Abstract
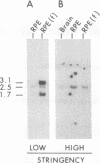
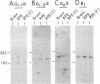
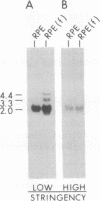
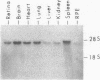
The expression of GTP-binding regulatory proteins (G proteins) in retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells was analyzed by RNA blot hybridization and cDNA amplification. Both adult and fetal human RPE cells contain mRNA for multiple G protein alpha subunits (G alpha) including Gs alpha, Gi-1 alpha, Gi-2 alpha, Gi-3 alpha, and Gz alpha (or Gx alpha), where Gs and Gi are proteins that stimulate or inhibit adenylyl cyclase, respectively, and Gz is a protein that may mediate pertussis toxin-insensitive events. Other G alpha-related mRNA transcripts were detected in fetal RPE cells by low-stringency hybridization to Gi-2 alpha and Gs alpha protein-coding cDNA probes. The diversity of G proteins in RPE cells was further studied by cDNA amplification with reverse transcriptase and the polymerase chain reaction. This approach revealed that, besides the above mentioned members of the G alpha gene family, at least two other G alpha subunits are expressed in RPE cells. Human retinal cDNA clones that encode one of the additional G alpha subunits were isolated and characterized. The results indicate that this G alpha subunit belongs to a separate subfamily of G proteins that may be insensitive to inhibition by pertussis toxin.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basu P. K., Sarkar P., Menon I., Carré F., Persad S. Bovine retinal pigment epithelial cells cultured in vitro: growth characteristics, morphology, chromosomes, phagocytosis ability, tyrosinase activity and effect of freezing. Exp Eye Res. 1983 May;36(5):671–683. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(83)90105-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beals C. R., Wilson C. B., Perlmutter R. M. A small multigene family encodes Gi signal-transduction proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7886–7890. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein P. S., Law W. C., Rando R. R. Isomerization of all-trans-retinoids to 11-cis-retinoids in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1849–1853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaumer L. G proteins in signal transduction. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1990;30:675–705. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.30.040190.003331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray P., Carter A., Simons C., Guo V., Puckett C., Kamholz J., Spiegel A., Nirenberg M. Human cDNA clones for four species of G alpha s signal transduction protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8893–8897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridges C. D. Vitamin A and the role of the pigment epithelium during bleaching and regeneration of rhodopsin in the frog eye. Exp Eye Res. 1976 May;22(5):435–455. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(76)90182-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOWLING J. E. Chemistry of visual adaptation in the rat. Nature. 1960 Oct 8;188:114–118. doi: 10.1038/188114a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dearry A., Edelman J. L., Miller S., Burnside B. Dopamine induces light-adaptive retinomotor movements in bullfrog cones via D2 receptors and in retinal pigment epithelium via D1 receptors. J Neurochem. 1990 Apr;54(4):1367–1378. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb01971.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzel C., Kurjan J. The yeast SCG1 gene: a G alpha-like protein implicated in the a- and alpha-factor response pathway. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1001–1010. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90166-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firtel R. A., van Haastert P. J., Kimmel A. R., Devreotes P. N. G protein linked signal transduction pathways in development: dictyostelium as an experimental system. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):235–239. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90837-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong H. K., Hurley J. B., Hopkins R. S., Miake-Lye R., Johnson M. S., Doolittle R. F., Simon M. I. Repetitive segmental structure of the transducin beta subunit: homology with the CDC4 gene and identification of related mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2162–2166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong H. K., Yoshimoto K. K., Eversole-Cire P., Simon M. I. Identification of a GTP-binding protein alpha subunit that lacks an apparent ADP-ribosylation site for pertussis toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3066–3070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frambach D. A., Valentine J. L., Weiter J. J. Alpha-1 adrenergic receptors on rabbit retinal pigment epithelium. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1988 May;29(5):737–741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman Z., Hackett S. F., Campochiaro P. A. Characterization of adenylate cyclase in human retinal pigment epithelial cells in vitro. Exp Eye Res. 1987 Apr;44(4):471–479. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(87)80158-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman Z., Hackett S. F., Campochiaro P. A. Human retinal pigment epithelial cells possess muscarinic receptors coupled to calcium mobilization. Brain Res. 1988 Apr 12;446(1):11–16. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91291-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman Z., Hackett S. F., Linden J., Campochiaro P. A. Human retinal pigment epithelial cells in culture possess A2-adenosine receptors. Brain Res. 1989 Jul 17;492(1-2):29–35. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90885-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes B. A., Miller S. S., Joseph D. P., Edelman J. L. cAMP stimulates the Na+-K+ pump in frog retinal pigment epithelium. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jan;254(1 Pt 1):C84–C98. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.254.1.C84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keohavong P., Thilly W. G. Fidelity of DNA polymerases in DNA amplification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9253–9257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. Y., Ang S. L., Bloch D. B., Bloch K. D., Kawahara Y., Tolman C., Lee R., Seidman J. G., Neer E. J. Identification of cDNA encoding an additional alpha subunit of a human GTP-binding protein: expression of three alpha i subtypes in human tissues and cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4153–4157. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koh S. W., Chader G. J. Retinal pigment epithelium in culture demonstrates a distinct beta-adrenergic receptor. Exp Eye Res. 1984 Jan;38(1):7–13. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(84)90133-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Translation of insulin-related polypeptides from messenger RNAs with tandemly reiterated copies of the ribosome binding site. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):971–978. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90554-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaVail M. M. Rod outer segment disc shedding in relation to cyclic lighting. Exp Eye Res. 1976 Aug;23(2):277–280. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(76)90209-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaVail M. M. Rod outer segment disk shedding in rat retina: relationship to cyclic lighting. Science. 1976 Dec 3;194(4269):1071–1074. doi: 10.1126/science.982063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang B. T., Hellmich M. R., Neer E. J., Galper J. B. Development of muscarinic cholinergic inhibition of adenylate cyclase in embryonic chick heart. Its relationship to changes in the inhibitory guanine nucleotide regulatory protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):9011–9021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lochrie M. A., Simon M. I. G protein multiplicity in eukaryotic signal transduction systems. Biochemistry. 1988 Jul 12;27(14):4957–4965. doi: 10.1021/bi00414a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luetje C. W., Tietje K. M., Christian J. L., Nathanson N. M. Differential tissue expression and developmental regulation of guanine nucleotide binding regulatory proteins and their messenger RNAs in rat heart. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):13357–13365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. S., Hughes B. A., Machen T. E. Fluid transport across retinal pigment epithelium is inhibited by cyclic AMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):2111–2115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.2111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. S., Steinberg R. H. Potassium modulation of taurine transport across the frog retinal pigment epithelium. J Gen Physiol. 1979 Aug;74(2):237–259. doi: 10.1085/jgp.74.2.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyajima I., Nakafuku M., Nakayama N., Brenner C., Miyajima A., Kaibuchi K., Arai K., Kaziro Y., Matsumoto K. GPA1, a haploid-specific essential gene, encodes a yeast homolog of mammalian G protein which may be involved in mating factor signal transduction. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1011–1019. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90167-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima Y., Nakajima S., Inoue M. Pertussis toxin-insensitive G protein mediates substance P-induced inhibition of potassium channels in brain neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3643–3647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osawa S., Heasley L. E., Dhanasekaran N., Gupta S. K., Woon C. W., Berlot C., Johnson G. L. Mutation of the Gs protein alpha subunit NH2 terminus relieves an attenuator function, resulting in constitutive adenylyl cyclase stimulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2931–2940. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathmann M., Simon M. I. G protein diversity: a distinct class of alpha subunits is present in vertebrates and invertebrates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9113–9117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathmann M., Wilkie T. M., Simon M. I. Diversity of the G-protein family: sequences from five additional alpha subunits in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7407–7409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. W., Bok D. Participation of the retinal pigment epithelium in the rod outer segment renewal process. J Cell Biol. 1969 Aug;42(2):392–403. doi: 10.1083/jcb.42.2.392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]