growth of the motor system in the axolotl. J Comp Neurol. 1991 Jan 22;303(4):534–550. doi: 10.1002/cne.903030403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones-Villeneuve E. M., McBurney M. W., Rogers K. A., Kalnins V. I. Retinoic acid induces embryonal carcinoma cells to differentiate into neurons and glial cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):253–262. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamoto T., Momoi T., Momoi M. The presence of a novel cellular retinoic acid-binding protein in chick embryos: purification and partial characterization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 30;157(3):1302–1308. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammer E. J., Chen D. T., Hoar R. M., Agnish N. D., Benke P. J., Braun J. T., Curry C. J., Fernhoff P. M., Grix A. W., Jr, Lott I. T. Retinoic acid embryopathy. N Engl J Med. 1985 Oct 3;313(14):837–841. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198510033131401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langman J., Welch G. W. Effect of vitamin a on development of the central nervous system. J Comp Neurol. 1966 Sep;128(1):1–16. doi: 10.1002/cne.901280102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maden M., Hunt P., Eriksson U., Kuroiwa A., Krumlauf R., Summerbell D. Retinoic acid-binding protein, rhombomeres and the neural crest. Development. 1991 Jan;111(1):35–43. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maden M., Ong D. E., Chytil F. Retinoid-binding protein distribution in the developing mammalian nervous system. Development. 1990 May;109(1):75–80. doi: 10.1242/dev.109.1.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maden M., Ong D. E., Summerbell D., Chytil F., Hirst E. A. Cellular retinoic acid-binding protein and the role of retinoic acid in the development of the chick embryo. Dev Biol. 1989 Sep;135(1):124–132. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90163-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maden M., Ong D. E., Summerbell D., Chytil F. The role of retinoid-binding proteins in the generation of pattern in the developing limb, the regenerating limb and the nervous system. Development. 1989;107 (Suppl):109–119. doi: 10.1242/dev.107.Supplement.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maden M. Vitamin A and pattern formation in the regenerating limb. Nature. 1982 Feb 25;295(5851):672–675. doi: 10.1038/295672a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Ong E. S., Dyck J. A., Evans R. M. Nuclear receptor that identifies a novel retinoic acid response pathway. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):224–229. doi: 10.1038/345224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen C. L., Bunge R. P. Requisites for growth and myelination of urodele sensory neurons in tissue culture. J Exp Zool. 1986 Jun;238(3):373–384. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402380310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Castro A. V., Toth-Rogler L. E., Wei L. N., Nguyen-Huu M. C. Spatial and temporal pattern of expression of the cellular retinoic acid-binding protein and the cellular retinol-binding protein during mouse embryogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8813–8817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petkovich M., Brand N. J., Krust A., Chambon P. A human retinoic acid receptor which belongs to the family of nuclear receptors. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):444–450. doi: 10.1038/330444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simeone A., Acampora D., Arcioni L., Andrews P. W., Boncinelli E., Mavilio F. Sequential activation of HOX2 homeobox genes by retinoic acid in human embryonal carcinoma cells. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):763–766. doi: 10.1038/346763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tessier-Lavigne M., Placzek M., Lumsden A. G., Dodd J., Jessell T. M. Chemotropic guidance of developing axons in the mammalian central nervous system. Nature. 1988 Dec 22;336(6201):775–778. doi: 10.1038/336775a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thaller C., Eichele G. Identification and spatial distribution of retinoids in the developing chick limb bud. Nature. 1987 Jun 18;327(6123):625–628. doi: 10.1038/327625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tickle C., Alberts B., Wolpert L., Lee J. Local application of retinoic acid to the limb bond mimics the action of the polarizing region. Nature. 1982 Apr 8;296(5857):564–566. doi: 10.1038/296564a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner M., Thaller C., Jessell T., Eichele G. Polarizing activity and retinoid synthesis in the floor plate of the neural tube. Nature. 1990 Jun 28;345(6278):819–822. doi: 10.1038/345819a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelent A., Krust A., Petkovich M., Kastner P., Chambon P. Cloning of murine alpha and beta retinoic acid receptors and a novel receptor gamma predominantly expressed in skin. Nature. 1989 Jun 29;339(6227):714–717. doi: 10.1038/339714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]