Abstract
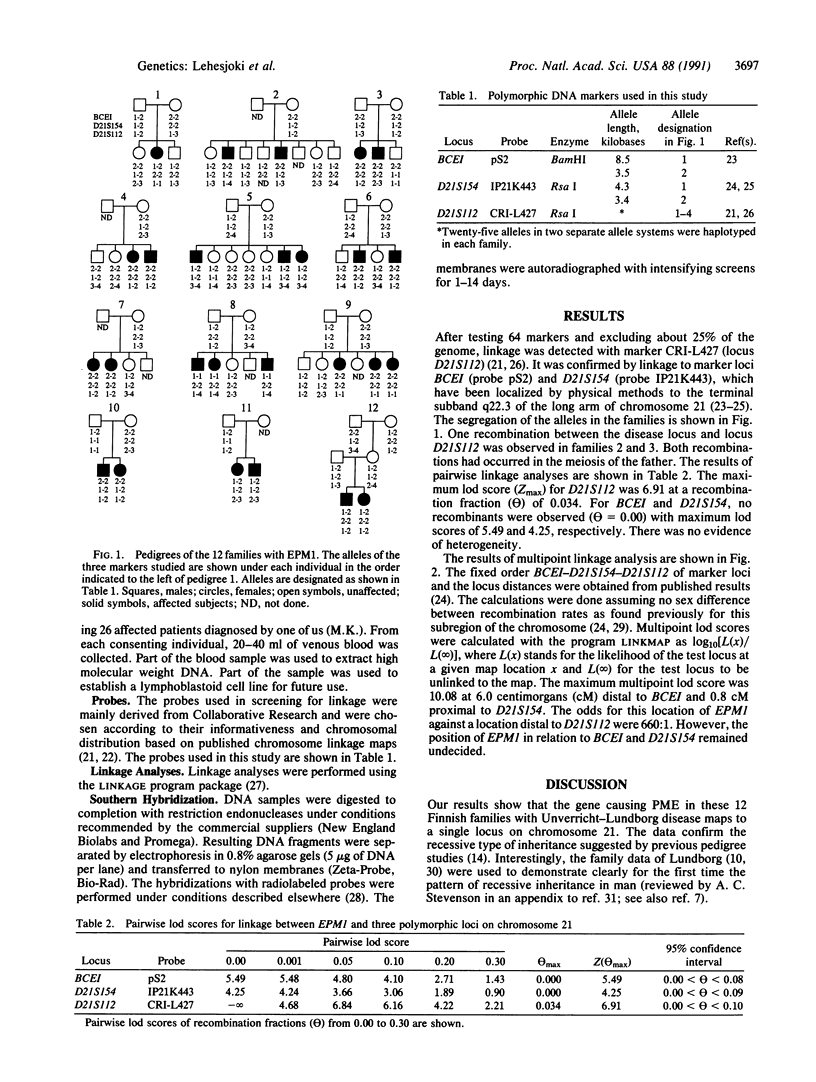
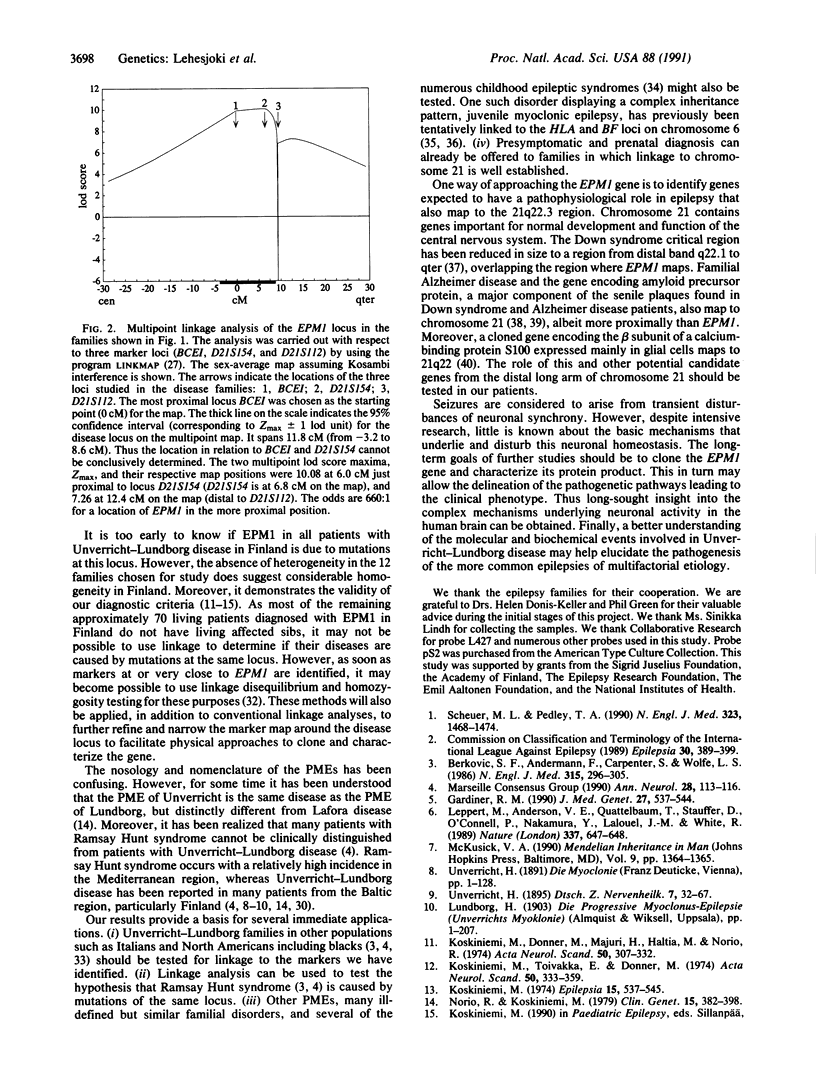
Progressive myoclonus epilepsy of Univerricht-Lundborg type is a clinically defined entity among the progressive myoclonus epilepsies. It is an autosomal recessive disorder. The underlying biochemical defect is unknown. We used linkage analysis to localize the gene in 12 families with the aid of polymorphic DNA markers. Close linkage was detected with three markers on distal chromosome 21. The loci BCEI and D21S154 gave the highest positive logarithm-of-odds (lod) scores of 5.49 and 4.25, respectively, at zero recombination. The third locus, D21S112, gave a lod score of 6.91 at a recombination fraction of 0.034. There was no evidence of heterogeneity. Multipoint lod scores calculated against a fixed map of the three marker loci gave a maximum four-point lod score of 10.08 at a location of the disease gene at 6.0 centimorgans distal to locus BCEI and 0.8 centimorgan proximal to locus D21S154. As markers BCEI and D21S154 have previously been localized to 21q22.3 by physical methods, our findings place the EMP1 gene locus (for progressive myoclonus epilepsy of the Unverricht-Lundborg type) in chromosome 21 band q22.3. This finding provides an opportunity to test several other epilepsy phenotypes, particularly the so-called Ramsay Hunt syndrome, for linkage to the same locus. It also is a starting point toward isolating and characterizing the gene and its protein product.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allore R., O'Hanlon D., Price R., Neilson K., Willard H. F., Cox D. R., Marks A., Dunn R. J. Gene encoding the beta subunit of S100 protein is on chromosome 21: implications for Down syndrome. Science. 1988 Mar 11;239(4845):1311–1313. doi: 10.1126/science.2964086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkovic S. F., Andermann F., Carpenter S., Wolfe L. S. Progressive myoclonus epilepsies: specific causes and diagnosis. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jul 31;315(5):296–305. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198607313150506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldridge R., Iivanainen M., Stern R., Koerber T., Wilder B. J. "Baltic" myoclonus epilepsy: hereditary disorder of childhood made worse by phenytoin. Lancet. 1983 Oct 8;2(8354):838–842. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90749-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner R. M. Genes and epilepsy. J Med Genet. 1990 Sep;27(9):537–544. doi: 10.1136/jmg.27.9.537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg D. A., Delgado-Escueta A. V., Widelitz H., Sparkes R. S., Treiman L., Maldonado H. M., Park M. S., Terasaki P. I. Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy (JME) may be linked to the BF and HLA loci on human chromosome 6. Am J Med Genet. 1988 Sep;31(1):185–192. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320310125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIMAN D. G., MILLAR J. H., STEVENSON A. C. Progressive familial myoclonic epilepsy in three families: its clinical features and pathological basis. Brain. 1955 Sep;78(3):325–349. doi: 10.1093/brain/78.3.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haltia M., Kristensson K., Sourander P. Neuropathological studies in three Scandinavian cases of progressive myoclonus epilepsy. Acta Neurol Scand. 1969;45(1):63–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1969.tb01220.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hästbacka J., Kaitila I., Sistonen P., de la Chapelle A. Diastrophic dysplasia gene maps to the distal long arm of chromosome 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):8056–8059. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.8056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenberg J. R., Kawashima H., Pulst S. M., Ikeuchi T., Ogasawara N., Yamamoto K., Schonberg S. A., West R., Allen L., Magenis E. Molecular definition of a region of chromosome 21 that causes features of the Down syndrome phenotype. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Aug;47(2):236–246. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koskiniemi M., Donner M., Majuri H., Haltia M., Norio R. Progressive myoclonus epilepsy. A clinical and histopathological study. Acta Neurol Scand. 1974;50(3):307–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koskiniemi M., Hyyppä M., Sainio K., Salmi T., Sarna S., Uotila L. Transient effect of L-tryptophan in progressive myoclonus epilepsy without Lafora bodies: clinical and electrophysiological study. Epilepsia. 1980 Aug;21(4):351–357. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1980.tb04082.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koskiniemi M., Palo J. Urinary excretion of indican in progressive myoclonus epilepsy without Lafora bodies. The effect of sodium valproate. J Neurol Sci. 1978 Dec;39(2-3):235–239. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(78)90125-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koskiniemi M. Psychological findings in progressive myoclonus epilepsy without Lafora bodies. Epilepsia. 1974 Dec;15(4):537–545. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1974.tb04027.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koskiniemi M., Toivakka E., Donner M. Progressive myoclonus epilepsy. Electroencephalographical findings. Acta Neurol Scand. 1974;50(3):333–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laakso J. T., Koskiniemi M. L., Wahlroos O., Härkönen M. Simultaneous determination of tryptophan and its 5-hydroxy metabolites in human cerebrospinal fluid by reversed phase liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1983 Oct;43(6):463–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E. S., Botstein D. Mapping complex genetic traits in humans: new methods using a complete RFLP linkage map. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):49–62. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leino E., MacDonald E., Airaksinen M. M., Riekkinen P. J. Homovanillic acid and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid levels in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with progressive myoclonus epilepsy. Acta Neurol Scand. 1980 Jul;62(1):41–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1980.tb03002.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppert M., Anderson V. E., Quattlebaum T., Stauffer D., O'Connell P., Nakamura Y., Lalouel J. M., White R. Benign familial neonatal convulsions linked to genetic markers on chromosome 20. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):647–648. doi: 10.1038/337647a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moisan J. P., Mattei M. G., Mandel J. L. Chromosome localization and polymorphism of an oestrogen-inducible gene specifically expressed in some breast cancers. Hum Genet. 1988 Jun;79(2):168–171. doi: 10.1007/BF00280558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norio R., Koskiniemi M. Progressive myoclonus epilepsy: genetic and nosological aspects with special reference to 107 Finnish patients. Clin Genet. 1979 May;15(5):382–398. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1979.tb01770.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson D., Gardiner K., Kao F. T., Tanzi R., Watkins P., Gusella J. F. Mapping of the gene encoding the beta-amyloid precursor protein and its relationship to the Down syndrome region of chromosome 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8266–8270. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouyer F., de la Chapelle A., Andersson M., Weissenbach J. An interspersed repeated sequence specific for human subtelomeric regions. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):505–514. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08137.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouyer F., de la Chapelle A., Weissenbach J. A polymorphic DNA sequence from the terminal part of chromosome 5p [D5S109]. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 25;18(6):1663–1663. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheuer M. L., Pedley T. A. The evaluation and treatment of seizures. N Engl J Med. 1990 Nov 22;323(21):1468–1474. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199011223232107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumm J. W., Knowlton R. G., Braman J. C., Barker D. F., Botstein D., Akots G., Brown V. A., Gravius T. C., Helms C., Hsiao K. Identification of more than 500 RFLPs by screening random genomic clones. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Jan;42(1):143–159. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace S. J. Childhood epileptic syndromes. Lancet. 1990 Aug 25;336(8713):486–488. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92024-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren A. C., Slaugenhaupt S. A., Lewis J. G., Chakravarti A., Antonarakis S. E. A genetic linkage map of 17 markers on human chromosome 21. Genomics. 1989 May;4(4):579–591. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90282-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



