Abstract
We investigate the hypothesis that two classes of Ca2+ currents, one quickly inactivated by Ca2+ and one slowly inactivated by voltage, contribute to bursting electrical activity in pancreatic islets. A mathematical model of these currents is fit to the experimental whole-cell current-voltage and inactivation profiles, thereby fixing the Ca2+ conductance and all activation and inactivation parameters. Incorporating these currents into a model that includes delayed rectifier K+ channels and ATP-sensitive K+ channels, we show that only abnormal bursting is obtained. Modification of activation parameters to increase Ca2+ channel open times, as suggested by experiment, yields a more robust bursting similar to that observed in intact islets. This reinforces the suggestion that in addition to ATP-sensitive K+ channels, Ca2+ channels may serve as glucose sensors in the beta cell.
Full text
PDF
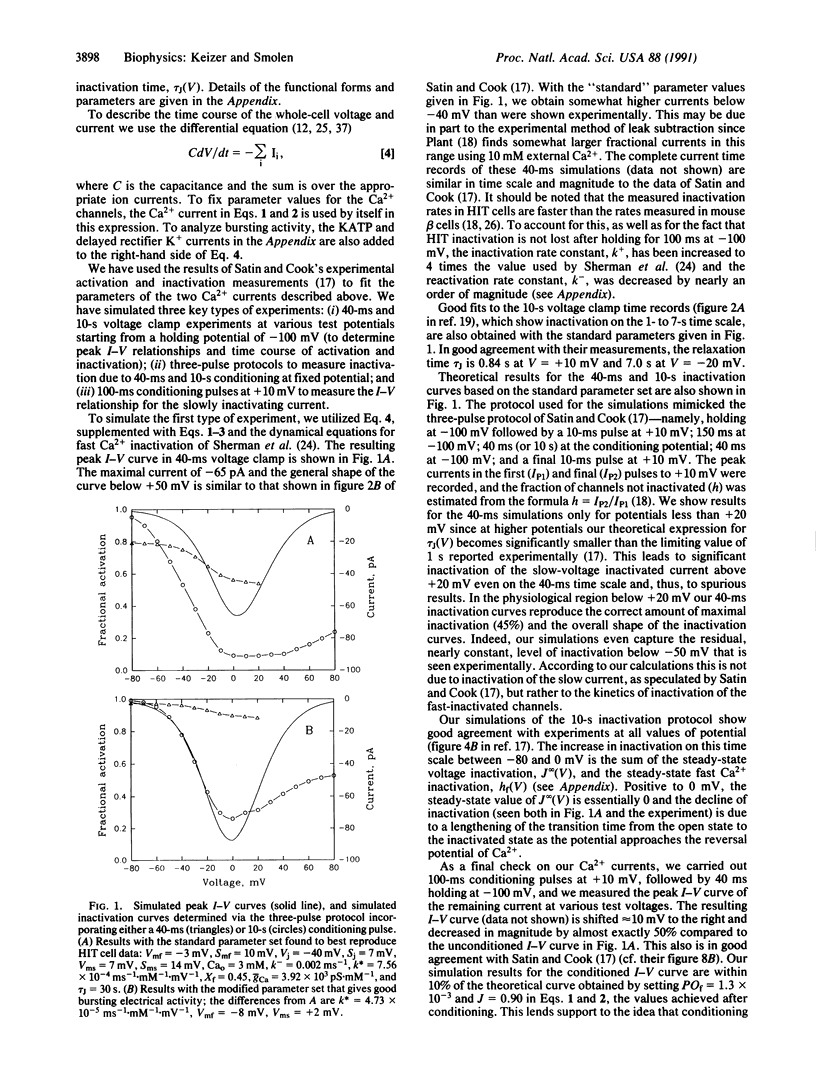
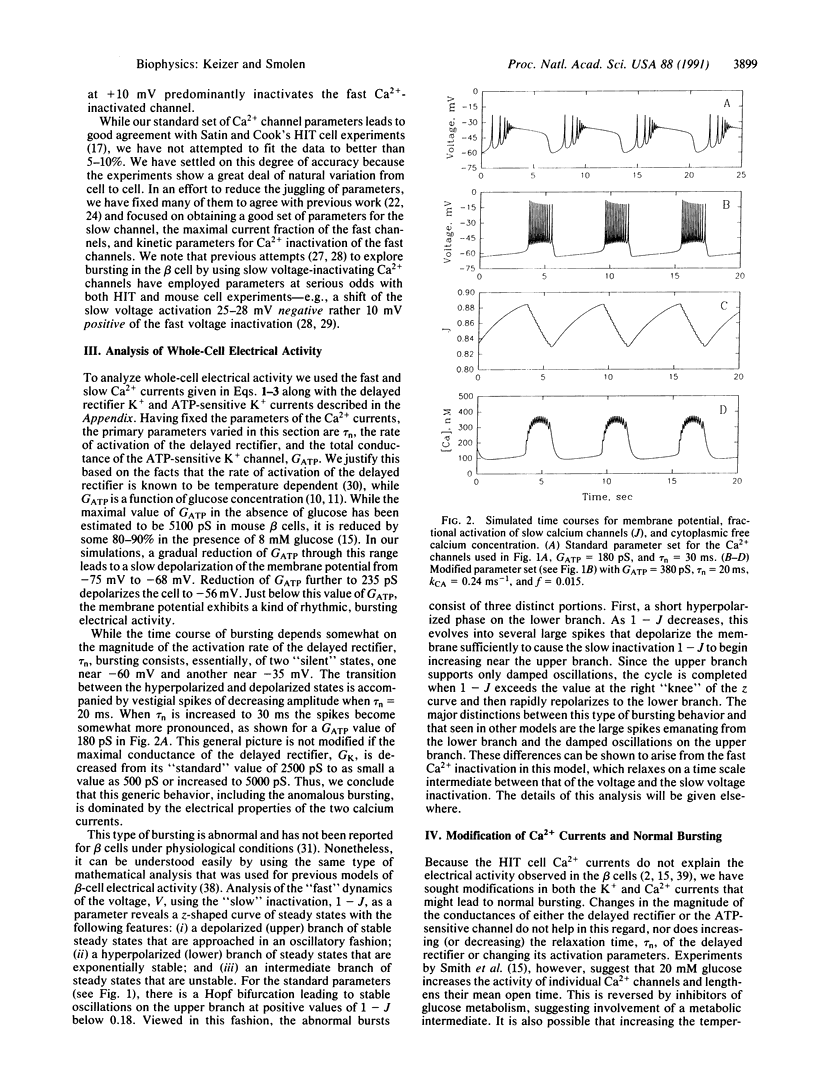


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashcroft F. M., Harrison D. E., Ashcroft S. J. Glucose induces closure of single potassium channels in isolated rat pancreatic beta-cells. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):446–448. doi: 10.1038/312446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atwater I., Dawson C. M., Ribalet B., Rojas E. Potassium permeability activated by intracellular calcium ion concentration in the pancreatic beta-cell. J Physiol. 1979 Mar;288:575–588. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atwater I., Dawson C. M., Scott A., Eddlestone G., Rojas E. The nature of the oscillatory behaviour in electrical activity from pancreatic beta-cell. Horm Metab Res Suppl. 1980;Suppl 10:100–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atwater I., Goncalves A., Herchuelz A., Lebrun P., Malaisse W. J., Rojas E., Scott A. Cooling dissociates glucose-induced insulin release from electrical activity and cation fluxes in rodent pancreatic islets. J Physiol. 1984 Mar;348:615–627. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd A. E., 3rd, Hill R. S., Oberwetter J. M., Berg M. Calcium dependency and free calcium concentrations during insulin secretion in a hamster beta cell line. J Clin Invest. 1986 Mar;77(3):774–781. doi: 10.1172/JCI112374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chay T. R. Bursting excitable cell models by a slow Ca2+ current. J Theor Biol. 1990 Feb 9;142(3):305–315. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(05)80555-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chay T. R. Effect of compartmentalized Ca2+ ions on electrical bursting activity of pancreatic beta-cells. Am J Physiol. 1990 May;258(5 Pt 1):C955–C965. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.5.C955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chay T. R., Keizer J. Minimal model for membrane oscillations in the pancreatic beta-cell. Biophys J. 1983 May;42(2):181–190. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84384-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook D. L., Hales C. N. Intracellular ATP directly blocks K+ channels in pancreatic B-cells. Nature. 1984 Sep 20;311(5983):271–273. doi: 10.1038/311271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean P. M., Matthews E. K. Glucose-induced electrical activity in pancreatic islet cells. J Physiol. 1970 Sep;210(2):255–264. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falke L. C., Gillis K. D., Pressel D. M., Misler S. 'Perforated patch recording' allows long-term monitoring of metabolite-induced electrical activity and voltage-dependent Ca2+ currents in pancreatic islet B cells. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 17;251(1-2):167–172. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81448-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B., Gylfe E., Grapengiesser E., Panten U., Schwanstecher C., Heipel C. Glucose induces temperature-dependent oscillations of cytoplasmic Ca2+ in single pancreatic beta-cells related to their electrical activity. Cell Calcium. 1990 Jun-Jul;11(6):413–418. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(90)90053-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins W. F., Satin L. S., Cook D. L. Inactivation kinetics and pharmacology distinguish two calcium currents in mouse pancreatic B-cells. J Membr Biol. 1991 Feb;119(3):229–239. doi: 10.1007/BF01868728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keahey H. H., Rajan A. S., Boyd A. E., 3rd, Kunze D. L. Characterization of voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels in beta-cell line. Diabetes. 1989 Feb;38(2):188–193. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.2.188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keizer J., Magnus G. ATP-sensitive potassium channel and bursting in the pancreatic beta cell. A theoretical study. Biophys J. 1989 Aug;56(2):229–242. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82669-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kukuljan M., Goncalves A. A., Atwater I. Charybdotoxin-sensitive K(Ca) channel is not involved in glucose-induced electrical activity in pancreatic beta-cells. J Membr Biol. 1991 Jan;119(2):187–195. doi: 10.1007/BF01871418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner H. P., Atwater I. J. The kinetics of electrical activity of beta cells in response to a "square wave" stimulation with glucose or glibenclamide. Horm Metab Res. 1976 Jan;8(1):11–16. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1093685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner H. P. Electrical characteristics of the beta-cells in pancreatic islets. J Physiol (Paris) 1976 Nov;72(6):757–767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misler S., Falke L. C., Gillis K., McDaniel M. L. A metabolite-regulated potassium channel in rat pancreatic B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7119–7123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant T. D. Properties and calcium-dependent inactivation of calcium currents in cultured mouse pancreatic B-cells. J Physiol. 1988 Oct;404:731–747. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribalet B., Beigelman P. M. Effects of divalent cations on beta-cell electrical activity. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jul;241(1):C59–C67. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1981.241.1.C59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojas E., Hidalgo J., Carroll P. B., Li M. X., Atwater I. A new class of calcium channels activated by glucose in human pancreatic beta-cells. FEBS Lett. 1990 Feb 26;261(2):265–270. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80568-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorsman P., Trube G. Calcium and delayed potassium currents in mouse pancreatic beta-cells under voltage-clamp conditions. J Physiol. 1986 May;374:531–550. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satin L. S., Cook D. L. Calcium current inactivation in insulin-secreting cells is mediated by calcium influx and membrane depolarization. Pflugers Arch. 1989 May;414(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF00585619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satin L. S., Cook D. L. Evidence for two calcium currents in insulin-secreting cells. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Apr;411(4):401–409. doi: 10.1007/BF00587719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman A., Keizer J., Rinzel J. Domain model for Ca2(+)-inactivation of Ca2+ channels at low channel density. Biophys J. 1990 Oct;58(4):985–995. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82443-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman A., Rinzel J., Keizer J. Emergence of organized bursting in clusters of pancreatic beta-cells by channel sharing. Biophys J. 1988 Sep;54(3):411–425. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)82975-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. A., Ashcroft F. M., Rorsman P. Simultaneous recordings of glucose dependent electrical activity and ATP-regulated K(+)-currents in isolated mouse pancreatic beta-cells. FEBS Lett. 1990 Feb 12;261(1):187–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80667-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdeolmillos M., Santos R. M., Contreras D., Soria B., Rosario L. M. Glucose-induced oscillations of intracellular Ca2+ concentration resembling bursting electrical activity in single mouse islets of Langerhans. FEBS Lett. 1989 Dec 18;259(1):19–23. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81484-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



