Abstract
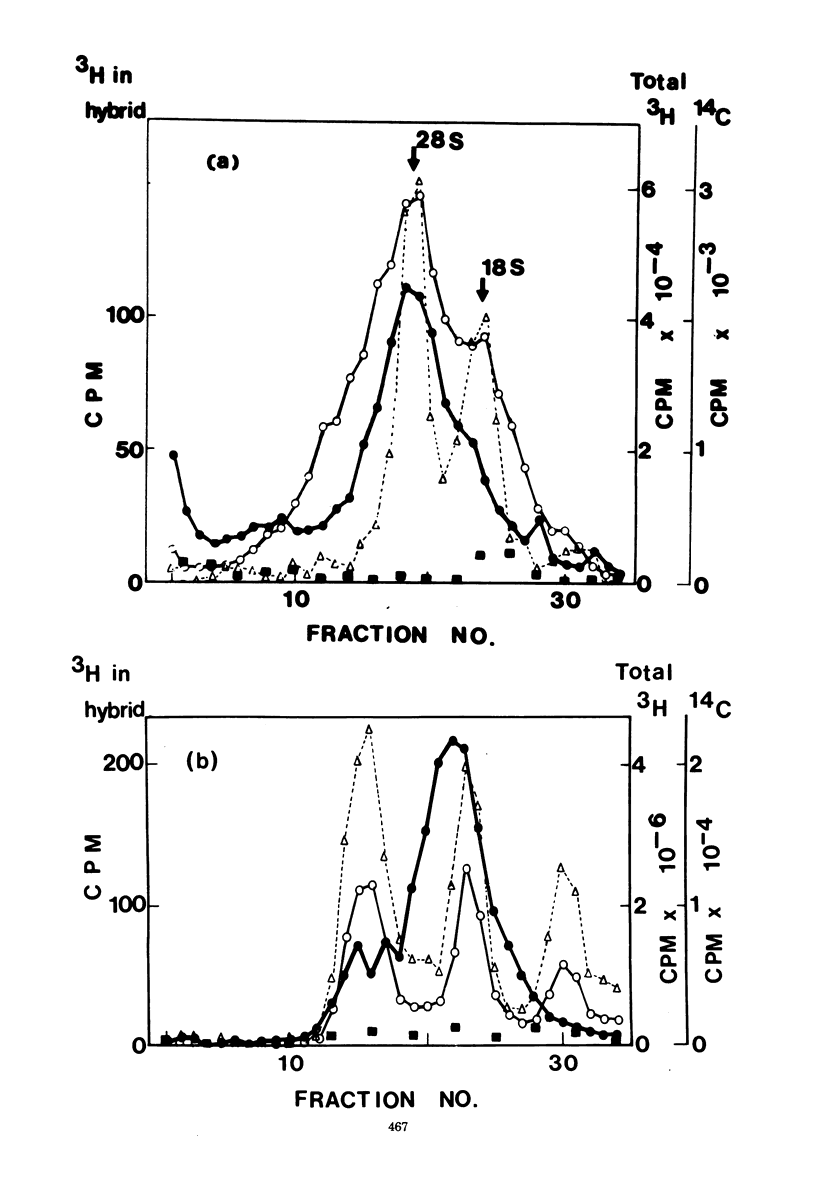
The virus-specific RNA in two independently derived clones of polyoma virus-transformed hamster cells was studied by hybridizing labeled RNA, with excess purified polyoma DNA, immoblized on filters. In one clone (PyBHK1), less than 25% of the total labeled virus-specific RNA was found in the cytoplasm, irrespective of the labeling time. In the other clone (PyBHK2), it was estimated that 39% of the total virus-specific RNA was present inthe cytoplasm after labeling for 3 h. Both the proportion of radioactive label incorporated into virus-specific RNA and the sedimentation pattern of total virus-specific RNA differed markedly between PyBHK and PyBHK2. Most of the virus-specific RNA of PyBHK1 sedimented in the range 25S-35S, whereas a prominent 18S component was present in PyBHK2. Most of the cytoplasmic virus-specific RNA in both clones sedimented at 18S-19S. The sedimentation patterns of virus-specific RNA from whole cells and from washed nuclei of PyBHK1 were closely similar: it was estimated from sedimentation analysis in dimethyl sulfoxide that the molecular weight of 50% of this RNA was within the range 1.1 X10(6) to 2.9 X 10(6). These results, demonstrating the accumulation of virus-specific RNA within the nucleus in at least one virus-transformed cell line, indicate that the large virus-specific RNA previously described in the nuclei of transformed cells may not have represented precursors of virus-specific mRNA.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acheson N. H., Buetti E., Scherrer K., Weil R. Transcription of the polyoma virus genome: synthesis and cleavage of giant late polyoma-specific RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2231–2235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adesnik M., Darnell J. E. Biogenesis and characterization of histone messenger RNA in HeLa cells. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 28;67(3):397–406. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90458-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLACK P. H., ROWE W. P., TURNER H. C., HUEBNER R. J. A SPECIFIC COMPLEMENT-FIXING ANTIGEN PRESENT IN SV40 TUMOR AND TRANSFORMED CELLS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Dec;50:1148–1156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.6.1148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beard P., Acheson N. H., Maxwell I. H. Strand-specific transcription of polyoma virus DNA-early in productive infection and in transformed cells. J Virol. 1975 Jan;17(1):20–26. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.1.20-26.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin T. L. Virus-specific RNA in cells productively infected or transformed by polyoma virus. J Mol Biol. 1966 Apr;16(2):359–373. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80179-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan M., McKenna G., Sharp P. A. Cleavage of mouse DNA by a restriction enzyme as a clue to the arrangement of genes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:383–395. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandner G., Mueller N., Graessmann A., Graessmann M., Niebel J., Hoffmann H. Inhibition by interferon of SV40 tumor antigen formation in cells injected with SV40 cRNA transcribed in vitro. FEBS Lett. 1974 Mar 1;39(3):249–251. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80122-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buetti E. Characterization of late polyoma mRNA. J Virol. 1974 Aug;14(2):249–260. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.2.249-260.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jelinek W. R., Molloy G. R. Biogenesis of mRNA: genetic regulation in mammalian cells. Science. 1973 Sep 28;181(4106):1215–1221. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4106.1215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelb L. D., Kohne D. E., Martin M. A. Quantitation of Simian virus 40 sequences in African green monkey, mouse and virus-transformed cell genomes. J Mol Biol. 1971 Apr 14;57(1):129–145. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90123-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HABEL K. SPECIFIC COMPLEMENT-FIXING ANTIGENS IN POLYOMA TUMORS AND TRANSFORMED CELLS. Virology. 1965 Jan;25:55–61. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90251-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Henner D., Defendi V. Hybridization of simian virus 40 complementary RNA with nucleolus-associated DNA isolated from simian virus 40-transformed Chinese hamster cells. Virology. 1974 Aug;60(2):588–591. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90354-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imaizumi T., Diggelmann H., Scherrer K. Demonstration of globin messenger sequences in giant nuclear precursors of messenger RNA of avian erythroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1122–1126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamen R., Lindstrom D. M., Shure H., Old R. W. Virus-specific RNA in cells productively infected or transformed by polyoma virus. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):187–198. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby K. S., Cook E. A. Isolation of deoxyribonucleic acid from mammalian tissues. Biochem J. 1967 Jul;104(1):254–257. doi: 10.1042/bj1040254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komano T., Sinsheimer R. L. Preparation and purification of phi X-RF component I. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jan 29;155(1):295–298. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg U., Darnell J. E. SV40-specific RNA in the nucleus and polyribosomes of transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Apr;65(4):1089–1096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.4.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loening U. E. Molecular weights of ribosomal RNA in relation to evolution. J Mol Biol. 1968 Dec;38(3):355–365. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90391-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACPHERSON I., MONTAGNIER L. AGAR SUSPENSION CULTURE FOR THE SELECTIVE ASSAY OF CELLS TRANSFORMED BY POLYOMA VIRUS. Virology. 1964 Jun;23:291–294. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90301-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell I. H. Artifacts in the centrifugation of ribosomal and heterogenous ribonucleic acid in "99%-dimethyl sulphoxide" gradients. Biochem J. 1976 Feb 1;153(2):509–512. doi: 10.1042/bj1530509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May E., May P., Weil R. Analysis of the events leading to SV40-induced chromosome replication and mitosis in primary mouse kidney cell cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1208–1211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy W., Attardi G. Stability of cytoplasmic messenger RNA in HeLa cels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):115–119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozanne B., Sharp P. A., Sambrook J. Transcription of simian virus 40. II. Hybridization of RNA extracted from different lines of transformed cells to the separated strands of simian virus 40 DNA. J Virol. 1973 Jul;12(1):90–98. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.1.90-98.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons J. T., Green M. Biochemical studies on adenovirus multiplication. 18. Resolution of early virus-specific RNA species in Ad 2 infected and transformed cells. Virology. 1971 Jul;45(1):154–162. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90122-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penman S. RNA metabolism in the HeLa cell nucleus. J Mol Biol. 1966 May;17(1):117–130. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80098-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P., Kelley D. E. Messenger RNA turnover in mouse L cells. J Mol Biol. 1973 Oct 5;79(4):681–696. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOKER M., MACPHERSON I. SYRIAN HAMSTER FIBROBLAST CELL LINE BHK21 AND ITS DERIVATIVES. Nature. 1964 Sep 26;203:1355–1357. doi: 10.1038/2031355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J. Transformation by polyoma virus and simian virus 40. Adv Cancer Res. 1972;16:141–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J., Westphal H., Srinivasan P. R., Dulbecco R. The integrated state of viral DNA in SV40-transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1288–1295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherrer K., Marcaud L. Messenger RNA in avian erythroblasts at the transcriptional and translational levels and the problem of regulation in animal cells. J Cell Physiol. 1968 Oct;72(2 Suppl):181+–181+. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040720413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schodhetman G., Perry R. P. Early appearance of histone messenger RNA in polyribosomes of cultured L cells. J Mol Biol. 1972 Feb 14;63(3):591–596. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90450-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer R. H., Penman S. Messenger RNA in HeLa cells: kinetics of formation and decay. J Mol Biol. 1973 Aug 5;78(2):321–334. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss J. H., Jr, Kelly R. B., Sinsheimer R. L. Denaturation of RNA with dimethyl sulfoxide. Biopolymers. 1968 Jun;6(6):793–807. doi: 10.1002/bip.1968.360060604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIL R., VINOGRAD J. THE CYCLIC HELIX AND CYCLIC COIL FORMS OF POLYOMA VIRAL DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Oct;50:730–738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.4.730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINOCOUR E. Purification of polyoma virus. Virology. 1963 Feb;19:158–168. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall R., Darnell J. E. Presence of cell and virus specific sequences in the same molecules of nuclear RNA from virus transformed cells. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jul 21;232(29):73–76. doi: 10.1038/newbio232073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall R., Weber J., Gage Z., Darnell J. E. Production of viral mRNA in adenovirus- transformed cells by the post- transcriptional processing of heterogeneous nuclear RNA containing viral and cell sequences. J Virol. 1973 Jun;11(6):953–960. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.6.953-960.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil R., Salomon E., May E., May P. A simplifying concept in tumor virology: virus-specific "pleiotropic effectors". Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):381–395. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A., Ben-Ishai Z., Newbold J. E. Simian virus 40 transcription in productively infected and transformed cells. J Virol. 1974 Jun;13(6):1263–1273. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.6.1263-1273.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A., Penman S. Processing of 45 s nucleolar RNA. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jan 28;47(2):169–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90337-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson R., Drewienkiewicz C. E., Paul J. Globin messenger sequences in high molecular weight RNA from embryonic mouse liver. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jan 17;241(107):66–68. doi: 10.1038/newbio241066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winocour E. Some aspects of the interaction between polyoma virus and cell DNA. Adv Virus Res. 1969;14:153–200. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60559-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D., Gosden J., Rogers J. SV40 virus-specific RNA synthesis in transformed human cells. Nat New Biol. 1973 Mar 7;242(114):16–18. doi: 10.1038/newbio242016a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



