Abstract
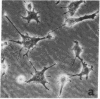
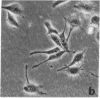
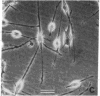
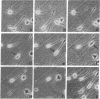
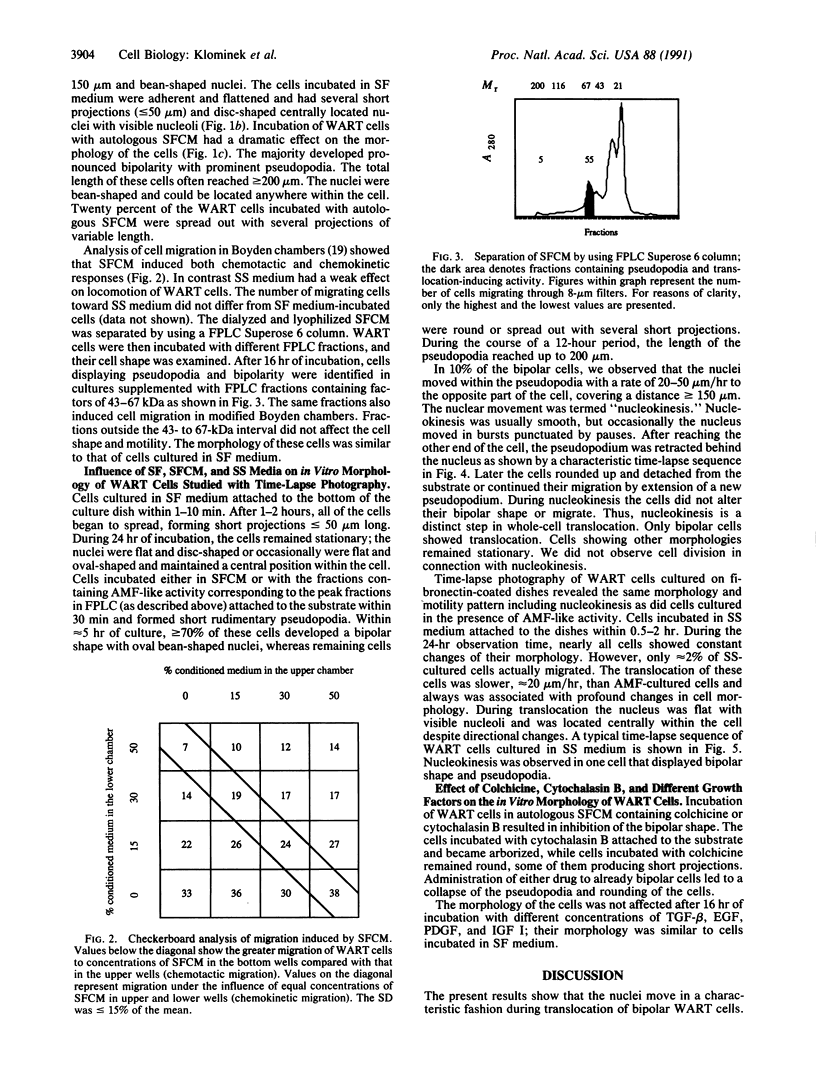
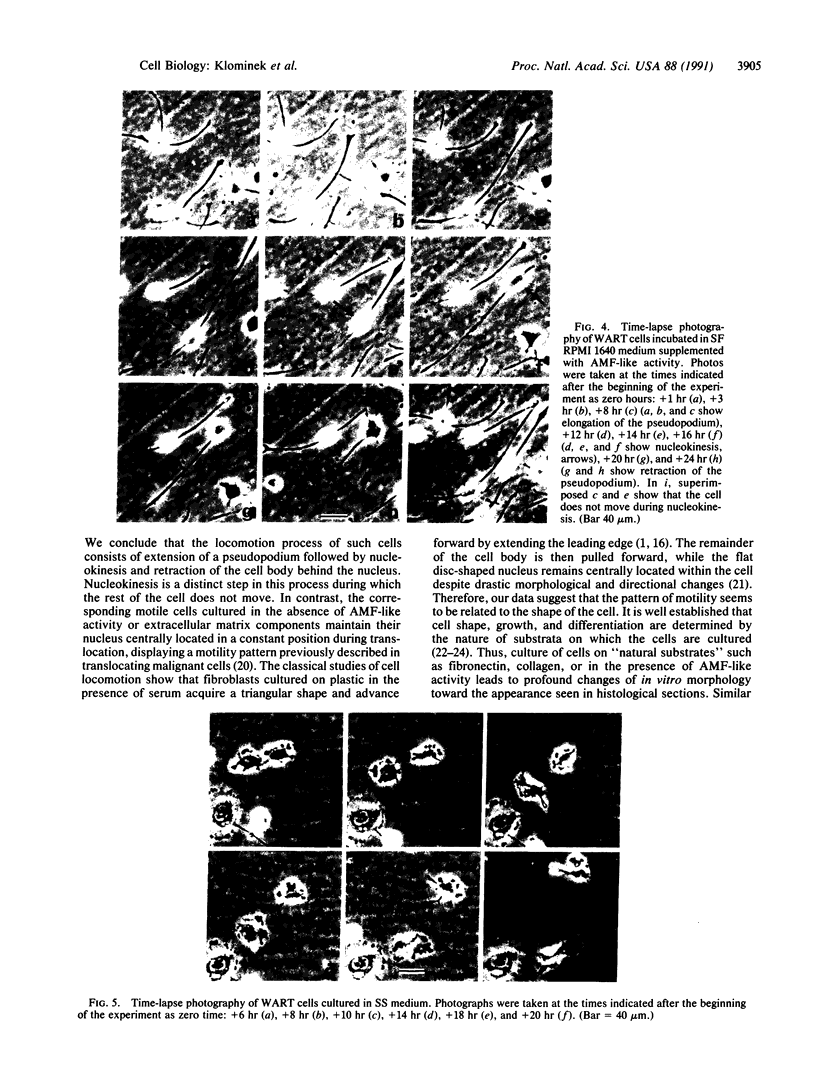
Human lung adenocarcinoma cells develop bipolar shape with prominent pseudopodia (greater than or equal to 200 microns) when cultured in the presence of autocrine motility factor (AMF)-like substance or on fibronectin-coated substrata. AMF was partially purified from a human lung adenocarcinoma cell line and has a peak biological activity at a molecular mass of 67 kDa. Using time-lapse photography, we observed that during AMF- or fibronectin-induced cell translocation, the nuclei of some bipolar cells are transported to the opposite end of the cell, while gross cell shape and position remain unchanged. Following this nuclear movement, which we call "nucleokinesis," the posterior pseudopodium is retracted behind the nucleus. Thus, extension of a pseudopodium followed by nucleokinesis in the same direction and retraction of the cell body behind the nucleus is a normal motile sequence in translocating bipolar cells. This suggests that nucleokinesis is a distinct step in whole-cell translocation of bipolar cells on biological substrata and that pseudopodia can be used as nuclear transport organs. In contrast, adenocarcinoma cells cultured on artificial substrata and in the absence of AMF display a fibroblast-like motility pattern with the nucleus centrally located within the migrating cell.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alvarez-Buylla A., Nottebohm F. Migration of young neurons in adult avian brain. Nature. 1988 Sep 22;335(6188):353–354. doi: 10.1038/335353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ze'ev A. Cell density and cell shape-related regulation of vimentin and cytokeratin synthesis. Inhibition of vimentin synthesis and appearance of a new 45 kD cytokeratin in dense epithelial cell cultures. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Apr;157(2):520–532. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90137-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berke G., Fishelson Z. Possible role of nucleus-membrane interaction in capping of surface membrane receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4580–4583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry M., Rogers A. W. The migration of neuroblasts in the developing cerebral cortex. J Anat. 1965 Oct;99(Pt 4):691–709. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUJITA S. Mitotic pattern and histogenesis of the central nervous system. Nature. 1960 Mar 5;185:702–703. doi: 10.1038/185702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Moscona A. Role of cell shape in growth control. Nature. 1978 Jun 1;273(5661):345–349. doi: 10.1038/273345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. D., Pollack R., Hopkins N. H. Preservation of normal behavior by enucleated cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):750–754. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. L., Vollmers H. P., Birchmeier W. Control of cell locomotion: perturbation with an antibody directed against specific glycoproteins. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):1029–1038. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grotendorst G. R., Seppä H. E., Kleinman H. K., Martin G. R. Attachment of smooth muscle cells to collagen and their migration toward platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3669–3672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guirguis R., Margulies I., Taraboletti G., Schiffmann E., Liotta L. Cytokine-induced pseudopodial protrusion is coupled to tumour cell migration. Nature. 1987 Sep 17;329(6136):261–263. doi: 10.1038/329261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haemmerli G., Sträuli P. In vitro motility of cells from human epidermoid carcinomas. A study by phase-contrast and reflection-contrast cinematography. Int J Cancer. 1981 May 15;27(5):603–610. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910270506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatten M. E. Riding the glial monorail: a common mechanism for glial-guided neuronal migration in different regions of the developing mammalian brain. Trends Neurosci. 1990 May;13(5):179–184. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90044-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh P., Chen L. B. Behavior of cells seeded in isolated fibronectin matrices. J Cell Biol. 1983 May;96(5):1208–1217. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.5.1208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova O. Y., Domnina L. V., Vasiliev J. M., Gelfand I. M. Migration of nuclei and perikaryal cytoplasm along the cytoplasmic processes of differentiated neuroblastoma cells. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1987 Oct;11(10):699–705. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(87)90128-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEONE V., HSU T. C., POMERAT C. M. Cytological studies on HeLa, a strain of human cervical carcinoma. II. On rotatory movements of the nuclei. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1955;41(5):481–492. doi: 10.1007/BF00345357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langman J., Guerrant R. L., Freeman B. G. Behavior of neuro-epithelial cells during closure of the neural tube. J Comp Neurol. 1966 Jul;127(3):399–411. doi: 10.1002/cne.901270308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurila P., Virtanen I., Stenman S. Intermediate filaments in enucleation of human fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Jan;131(1):41–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90403-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E. Intermediate filaments as mechanical integrators of cellular space. Nature. 1980 Jan 17;283(5744):249–256. doi: 10.1038/283249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehto V. P., Virtanen I., Kurki P. Intermediate filaments anchor the nuclei in nuclear monolayers of cultured human fibroblasts. Nature. 1978 Mar 9;272(5649):175–177. doi: 10.1038/272175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A., Mandler R., Murano G., Katz D. A., Gordon R. K., Chiang P. K., Schiffmann E. Tumor cell autocrine motility factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3302–3306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messier P. E., Auclair C. Effect of cytochalasin B on interkinetic nuclear migration in the chick embryo. Dev Biol. 1974 Jan;36(1):218–223. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(74)90206-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morest D. K. The differentiation of cerebral dendrites: A study of the post-migratory neuroblast in the medial nucleus of the trapezoid body. Z Anat Entwicklungsgesch. 1969;128(4):271–289. doi: 10.1007/BF00522528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otteskog P., Ege T., Sundqvist K. G. A possible role of the nucleus in cytochalasin B-induced capping. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Nov;136(1):203–213. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paddock S. W., Albrecht-Buehler G. Distribution of microfilament bundles during rotation of the nucleus in 3T3 cells treated with monensin. Exp Cell Res. 1986 Apr;163(2):525–538. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90083-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postlethwaite A. E., Snyderman R., Kang A. H. The chemotactic attraction of human fibroblasts to a lymphocyte-derived factor. J Exp Med. 1976 Nov 2;144(5):1188–1203. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.5.1188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakic P. Mode of cell migration to the superficial layers of fetal monkey neocortex. J Comp Neurol. 1972 May;145(1):61–83. doi: 10.1002/cne.901450105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakic P. Neuron-glia relationship during granule cell migration in developing cerebellar cortex. A Golgi and electronmicroscopic study in Macacus Rhesus. J Comp Neurol. 1971 Mar;141(3):283–312. doi: 10.1002/cne.901410303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos E., Dingemans K. P., van de Pavert I. V., van den Bergh-Weerman M. Invasion of lymphosarcoma cells into the perfused mouse liver. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1977 Feb;58(2):399–407. doi: 10.1093/jnci/58.2.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos E., Van de Pavert I. V., Middelkoop O. P. Infiltration of tumour cells into cultures of isolated hepatocytes. J Cell Sci. 1981 Feb;47:385–397. doi: 10.1242/jcs.47.1.385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schor S. L. Cell proliferation and migration on collagen substrata in vitro. J Cell Sci. 1980 Feb;41:159–175. doi: 10.1242/jcs.41.1.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasek J. J., Hay E. D. Analysis of the role of microfilaments and microtubules in acquisition of bipolarity and elongation of fibroblasts in hydrated collagen gels. J Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;99(2):536–549. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.2.536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasek J. J., Hay E. D., Fujiwara K. Collagen modulates cell shape and cytoskeleton of embryonic corneal and fibroma fibroblasts: distribution of actin, alpha-actinin, and myosin. Dev Biol. 1982 Jul;92(1):107–122. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90155-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ungar F., Geiger B., Ben-Ze'ev A. Cell contact- and shape-dependent regulation of vinculin synthesis in cultured fibroblasts. 1986 Feb 27-Mar 5Nature. 319(6056):787–791. doi: 10.1038/319787a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlodavsky I., Lui G. M., Gospodarowicz D. Morphological appearance, growth behavior and migratory activity of human tumor cells maintained on extracellular matrix versus plastic. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):607–616. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80037-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond S. H., Hirsch J. G. Leukocyte locomotion and chemotaxis. New methods for evaluation, and demonstration of a cell-derived chemotactic factor. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):387–410. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]