Abstract
The ml-o locus in barley confers resistance to all known races of the fungus Erysiphe graminis f.sp. hordei. Since the molecular mechanisms underlying ml-o-mediated resistance are currently undefined, experiments have been initiated to isolate the gene by means of its map position. A collection of backcross lines containing ml-o alleles derived from six barley genotypes allowed us to identify a set of DNA markers very tightly linked to the resistance locus. These markers span an unexpectedly small segment of 8.6 centimorgans on chromosome 4 that includes the Ml-o locus. Two of the markers cosegregate with the resistance locus on the basis of 44 homozygous resistant plants identified within a segregating F2 population derived from an intravarietal cross. Colinearity of the resistance-linked markers was confirmed in an F2 mapping population derived from a wide cross between Hordeum vulgare subsp. vulgare and Hordeum vulgare subsp. spontaneum. The two markers cosegregating with the resistance locus in the former cross define in the latter cross an interval of 2.4 centimorgans within which Ml-o is most probably situated. The set of linked markers opens up the possibility of carrying out a bidirectional chromosomal walk or jump to the gene.
Full text
PDF

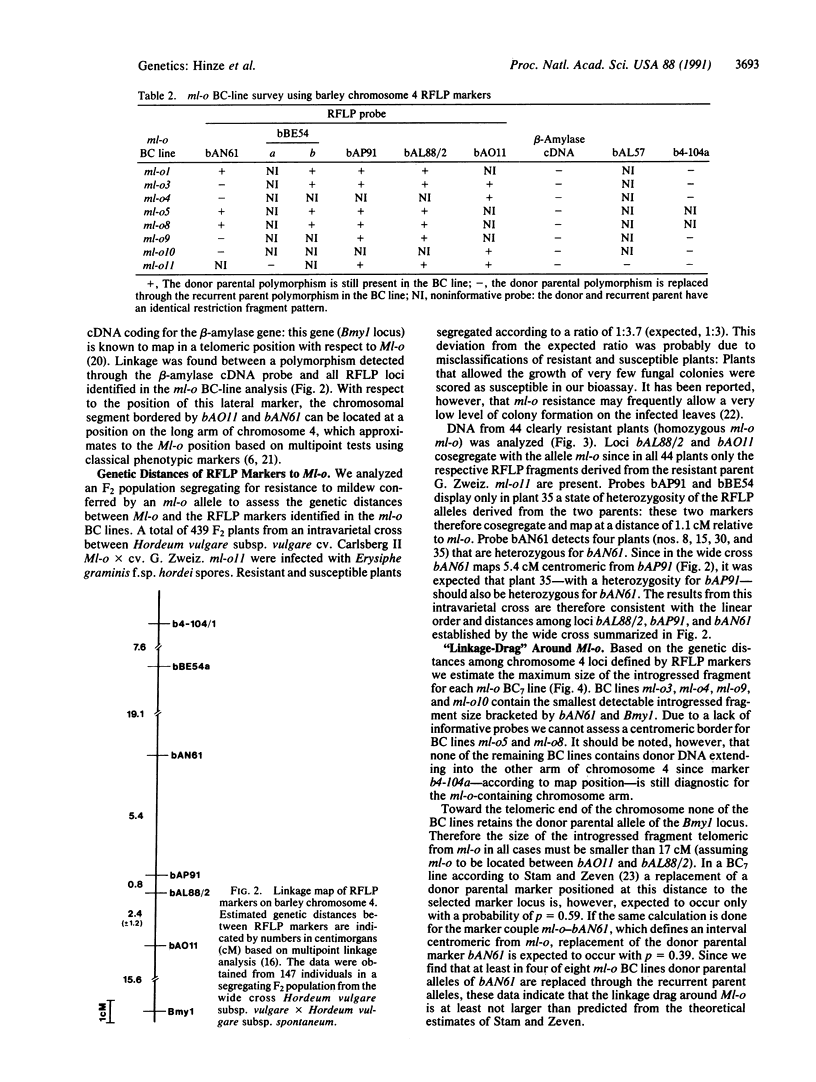
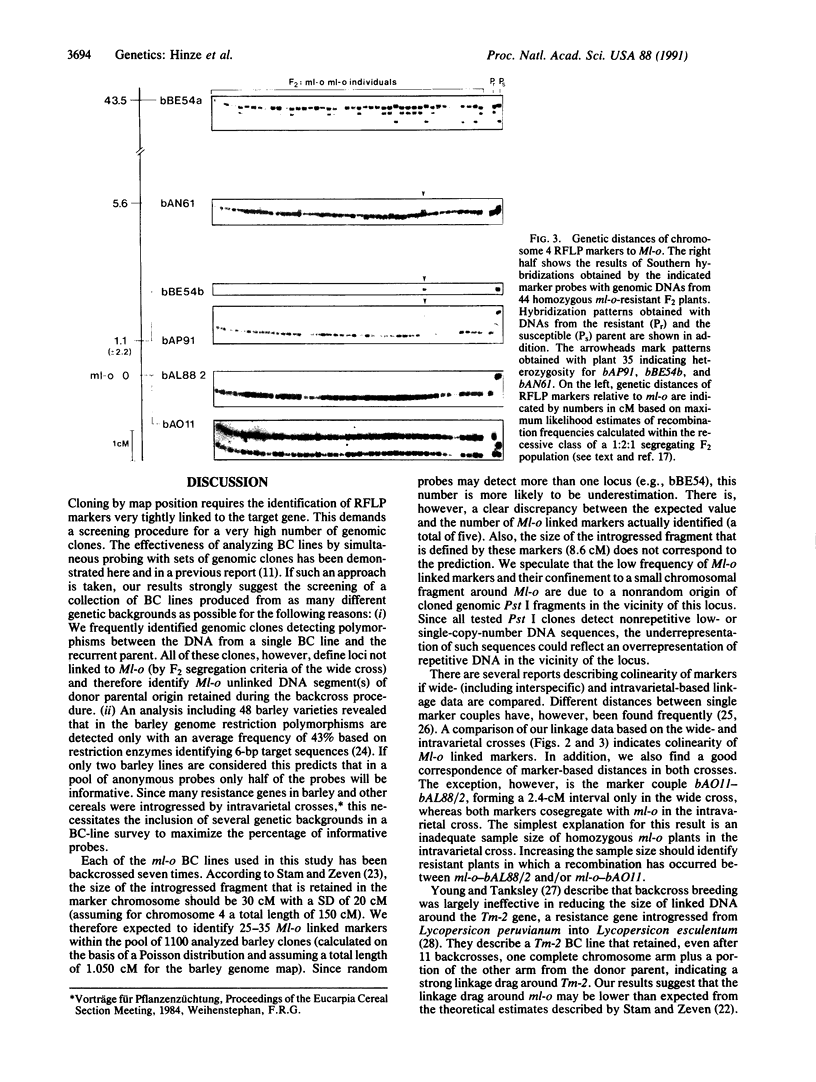

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H. Reverse genetics and human disease. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):845–850. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90799-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson A. H., Lander E. S., Hewitt J. D., Peterson S., Lincoln S. E., Tanksley S. D. Resolution of quantitative traits into Mendelian factors by using a complete linkage map of restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):721–726. doi: 10.1038/335721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poustka A., Pohl T., Barlow D. P., Zehetner G., Craig A., Michiels F., Ehrich E., Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H. Molecular approaches to mammalian genetics. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):131–139. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rick C. M. Controlled Introgression of Chromosomes of SOLANUM PENNELLII into LYCOPERSICON ESCULENTUM: Segregation and Recombination. Genetics. 1969 Aug;62(4):753–768. doi: 10.1093/genetics/62.4.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritter E., Gebhardt C., Salamini F. Estimation of recombination frequencies and construction of RFLP linkage maps in plants from crosses between heterozygous parents. Genetics. 1990 Jul;125(3):645–654. doi: 10.1093/genetics/125.3.645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Minard K., Horvath S., McNicholas J., Srelinger J., Wake C., Long E., Mach B., Hood L. A molecular map of the immune response region from the major histocompatibility complex of the mouse. Nature. 1982 Nov 4;300(5887):35–42. doi: 10.1038/300035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiberg A. Genetical studies of spontaneous sources of resistance to powdery mildew in barley. Hereditas. 1974;77(1):89–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1974.tb01357.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young N. D., Miller J. C., Tanksley S. D. Rapid chromosomal assignment of multiple genomic clones in tomato using primary trisomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9339–9348. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young N. D., Zamir D., Ganal M. W., Tanksley S. D. Use of isogenic lines and simultaneous probing to identify DNA markers tightly linked to the tm-2a gene in tomato. Genetics. 1988 Oct;120(2):579–585. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.2.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]