Abstract
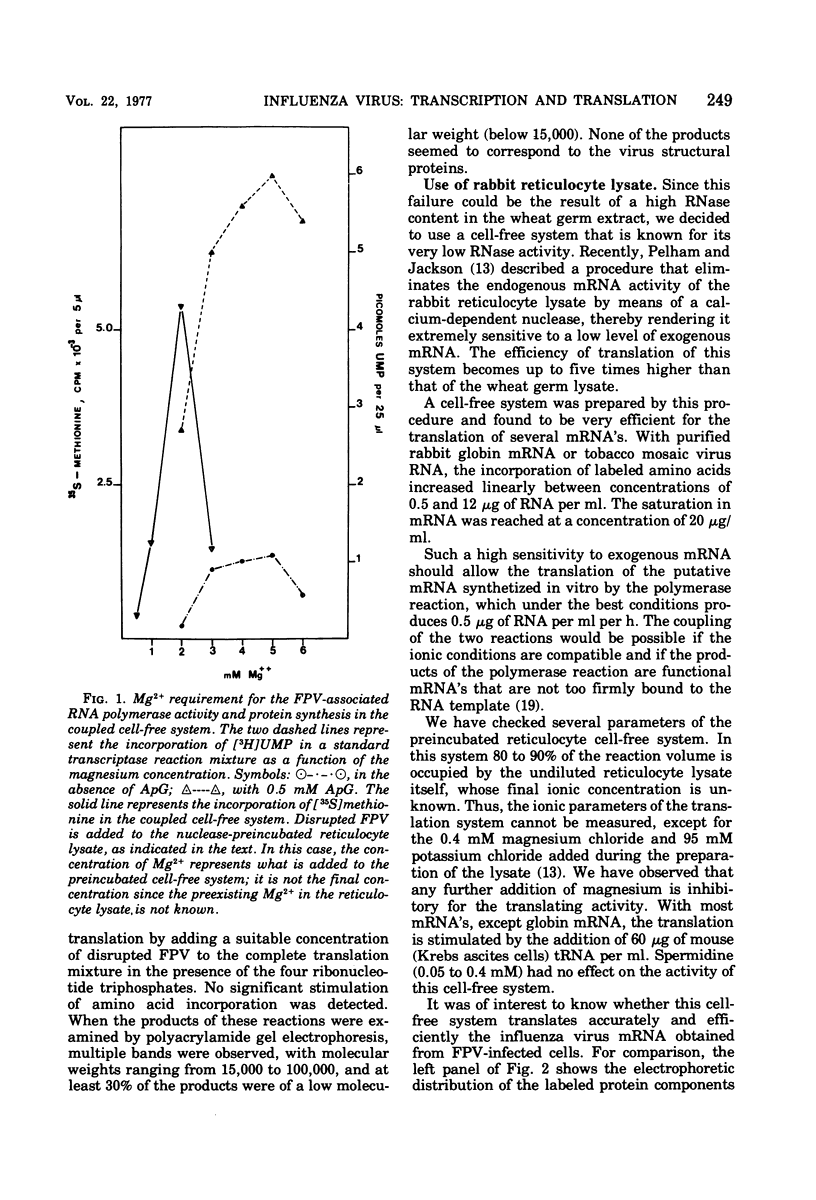
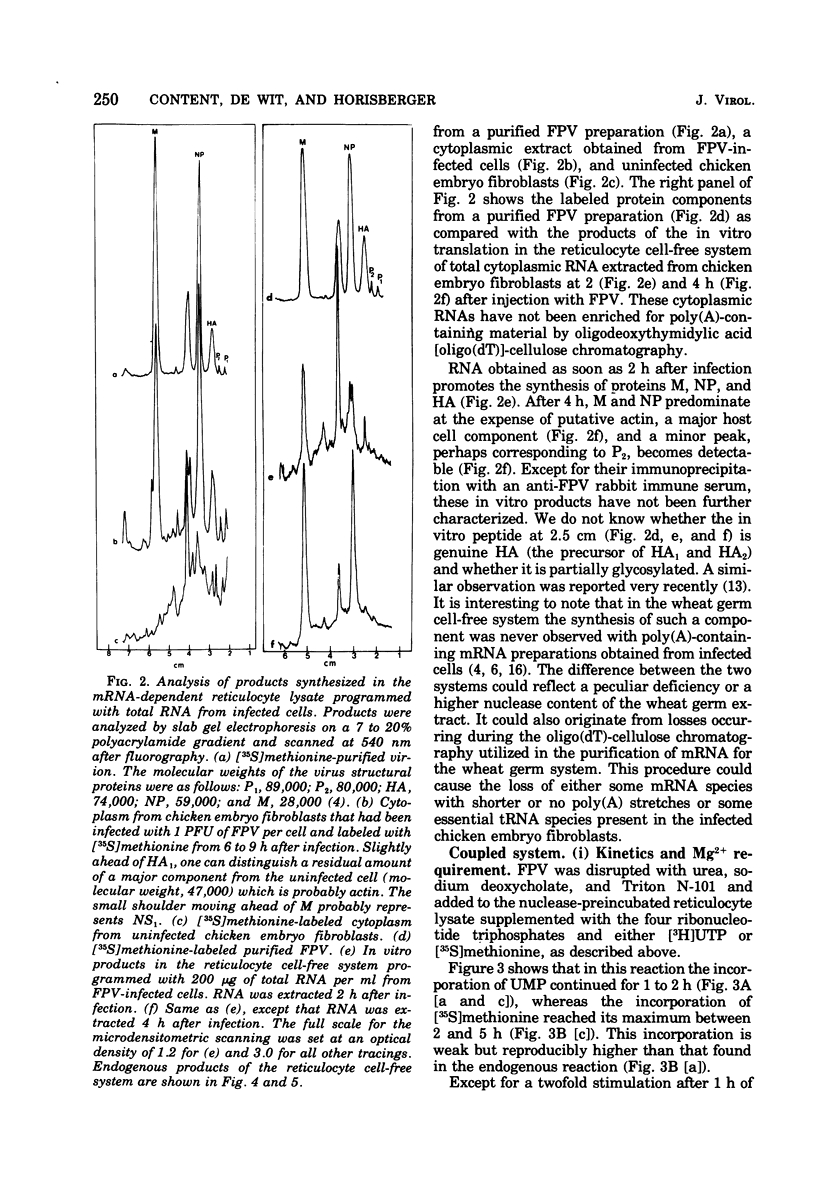
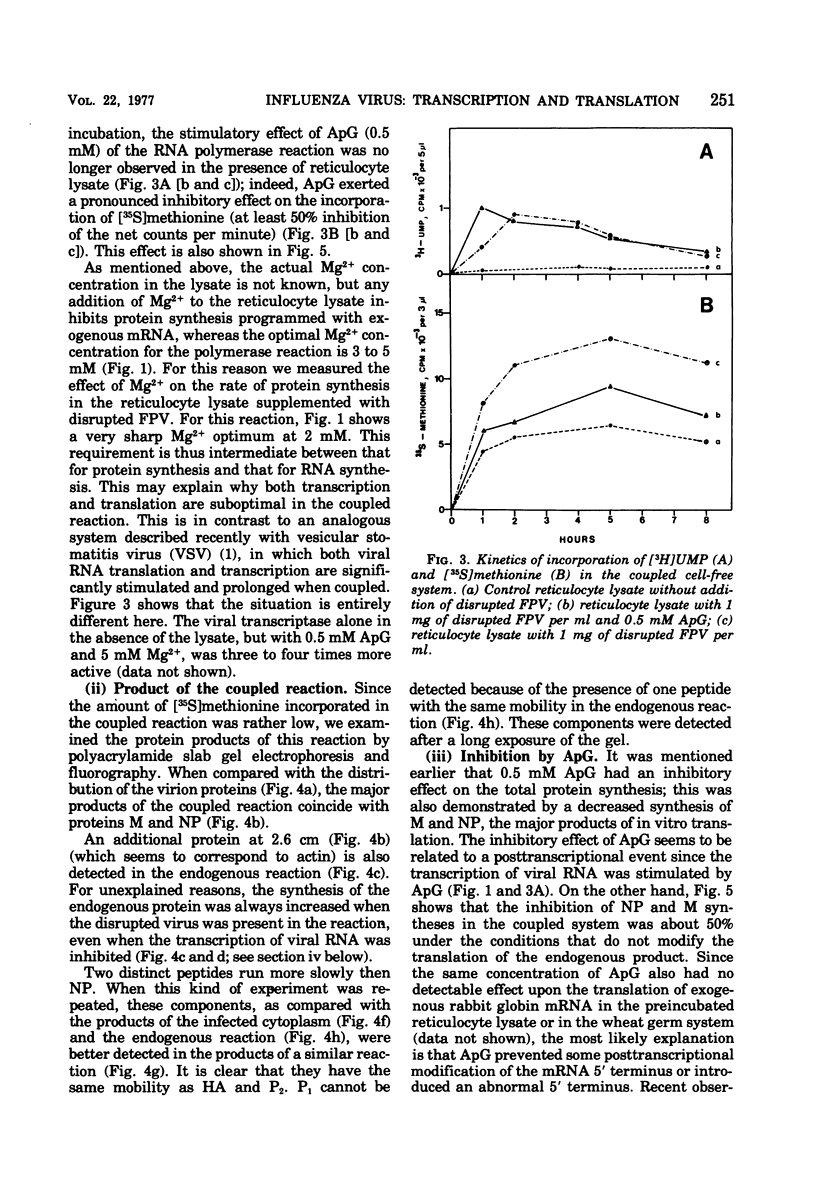
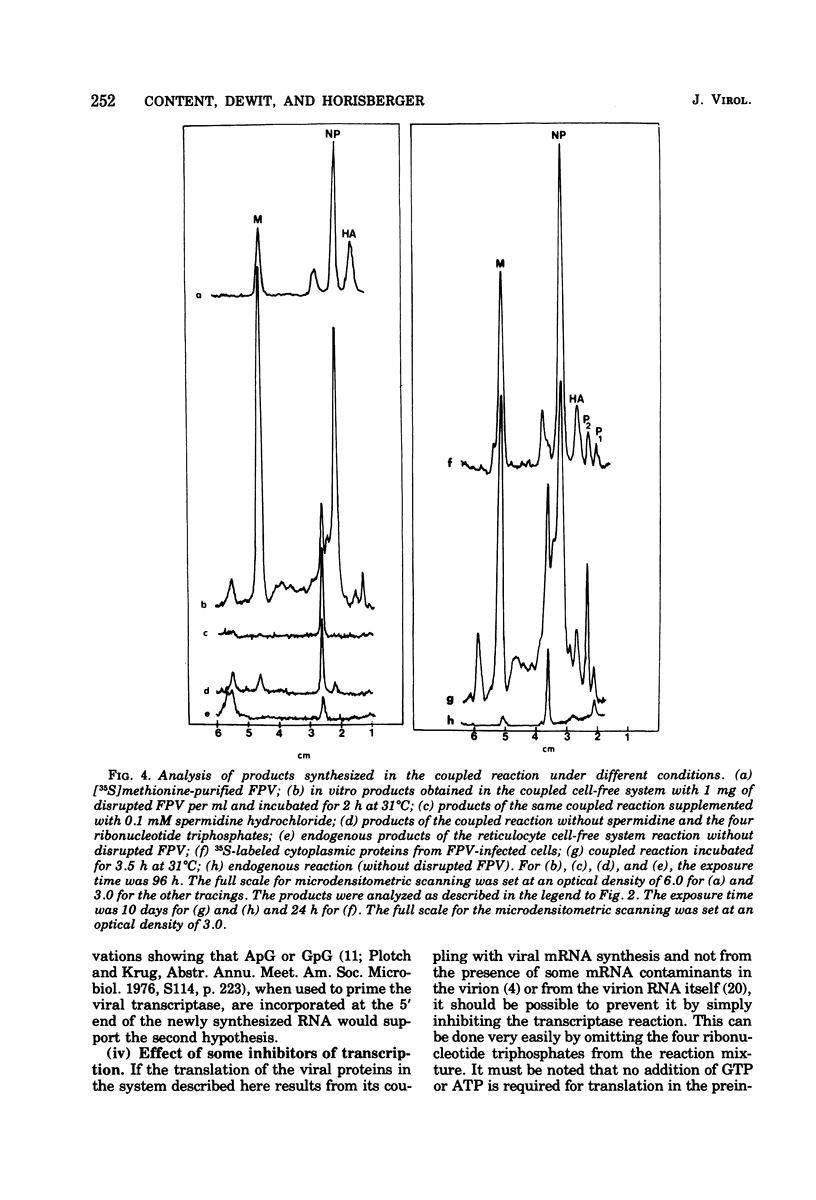
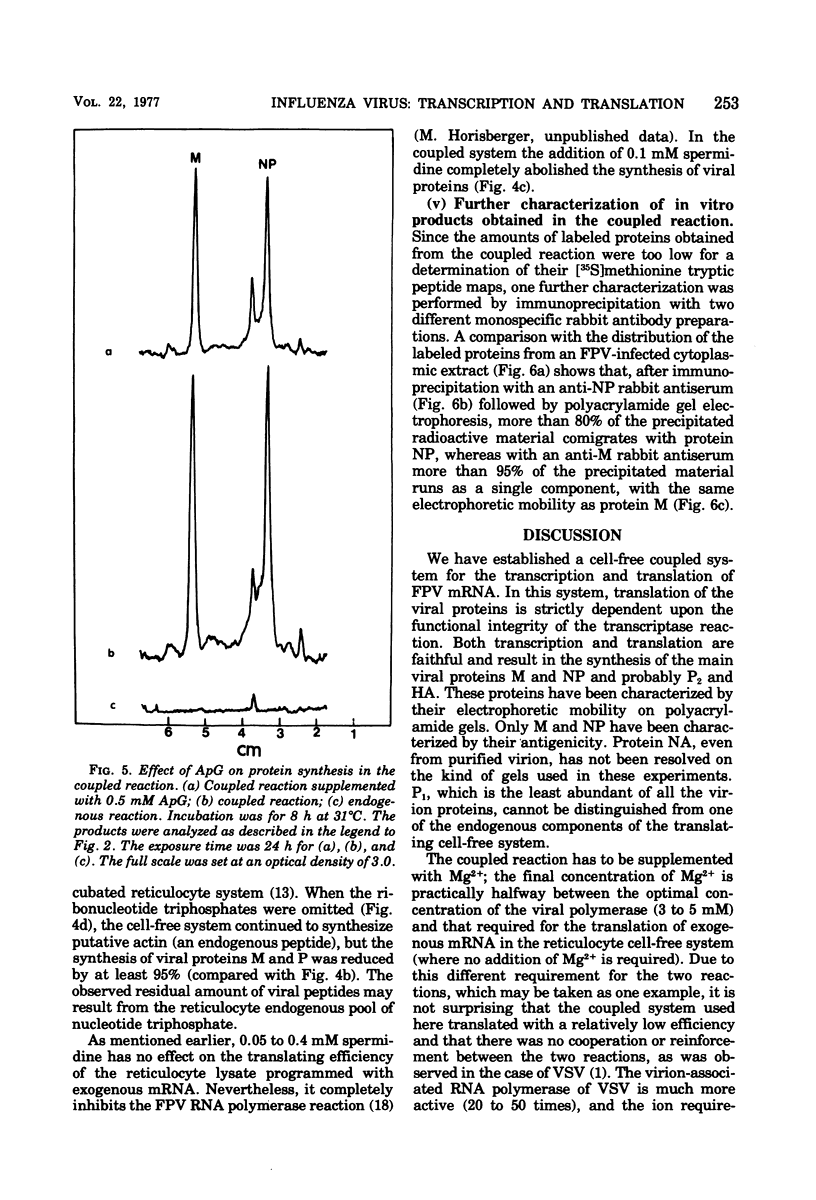
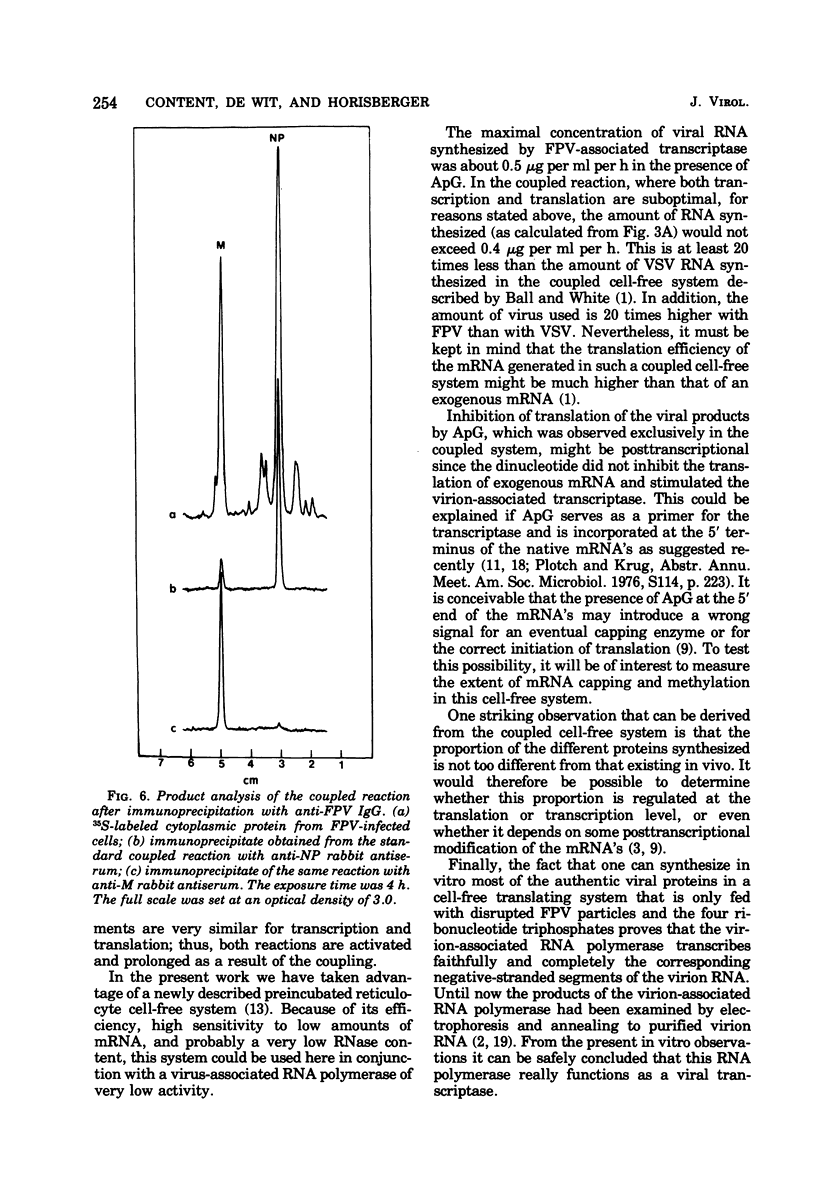
A cell-free coupled system for the transcription and translation of fowl plague virus RNA is described. The system utilizes a new nuclease-preincubated rabbit reticulocyte lysate that has a high sensitivity to exogenous mRNA and a very low level of nuclease activity. Translation of the viral proteins in the coupled system is strictly dependent upon the viral transcriptase activity. In the coupled system the optimal concentration of magnesium is intermediate between the optimum for transcription and that for translation. Translation of the viral proteins seems faithful. The products represent the major viral peptides M and NP and two peptides with the same electrophoretic mobility as HA and P2. Viron NA is not resolved in the kind of polyacrylamide gels described. Proteins M and NP were immunoprecipitable with monospecific antisera. It is concluded that the virion-associated RNA polymerase transcribes the negative-stranded segments of the viral genome coding for these major structural proteins into fully functional mRNA's.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ball L. A., White C. N. Order of transcription of genes of vesicular stomatitis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):442–446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. H., Obijeski J. F., Simpson R. W. Transcription of the influenza ribonucleic acid genome by a virion polymerase. II. Nature of the in vitro polymerase product. J Virol. 1971 Jul;8(1):74–80. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.1.74-80.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breindl M., Holland J. J. Studies on the in vitro transcription and translation of vesicular stomatitis virus mRNA. Virology. 1976 Aug;73(1):106–118. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Content J. Cell-free translation of influenza virus mRNA. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):604–618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.604-618.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etkind P. R., Krug R. M. Influenza viral messenger RNA. Virology. 1974 Nov;62(1):38–45. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90301-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etkind P. R., Krug R. M. Purification of influenza viral complementary RNA: its genetic content and activity in wheat germ cell-free extracts. J Virol. 1975 Dec;16(6):1464–1475. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.6.1464-1475.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horisberger M. The in vitro stimulation of the influenza transcriptase by ribosomes. FEBS Lett. 1976 Mar 15;63(1):134–136. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80210-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Housman D., Jacobs-Lorena M., Rajbhandary U. L., Lodish H. F. Initiation of haemoglobin synthesis by methionyl-tRNA. Nature. 1970 Aug 29;227(5261):913–918. doi: 10.1038/227913a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krug R. M., Morgan M. A., Shatkin A. J. Influenza viral mRNA contains internal N6-methyladenosine and 5'-terminal 7-methylguanosine in cap structures. J Virol. 1976 Oct;20(1):45–53. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.1.45-53.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D., Kitron N. Influenza virion RNA-dependent RNA polymerase: stimulation by guanosine and related compounds. J Virol. 1975 Apr;15(4):686–695. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.4.686-695.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison T. G. Site of synthesis of membrane and nonmembrane proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 10;250(17):6955–6962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pons M. W. The inhibition of influenza virus RNA synthesis by actinomycin D and cycloheximide. Virology. 1973 Jan;51(1):120–128. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90372-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richey M. B., Palese P. In vitro translation of influenza virus messenger RNAs. Virology. 1976 Jul 15;72(2):410–420. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90170-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. E., Paterson B. M. Efficient translation of tobacco mosaic virus RNA and rabbit globin 9S RNA in a cell-free system from commercial wheat germ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochovansky O. M. RNA synthesis by ribonucleoprotein-polymerase complexes isolated from influenza virus. Virology. 1976 Sep;73(2):327–338. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90394-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tekamp P., Penhoet E. E. Message activity of influenza viral RNA. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):812–816. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.812-816.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber L. A., Feman E. R., Baglioni C. A cell free system from HeLa cells active in initiation of protein synthesis. Biochemistry. 1975 Dec 2;14(24):5315–5321. doi: 10.1021/bi00695a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


