Abstract
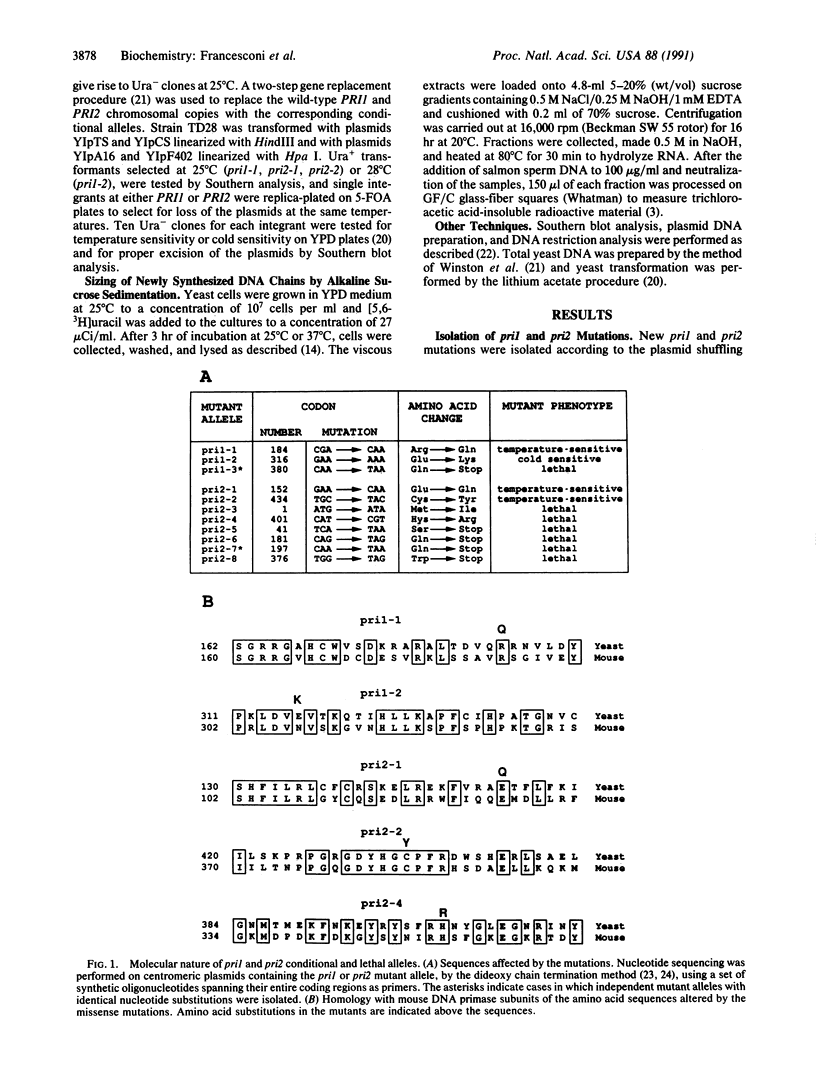
To assess the role of eukaryotic DNA primase in vivo, we have produced conditional and lethal point mutations by random in vitro mutagenesis of the PR11 and PR12 genes, which encode the small and large subunits of yeast DNA primase. We replaced the wild-type copies of PRI1 and PRI2 with two pri1 and two pri2 conditional alleles. When shifted to the restrictive temperature, these strains showed altered DNA synthesis and reduced ability to synthesize high molecular weight DNA products, thus providing in vivo evidence for the essential role of DNA primase in eukaryotic DNA replication. Furthermore, mapping of the mutations at the nucleotide level has shown that the two pri1 and two pri2 conditional alleles and one pri2 lethal allele have suffered single base-pair substitutions causing a change in amino acid residues conserved in the corresponding mouse polypeptide.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boeke J. D., Trueheart J., Natsoulis G., Fink G. R. 5-Fluoroorotic acid as a selective agent in yeast molecular genetics. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:164–175. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54076-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D., Falco S. C., Stewart S. E., Brennan M., Scherer S., Stinchcomb D. T., Struhl K., Davis R. W. Sterile host yeasts (SHY): a eukaryotic system of biological containment for recombinant DNA experiments. Gene. 1979 Dec;8(1):17–24. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budd M. E., Wittrup K. D., Bailey J. E., Campbell J. L. DNA polymerase I is required for premeiotic DNA replication and sporulation but not for X-ray repair in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):365–376. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foiani M., Lindner A. J., Hartmann G. R., Lucchini G., Plevani P. Affinity labeling of the active center and ribonucleoside triphosphate binding site of yeast DNA primase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):2189–2194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foiani M., Santocanale C., Plevani P., Lucchini G. A single essential gene, PRI2, encodes the large subunit of DNA primase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):3081–3087. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.3081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Sakaki Y. Dideoxy sequencing method using denatured plasmid templates. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):232–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90403-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm C., Goto T., Wang J. C., Botstein D. DNA topoisomerase II is required at the time of mitosis in yeast. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):553–563. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. M., Snyder M., Chang L. M., Davis R. W., Campbell J. L. Isolation of the gene encoding yeast DNA polymerase I. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):369–377. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90042-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston L. H., White J. H., Johnson A. L., Lucchini G., Plevani P. The yeast DNA polymerase I transcript is regulated in both the mitotic cell cycle and in meiosis and is also induced after DNA damage. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5017–5030. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaguni L. S., Lehman I. R. Eukaryotic DNA polymerase-primase: structure, mechanism and function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jul 13;950(2):87–101. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90001-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucchini G., Brandazza A., Badaracco G., Bianchi M., Plevani P. Identification of the yeast DNA polymerase I gene with antibody probes. Curr Genet. 1985;10(4):245–252. doi: 10.1007/BF00365620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucchini G., Francesconi S., Foiani M., Badaracco G., Plevani P. Yeast DNA polymerase--DNA primase complex; cloning of PRI 1, a single essential gene related to DNA primase activity. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):737–742. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04815.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucchini G., Mazza C., Scacheri E., Plevani P. Genetic mapping of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae DNA polymerase I gene and characterization of a pol1 temperature-sensitive mutant altered in DNA primase-polymerase complex stability. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Jun;212(3):459–465. doi: 10.1007/BF00330850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucchini G., Muzi Falconi M., Pizzagalli A., Aguilera A., Klein H. L., Plevani P. Nucleotide sequence and characterization of temperature-sensitive pol1 mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1990 May 31;90(1):99–104. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90444-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newlon C. S. Yeast chromosome replication and segregation. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Dec;52(4):568–601. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.4.568-601.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzagalli A., Valsasnini P., Plevani P., Lucchini G. DNA polymerase I gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: nucleotide sequence, mapping of a temperature-sensitive mutation, and protein homology with other DNA polymerases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3772–3776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plevani P., Foiani M., Muzi Falconi M., Pizzagalli A., Santocanale C., Francesconi S., Valsasnini P., Comedini A., Piatti S., Lucchini G. The yeast DNA polymerase-primase complex: genes and proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Dec 20;951(2-3):268–273. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90096-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plevani P., Foiani M., Valsasnini P., Badaracco G., Cheriathundam E., Chang L. M. Polypeptide structure of DNA primase from a yeast DNA polymerase-primase complex. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):7102–7107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plevani P., Francesconi S., Lucchini G. The nucleotide sequence of the PRI1 gene related to DNA primase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7975–7989. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prussak C. E., Almazan M. T., Tseng B. Y. Mouse primase p49 subunit molecular cloning indicates conserved and divergent regions. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):4957–4963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston F., Chumley F., Fink G. R. Eviction and transplacement of mutant genes in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:211–228. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]