Abstract
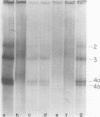
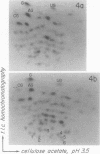
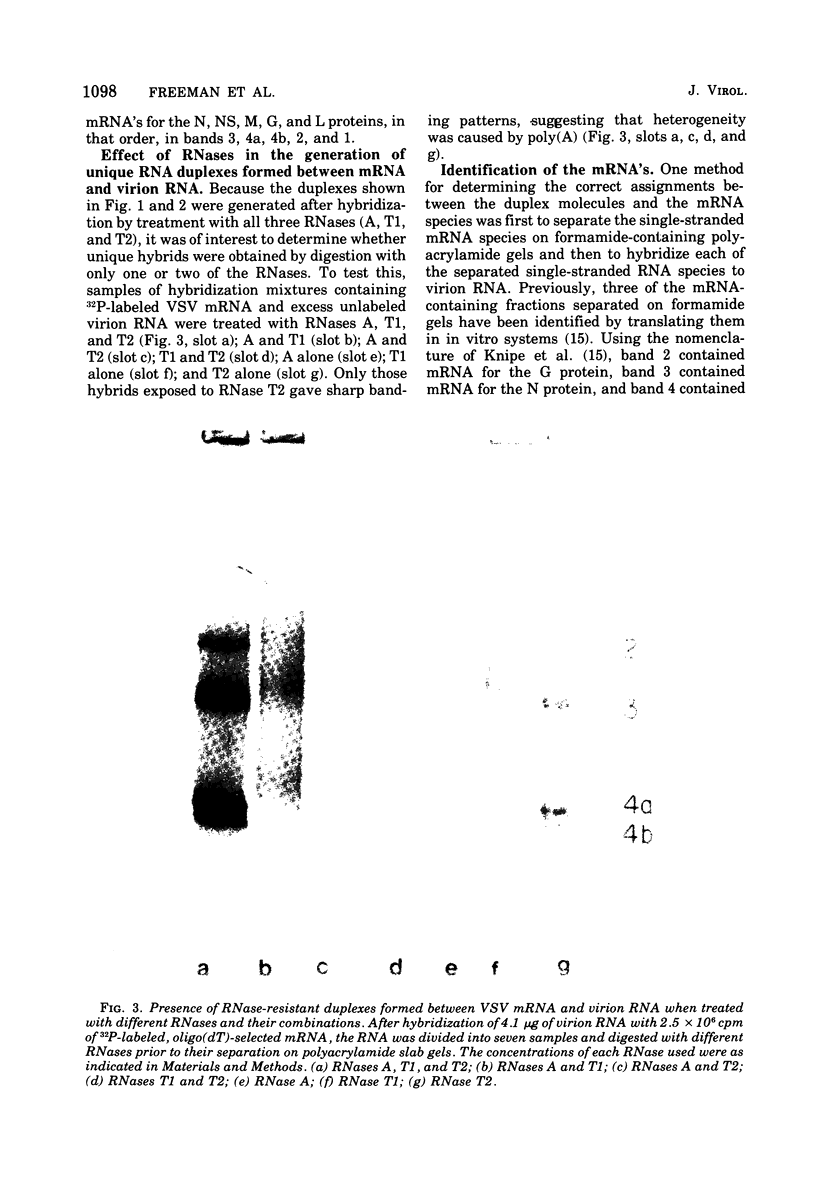
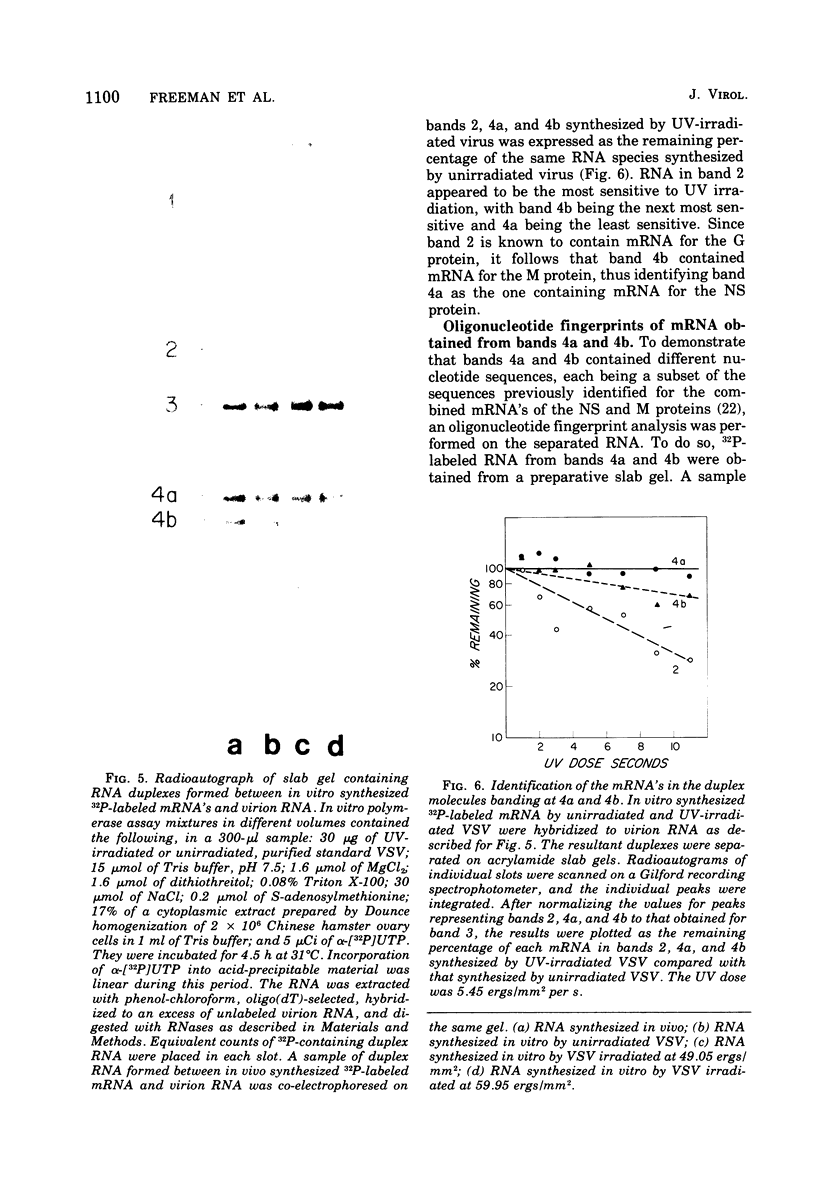
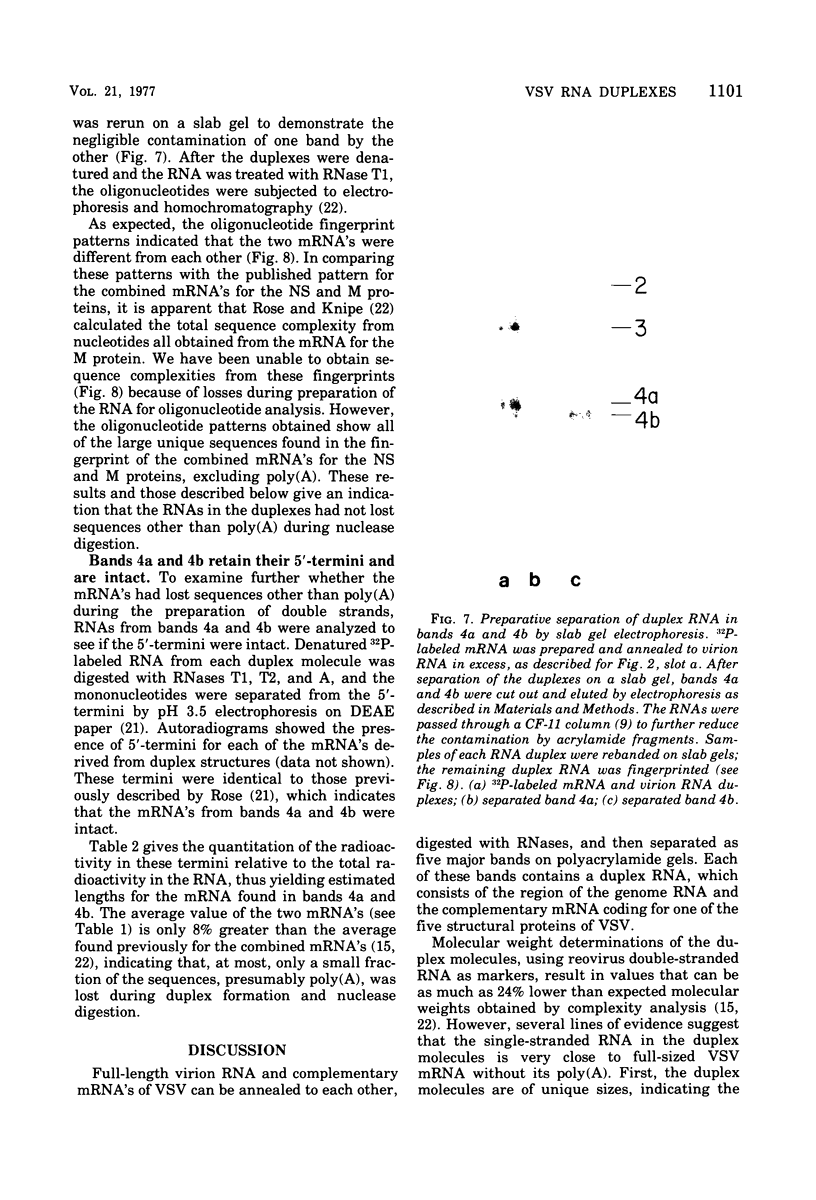
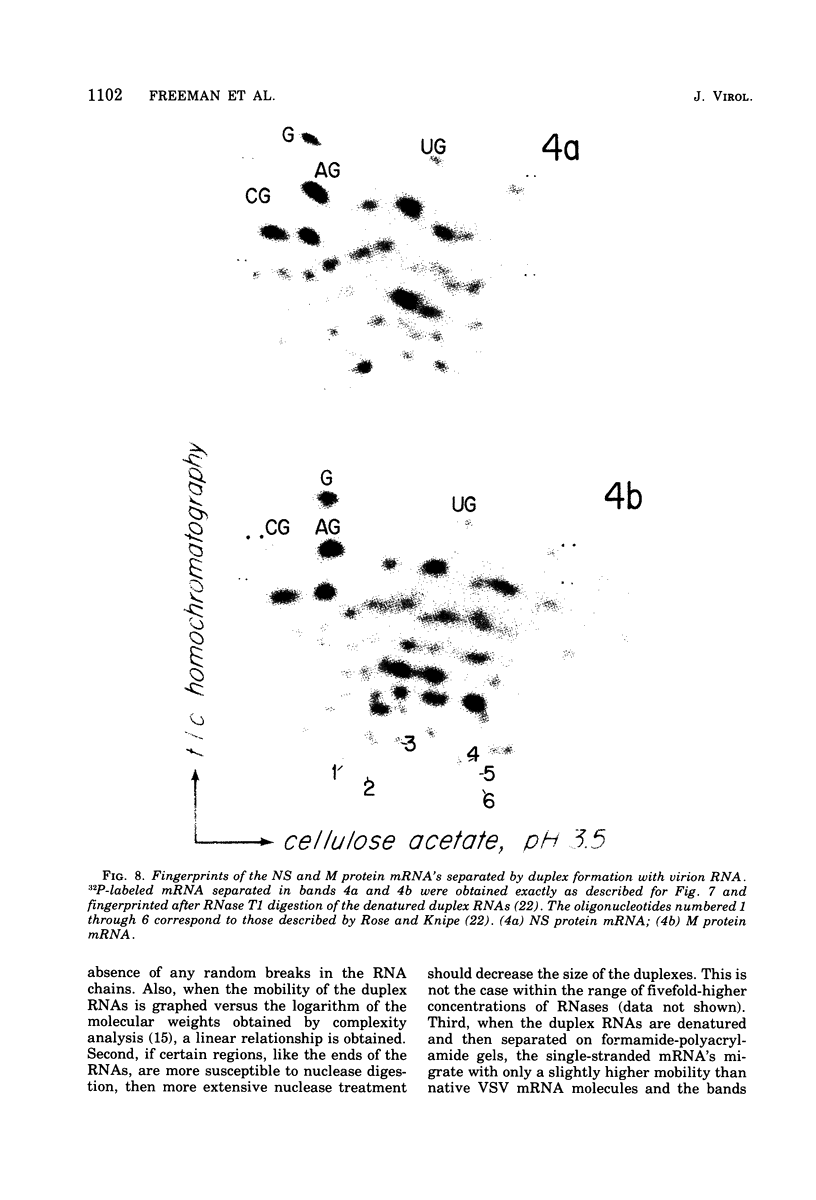
Full-length virion RNA and complementary mRNA's of vesicular stomatitis virus can be annealed to each other, digested with RNases, and then separated as five unique duplex RNA molecules on polyacrylamide slab gels. Similar RNA duplexes were detected whether mRNA or virion RNA was the radioactive component and whether the mRNA was synthesized in vitro or in vivo. The sharp banding pattern of these RNA molecules was dependent on treatment with RNase T2, suggesting that removal of poly(A) is necessary. Identification of the coding region contained in each RNA duplex was based on their previous identification as single-stranded mRNA on formamide-containing, polyacrylamide gels. Because the two smallest mRNA'S had not been previously separated, their identification was based on their in vitro transcriptional gene order. In the order of increasing mobilities on the slab gels, the RNA duplexes are identified as the hybrid of the region of the genome RNA hybridized to the complementary mRNA coding for the large protein, the glycoprotein, the nucleocapsid protein, the core-associated NS protein, and the matrix protein (L,G,N,NS, and M). Several lines of evidence support the presence of undegraded complete mRNA, excluding poly(A), in these RNA duplexes. Also, the two smallest mRNA's, separated by duplex formation, were denatured, and their individual oligonucleotide fingerprints were determined. From chemical length determinations, the molecular weights of the mRNA, minus poly(A), are 2.78 X 10(5) and 2.5 X 10(5), respectively, for the mRNA's of the NS and M proteins.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham G., Rhodes D. P., Banerjee A. K. The 5' terminal structure of the methylated mRNA synthesized in vitro by vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1975 May;5(1):51–58. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90091-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball L. A. Transcriptional mapping of vesicular stomatitis virus in vivo. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):411–414. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.411-414.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball L. A., White C. N. Order of transcription of genes of vesicular stomatitis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):442–446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Both G. W., Moyer S. A., Banerjee A. K. Translation and identification of the viral mRNA species isolated from subcellular fractions of vesicular stomatitis virus-infected cells. J Virol. 1975 Apr;15(4):1012–1019. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.4.1012-1019.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonno R. J., Banerjee A. K. A unique RNA species involved in initiation of vesicular stomatitis virus RNA transcription in vitro. Cell. 1976 Jun;8(2):197–204. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross R. K., Fields B. N. Temperature-sensitive mutants of reovirus type 3: studies on the synthesis of viral RNA. Virology. 1972 Dec;50(3):799–809. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90434-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenfeld E., Summers D. F. Adenylate-rich sequences in vesicular stomatitis virus messenger ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):683–688. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.683-688.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin R. M. Purification and properties of the replicative intermediate of the RNA bacteriophage R17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jun;55(6):1504–1511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.6.1504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Baltimore D., Stampfer M. Ribonucleic acid synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus. 3. Multiple complementary messenger RNA molecules. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):946–957. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90343-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Wagner R. R. Comparative sedimentation coefficients of RNA extracted from plaque-forming and defective particles of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Mol Biol. 1966 Dec 28;22(2):381–384. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90143-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Joklik W. K. Temperature-sensitive mutants of reovirus. I. Patterns of gene expression by mutants of groups C, D, and E. Virology. 1972 Oct;50(1):189–201. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90359-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Joklik W. K. Temperature-sensitive mutants of reovirus. II. Anomalous electrophoretic migration of certain hybrid RNA molecules composed of mutant plus strands and wild-type minus strands. Virology. 1972 Oct;50(1):202–208. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90360-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipe D., Rose J. K., Lodish H. F. Translation of individual species of vesicular stomatitis viral mRNA. J Virol. 1975 Apr;15(4):1004–1011. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.4.1004-1011.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison T., Stampfer M., Baltimore D., Lodish H. F. Translation of vesicular stomatitis messenger RNA by extracts from mammalian and plant cells. J Virol. 1974 Jan;13(1):62–72. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.1.62-72.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudd J. A., Summers D. F. Polysomal ribonucleic acid of vesicular stomatitis virus-infected HeLa cells. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):958–968. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90344-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repik P., Bishop D. H. Determination of the molecular weight of animal RNA viral genomes by nuclease digestions. I. Vesicular stomatitis virus and its defective T particle. J Virol. 1973 Nov;12(5):969–983. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.5.969-983.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D. P., Moyer S. A., Banerjee A. K. In vitro synthesis of methylated messenger RNA by the virion-associated RNA polymerase of vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1974 Dec;3(4):327–333. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K. Heterogneeous 5'-terminal structures occur on vesicular stomatitis virus mRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 25;250(20):8098–8104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Knipe D. Nucleotide sequence complexities, molecular weights, and poly(A) content of the vesicular stomatitis virus mRNA species. J Virol. 1975 Apr;15(4):994–1003. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.4.994-1003.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soria M., Huang A. S. Association of polyadenylic acid with messenger RNA of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Mol Biol. 1973 Jul 5;77(3):449–455. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90450-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stampfer M., Baltimore D., Huang A. S. Ribonucleic acid synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus. I. Species of ribonucleic acid found in Chinese hamster ovary cells infected with plaque-forming and defective particles. J Virol. 1969 Aug;4(2):154–161. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.2.154-161.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stampfer M., Baltimore D. Identification of the vesicular stomatitis virus large protein as a unique viral protein. J Virol. 1973 Apr;11(4):520–526. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.4.520-526.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasquez C., Kleinschmidt A. K. Electron microscopy of RNA strands released from individual Reovirus particles. J Mol Biol. 1968 May 28;34(1):137–147. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90240-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villarreal L. P., Breindl M., Holland J. J. Determination of molar ratios of vesicular stomatitis virus induced RNA species in BHK21 cells. Biochemistry. 1976 Apr 20;15(8):1663–1667. doi: 10.1021/bi00653a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]