Abstract
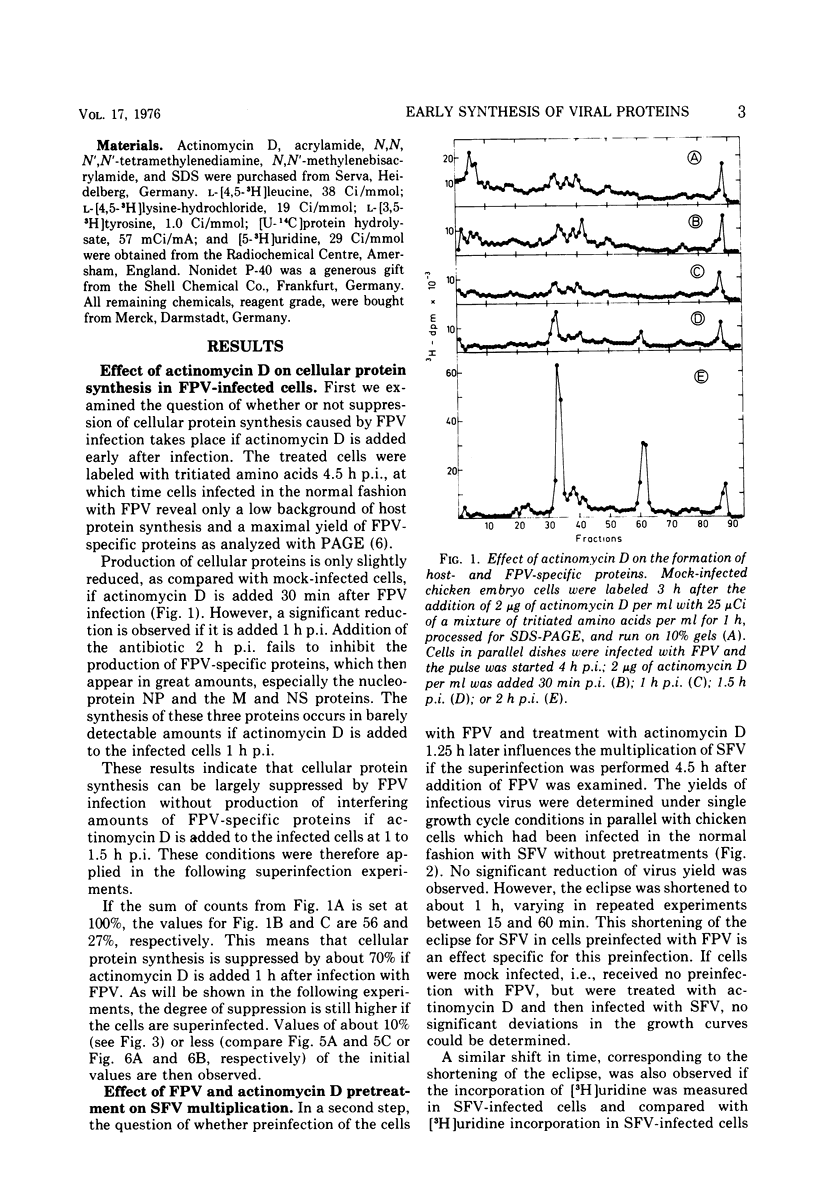
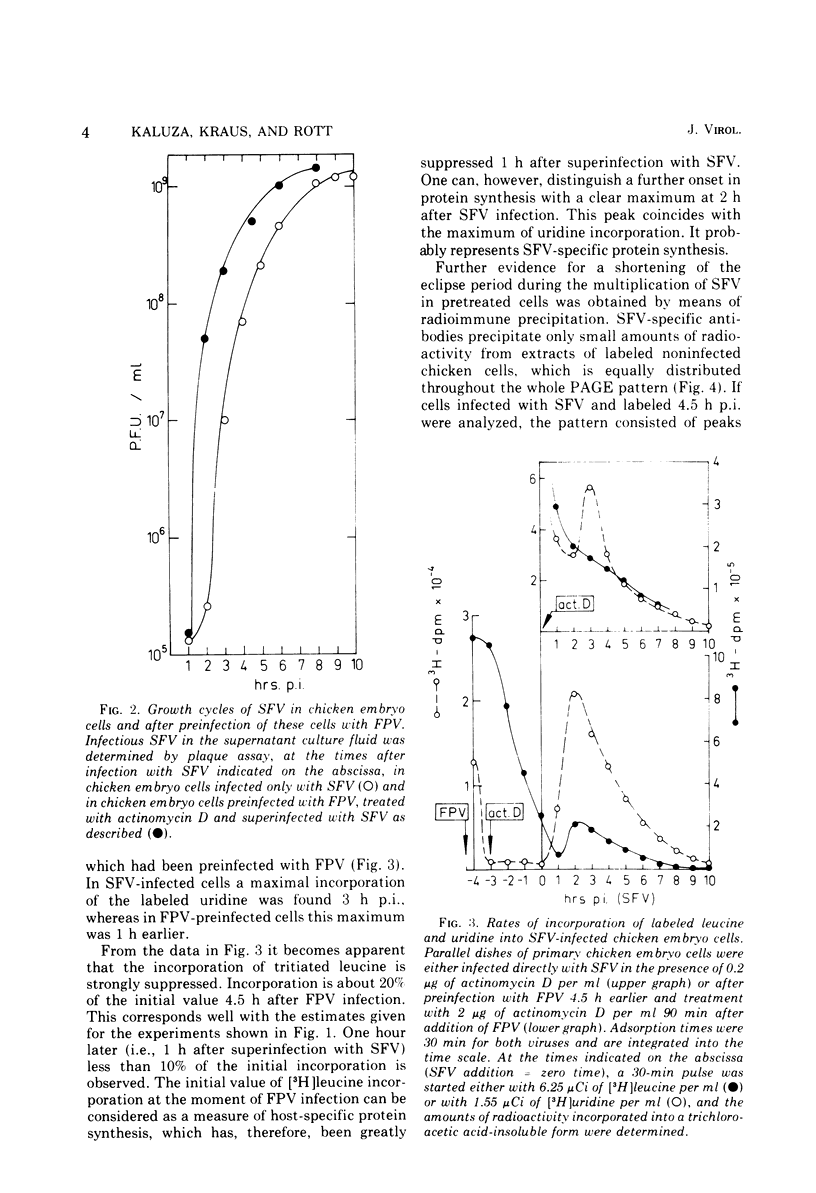
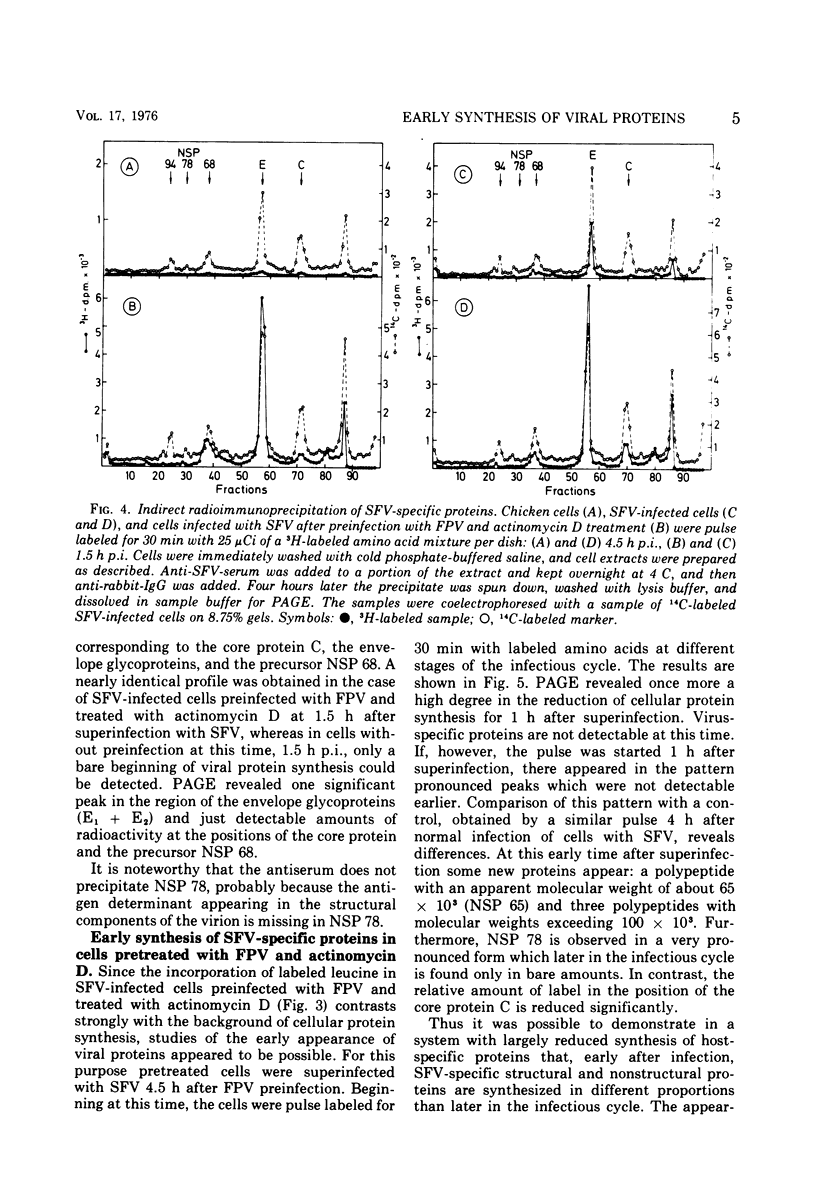
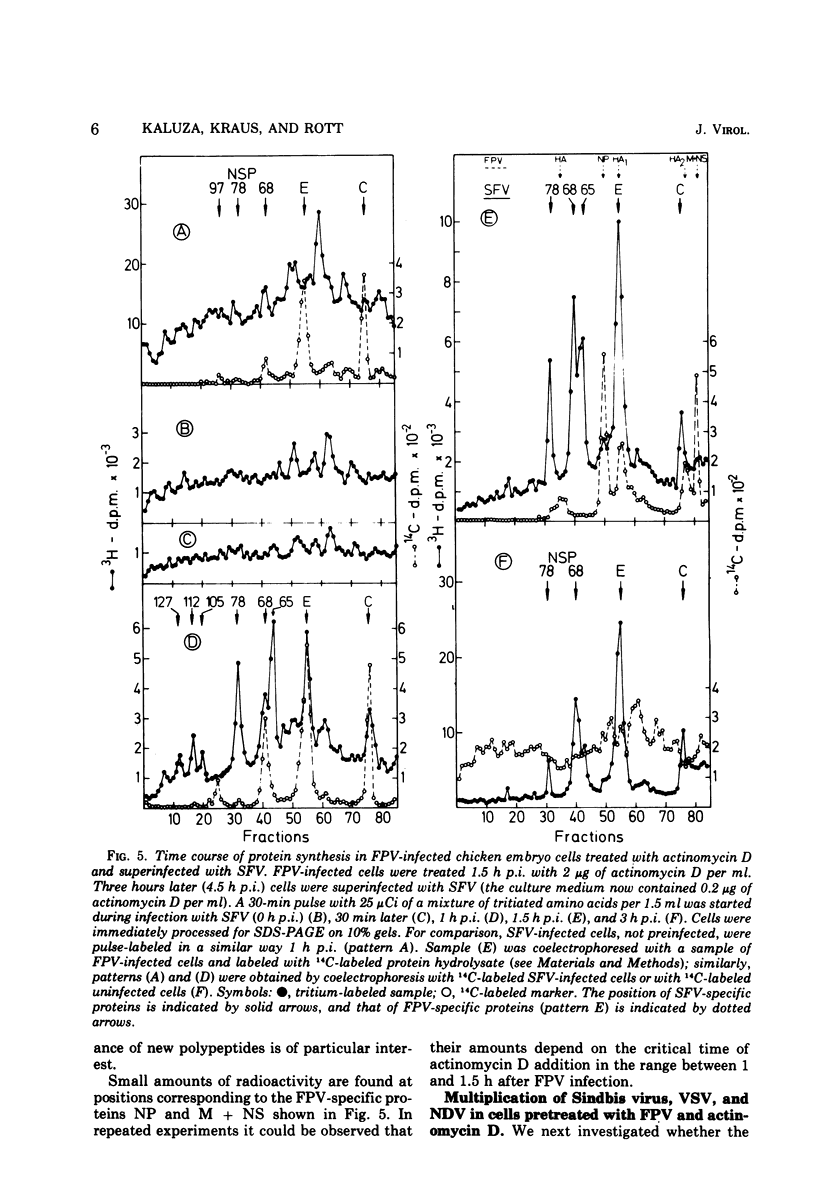
A method is described for analysis of viral protein synthesis early after infection when minute amounts of viral proteins are effectively concealed by large amounts of produced host-specific proteins. The method is superior to a radioimmune assay, since all virus-induced proteins can be measured independent of their immunological reactivity. Host-specific protein synthesis can be suppressed by infection with fowl plague virus. Addition of actinomycin D 1.25 h postinfection does not prevent this suppression, but it does block effectively the formation of fowl plague virus-specific proteins. Such cells synthesize only small amounts of cellular proteins, as revealed by polyacrylamide electrophoresis. They can be superinfected with several different enveloped viruses, however, without significant diminution of virus yields. In pretreated cells the eclipse is shortened for Semliki Forest virus, Sindbis virus, and vesicular stomatitis virus, but prolonged for Newcastle disease virus. The onset of protein synthesis, specific for the superinfecting virus, could be clearly demonstrated within 1 h after superinfection. At this time, in cells superinfected with Semliki Forest virus, great amounts of NSP 78 (nonstructural protein; molecular weight, 78 × 103) and reduced amounts of the core protein C could be demonstrated. The precursor glycoprotein NSP 68 is followed by a new polypeptide, NSP 65; three proteins with molecular weights exceeding 100 × 103 were observed which are missing later in the infectious cycle. Similar results were obtained after superinfection with Sindbis virus. The formation of a new polypeptide with a molecular weight of about 80 × 103 was detected. After superinfection with vesicular stomatitis virus or Newcastle disease virus the formation of new proteins, characteristic for the early stage of infection, was not observed.
Full text
PDF

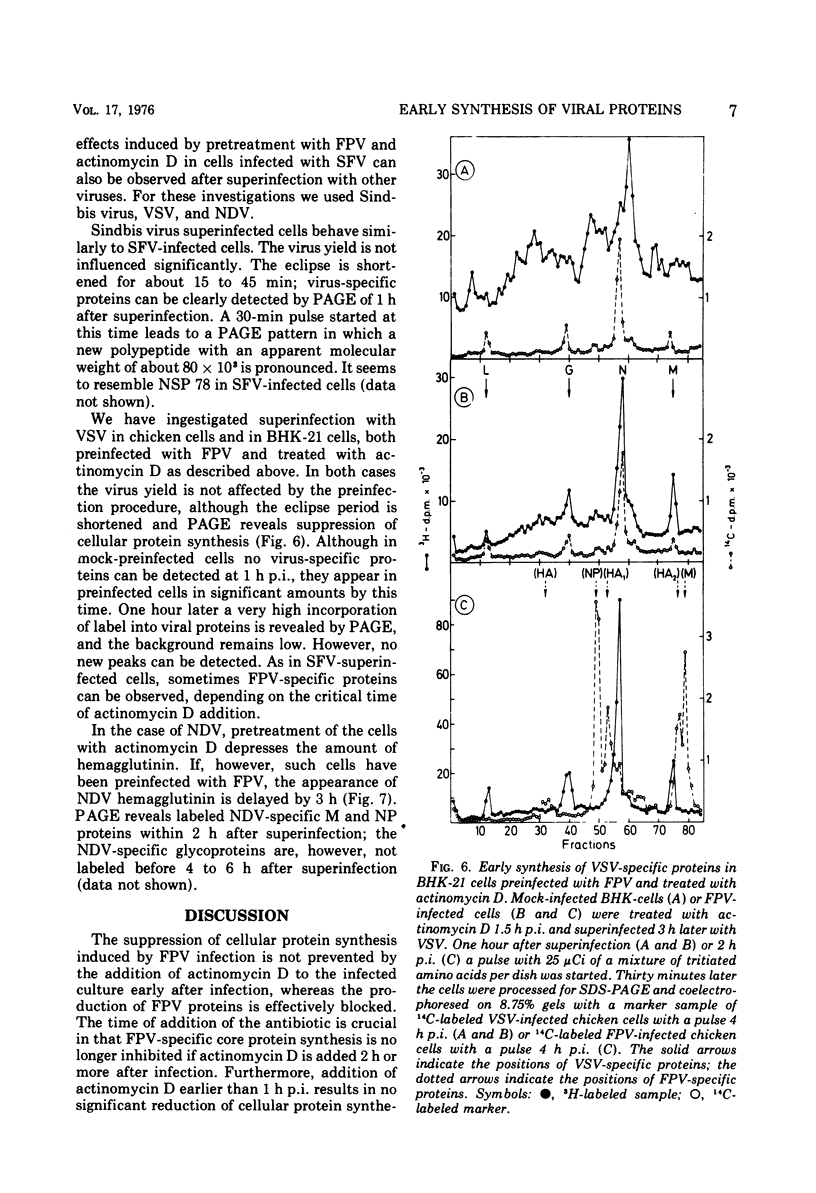
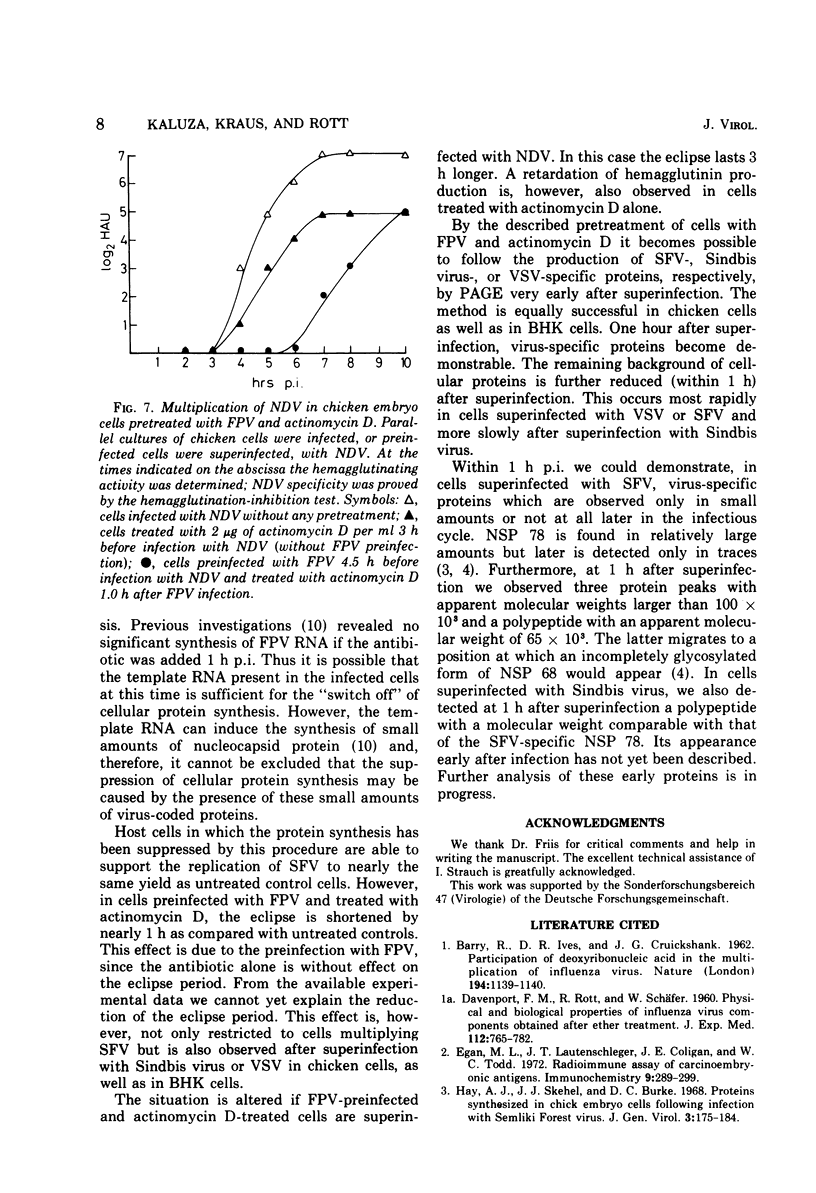

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARRY R. D., IVES D. R., CRUICKSHANK J. G. Participation of deoxyribonucleic acid in the multiplication of influenza virus. Nature. 1962 Jun 23;194:1139–1140. doi: 10.1038/1941139a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVENPORT F. M., ROTT R., SCHAEFER W. Physical and biological properties of influenza virus components obtained after ether treatment. J Exp Med. 1960 Nov 1;112:765–782. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.5.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan M. L., Lautenschleger J. T., Coligan J. E., Todd C. W. Radioimmune assay of carcinoembryonic antigen. Immunochemistry. 1972 Mar;9(3):289–299. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90093-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay A. J., Skehel J. J., Burke D. C. Proteins synthesized in chick cells following infection with Semliki Forest virus. J Gen Virol. 1968 Sep;3(2):175–184. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-3-2-175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaluza G. Effect of impaired glycosylation on the biosynthesis of Semliki forest virus glycoproteins. J Virol. 1975 Sep;16(3):602–612. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.3.602-612.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Caliguiri L. A., Choppin P. W. The proteins of the parainfluenza virus SV5. II. The carbohydrate content and glycoproteins of the virion. Virology. 1970 Oct;42(2):473–481. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90290-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Rott R., Becht H. On the structure of the influenza virus envelope. Virology. 1972 Mar;47(3):579–591. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90547-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pons M. W. The inhibition of influenza virus RNA synthesis by actinomycin D and cycloheximide. Virology. 1973 Jan;51(1):120–128. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90372-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTT R., SCHOLTISSEK C. EINFLUSS VON ACTINOMYCIN AUF DIE VERMEHRUNG VON MYXOVIREN. Z Naturforsch B. 1964 Apr;19:316–323. doi: 10.1007/BF01191316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rott R., Scholtissek C., Klenk H. D., Kaluza G. Intrinsic interference between different enveloped RNA viruses. J Gen Virol. 1972 Dec;17(3):255–264. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-17-3-255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtissek C., Rott R. Synthesis in vivo of influenza virus plus and minus strand RNA and its preferential inhibition by antibiotics. Virology. 1970 Apr;40(4):989–996. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90145-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons K., Keränen S., Käriänen L. Identification of a precursor for one of the Semliki forest virus membrane proteins. FEBS Lett. 1973 Jan 15;29(2):87–91. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80532-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt V. M., Eisenman R. Identification of a large polypeptide precursor of avian oncornavirus proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1734–1738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. R., Prevec L., Brown F., Summers D. F., Sokol F., MacLeod R. Classification of rhabdovirus proteins: a proposal. J Virol. 1972 Dec;10(6):1228–1230. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.6.1228-1230.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIMMERMANN T., SCHAEFER W. Effect of p-fluorophenyl-alanine of fowl plague virus multiplication. Virology. 1960 Aug;11:676–698. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(60)90114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



