Abstract
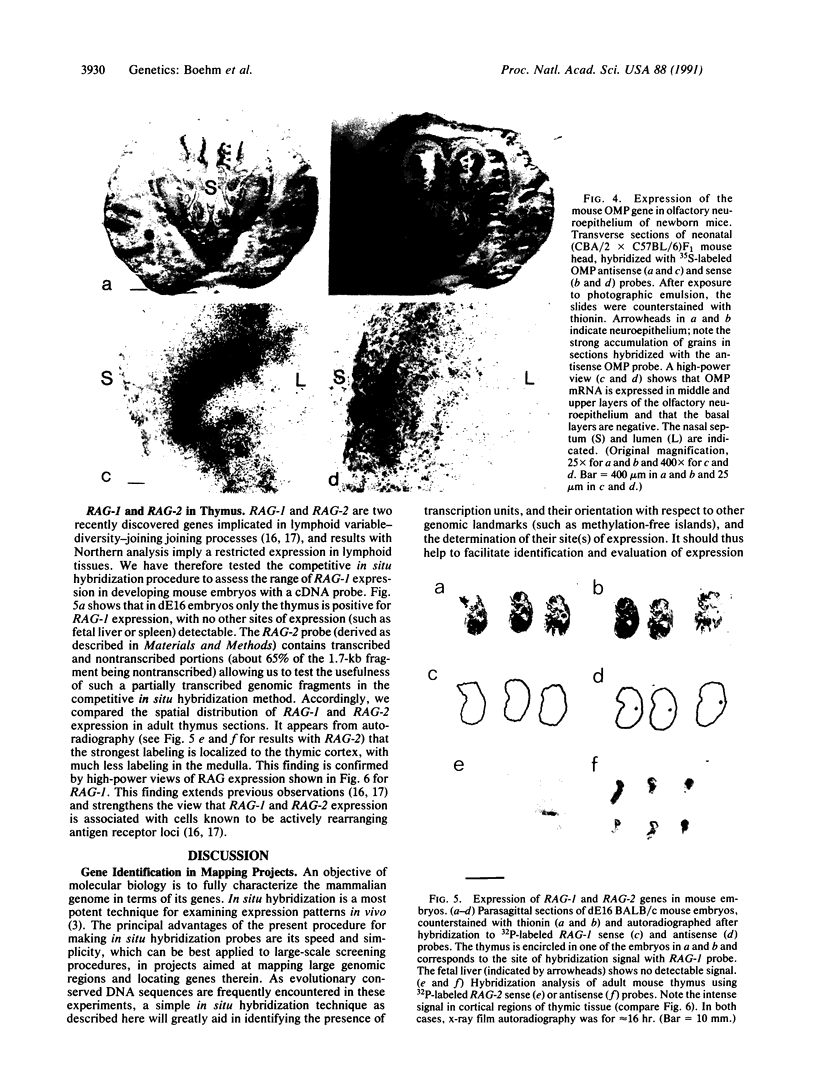
Two major problems have to be solved in studies of genes near breakpoints of chromosome abnormalities and in large-scale genomic mapping projects: (i) the identification of genes within the large amount on nontranscribed DNA and (ii) the determination of the tissues in which the identified genes are transcribed. In situ hybridization to mRNA is ideally suited to assess gene expression in all tissues but probe preparation presents major difficulties for adapting the technique for rapid screening. Here, we present a procedure to easily generate strand-specific DNA probes for in situ hybridization. In this method, a DNA fragment to be tested in uniformly labeled, denatured, and prehybridized to an excess of competitor single-stranded DNA corresponding to either positive or negative strands of the test fragment. No sequence information is needed. The prehybridized mixture is used directly for hybridization to whole embryo or tissue sections. We demonstrate the utility of this approach for any nonrepetitive fragment by using cDNA probes, intronless genomic probes, or genomic probes comprising transcribed and nontranscribed DNA. As an example, we show that mRNA for the recombination-activating genes (RAG) RAG-1 and RAG-2 is found in thymus of dE16 mouse embryos. Within the thymus, high levels of expression of RAG-1 and RAG-2 are detectable in the cortex but not in the medullary region. This supports the view that RAG-1 and RAG-2 expression is associated with cells known to actively rearrange antigen receptor loci.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker H., Grillo M., Margolis F. L. Biochemical and immunocytochemical characterization of olfactory marker protein in the rodent central nervous system. J Comp Neurol. 1989 Jul 8;285(2):246–261. doi: 10.1002/cne.902850207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boehm T., Baer R., Lavenir I., Forster A., Waters J. J., Nacheva E., Rabbitts T. H. The mechanism of chromosomal translocation t(11;14) involving the T-cell receptor C delta locus on human chromosome 14q11 and a transcribed region of chromosome 11p15. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):385–394. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boehm T., Foroni L., Kennedy M., Rabbitts T. H. The rhombotin gene belongs to a class of transcriptional regulators with a potential novel protein dimerisation motif. Oncogene. 1990 Jul;5(7):1103–1105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boehm T., Greenberg J. M., Buluwela L., Lavenir I., Forster A., Rabbitts T. H. An unusual structure of a putative T cell oncogene which allows production of similar proteins from distinct mRNAs. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):857–868. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08183.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend S. H., Bernards R., Rogelj S., Weinberg R. A., Rapaport J. M., Albert D. M., Dryja T. P. A human DNA segment with properties of the gene that predisposes to retinoblastoma and osteosarcoma. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):643–646. doi: 10.1038/323643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gal S., Hohn B. Direct sequencing of double-stranded DNA PCR products via removing the complementary strand with single-stranded DNA of an M13 clone. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):1076–1076. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.1076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M. Neuronal localization of amyloid beta protein precursor mRNA in normal human brain and in Alzheimer's disease. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3627–3632. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02694.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J. M., Boehm T., Sofroniew M. V., Keynes R. J., Barton S. C., Norris M. L., Surani M. A., Spillantini M. G., Rabbitts T. H. Segmental and developmental regulation of a presumptive T-cell oncogene in the central nervous system. Nature. 1990 Mar 8;344(6262):158–160. doi: 10.1038/344158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn J., Matthes H. W., Gait M. J., Brenner S. A new selective phage cloning vector, lambda 2001, with sites for XbaI, BamHI, HindIII, EcoRI, SstI and XhoI. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(1-2):217–224. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90049-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire E. A., Hockett R. D., Pollock K. M., Bartholdi M. F., O'Brien S. J., Korsmeyer S. J. The t(11;14)(p15;q11) in a T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell line activates multiple transcripts, including Ttg-1, a gene encoding a potential zinc finger protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2124–2132. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monti-Graziadei G. A., Margolis F. L., Harding J. W., Graziadei P. P. Immunocytochemistry of the olfactory marker protein. J Histochem Cytochem. 1977 Dec;25(12):1311–1316. doi: 10.1177/25.12.336785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oettinger M. A., Schatz D. G., Gorka C., Baltimore D. RAG-1 and RAG-2, adjacent genes that synergistically activate V(D)J recombination. Science. 1990 Jun 22;248(4962):1517–1523. doi: 10.1126/science.2360047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbitts T. H., Boehm T. LIM domains. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):418–418. doi: 10.1038/346418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers K. E., Dasgupta P., Gubler U., Grillo M., Khew-Goodall Y. S., Margolis F. L. Molecular cloning and sequencing of a cDNA for olfactory marker protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1704–1708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommens J. M., Iannuzzi M. C., Kerem B., Drumm M. L., Melmer G., Dean M., Rozmahel R., Cole J. L., Kennedy D., Hidaka N. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: chromosome walking and jumping. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1059–1065. doi: 10.1126/science.2772657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz D. G., Oettinger M. A., Baltimore D. The V(D)J recombination activating gene, RAG-1. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1035–1048. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90760-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]