Abstract
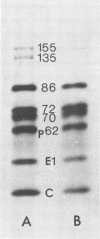
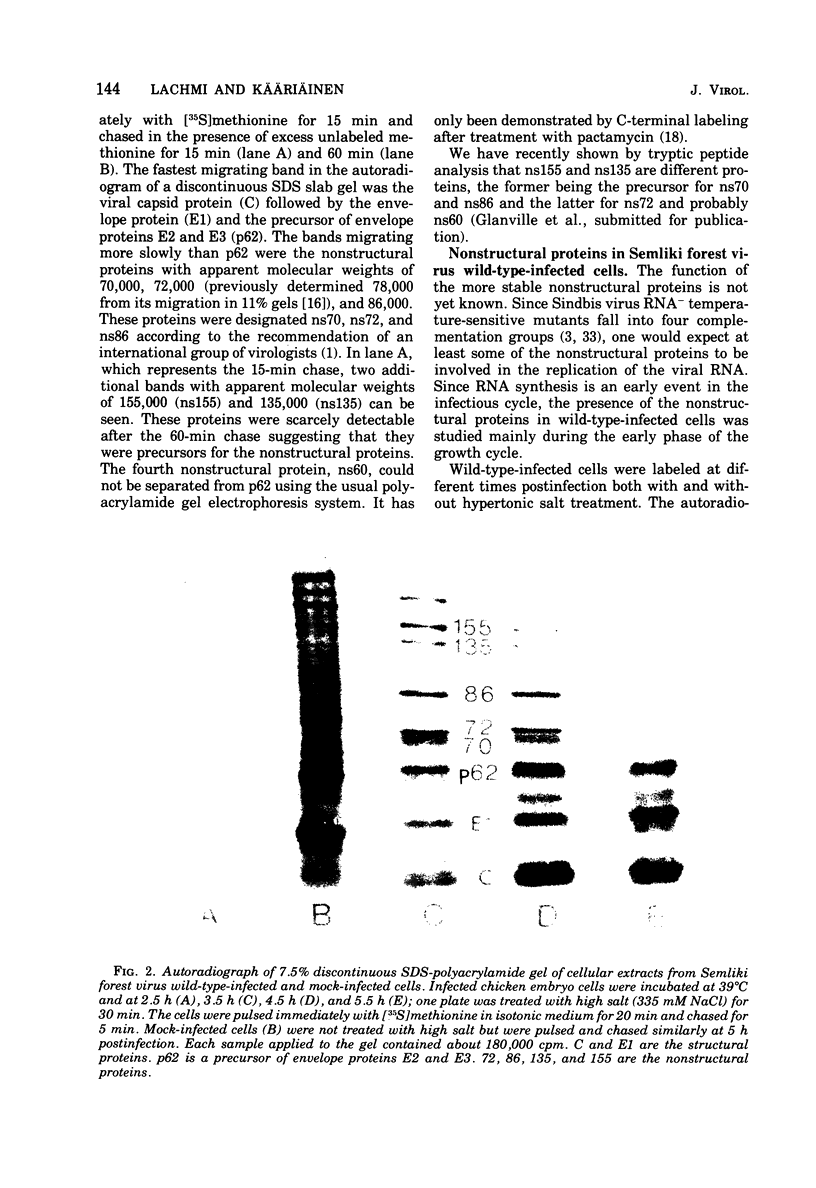
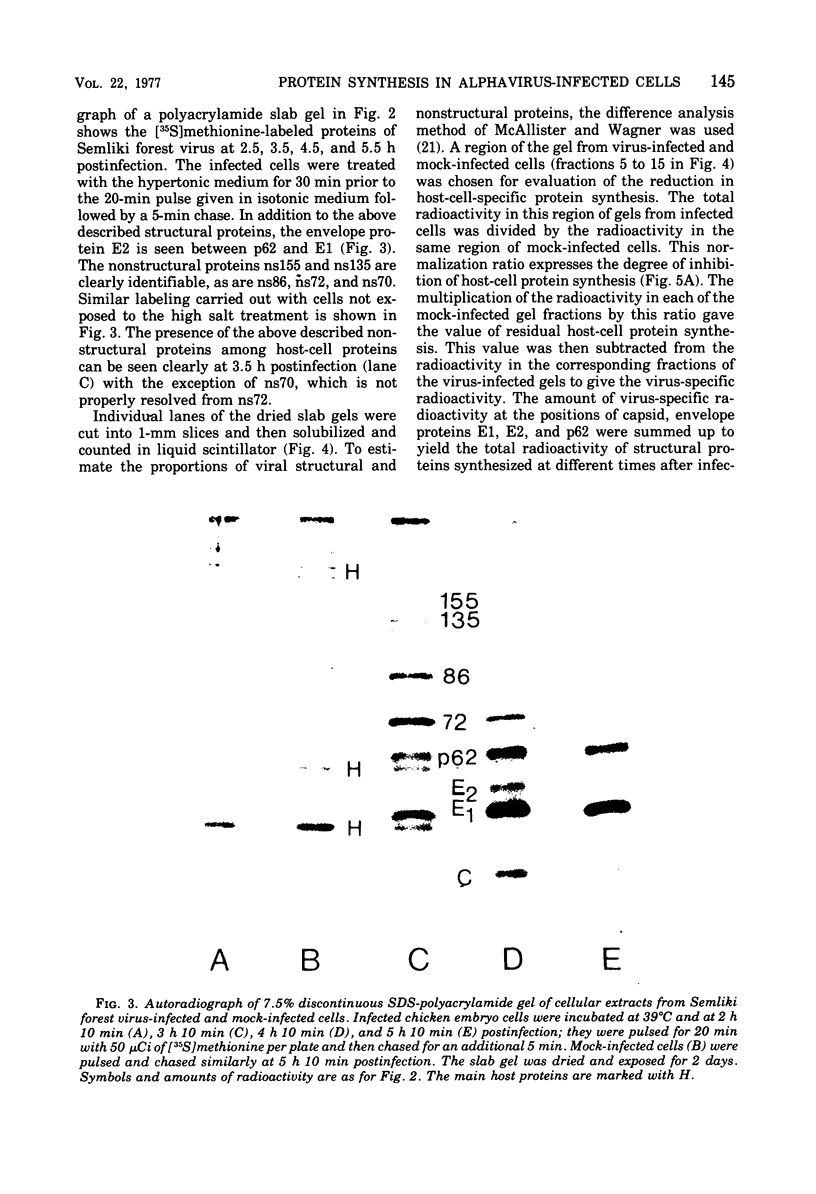
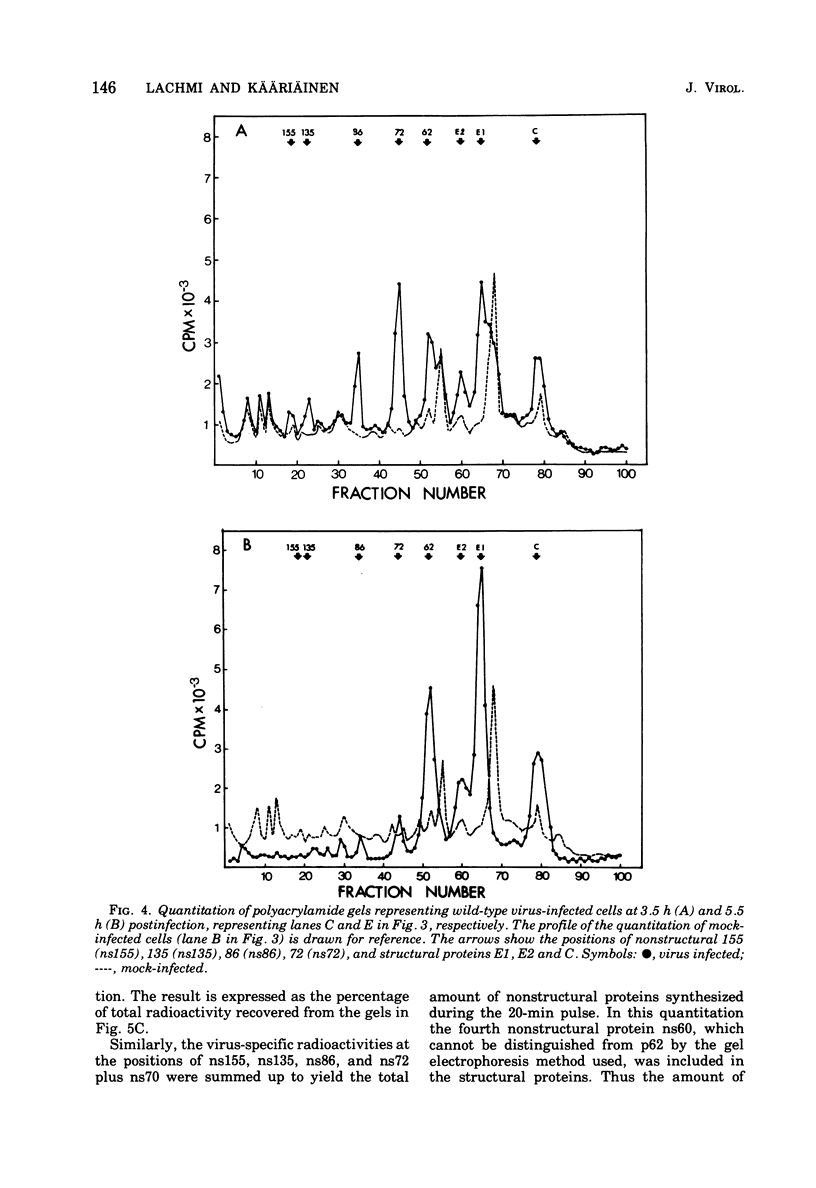
Protein synthesis in Semliki forest virus-infected chicken embryo cells was studied by labeling them with [35S]methionine for short periods at different times after infection, with or without synchronization of protein synthesis by the hypertonic block technique. The rate of host-cell protein synthesis declined almost linearly in inverse correlation to the increase in the amount of virus specific RNA. At 5.5 h postinfection, the host-cell protein synthesis was reduced by about 70%. The viral structural proteins were detectable with certainty at 3.5 h postinfection, and their rate of synthesis increased linearly parallel to the amount of their messenger, the 26S RNA. This suggests that the rate of synthesis of the structural proteins is controlled at the level of transcription. The rate of synthesis of the virus-specific nonstructural proteins attained its maximum between 3 and 4 h postinfection and declined thereafter, wheras the amount of their messenger, the 42S RNA, continued to increase linearly in the cells. Thus, the messenger activity of the 42S RNA is reduced in the late phase of infection compared with its activity in the early phase.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burge B. W., Pfefferkorn E. R. Complementation between temperature-sensitive mutants of Sindbis virus. Virology. 1966 Oct;30(2):214–223. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90097-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cancedda R., Schlesinger M. J. Formation of Sindbis virus capsid protein in mammalian cell-free extracts programmed with viral messenger RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1843–1847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cancedda R., Villa-Komaroff L., Lodish H. F., Schlesinger M. Initiation sites for translation of sindbis virus 42S and 26S messenger RNAs. Cell. 1975 Oct;6(2):215–222. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. C., Kennedy S. I. Initiation of synthesis of the structural proteins of Semliki Forest virus. J Mol Biol. 1975 Oct 5;97(4):401–411. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80050-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. C. Sequential translation of capsid and membrane protein genes of alphaviruses. Nature. 1975 Apr 3;254(5499):454–455. doi: 10.1038/254454a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glanville N., Morser J., Uomala P., Käri5AAINEN L. Simultaneous translation of structural and nonstructural proteins from Semliki-forest-virus RNA in two eukaryotic systems in vitro. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Apr 15;64(1):167–175. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10285.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glanville N., Ranki M., Morser J., Käriäinen L., Smith A. E. Initiation of translation directed by 42S and 26S RNAs from Semliki Forest virus in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3059–3063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glanville N., Ulmanen I. Biological activity of in vitro synthesised protein: binding of Semliki Forest virus capsid protein to the large ribosomal subunit. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jul 12;71(1):393–399. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90295-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy S. I. Isolation and identification of the virus-specified RNA species found on membrane-bound polyribosomes of chick embryo cells infected with Semliki Forest virus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Sep 5;48(5):1254–1258. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90846-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keränen S., Käriäinen L. Isolation and basic characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants from Semliki Forest virus;. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Dec;82(6):810–820. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1974.tb02378.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keränen S., Käriäinen L. Proteins synthesized by Semliki Forest virus and its 16 temperature-sensitive mutants. J Virol. 1975 Aug;16(2):388–396. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.2.388-396.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käriäinen L., Keränen S., Lachmi B., Söderlund H., Tuomi K., Ulmanen I. Replication of Semliki Forest virus. Med Biol. 1975 Oct;53(5):342–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käriäinen L., Simons K., von Bonsdorff C. H. Studies in subviral components of Semliki Forest virus. Ann Med Exp Biol Fenn. 1969;47(4):235–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kärläinen L., Lachmi B. E., Glanville N. Transitional control in Semliki forest virus infected cells. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1976 Jan;127A(1):197–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmi B. E., Glanville N., Keränen S., Läriäinen L. Tryptic peptide analysis on nonstructural and structural precursor proteins from Semliki Forest virus mutant-infected cells. J Virol. 1975 Dec;16(6):1615–1629. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.6.1615-1629.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmi B. E., Käriäinen L. Sequential translation of nonstructural proteins in cells infected with a Semliki Forest virus mutant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1936–1940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J. G., Friedman R. M. Analysis of arbovirus ribonucleic acid forms by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Virol. 1971 Apr;7(4):504–514. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.4.504-514.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister P. E., Wagner R. R. Differential inhibition of host protein synthesis in L cells infected with RNA - temperature-sensitive mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):550–558. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.550-558.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowshowitz D. Identification of polysomal RNA in BHK cells infected by sindbis virus. J Virol. 1973 Apr;11(4):535–543. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.4.535-543.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr Molecular weight determination of protein-dodecyl sulfate complexes by gel electrophoresis in a discontinuous buffer system. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6328–6334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuss D. L., Oppermann H., Koch G. Selective blockage of initiation of host protein synthesis in RNA-virus-infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1258–1262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proposed nomenclature for alphavirus polypeptides. J Gen Virol. 1976 Feb;30(2):273–273. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-30-2-273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saborio J. L., Pong S. S., Koch G. Selective and reversible inhibition of initiation of protein synthesis in mammalian cells. J Mol Biol. 1974 May 15;85(2):195–211. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90360-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. T., Strauss J. H. Replication of Sindbis virus. I. Relative size and genetic content of 26 s and 49 s RNA. J Mol Biol. 1972 Nov 28;71(3):599–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. T., Strauss J. H. Replication of Sindbis virus. V. Polyribosomes and mRNA in infected cells. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):552–559. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.552-559.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. T., Strauss J. H. Translation of Sindbis virus 26 S RNA and 49 S RNA in lysates of rabbit reticulocytes. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jun 25;86(2):397–409. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss E. G., Lenches E. M., Strauss J. H. Mutants of sindbis virus. I. Isolation and partial characterization of 89 new temperature-sensitive mutants. Virology. 1976 Oct 1;74(1):154–168. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90137-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderlund H. Kinetics of formation of the Semliki Forest virus nucleocapsid. Intervirology. 1973;1(5-6):354–361. doi: 10.1159/000148864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderlund H., Käriäinen L. Association of capsid protein with Semliki Forest virus messenger RNAs. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Feb;82(1):33–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1974.tb02289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderlund H. The post-translational processing of Semliki forest virus structural polypeptides in puromycin treated cells. FEBS Lett. 1976 Mar 15;63(1):56–58. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80193-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temple G., Lodish H. F. Competition between alpha and beta globin messenger RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Apr 21;63(4):971–979. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90664-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuomi K., Kädäridäinen L., Söderlund H. Quantitation of Semlike Forest virus RNAs in infected cells using 32-P equilibrium labelling. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Apr;2(4):555–565. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.4.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulmanen I., Söderlund H., Käriäinen L. Semliki Forest virus capsid protein associates with the 60S ribosomal subunit in infected cells. J Virol. 1976 Oct;20(1):203–210. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.1.203-210.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Beato M., Hackemack B. A. Translation of 26 S virus-specific RNA from Semliki Forest virus-infected cells in vitro. Virology. 1974 Sep;61(1):120–128. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90247-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Wengler G. Localization of the 26-S RNA sequence on the viral genome type 42-S RNA isolated from SFV-infected cells. Virology. 1976 Aug;73(1):190–199. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]