Abstract
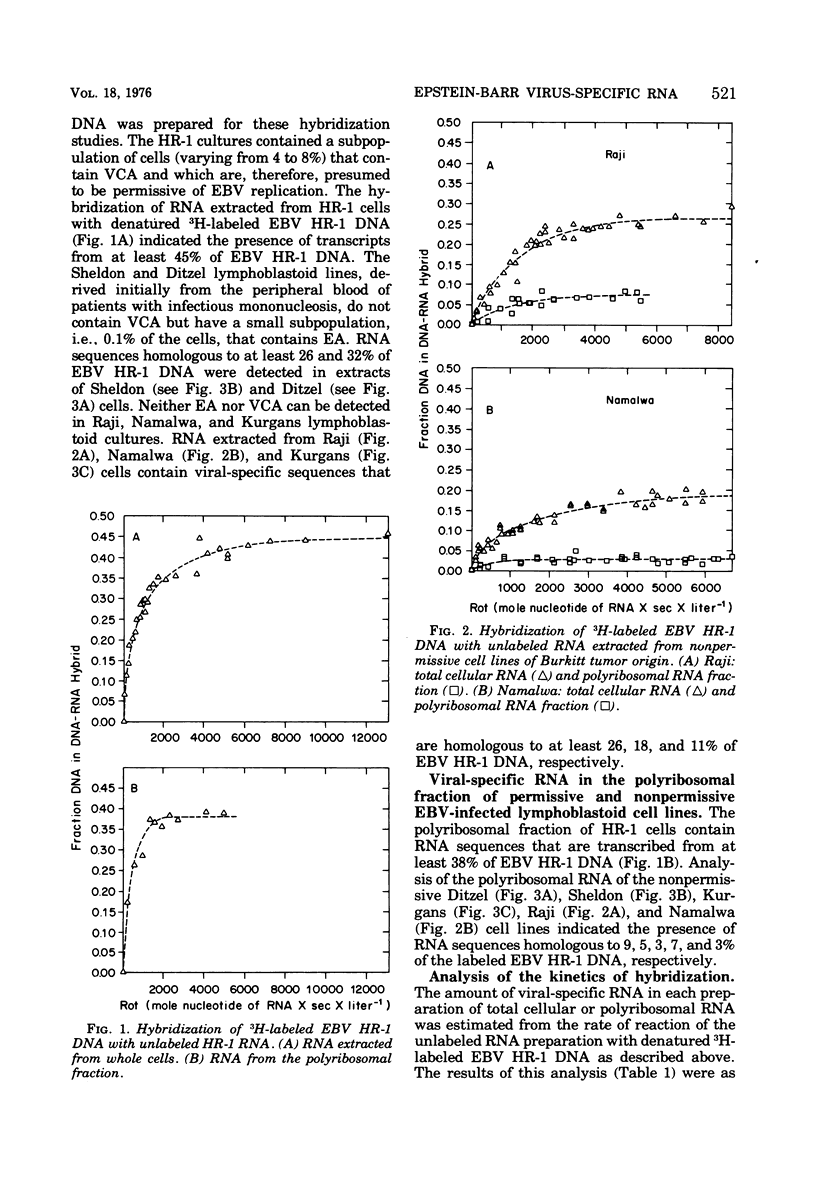
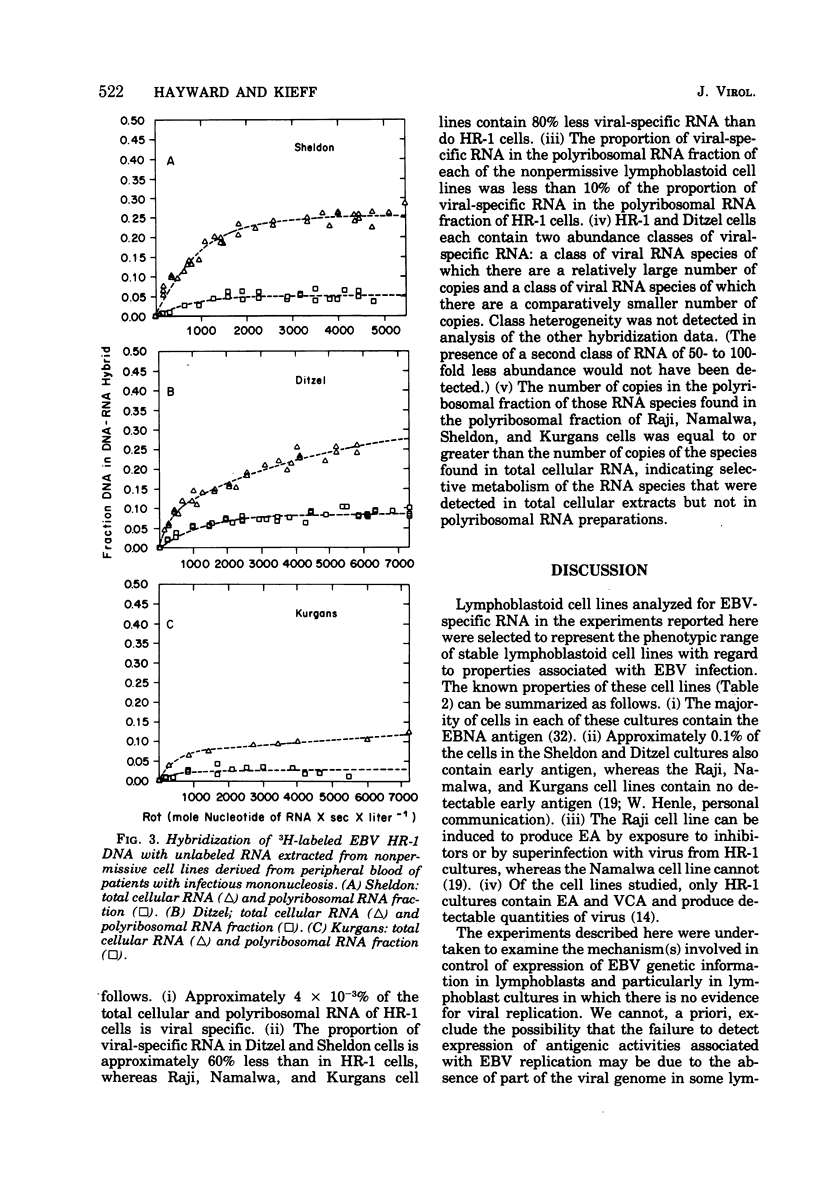
We analyzed the viral RNA in permissive and nonpermissive Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) Pinfected lymphoblastoid cell lines by observing the kinetics of hybridization of labeled EBV HR-1 DNA with unalabeled RNA extracted from whole cells or from the polyribosomal fraction. The data indicate the following. (i) RNA, homologous to only 3% of the EBV HR-1 DNA, is present in the polyribosomal fraction of the nonpermissive Namalwa and Kurgans cells, suggesting that the function of only a small fraction of the EBV genome is required for the expression of the EBV-related intranuclear antigen and to maintain lymphoblastoid cells in a transformed state. (ii) In general, the extent of the viral DNA sequences transcribed into stable RNA correlates with the extent of phenotypic expression of the EBV geonome. RNA extracted from virus-producing HR-1 cells contains RNA sequences transcribed from at least 45% of the viral DNA, whereas the nonpermissive cell lines contain transcripts homologous to a much smaller proportion of the EBV DNA. (iii) Viral RNA sequences found in the polyribosomal fraction of HR-1 cells arise from almost the same template as the viral RNA sequences in extracts of infractionated HR-1 cells. In contrast, in nonpermissive lymphoblastoid cells, less than 30% of the viral RNA species found in whole-cell extracts can be identified in the polyribosomal fraction. We interpret these observations to indicate that the expression of EBV genetic information is regulated in at least two ways: first, by some mechanism that regulates which DNA sequences give rise to stable RNA; second, through a mechanism whereby certain viral RBA transcripts are selectively excluded from stable association with the polyribosomes.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Frenkel N., Roizman B. Ribonucleic acid synthesis in cells infected with herpes simplex virus: controls of transcription and of RNA abundance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2654–2658. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber P. Activation of Epstein-Barr virus by 5-bromodeoxyuridine in "virus-free" human cells (complement-fixing antigen-immunofluorescence-leukocytes). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):83–85. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gergely L., Klein G., Ernberg I. Appearance of Epstein-Barr virus-associated antigens in infected Raji cells. Virology. 1971 Jul;45(1):10–21. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90107-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gergely L., Klein G., Ernberg I. Host cell macromolecular synthesis in cells containing EBV-induced early antigens, studied by combined immunofluorescence and radioautography. Virology. 1971 Jul;45(1):22–29. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90108-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gergely L., Klein G., Ernberg I. The action of DNA antagonists on Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated early antigen (EA) in Burkitt lymphoma lines. Int J Cancer. 1971 Mar 15;7(2):293–302. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910070214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerper P., Whang-Peng J., Monroe J. H. Transformation and chromosome changes induced by Epstein-Barr virus in normal human leukocyte cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jul;63(3):740–747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.3.740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampar B., Derge J. G., Martos L. M., Walker J. L. Synthesis of Epstein-Barr virus after activation of the viral genome in a "virus-negative" human lymphoblastoid cell (Raji) made resistant to 5-bromodeoxyuridine (thymidine kinase-virus antigen-immunofluorescence-herpesvirus fingerprints). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):78–82. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W. Immunofluorescence in cells derived from Burkitt's lymphoma. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1248–1256. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1248-1256.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Diehl V., Kohn G., Zur Hausen H., Henle G. Herpes-type virus and chromosome marker in normal leukocytes after growth with irradiated Burkitt cells. Science. 1967 Sep 1;157(3792):1064–1065. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3792.1064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Henle G., Zajac B. A., Pearson G., Waubke R., Scriba M. Differential reactivity of human serums with early antigens induced by Epstein-Barr virus. Science. 1970 Jul 10;169(3941):188–190. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3941.188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinuma Y., Konn M., Yamaguchi J., Wudarski D. J., Blakeslee J. R., Jr, Grace J. T., Jr Immunofluorescence and herpes-type virus particles in the P3HR-1 Burkitt lymphoma cell line. J Virol. 1967 Oct;1(5):1045–1051. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.5.1045-1051.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutton J. R., Wetmur J. G. Renaturation of bacteriophage phiX174 DNA-RNA hybrid: RNA length effect and nucleation rate constant. J Mol Biol. 1973 Jul 15;77(4):495–500. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90218-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai Y., Nonoyama M., Pagano J. S. Reassociation kinetics for Epstein-Barr virus DNA: nonhomology to mammalian DNA and homology of viral DNA in various diseases. J Virol. 1973 Nov;12(5):1006–1012. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.5.1006-1012.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. B., Cozzarelli N. R., Deutscher M. P., Lehman I. R., Kornberg A. Enzymatic synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid. XXXII. Replication of duplex deoxyribonucleic acid by polymerase at a single strand break. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jan 10;245(1):39–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieff E., Levine J. Homology between Burkitt herpes viral DNA and DNA in continuous lymphoblastoid cells from patients with infectious mononucleosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):355–358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Dombos L. Relationship between the sensitivity of EBV-carrying lymphoblastoid lines to superinfection and the inducibility of the resident viral genome. Int J Cancer. 1973 Mar 15;11(2):327–337. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910110210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. Y., Mendecki J., Brawerman G. A polynucleotide segment rich in adenylic acid in the rapidly-labeled polyribosomal RNA component of mouse sarcoma 180 ascites cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1331–1335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T., Klein G., Reedman B. M., Johansson B., Singh S. Relationship between Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DNA and the EBV-determined nuclear antigen (EBNA) in Burkitt lymphoma biopsies and other lymphoproliferative malignancies. Int J Cancer. 1974 Jun 15;13(6):764–772. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910130605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayyasi S. A., Schidlovsky G., Bulfone L. M., Buscheck F. T. The coating reaction of the herpes-type virus isolated from malignant tissues with an antibody present in sera. Cancer Res. 1967 Nov;27(11):2020–2024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Shope T., Lisco H., Stitt D., Lipman M. Epstein-Barr virus: transformation, cytopathic changes, and viral antigens in squirrel monkey and marmoset leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):383–387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson K. High-frequency establishment of human immunoglobulin-producing lymphoblastoid lines from normal and malignant lymphoid tissue and peripheral blood. Int J Cancer. 1971 Nov 15;8(3):432–442. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910080311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano J. S., Huang C. H., Levine P. Absence of Epstein-Barr viral DNA in Amercian Burkitt's lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 1973 Dec 27;289(26):1395–1399. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197312272892604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope J. H., Horne M. K., Scott W. Transformation of foetal human keukocytes in vitro by filtrates of a human leukaemic cell line containing herpes-like virus. Int J Cancer. 1968 Nov 15;3(6):857–866. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910030619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchett R. F., Hayward S. D., Kieff E. D. DNA of Epstein-Barr virus. I. Comparative studies of the DNA of Epstein-Barr virus from HR-1 and B95-8 cells: size, structure, and relatedness. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):556–559. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.556-559.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabin E. Z., Preiss B., Fraser M. J. A nuclease from Neurospora crassa conidia specific for single-stranded nucleic acids. Prep Biochem. 1971;1(4):283–307. doi: 10.1080/00327487108081946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedman B. M., Klein G. Cellular localization of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated complement-fixing antigen in producer and non-producer lymphoblastoid cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1973 May;11(3):499–520. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910110302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedman B. M., Klein G., Pope J. H., Walters M. K., Hilgers J., Singh S., Johansson B. Epstein-Barr virus-associated complement-fixing and nuclear antigens in Burkitt lymphoma biopsies. Int J Cancer. 1974 Jun 15;13(6):755–763. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910130604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J., Sharp P. A., Keller W. Transcription of Simian virus 40. I. Separation of the strands of SV40 DNA and hybridization of the separated strands to RNA extracted from lytically infected and transformed cells. J Mol Biol. 1972 Sep 14;70(1):57–71. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90163-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H., Henle W., Hummeler K., Diehl V., Henle G. Comparative study of cultured Burkitt tumor cells by immunofluorescence, autoradiography, and electron microscopy. J Virol. 1967 Aug;1(4):830–837. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.4.830-837.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



