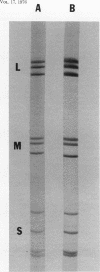
Abstract
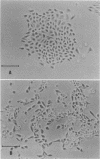
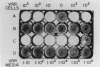
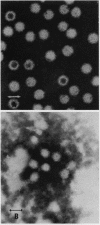
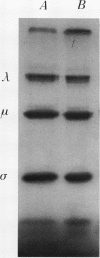
We obtained a persistently infected line of Chinese hamster ovary cells by selection for resistance to reovirus infection. The cells were persistently infected by a population of viruses that were (i) cytopathic for parental chinese hamster ovary cells and (ii) similar to wild-type reovirus in molecular characteristics. The growth rate, plating efficiency, and morphology of the cells were altered. A large majority of the cells in the population were infected. There was no detectable interferon present in the medium. The cells were relatively resistant to a wide range of viruses.
Full text
PDF

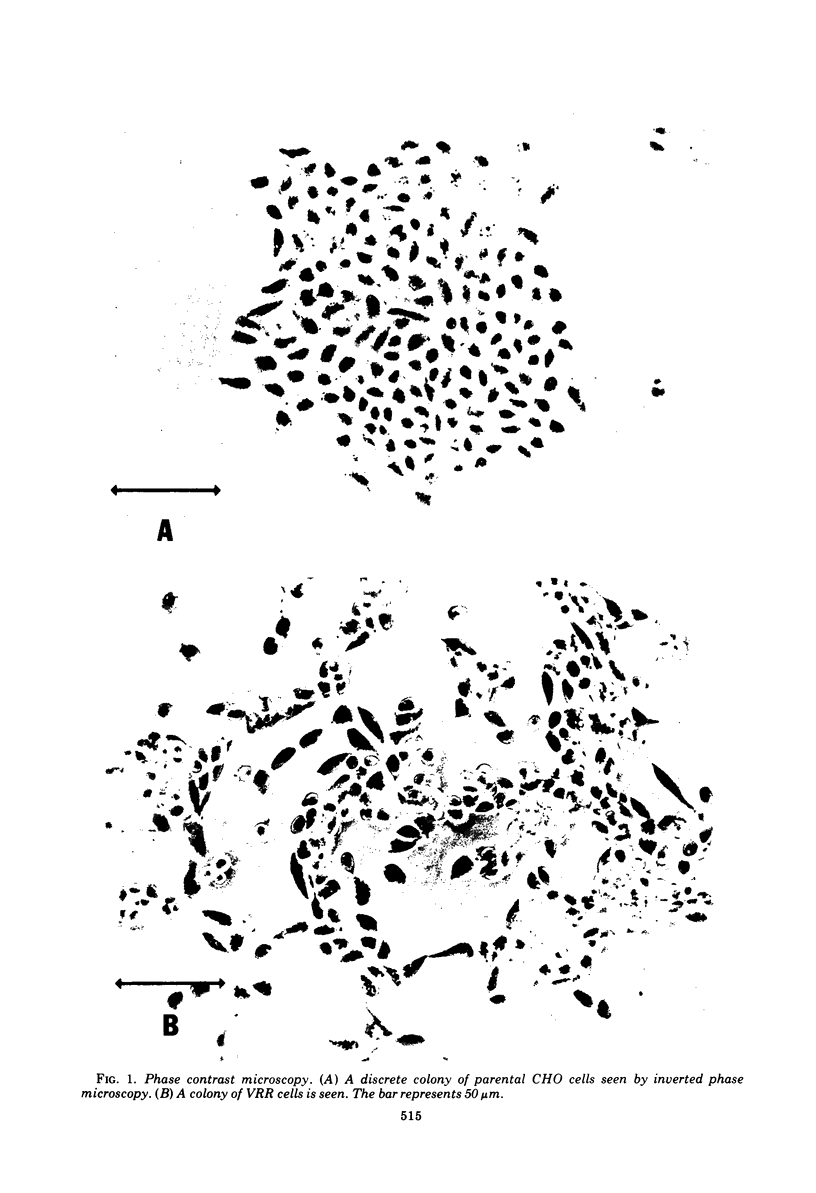
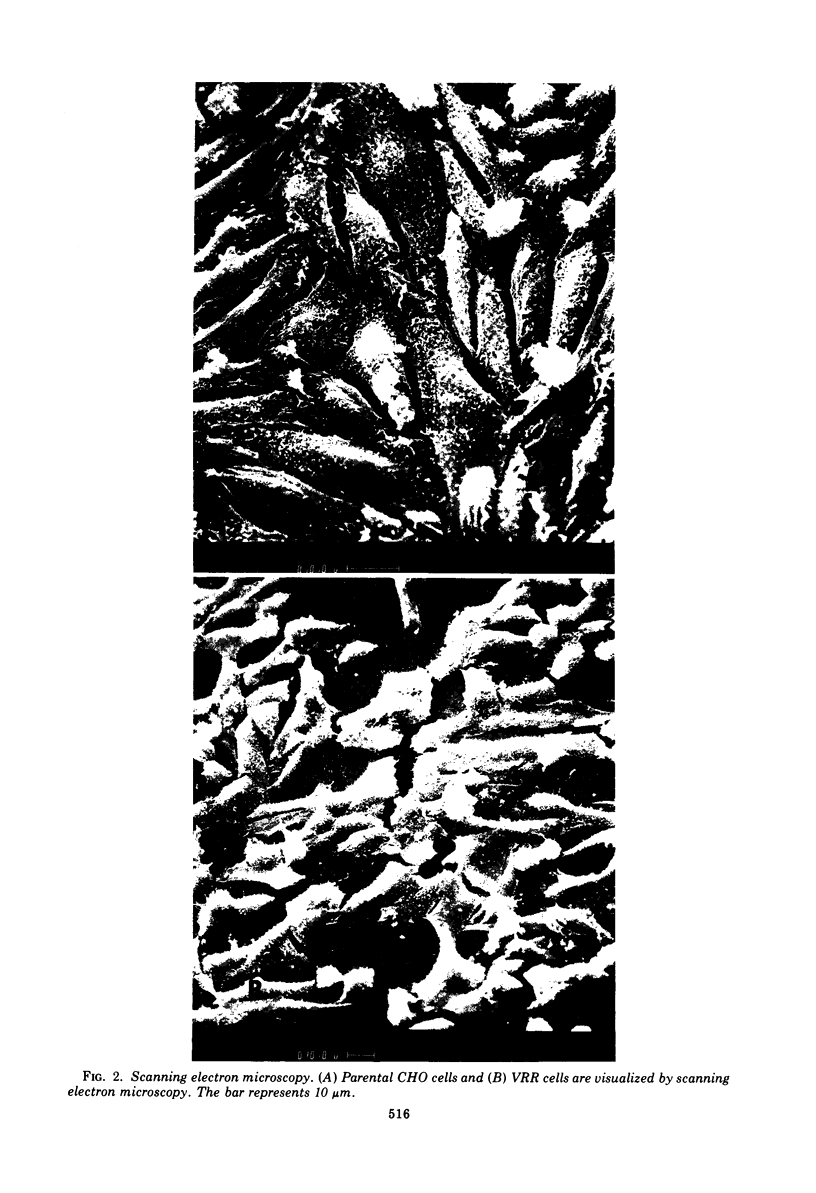

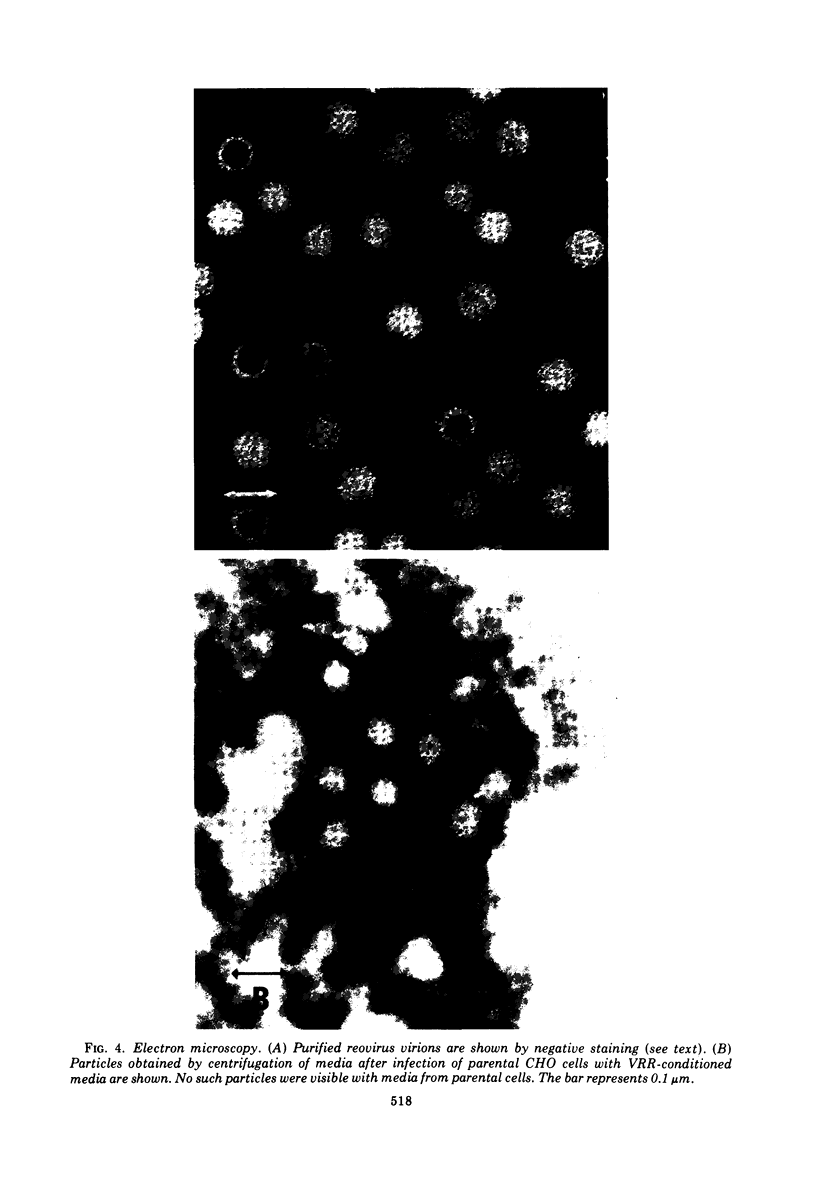
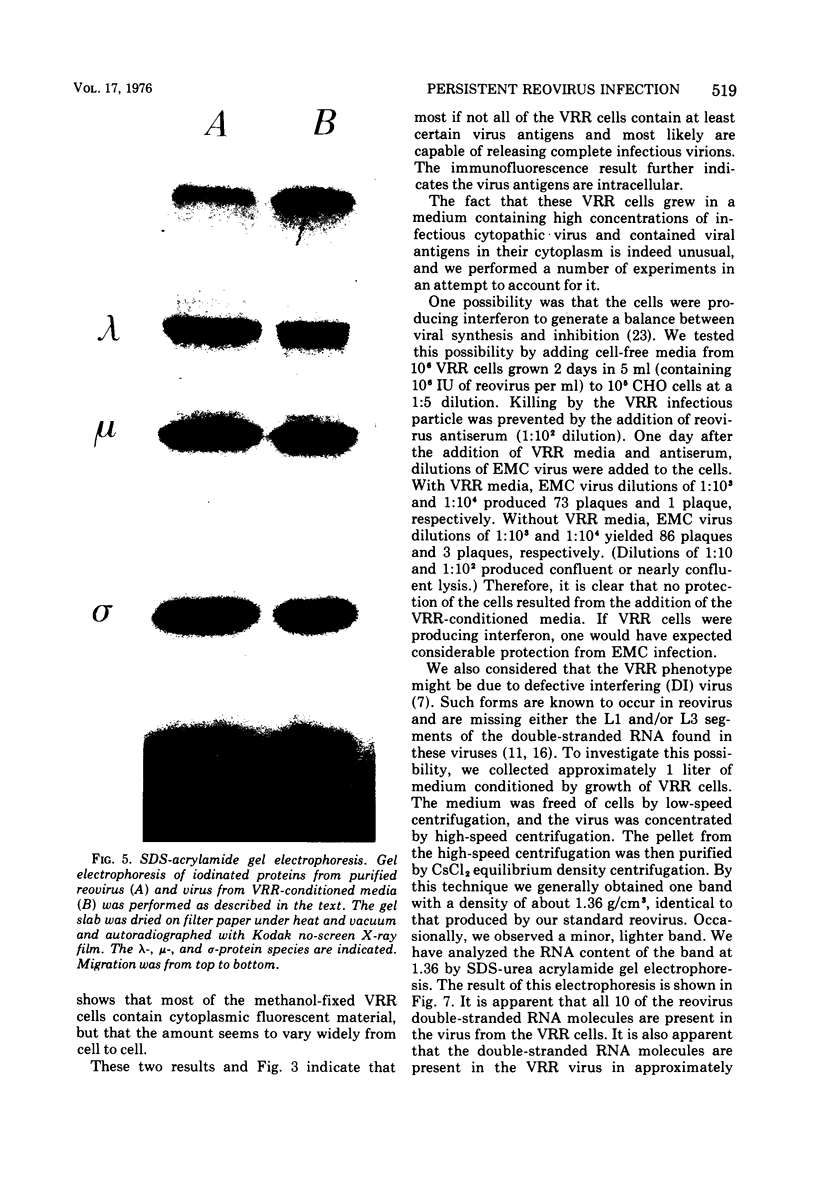
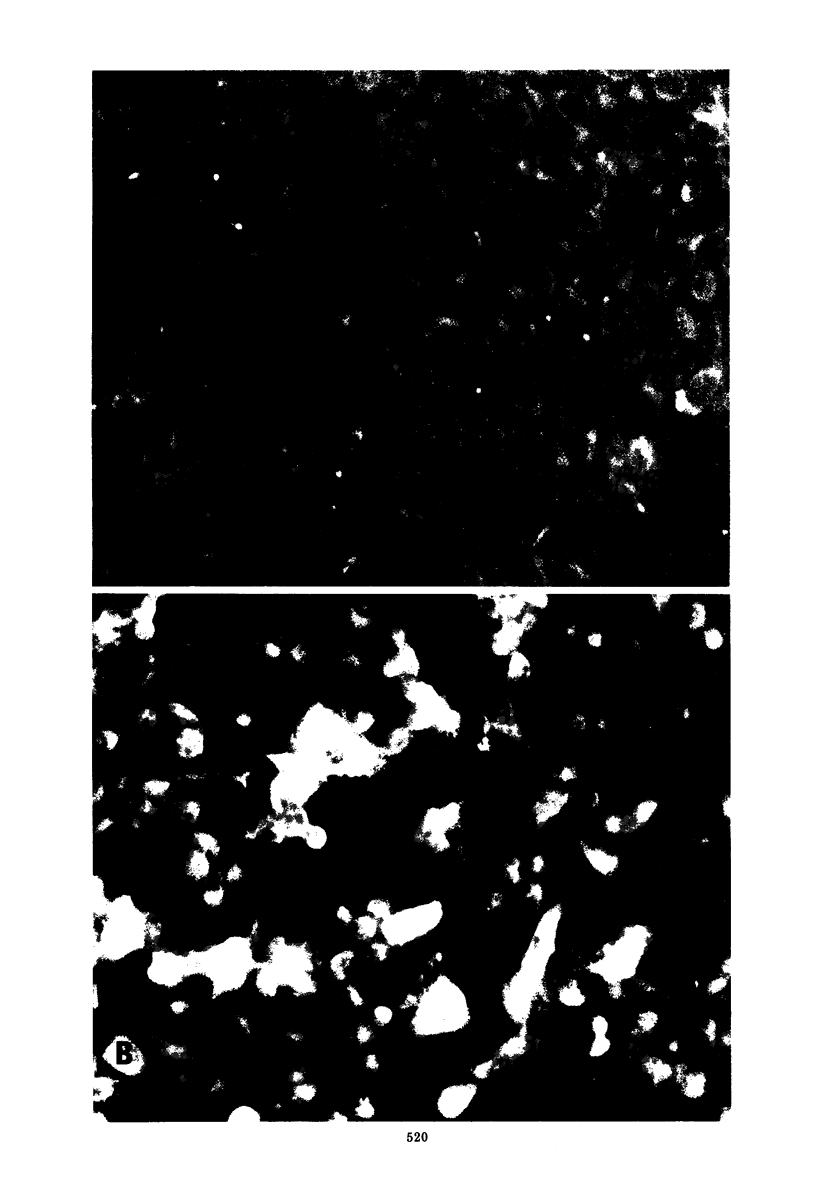
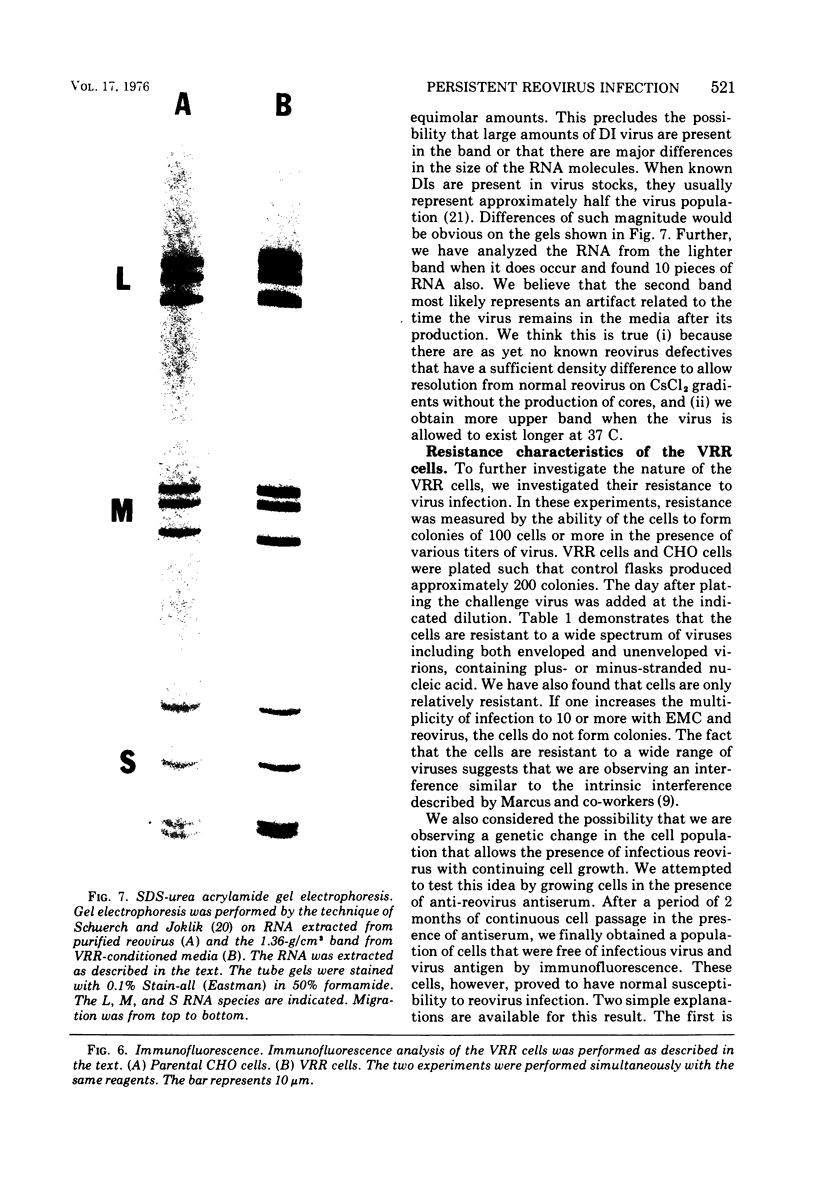


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell T. M., Ross M. G. Persistent latent infection of human embryonic cells with reovirus type 3. Nature. 1966 Oct 22;212(5060):412–414. doi: 10.1038/212412a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstein T., Jacobsen L. B., Zeman W., Chen T. T. Persistent infection of BSC-1 cells by defective measles virus derived from subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Infect Immun. 1974 Dec;10(6):1378–1382. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.6.1378-1382.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERNANDES M. V., WIKTOR T. J., KOPROWSKI H. MECHANISM OF THE CYTOPATHIC EFFECT OF RABIES VIRUS IN TISSUE CULTURE. Virology. 1963 Sep;21:128–131. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90312-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fay F. S., Delise C. M. Contraction of isolated smooth-muscle cells--structural changes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):641–645. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavrilov V. I., Deryabin P. G., Lozinsky T. F., Loghinova N. V., Karpova E. F., Zhdanov V. M. Continuous mouse brain cell lines chronically infected with Japanese encephalitis virus. J Gen Virol. 1974 Aug;24(2):293–300. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-2-293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAM R. G. CLONAL GROWTH OF MAMMALIAN CELLS IN A CHEMICALLY DEFINED, SYNTHETIC MEDIUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Feb;53:288–293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.2.288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard A. L., Cohn Z. A. The enzymatic iodination of the red cell membrane. J Cell Biol. 1972 Nov;55(2):390–405. doi: 10.1083/jcb.55.2.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt J. M., Marcus P. I. Mechanism of Sindbis virus-induced intrinsic interference with vesicular stomatitis virus replication. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):99–109. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.99-109.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao F. T., Puck T. T. Genetics of somatic mammalian cells. IV. Properties of Chinese hamster cell mutants with respect to the requirement for proline. Genetics. 1967 Mar;55(3):513–524. doi: 10.1093/genetics/55.3.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A., Henle G., Henle W., Zajac B. A. Effect of reovirus type 3 on cultured Burkitt's tumour cells. Nature. 1968 Nov 9;220(5167):607–608. doi: 10.1038/220607a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menna J. H., Collins A. R., Flanagan T. D. Characterization of an in vitro persistent-state measles virus infection: establishment and virological characterization of the BGM/MV cell line. Infect Immun. 1975 Jan;11(1):152–158. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.1.152-158.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan M. J., Colby C., Jr, Hulse J. L. Isolation and characterization of virus-resistant mouse embryo fibroblasts. J Gen Virol. 1973 Sep;20(3):377–385. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-20-3-377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonoyama M., Watanabe Y., Graham A. F. Defective virions of reovirus. J Virol. 1970 Aug;6(2):226–236. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.2.226-236.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preble O. T., Youngner J. S. Temperature-sensitive viruses and the etiology of chronic and inapparent infections. J Infect Dis. 1975 Apr;131(4):467–473. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.4.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawls W. E. Congenital rubella: the significance of virus persistence. Prog Med Virol. 1968;10:238–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuerch A. R., Joklik W. K. Temperature-sensitive mutants of reovirus. IV. Evidence that anomalous electrophoretic migration behavior of certain double-stranded RNA hybrid species is mutant group-specific. Virology. 1973 Nov;56(1):218–229. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90301-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuerch A. R., Matsuhisa T., Joklik W. K. Temperature-sensitive mutants of reovirus. VI. Mutant ts 447 and ts 556 particles that lack either one or two genome RNA segments. Intervirology. 1974;3(1-2):36–46. doi: 10.1159/000149740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanwick T. L., Hallum J. V. Role of interferon in six cell lines persistently infected with rubella virus. Infect Immun. 1974 Oct;10(4):810–815. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.4.810-815.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thacore H., Youngner J. S. Cells persistently infected with newcastle disease virus: I. Properties of mutants isolated from persistently infected L cells. J Virol. 1969 Sep;4(3):244–251. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.3.244-251.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALKER D. L., HINZE H. C. A carrier state of mumps virus in human conjunctiva cells. I. General characteristics. J Exp Med. 1962 Nov 1;116:739–750. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.5.739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALKER D. L. THE VIRAL CARRIER STATE IN ANIMAL CELL CULTURES. Prog Med Virol. 1964;6:111–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston S. H., Rustigian R., Bratt M. A. Persistent infection of cells in culture by measles virus. 3. Comparison of virus-specific RNA synthesized in primary persistent infection in HeLa cells. J Virol. 1973 Jun;11(6):926–932. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.6.926-932.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhdanov V. M. Integration of viral genomes. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):471–473. doi: 10.1038/256471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]