Abstract
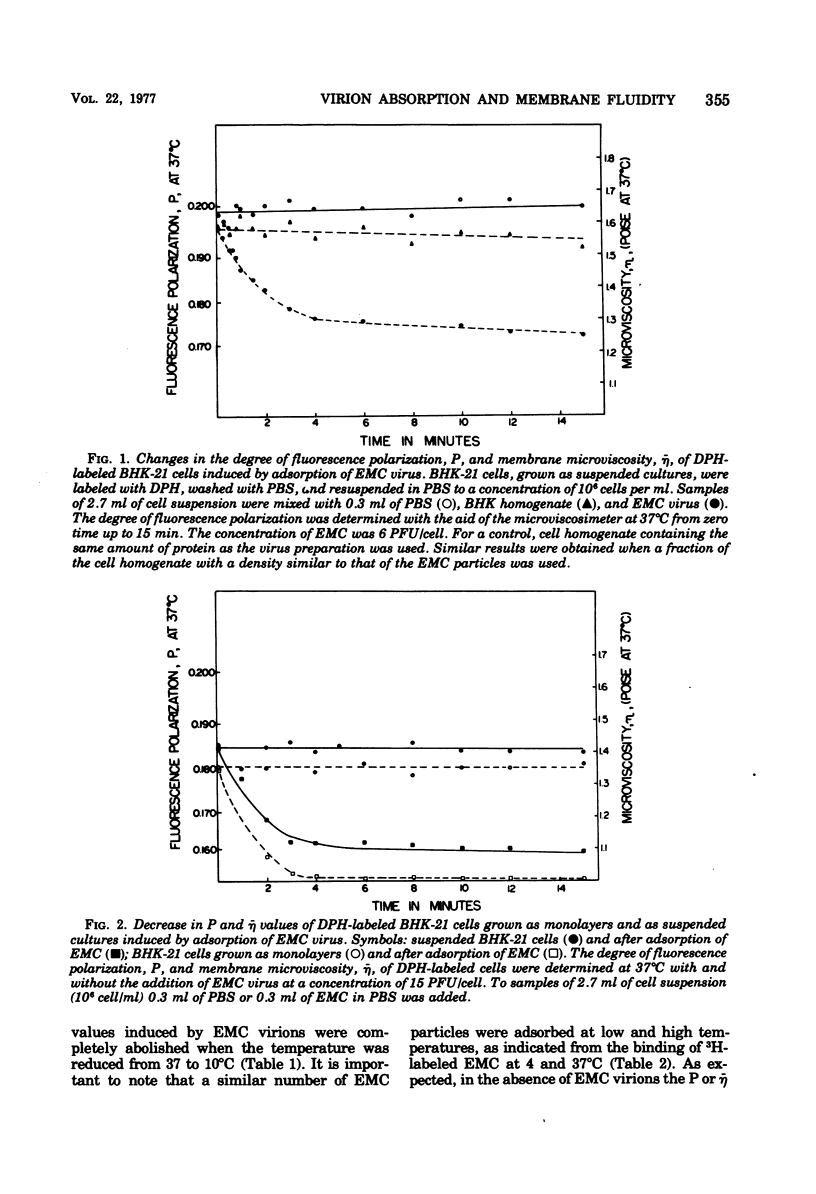
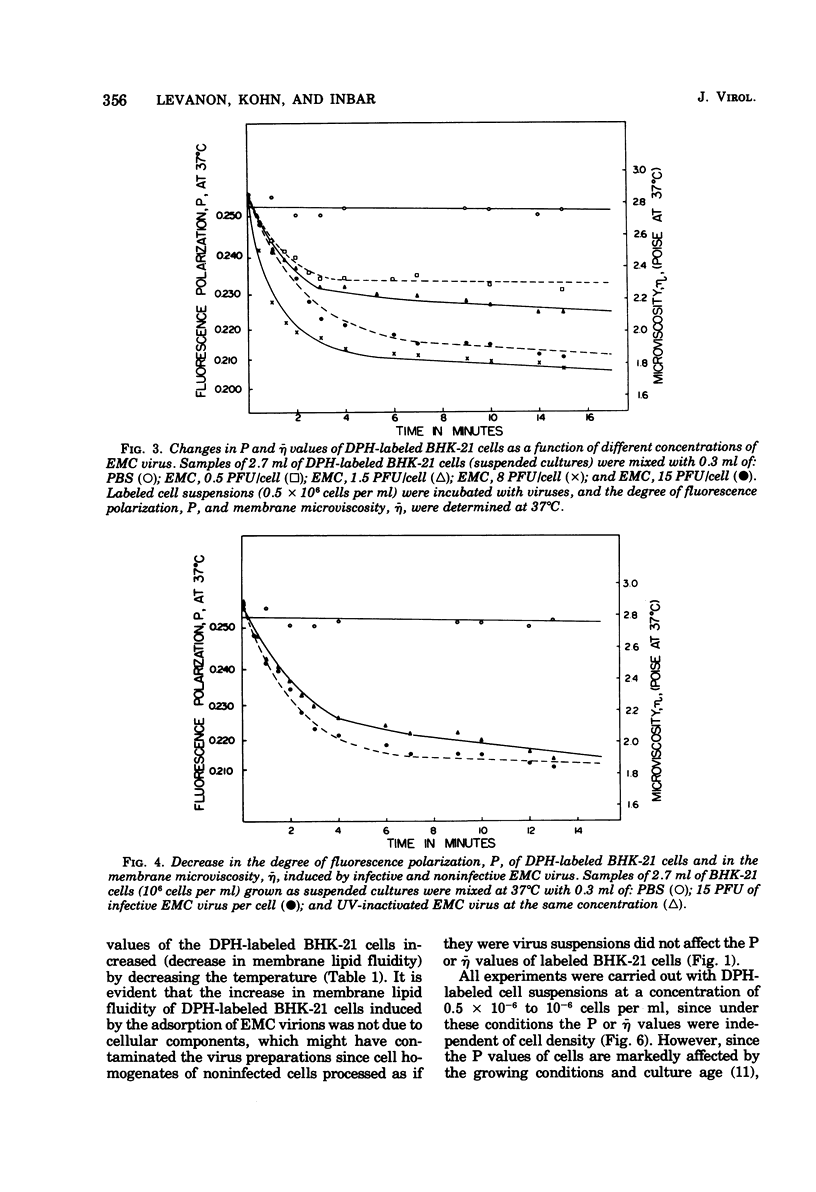
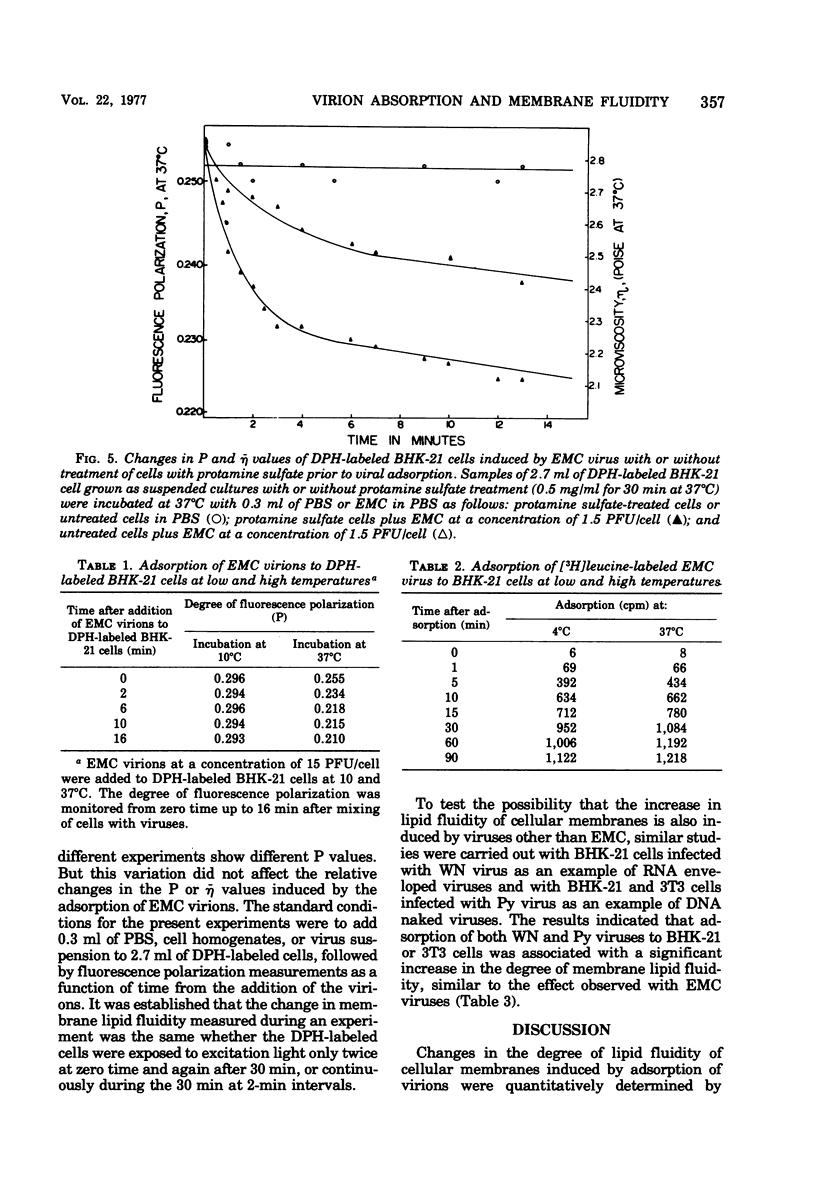
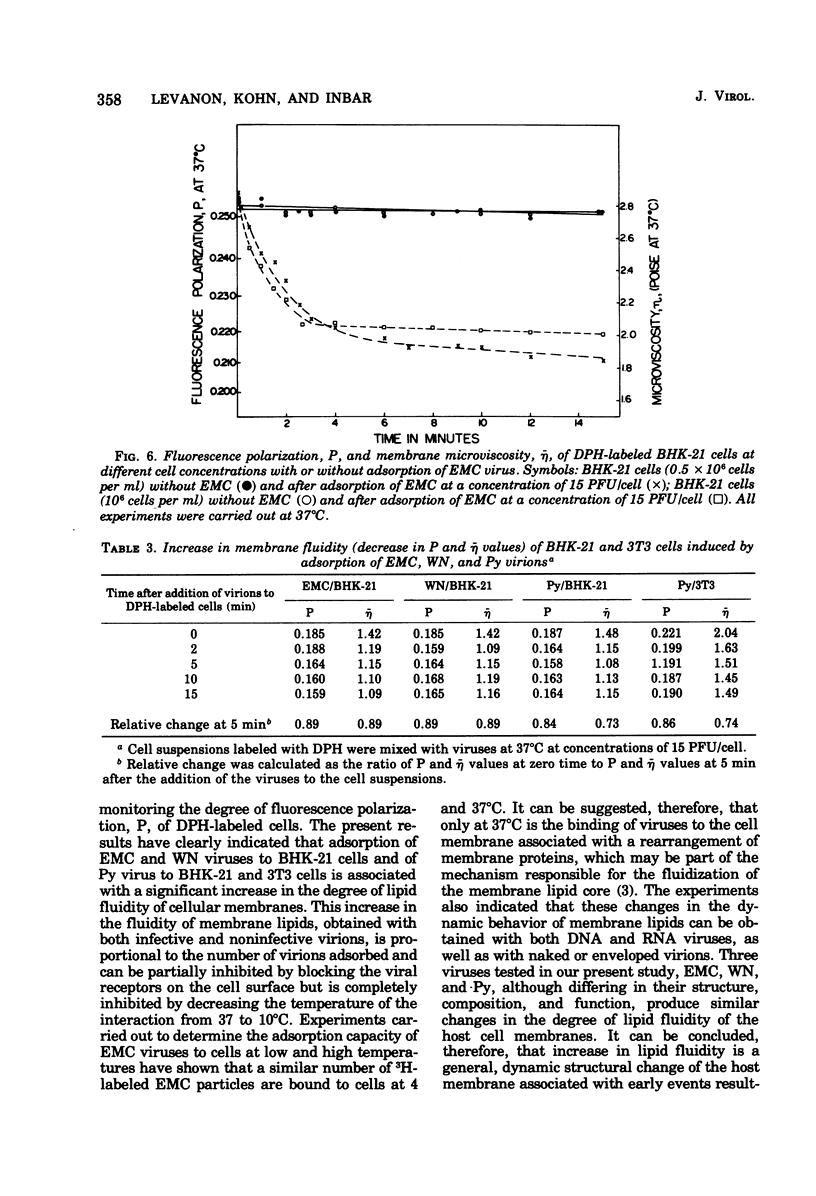
Changes in the dynamic behavior of membrane lipids of mammalian cells induced by adsorption of animal viruses were quantitatively monitored by fluorescence polarization analysis with the aid of the fluorescent probe 1,6-diphenyl 1,3,5-hexatriene embedded in the surface membrane lipid core of intact cells. Adsorption of encephalomyocarditis, West Nile, and polyoma viruses to hamster (baby hamster kidney) and mouse (3T3) cells is accompanied by a rapid and significant increase in the degree of fluidity of membrane lipids of the infected cells. These changes in membrane fluidity, which are virus dose dependent, are inhibited by low temperature and by treatment of the cells before-hand with compounds known to block viral receptors on the cell surface. It is suggested that increase in membrane lipid fluidity, induced by the adsorption of virions, is an early event in the process of cell-virus interactions.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADA G. L., ABBOT A., ANDERSON S. G., COLLINS F. D. Particle counts and some chemical properties of Murray Valley encephalitis virus. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Sep;29:165–170. doi: 10.1099/00221287-29-1-165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett R. E., Scott R. E., Furcht L. T., Kersey J. H. Evidence that mitogenic lectins induce changes in lymphocyte membrane fluidity. Nature. 1974 May 31;249(456):465–466. doi: 10.1038/249465a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bächi T., Aguet M., Howe C. Fusion of erythrocytes by Sendai virus studied by immuno-freeze-etching. J Virol. 1973 Jun;11(6):1004–1012. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.6.1004-1012.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLTER J. S., DAVIES M. A., CAMPBELL J. B. STUDIES OF THREE VARIANTS OF MENGO ENCEPHALOMYELITIS VIRUS. II. INHIBITION OF INTERACTION WITH L CELLS BY AN AGAR INHIBITOR AND BY PROTAMINE. Virology. 1964 Dec;24:578–585. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90210-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edidin M. Rotational and translational diffusion in membranes. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1974;3(0):179–201. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.03.060174.001143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs P., Giberman E. Enhancement of potassium influx, in baby hamster kidney cells and chicken erythrocytes, during adsorption of parainfluenza 1 (Sendai) virus. FEBS Lett. 1973 Apr 1;31(1):127–130. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80089-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs P., Parola A., Robbins P. W., Blout E. R. Fluorescence polarization and viscosities of membrane lipids of 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3351–3354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitler C. Plasticity of biological membranes. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1972;1:51–92. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.01.060172.000411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inbar M., Ben-Bassat H. Fluidity difference in the surface membrane lipid core of human lymphoblastoid and lymphoma cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1976 Sep 15;18(3):293–297. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910180305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inbar M. Fluidity of membrane lipids: a single cell analysis of mouse normal lymphocytes and malignant lymphoma cells. FEBS Lett. 1976 Aug 15;67(2):180–185. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80361-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inbar M., Shinitzky M. Cholesterol as a bioregulator in the development and inhibition of leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4229–4231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inbar M., Shinitzky M., Sachs L. Rotational relaxation time of concanavalin A bound to the surface membrane of normal and malignant transformed cells. J Mol Biol. 1973 Dec 5;81(2):245–253. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90192-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr I. M., Martin E. M. Simple method for the isolation of encephalomyocarditis virus ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1972 Mar;9(3):559–561. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.3.559-561.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda T., Asano A., Oki K., Okada Y., Onishi S. A spin-label study on fusion of red blood cells induced by hemagglutinating virus of Japan. Biochemistry. 1975 Aug 26;14(17):3736–3741. doi: 10.1021/bi00688a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLIMANS W. F., DAVIS E. V., GLOVER F. L., RAKE G. W. The submerged culture of mammalian cells; the spinner culture. J Immunol. 1957 Nov;79(5):428–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore N. F., Barenholz Y., Wagner R. R. Microviscosity of togavirus membranes studied by fluorescence depolarization: influence of envelope proteins and the host cell. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):126–135. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.126-135.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHARP D. G. QUANTITATIVE USE OF THE ELECTRON MICROSCOPE IN VIRUS RESEARCH. METHODS AND RECENT RESULTS OF PARTICLE COUNTING. Lab Invest. 1965 Jun;14:831–863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinitzky M., Inbar M. Difference in microviscosity induced by different cholesterol levels in the surface membrane lipid layer of normal lymphocytes and malignant lymphoma cells. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jan 5;85(4):603–615. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90318-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinitzky M., Inbar M. Microviscosity parameters and protein mobility in biological membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 16;433(1):133–149. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90183-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J., Nicolson G. L. The fluid mosaic model of the structure of cell membranes. Science. 1972 Feb 18;175(4023):720–731. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4023.720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINOCOUR E. Purification of polyoma virus. Virology. 1963 Feb;19:158–168. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


