Abstract
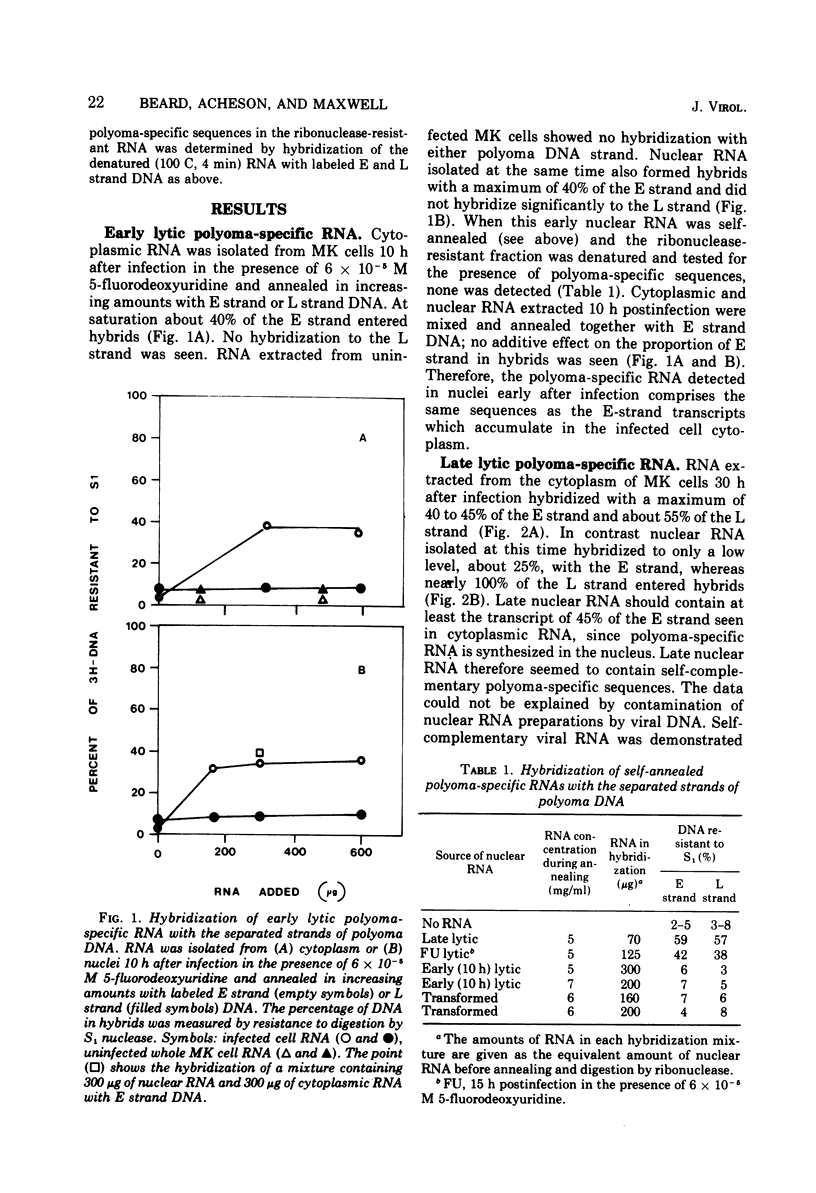
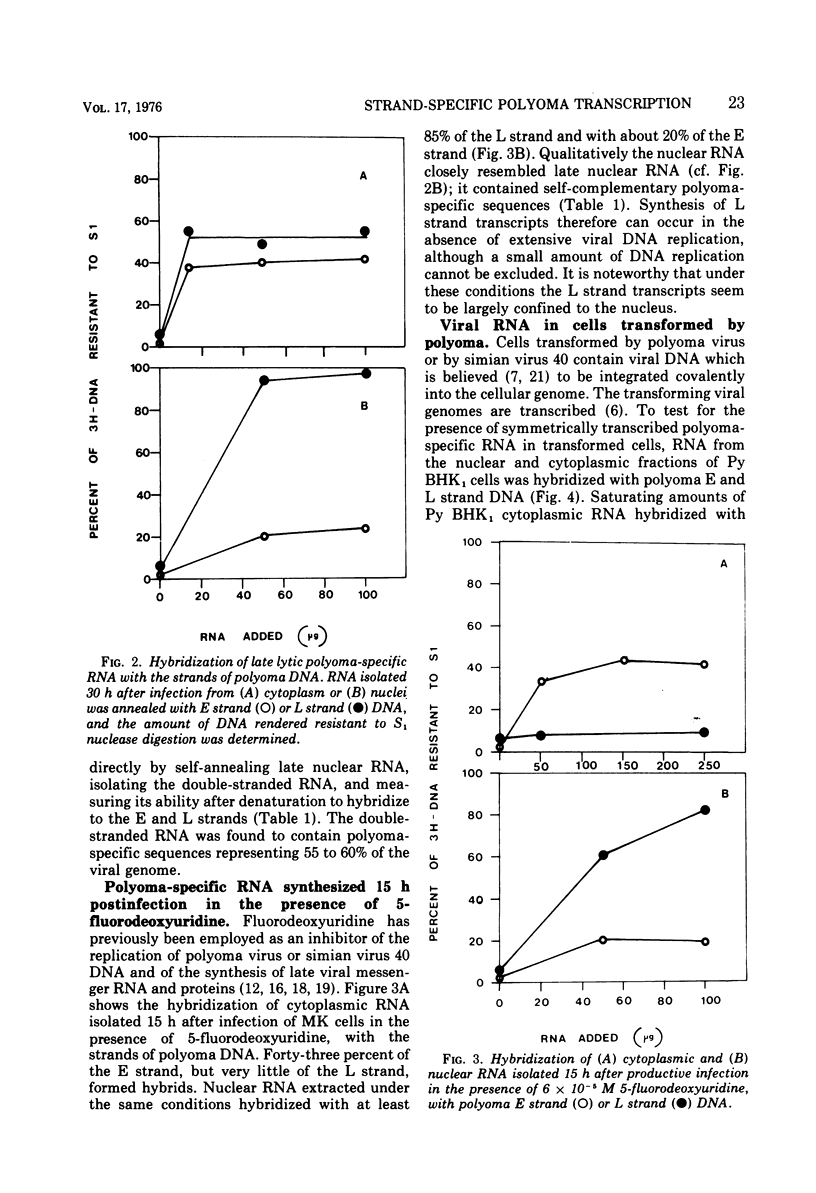
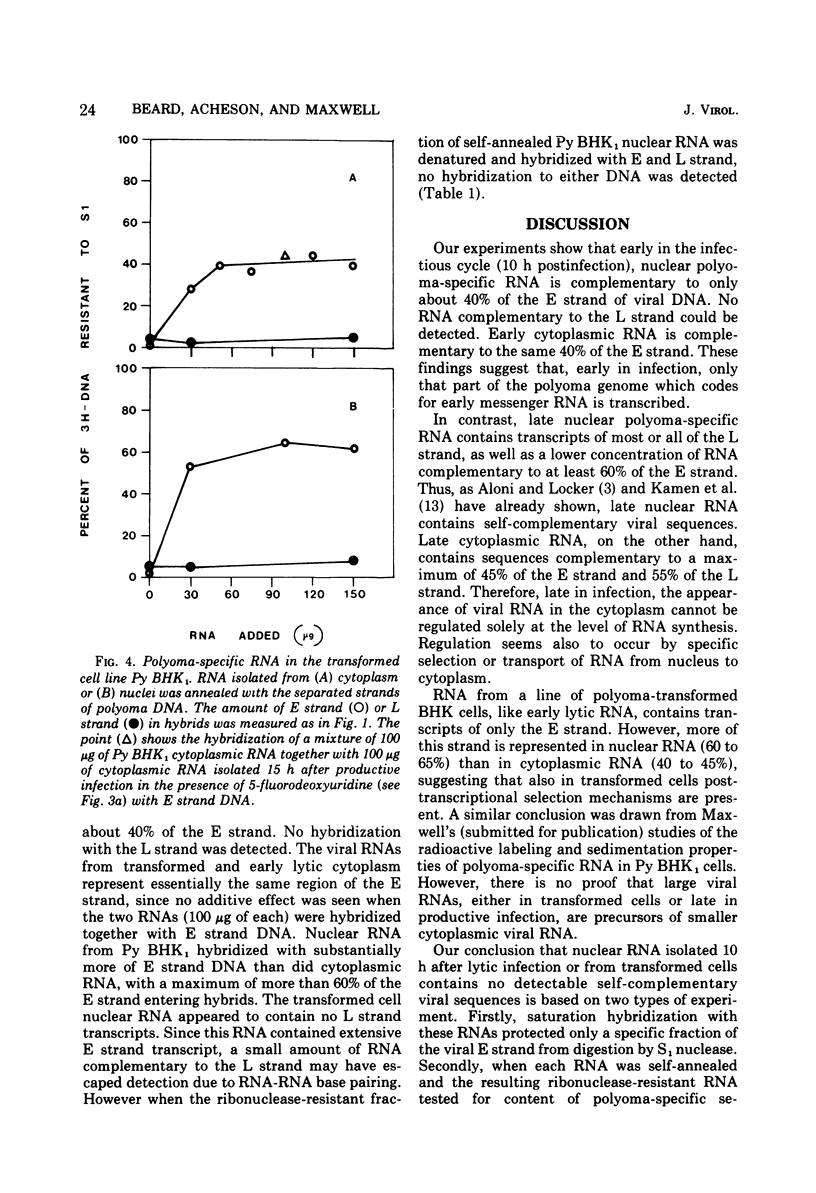
The DNA strand origin of nuclear and cytoplasmic polyoma-specific RNA in productively infected mouse cells and in a line of polyoma-transformed hamster cells was determined by hybridization of unlabeled RNA with radioactively labeled separated strands of polyoma DNA. Early in the productive cycle (10 h postinfection) nuclear viral RNA is complementary to only about 40% of the E strand of viral DNA. No RNA complementary to the L strand was detected even when the RNA was first self-annealed to enrich for possible minor species. Early cytoplasmic RNA is complementary to the same 40% of the E strand. Thus, only that part of the polyoma genome which codes for early viral messenger RNA appears to be transcribed. Late in infection, nuclear viral RNA is complementary to most or all of the L strand and to at least 60% of the E strand. Late cytoplasmic viral RNA hybridizes to 40 to 45% of the E strand and 50 to 55% of the L strand. The transformed cell nuclear viral RNA is complementary to 60% of the E strand, whereas cytoplasmic RNA is complementary to 40% of the E strand and comprises the same polyoma-specific sequences as are found in RNA early in productive infection. No L strand transcripts could be detected. Thus, in the transformed cells and late in productive infection, viral RNA sequences in the cytoplasm are a specific subset of those in the nucleus.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acheson N. H., Buetti E., Scherrer K., Weil R. Transcription of the polyoma virus genome: synthesis and cleavage of giant late polyoma-specific RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2231–2235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aloni Y. Extensive symmetrical transcription of Simian Virus 40 DNA in virus-yielding cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2404–2409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aloni Y., Locker H. Symmetrical in vivo transcription of polyoma DNA and the separation of self-complementary viral and cell RNA. Virology. 1973 Aug;54(2):495–505. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90159-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babiuk L. A., Hudson J. B. 'Integration' of polyoma virus DNA into mammalian genomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Apr 14;47(1):111–118. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barzilai R. SV40 DNA: quantitative conversion of closed circular to open circular form by an ethidium bromide-restricted endonuclease. J Mol Biol. 1973 Mar 15;74(4):739–742. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin T. L. Virus-specific RNA in cells productively infected or transformed by polyoma virus. J Mol Biol. 1966 Apr;16(2):359–373. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80179-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan M., McKenna G., Sharp P. A. Cleavage of mouse DNA by a restriction enzyme as a clue to the arrangement of genes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:383–395. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buetti E. Characterization of late polyoma mRNA. J Virol. 1974 Aug;14(2):249–260. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.2.249-260.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin R. M. Purification and properties of the replicative intermediate of the RNA bacteriophage R17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jun;55(6):1504–1511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.6.1504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germond J. E., Vogt V. M., Hirt B. Characterization of the single-strand-specific nuclease S1 activity on double-stranded supercoiled polyoma DNA. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Apr 16;43(3):591–600. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03446.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Defendi V. Integration of simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid into the deoxyribonucleic acid of permissive monkey kidney cells. J Virol. 1972 Apr;9(4):705–707. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.4.705-707.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson J., Goldstein D., Weil R. A study on the transcription of the polyoma viral genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jan;65(1):226–233. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.1.226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamen R., Lindstrom D. M., Shure H., Old R. W. Virus-specific RNA in cells productively infected or transformed by polyoma virus. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):187–198. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., Howley P., Nathans D., Martin M. Posttranscriptional selection of simian virus 40-specific RNA. J Virol. 1975 Feb;15(2):433–437. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.2.433-437.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., Martin M. A., Lee T. N., Danna K. J., Nathans D. A map of simian virus 40 transcription sites expressed in productively infected cells. J Mol Biol. 1973 Aug 5;78(2):377–389. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90123-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MELNICK J. L., STINEBAUGH S. E., RAPP F. INCOMPLETE SIMIAN PAPOVAVIRUS SV40. FORMATION OF NON-INFECTIOUS VIRAL ANTIGEN IN THE PRESENCE OF FLUOROURACIL. J Exp Med. 1964 Feb 1;119:313–326. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.2.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P., La Torre J., Kelley D. E., Greenberg J. R. On the lability of poly(A) sequences during extraction of messenger RNA from polyribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Mar 14;262(2):220–226. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90236-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J., Sharp P. A., Keller W. Transcription of Simian virus 40. I. Separation of the strands of SV40 DNA and hybridization of the separated strands to RNA extracted from lytically infected and transformed cells. J Mol Biol. 1972 Sep 14;70(1):57–71. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90163-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J., Sugden B., Keller W., Sharp P. A. Transcription of simian virus 40. 3. Mapping of "early" and "late" species of RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3711–3715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J., Westphal H., Srinivasan P. R., Dulbecco R. The integrated state of viral DNA in SV40-transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1288–1295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt V. M. Purification and further properties of single-strand-specific nuclease from Aspergillus oryzae. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Feb 15;33(1):192–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02669.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINOCOUR E. Purification of polyoma virus. Virology. 1963 Feb;19:158–168. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil R., Kára J. Polyoma "tumor antigen": an activator of chromosome replication? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):1011–1017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.1011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil R., Salomon E., May E., May P. A simplifying concept in tumor virology: virus-specific "pleiotropic effectors". Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):381–395. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



