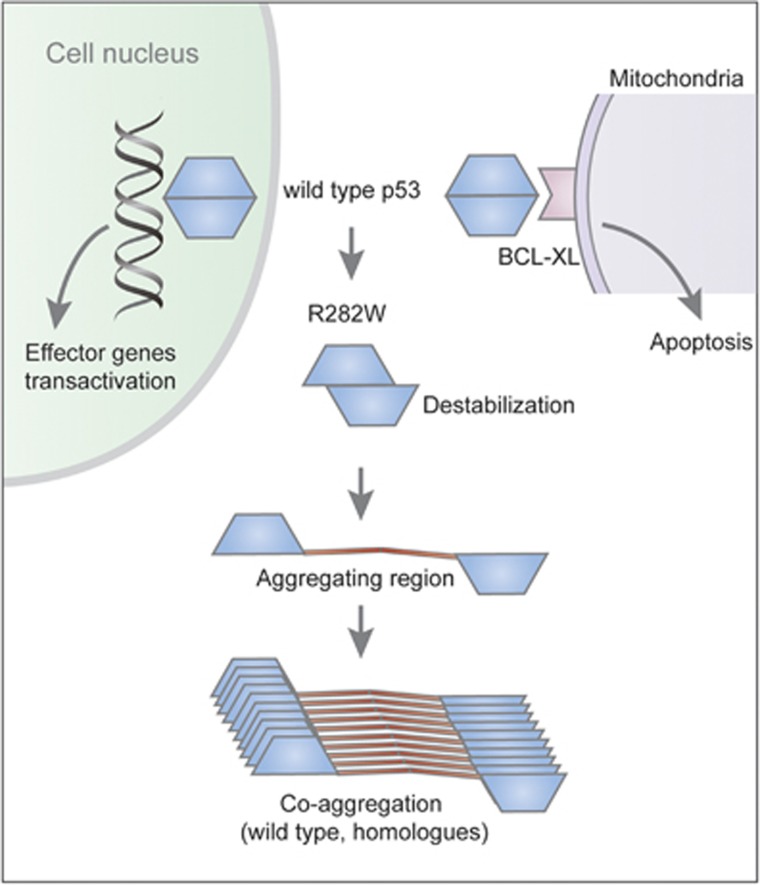
Figure 2.
Structural effects of R282W mutation. In response to DNA damage, the wild-type p53 binds to DNA in the nucleus and transactivates downstream effector genes, and it interacts with BCL-XL in the mitochondria and induces mitochondrial apoptosis. The R282W mutation causes destabilization of the protein structure, impairing its binding to DNA and BCL-XL. Moreover, the mutation induces exposure of the aggregation-prone region that is normally buried in the hydrophobic core of p53 protein. This induces coaggregation of the wild-type p53 and its homologues p63 and p73.