Abstract
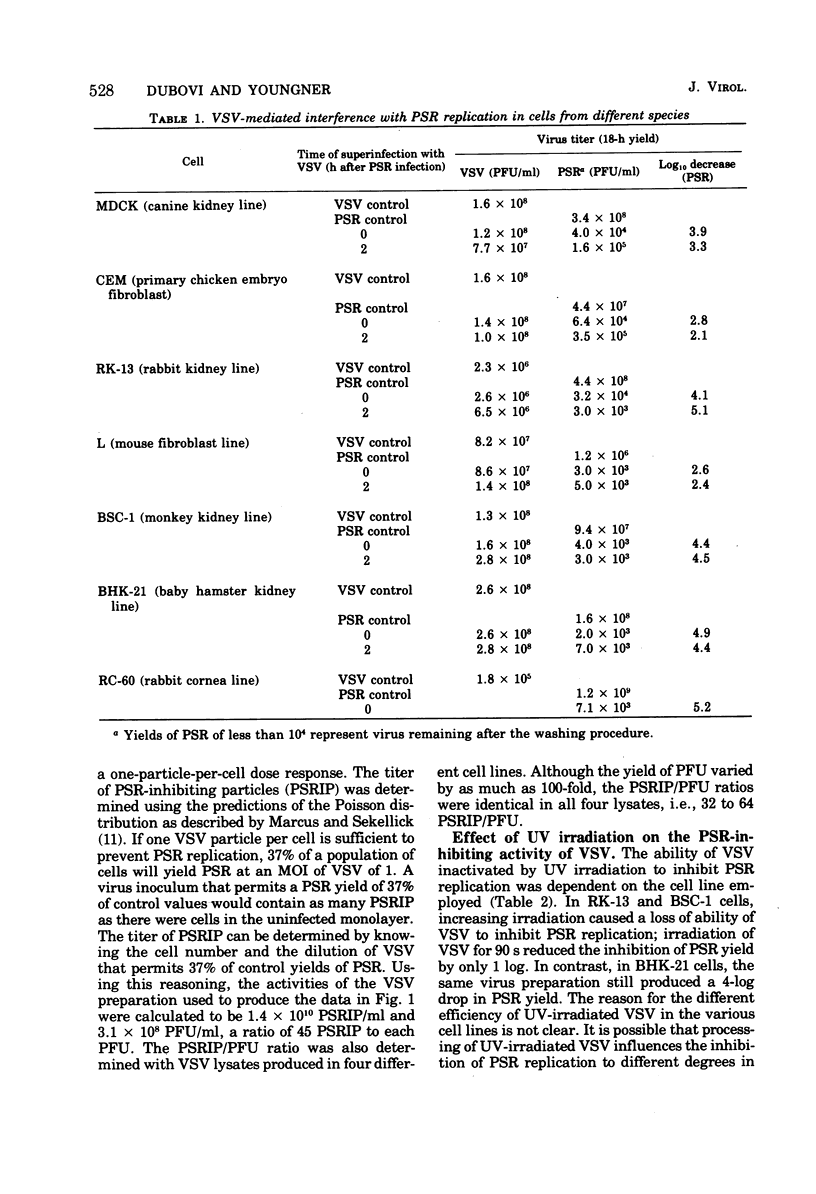
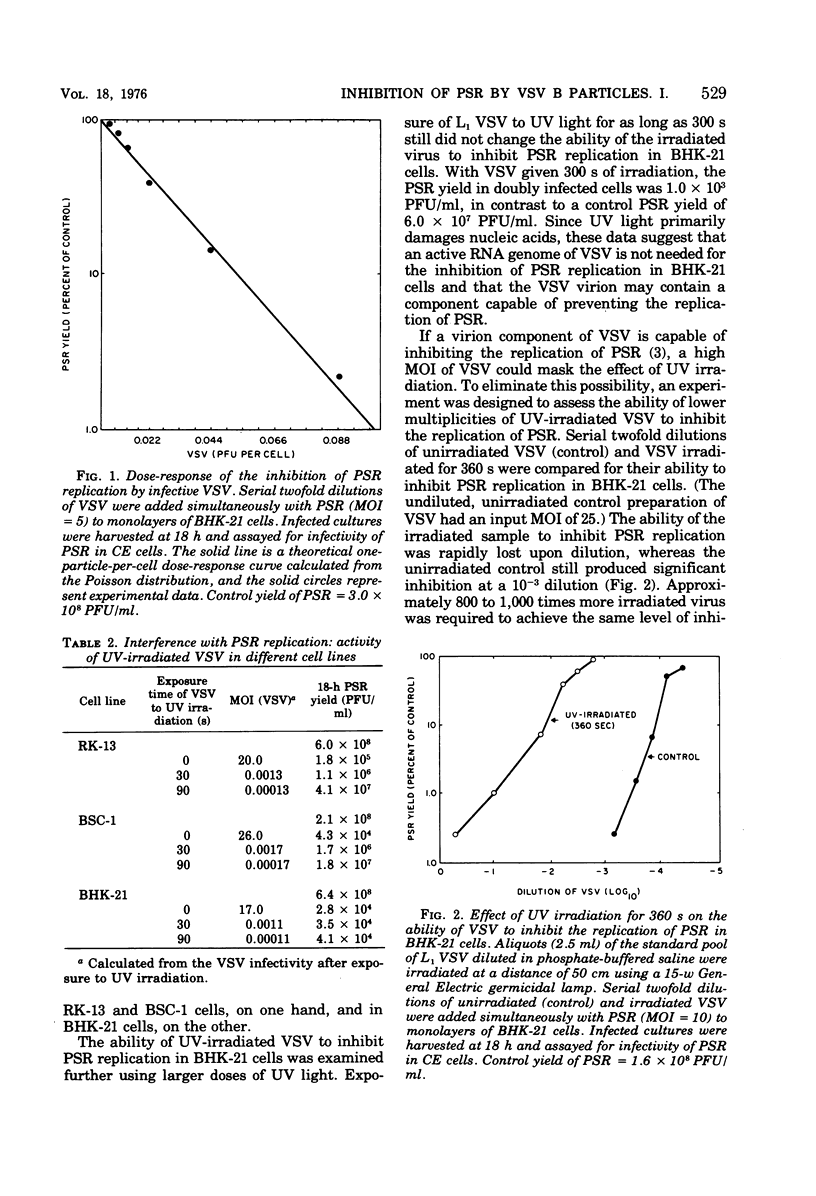
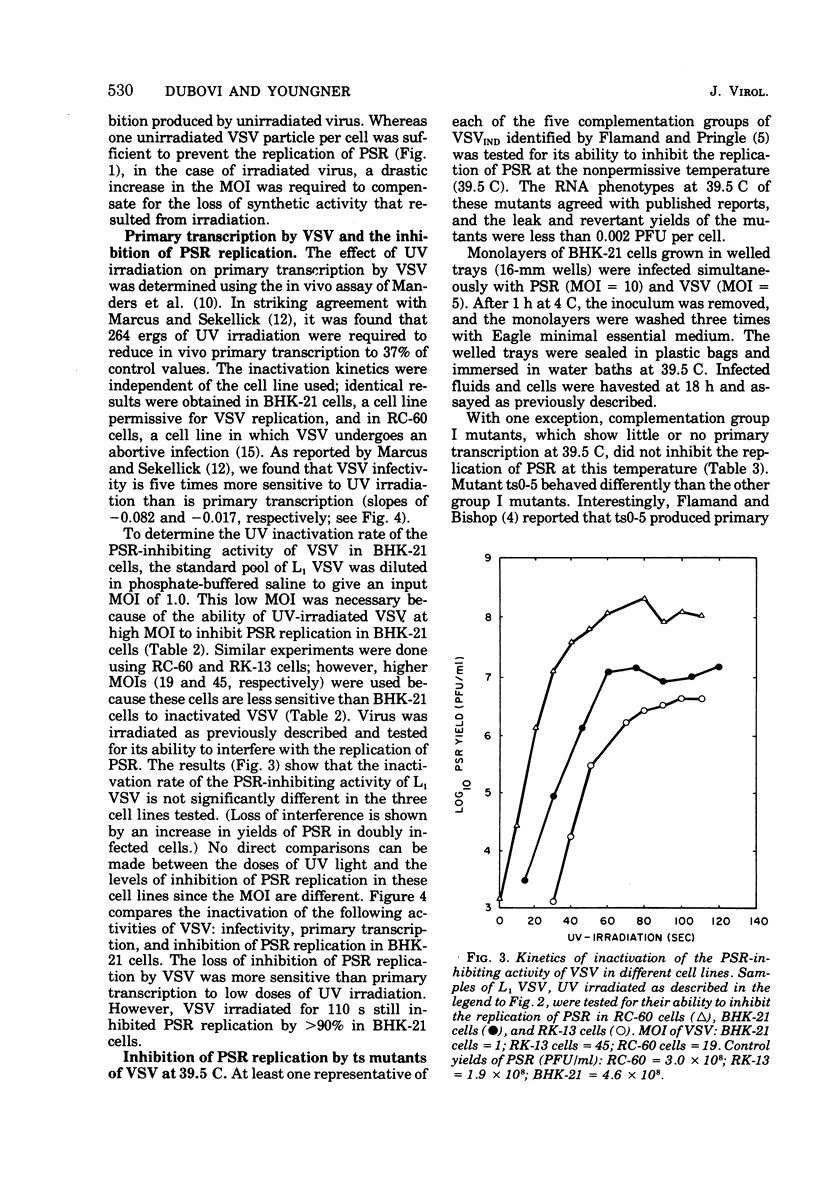
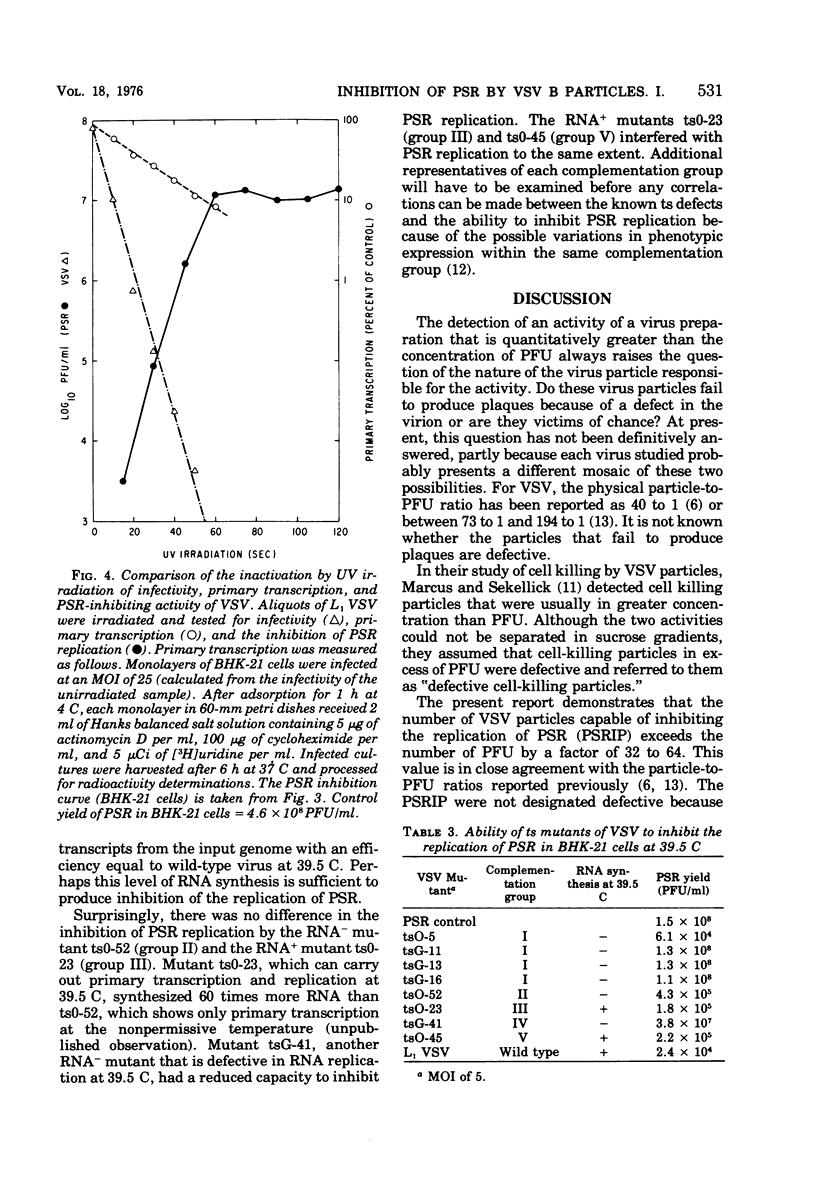
Infectious B particles of vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) are capable of inhibiting the replication of pseudorabies virus (PSR) in a variety of cell lines. Even under conditions of an abortive infection in a continuous line of rabbit cornea cells (RC-6O), B particles interfere with the replication of PSR with high efficiency. Particle per cell dose-response analysis of B particle populations revealed that the number of VSV particles capable of inhibiting PSR replication exceeds the number of PFU by a factor of 32 to 64. When B particles are treated with UV irradiation, a drastic increase in the multiplicity of infection is required to inhibit PSR replication. Whereas one infective B particles per cell is sufficient to prevent replication of PSR, 800 to 1,000 VSV particles rendered noninfective by UV irradiation are required to compensate for the loss of VSV synthetic activity that results from irradiation. Temperature-sensitive mutants representing five complementation groups of VSV were tested at low multiplicities of infection for their effect on PSR replication at the nonpermissive temperature. Generally, the ability of the different complementation groups to amplify virion products at the nonpermissive temperature is associated with their ability to inhibit PSR replication. These results imply that at low multiplicities of infection, amplification of infecting VSV components is necessary for inhibition of PSR replication., but at high multiplicities of infection with VSV, a virion component can prevent PSR replication in the absence of de novo VSV RNA or protein synthesis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CANTELL K., SKURSKA Z., PAUCKER K., HENLE W. Quantitative studies on viral interference in suspended L cells. II. Factors affecting interference by UV-irradiated Newcastle disease virus against vesicular stomatitis virus. Virology. 1962 Jun;17:312–323. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90122-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubovi E. J., Youngner J. S. Inhibition of pseudorabies virus replication by vesicular stomatitis virus. II Activity of defective interfering particles. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):534–541. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.534-541.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flamand A., Bishop D. H. Primary in vivo transcription of vesicular stomatitis virus and temperature-sensitive mutants of five vesicular stomatitis virus complementation groups. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1238–1252. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1238-1252.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flamand A., Pringle C. R. The homologies of spontaneous and induced temperature-sensitive mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus isolated in chick embryo and BHK 21 cells. J Gen Virol. 1971 May;11(2):81–85. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-11-2-81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWATSON A. F., WHITMORE G. F. The development and structure of vesicular stomatitis virus. Virology. 1962 Apr;16:466–478. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90228-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Greenawalt J. W., Wagner R. R. Defective T particles of vesicular stomatitis virus. I. Preparation, morphology, and some biologic properties. Virology. 1966 Oct;30(2):161–172. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90092-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Wagner R. R. Inhibition of cellular RNA synthesis by nonreplicating vesicular stomatitis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Dec;54(6):1579–1584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.6.1579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAGGER J. A small and inexpensive ultraviolet dose-rate meter useful in biological experiements. Radiat Res. 1961 Apr;14:394–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manders E. K., Tilles J. G., Huang A. S. Interferon-mediated inhibition of virion-directed transcription. Virology. 1972 Aug;49(2):573–581. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90508-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus P. I., Sekellick M. J. Cell killing by viruses. I. Comparison of cell-killing, plaque-forming, and defective-interfering particles of vesicular stomatitis virus. Virology. 1974 Feb;57(2):321–338. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90172-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus P. I., Sekellick M. J. Cell killing by viruses. II. Cell killing by vesicular stomatitis virus: a requirement for virion-derived transcription. Virology. 1975 Jan;63(1):176–190. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90383-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCombs R. M., Melnick M. B., Brunschwig J. P. Biophysical studies of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):803–812. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.803-812.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSharry J., Benzinger R. Concentration and purification of vesicular stomatitis virus by polyethylene glycol "precipitation". Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):745–746. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90219-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thacore H. R., Youngner J. S. Abortive infection of a rabbit cornea cell line by vesicular stomatitis virus: conversion to productive infection by superinfection with vaccinia virus. J Virol. 1975 Aug;16(2):322–329. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.2.322-329.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertz G. W., Youngner J. S. Inhibition of protein synthesis in L cells infected with vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1972 Jan;9(1):85–89. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.1.85-89.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertz G. W., Youngner J. S. Interferon production and inhibition of host synthesis in cells infected with vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1970 Oct;6(4):476–484. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.4.476-484.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki S., Wagner R. R. Action of interferon: kinetics and differential effects on viral functions. J Virol. 1970 Oct;6(4):421–429. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.4.421-429.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaoi Y., Mitsui H., Amano M. Effect of U.v.-irradiated vesicular stomatitis virus on nucleic acid synthesis in chick embryo cells. J Gen Virol. 1970 Sep;8(3):165–172. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-8-3-165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngner J. S., Thacore H. R., Kelly M. E. Sensitivity of ribonucleic acid and deoxyribonucleic acid viruses to different species of interferon in cell cultures. J Virol. 1972 Aug;10(2):171–178. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.2.171-178.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


