Abstract
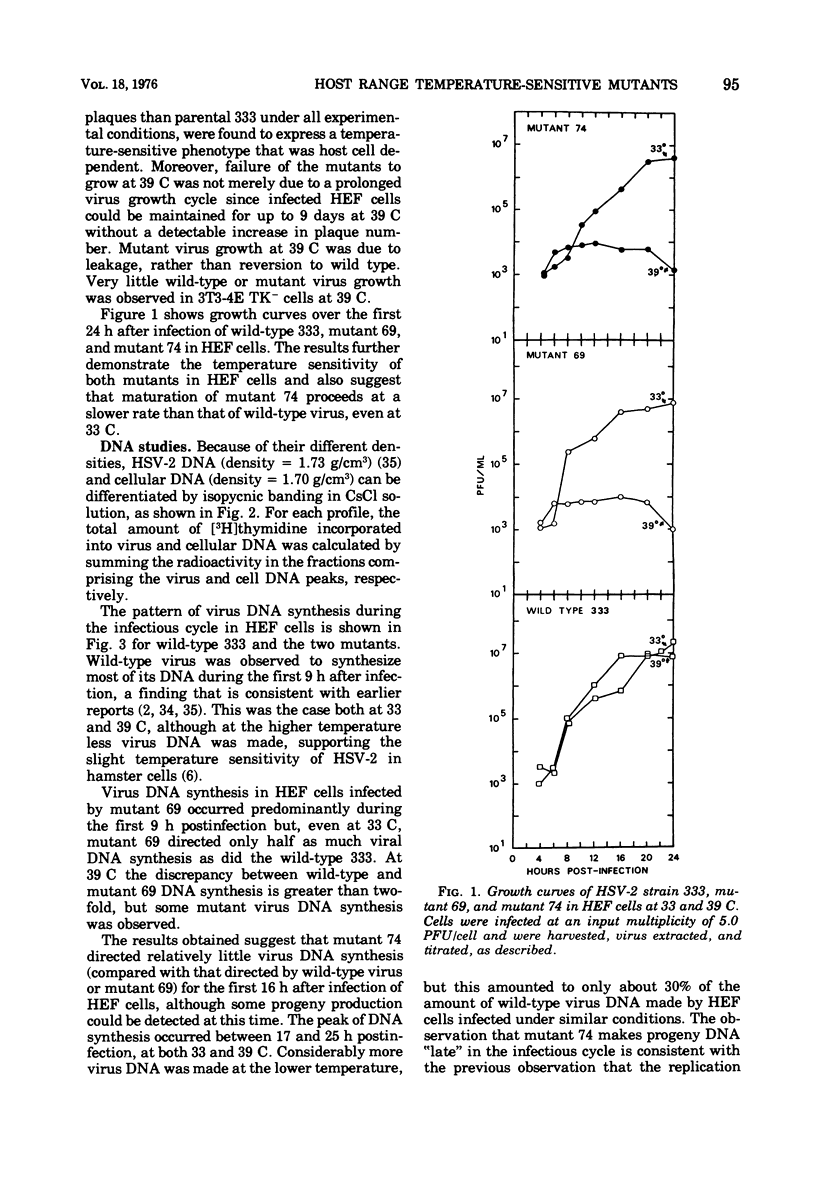
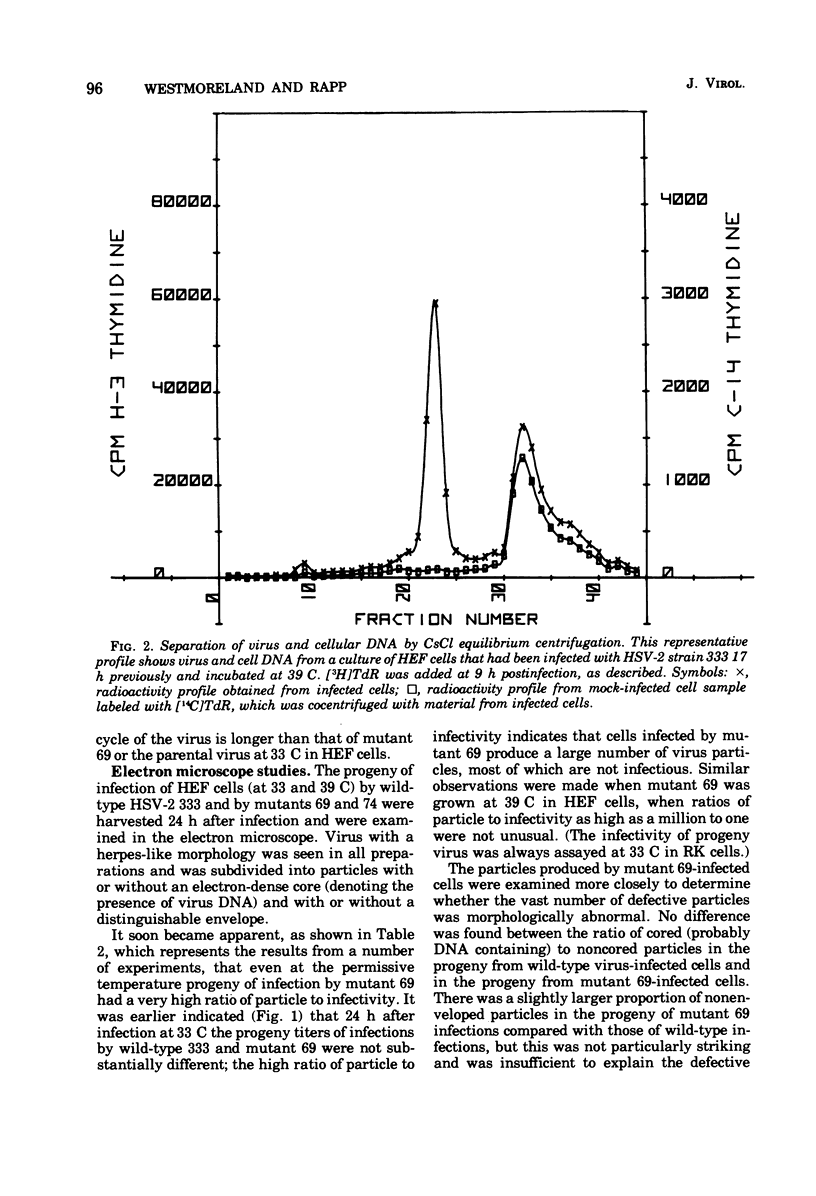
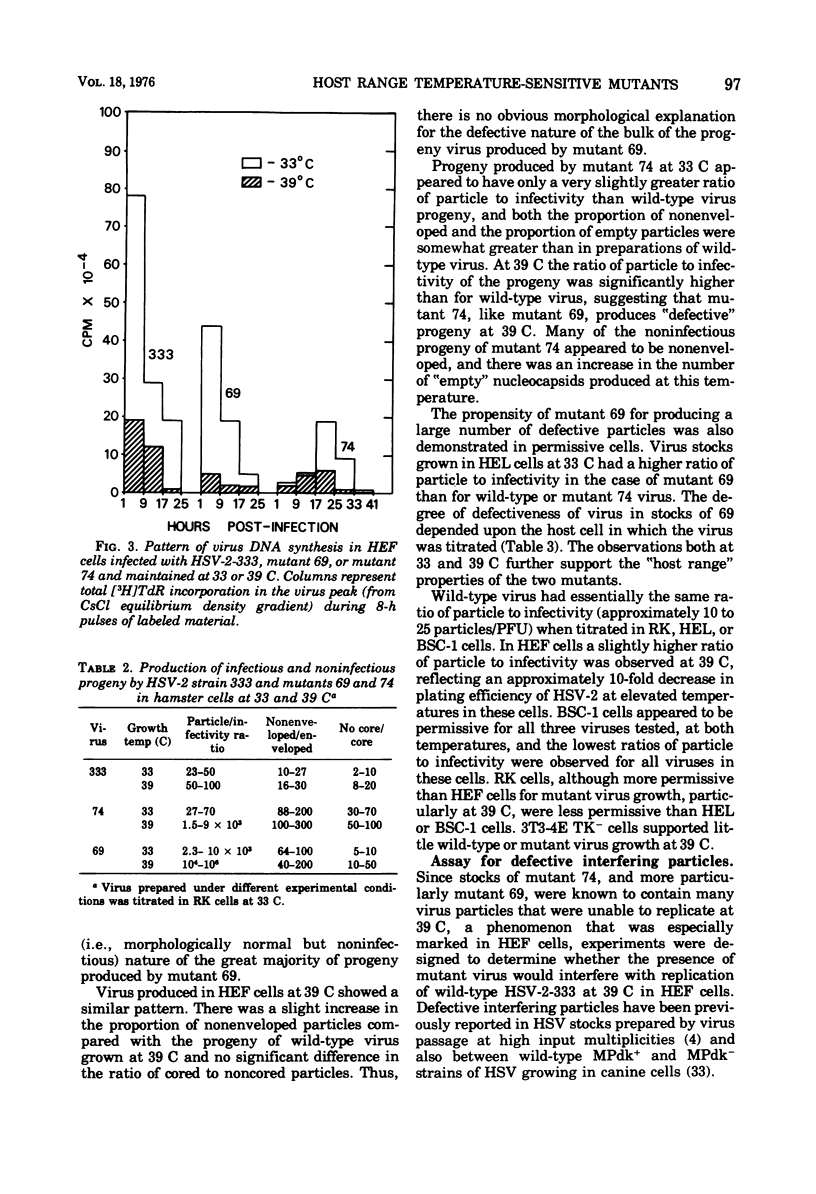
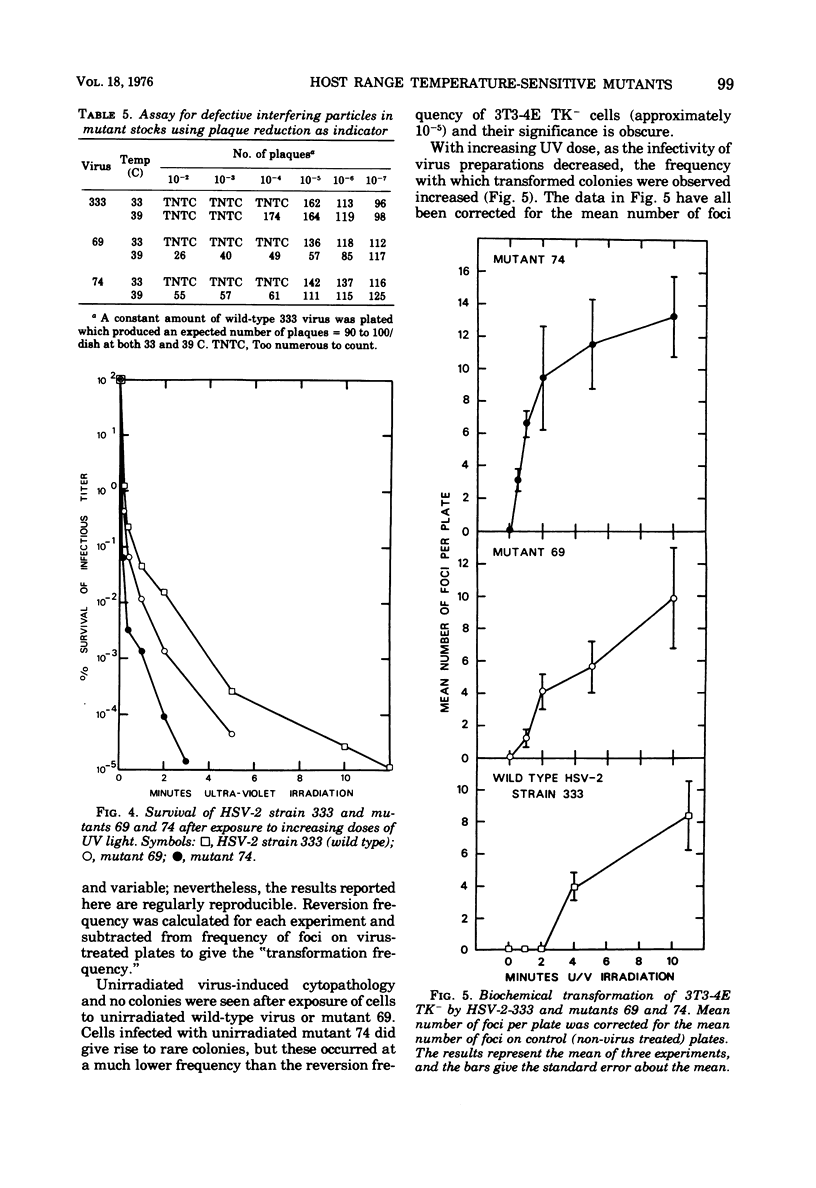
Two small-plaque mutants of herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2) (strain 333), whose growth at 39 C was blocked in certain cell types (cell-dependent temperature sensitivity), were compared compared with parental virus in a number of biological assays. One mutant (no. 69) was found to produce a large number of morphologically normal, but noninfectious, particles; under nonpermissive conditions, these mutant particles were able to interfere with the replication of wild-type HSV-2. The other mutant (no. 74), which is known to belong to a different complementation group, appeared to direct little virus DNA synthesis, even at the permissive temperature. Progeny production and virus DNA synthesis in cells infected by mutant 74 were delayed in comparison with wild-type virus-infected cells. Both mutants were found to be more sensitive to UV irradiation than the parental virus; this was especially marked in the case of mutant 74. Moreover, this mutant was found to have a high transforming efficiency at much lower doses of irradiation than those needed to abolish the cytopathic effect of wildtype HSV-2.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aron G. M., Purifoy D. J., Schaffer P. A. DNA synthesis and DNA polymerase activity of herpes simplex virus type 1 temperature-sensitive mutants. J Virol. 1975 Sep;16(3):498–507. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.3.498-507.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benyesh-Melnick M., Schaffer P. A., Courtney R. J., Esparza J., Kimura S. Viral gene functions expressed and detected by temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 2):731–746. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bronson D. L., Dreesman G. R., Biswal N., Benyesh-Melnick M. Defective virions of herpes simplex viruses. Intervirology. 1973;1(3):141–153. doi: 10.1159/000148841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. M., Ritchie D. A., Subak-Sharpe J. H. Genetic studies with herpes simplex virus type 1. The isolation of temperature-sensitive mutants, their arrangement into complementation groups and recombination analysis leading to a linkage map. J Gen Virol. 1973 Mar;18(3):329–346. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-18-3-329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouch N. A., Rapp F. Cell-dependent differences in the production of infectious herpes simplex virus at a supraoptimal temperature. J Virol. 1972 Feb;9(2):223–230. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.2.223-230.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis D. B., Munyon W., Buchsbaum R., Chawda R. Virus type-specific thymidine kinase in cells biochemically transformed by herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Virol. 1974 Jan;13(1):140–145. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.1.140-145.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty J. J., Chopan M. The latent herpes simplex virus. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Dec;38(4):337–355. doi: 10.1128/br.38.4.337-355.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duff R., Rapp F. Oncogenic transformation of hamster cells after exposure to herpes simplex virus type 2. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 8;233(36):48–50. doi: 10.1038/newbio233048a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duff R., Rapp F. Oncogenic transformation of hamster embryo cells after exposure to inactivated herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1973 Aug;12(2):209–217. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.2.209-217.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duff R., Rapp F. Properties of hamster embryo fibroblasts transformed in vitro after exposure to ultraviolet-irradiated herpes simplex virus type 2. J Virol. 1971 Oct;8(4):469–477. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.4.469-477.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duff R., Rapp F. Quantitative assay for transformation of 3T3 cells by herpes simplex virus type 2. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):490–496. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.490-496.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duff R., Rapp F. Quantitative characteristics of the transformation of hamster cells by PARA (defective simian virus 40)-adenovirus 7. J Virol. 1970 May;5(5):568–577. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.5.568-577.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esparza J., Purifoy D. J., Schaffer P. A., Benyesh-Melnick M. Isolation, complementation and preliminary phenotypic characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus type 2. Virology. 1974 Feb;57(2):554–565. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90194-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliburton I. W., Timbury M. C. Characterisation of temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus type 2. Growth and DNA synthesis. Virology. 1973 Jul;54(1):60–68. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90114-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. XI. Identification and relative molar rates of synthesis of structural and nonstructural herpes virus polypeptides in the infected cell. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1347–1365. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1347-1365.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. I. Cascade regulation of the synthesis of three groups of viral proteins. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):8–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.8-19.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis: sequential transition of polypeptide synthesis requires functional viral polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1276–1280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIT S., DUBBS D. R. Acquisition of thymidine kinase activity by herpes simplex-infected mouse fibroblast cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Apr 2;11:55–59. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemperer H. G., Haynes G. R., Shedden W. I., Watson D. H. A virus-specific thymidine kinase in BHK-21 cells infected with herpes simplex virus. Virology. 1967 Jan;31(1):120–128. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koment R. W., Rapp F. In vivo characteristics of temperature-sensitive host range mutants of herpes simplex virus type 2. Intervirology. 1975;5(1-2):10–20. doi: 10.1159/000149876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koment R. W., Rapp F. Temperature-sensitive host range mutants of herpes simplex virus type 2. J Virol. 1975 Apr;15(4):812–819. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.4.812-819.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koment R. W., Rapp F. Variation in susceptibility of different cell types to temperature-sensitive host range mutants of herpes simplex virus type 2. Virology. 1975 Mar;64(1):164–169. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90088-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLEFIELD J. W. STUDIES ON THYMIDINE KINASE IN CULTURED MOUSE FIBROBLASTS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jan 11;95:14–22. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90206-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab J. C. Transformation of rat embryo cells by temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus. J Gen Virol. 1974 Jul;24(1):143–153. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-1-143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Robinson J., Heston L. Immortalizing and nonimmortalizing laboratory strains of Epstein-Barr Virus. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 2):773–781. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Robinson J., Heston L., Lipman M. Differences between laboratory strains of Epstein-Barr virus based on immortalization, abortive infection, and interference. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4006–4010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monroe J. H., Brandt P. M. Rapid semiquantitative method for screening large numbers of virus samples by negative staining electron microscopy. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Aug;20(2):259–262. doi: 10.1128/am.20.2.259-262.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munyon W., Kraiselburd E., Davis D., Mann J. Transfer of thymidine kinase to thymidine kinaseless L cells by infection with ultraviolet-irradiated herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1971 Jun;7(6):813–820. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.6.813-820.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPP F. VARIANTS OF HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUS: ISOLATION, CHARACTERIZATION, AND FACTORS INFLUENCING PLAQUE FORMATION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Nov;86:985–991. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.5.985-991.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROIZMAN B., ROANE P. R., Jr THE MULTIPLICATION OF HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUS. II. THE RELATION BETWEEN PROTEIN SYNTHESIS AND THE DUPLICATION OF VIRAL DNA IN INFECTED HEP-2 CELLS. Virology. 1964 Feb;22:262–269. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roizman B. Abortive infection of canine cells by herpes simplex virus. 3. The interference of conditional lethal virus with an extended host range mutant. Virology. 1965 Sep;27(1):113–117. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90148-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer P. A., Aron G. M., Biswal N., Benyesh-Melnick M. Temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1: isolation, complementation and partial characterization. Virology. 1973 Mar;52(1):57–71. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90398-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer P. A., Brunschwig J. P., McCombs R. M., Benyesh-Melnick M. Electron microscopic studies of temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1974 Dec;62(2):444–457. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90406-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subak-Sharpe J. H., Brown S. M., Ritchie D. A., Timbury M. C., Macnab J. C., Marsden H. S., Hay J. Genetic and biochemical studies with herpesvirus. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 2):717–730. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Yamanishi K. Transformation of hamster embryo and human embryo cells by temperature sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus type 2. Virology. 1974 Sep;61(1):306–311. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90267-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie N. M., Clements J. B., Macnab J. C., Subak-Sharpe J. H. The structure and biological properties of herpes simplex virus DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 2):657–666. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



