Abstract
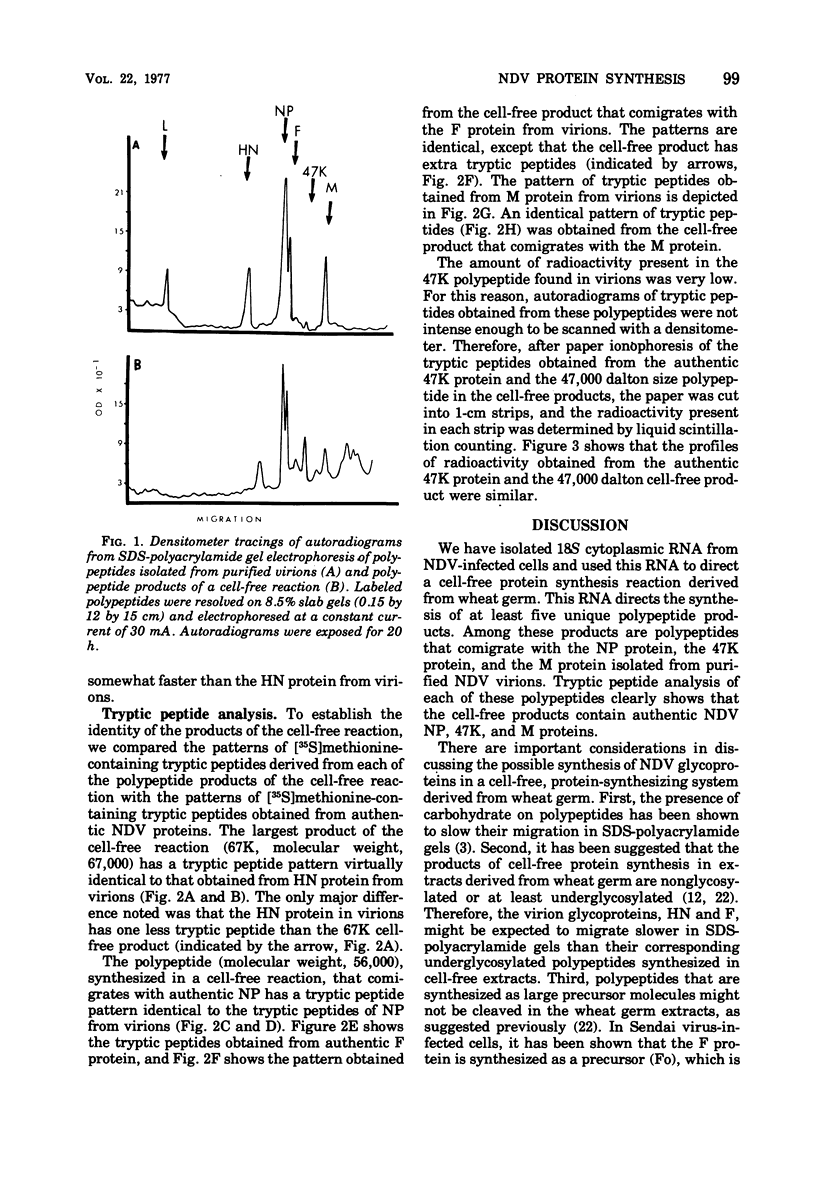
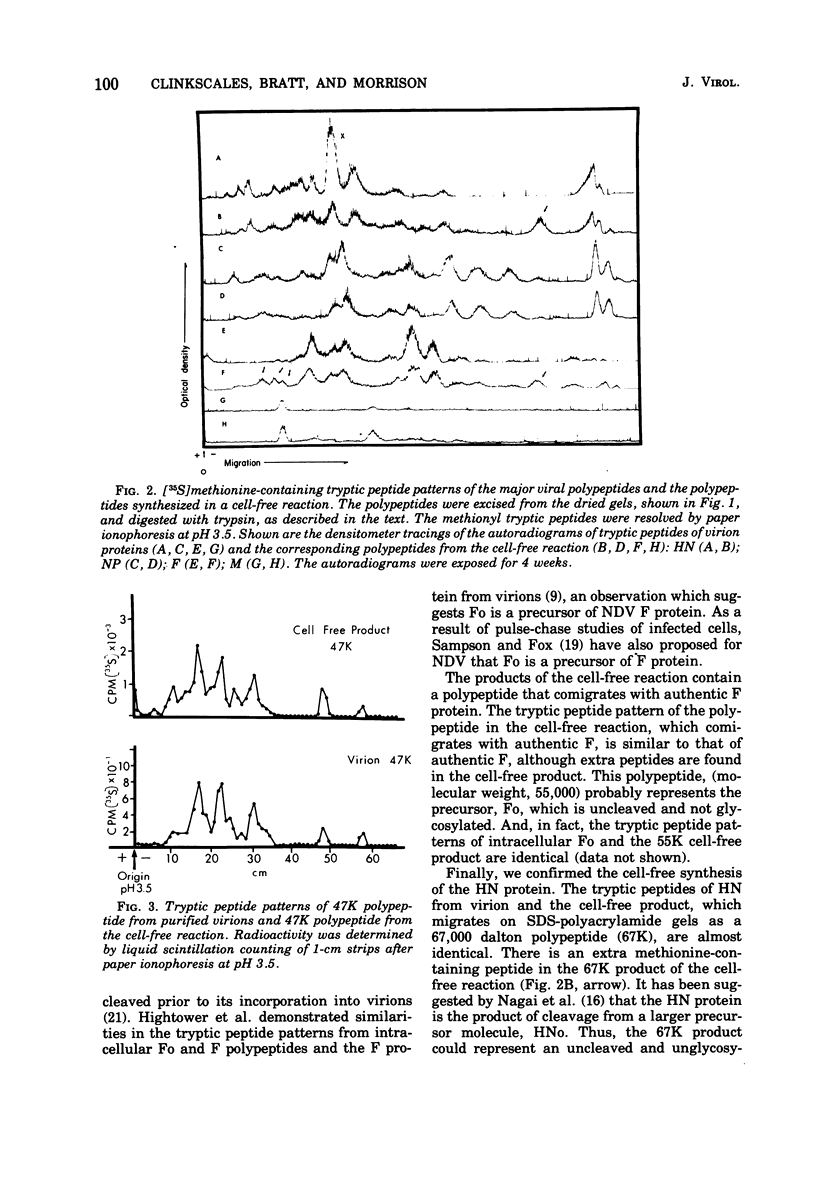
We have isolated 18S RNA from cytoplasmic extracts of Newcastle disease virus-infected Chinese hamster ovary cells and tested its ability to direct protein synthesis in extracts derived from wheat germ. The products of the cell-free reaction directed by this RNA contain polypeptides that comigrate with NP, M,F, and 47K roteins from virions. In addition, the products contain a polypeptide (67K) that migrates on polyacrylamide gels slightly faster than the HN protein from virions. Tryptic peptide analysis of the cell-free products and proteins from virions confirms their identity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D. Expression of animal virus genomes. Bacteriol Rev. 1971 Sep;35(3):235–241. doi: 10.1128/br.35.3.235-241.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher M. S. Major human erythrocyte glycoprotein spans the cell membrane. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):229–232. doi: 10.1038/newbio231229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. W., Portner A., Kingsbury D. W. Synthesis of Sendai virus polypeptides by a cell-free extract from wheat germ. J Gen Virol. 1976 Oct;33(1):117–123. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-1-117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman E., Lodish H. F. Inhibition of replication of ribonucleic acid bacteriophage f2 by superinfection with bacteriophage T4. J Virol. 1971 Oct;8(4):417–429. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.4.417-429.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hightower L. E., Bratt M. A. Protein metabolism during the steady state of Newcastle disease virus infection. I. Kinetics of amino acid and protein accumulation. J Virol. 1975 Apr;15(4):696–706. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.4.696-706.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hightower L. E., Bratt M. A. Protein synthesis in Newcastle disease virus-infected chicken embryo cells. J Virol. 1974 Apr;13(4):788–800. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.4.788-800.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hightower L. E., Morrison T. G., Bratt M. A. Relationships among the polypeptides of Newcastle disease virus. J Virol. 1975 Dec;16(6):1599–1607. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.6.1599-1607.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F. Bacteriophage f2 RNA: control of translation and gene order. Nature. 1968 Oct 26;220(5165):345–350. doi: 10.1038/220345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison T. G. Site of synthesis of membrane and nonmembrane proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 10;250(17):6955–6962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mountcastle W. E., Compans R. W., Caliguiri L. A., Choppin P. W. Nucleocapsid protein subunits of simian virus 5, Newcastle disease virus, and Sendai virus. J Virol. 1970 Nov;6(5):677–684. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.5.677-684.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mountcastle W. E., Compans R. W., Choppin P. W. Proteins and glycoproteins of paramyxoviruses: a comparison of simian virus 5, Newcastle disease virus, and Sendai virus. J Virol. 1971 Jan;7(1):47–52. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.1.47-52.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai Y., Klenk H. D., Rott R. Proteolytic cleavage of the viral glycoproteins and its significance for the virulence of Newcastle disease virus. Virology. 1976 Jul 15;72(2):494–508. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90178-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D. Magnesium precipitation of ribonucleoprotein complexes. Expedient techniques for the isolation of undergraded polysomes and messenger ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1974 Aug 13;13(17):3606–3615. doi: 10.1021/bi00714a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. E., Paterson B. M. Efficient translation of tobacco mosaic virus RNA and rabbit globin 9S RNA in a cell-free system from commercial wheat germ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. E., Paterson B. M., Sperling R. The cell-free synthesis and assembly of viral specific polypeptides into TMV particles. Virology. 1974 May;59(1):307–313. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90227-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samson A. C., Fox C. F. Precursor protein for Newcastle disease virus. J Virol. 1973 Sep;12(3):579–587. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.3.579-587.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Identification of biological activities of paramyxovirus glycoproteins. Activation of cell fusion, hemolysis, and infectivity of proteolytic cleavage of an inactive precursor protein of Sendai virus. Virology. 1974 Feb;57(2):475–490. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90187-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Isolation and purification of the envelope proteins of Newcastle disease virus. J Virol. 1973 Feb;11(2):263–271. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.2.263-271.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. R., Bratt M. A. Comparative electrophoresis of the 18-22S RNAs of Newcastle disease virus. J Virol. 1976 Apr;18(1):316–323. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.1.316-323.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. R., Bratt M. A. Polyadenylate sequences on Newcastle disease virus mRNA synthesized in vivo and in vitro. J Virol. 1974 Jun;13(6):1220–1230. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.6.1220-1230.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



