Abstract
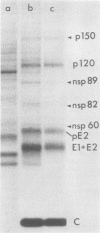
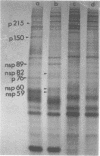
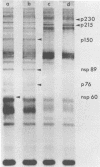
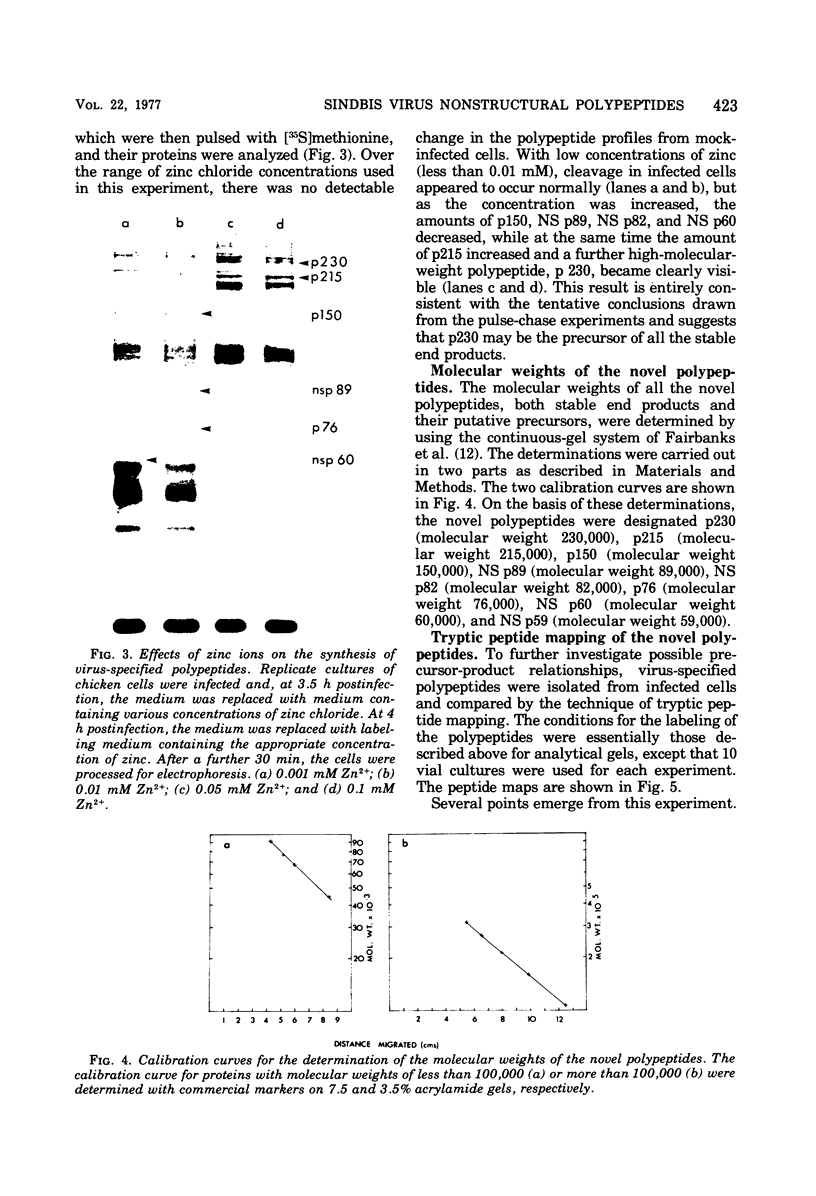
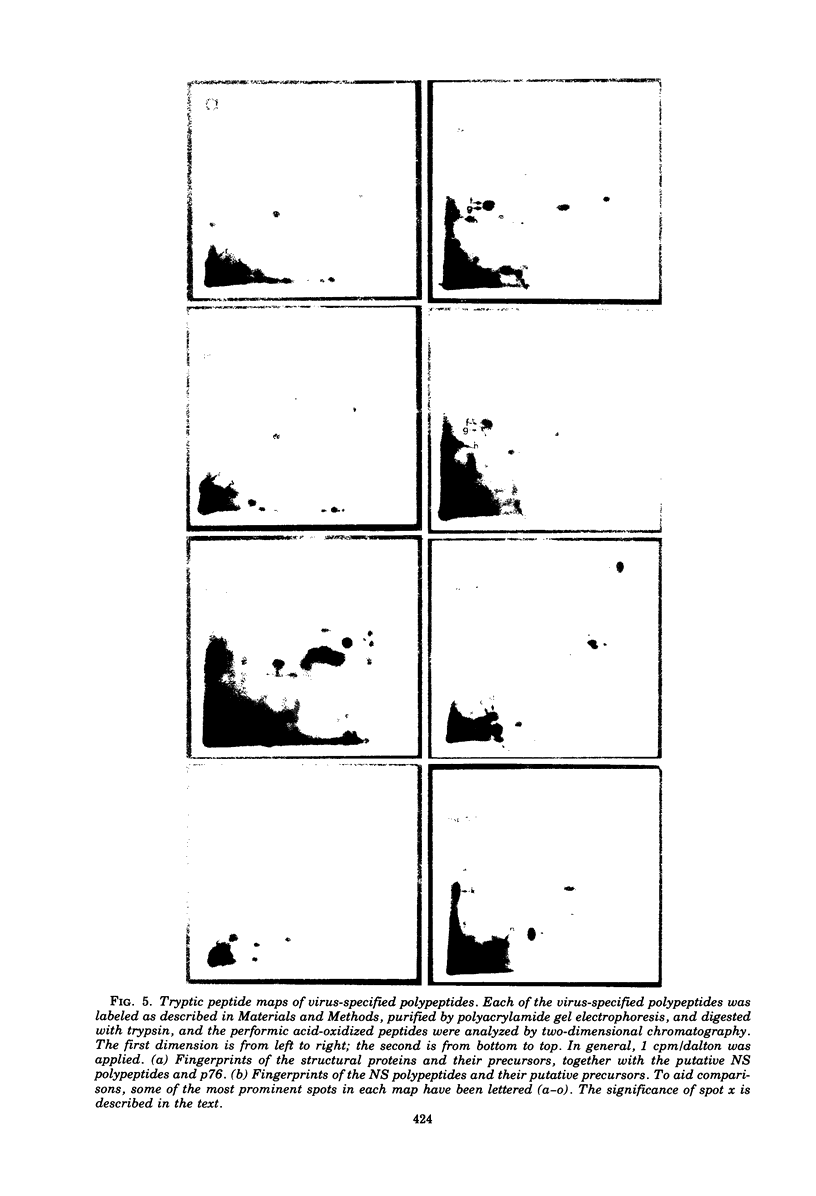
The identification of eight previously undescribed polypeptides in chicken embryo cells infected with Sindbis virus is reported. Seven of these polypeptides were distinguishable from the virus structural polypeptides and their precursors by their molecular weights and tryptic peptide maps. The eighth was closely related to pE2 (Schlesinger and Schlesinger, 1973), a precursor to one of the virus particle glycoproteins. Pulse-chase experiments and the use of an inhibitor of proteolytic cleavage allowed a division of the seven nonstructural (NS) polypeptides into three stable end products (NS p89, NS p82, and NS p60) and four precursors (p230, p215, p150, and p76). The labeling kinetics after synchronous initiation of translation indicated that synthesis of the NS polypeptides started at a single site and showed that the order of the genes coding for the NS polypeptides was (5' leads to 3') NS p60, NS p89, and NS p82. Short-pulse experiments under conditions of both synchronized and nonsynchronized translation suggested that cleavage of the primary translation product of the NS genes occurred only after its synthesis was completed and that the first cleavage removed the C-terminal polypeptide. From these and other experiments, we propose a detailed scheme for the synthesis and processing of Sindbis virus NS polypeptides.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkins G. J., Samuels J., Kennedy S. I. Isolation and preliminary characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of Sindbis virus strain AR339. J Gen Virol. 1974 Dec;25(3):371–380. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-25-3-371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. I. Presence of proteolytically processed and unprocessed nascent immunoglobulin light chains on membrane-bound ribosomes of murine myeloma. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):835–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth B. E., Korant B. D. Characterization of the large picornaviral polypeptides produced in the presence of zinc ion. J Virol. 1974 Aug;14(2):282–291. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.2.282-291.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cancedda R., Swanson R., Schlesinger M. J. Effects of different RNAs and components of the cell-free system on in vitro synthesis of Sindbis viral proteins. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):652–663. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.652-663.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cancedda R., Villa-Komaroff L., Lodish H. F., Schlesinger M. Initiation sites for translation of sindbis virus 42S and 26S messenger RNAs. Cell. 1975 Oct;6(2):215–222. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. C., Brzeski H., Kennedy S. I. RNA polymerase components in Semliki Forest virus-infected cells: synthesis from large precursors. J Gen Virol. 1976 Sep;32(3):413–430. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-32-3-413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. C., Kennedy S. I. In vitro synthesis of structural proteins of Semliki Forest virus directed by isolated 26 S RNA from infected cells. FEBS Lett. 1974 Jun 15;42(3):327–330. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80757-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. C., Kennedy S. I. Initiation of synthesis of the structural proteins of Semliki Forest virus. J Mol Biol. 1975 Oct 5;97(4):401–411. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80050-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. C. Sequential translation of capsid and membrane protein genes of alphaviruses. Nature. 1975 Apr 3;254(5499):454–455. doi: 10.1038/254454a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewley J. P., Kennedy S. I. Purification and polypeptide composition of Semliki Forest virus RNA polymerase. J Gen Virol. 1976 Sep;32(3):395–411. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-32-3-395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M., Levin J. G., Grimley P. M., Berezesky I. K. Membrane-associated replication complex in arbovirus infection. J Virol. 1972 Sep;10(3):504–515. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.3.504-515.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M., Levy H. B., Carter W. B. Replication of semliki forest virus: three forms of viral RNA produced during infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):440–446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garoff H., Simons K., Renkonen O. Isolation and characterization of the membrane proteins of Semliki Forest virus. Virology. 1974 Oct;61(2):493–504. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90285-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glanville N., Ranki M., Morser J., Käriäinen L., Smith A. E. Initiation of translation directed by 42S and 26S RNAs from Semliki Forest virus in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3059–3063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaluza G. Early synthesis of Semliki Forest virus-specific proteins in infected chicken cells. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):1–12. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.1-12.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaluza G., Kraus A. A., Rott R. Inhibition of cellular protein synthesis by simultaneous pretreatment of host cells with fowl plague virus and actinomycin D: a method for studying early protein synthesis of several RNA viruses. J Virol. 1975 Jan;17(1):1–9. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.1.1-9.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy S. I. Sequence relationships between the genome and the intracellular RNA species of standard and defective-interfering Semliki Forest virus. J Mol Biol. 1976 Dec;108(2):491–511. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80132-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmi B. E., Glanville N., Keränen S., Läriäinen L. Tryptic peptide analysis on nonstructural and structural precursor proteins from Semliki Forest virus mutant-infected cells. J Virol. 1975 Dec;16(6):1615–1629. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.6.1615-1629.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmi B. E., Käriäinen L. Sequential translation of nonstructural proteins in cells infected with a Semliki Forest virus mutant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1936–1940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin B. A., Burke D. C. The replication of Semliki Forest virus. J Gen Virol. 1974 Jul;24(1):45–66. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-1-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin E. M., Sonnabend J. A. Ribonucleic acid polymerase catalyzing synthesis of double-stranded arbovirus ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1967 Feb;1(1):97–109. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.1.97-109.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morser M. J., Burke D. C. Cleavage of virus-specified polypeptides in cells infected with Semliki Forest Virus. J Gen Virol. 1974 Mar;22(3):395–409. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-22-3-395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheele C. M., Pfefferkorn E. R. Inhibition of interjacent ribonucleic acid (26S) synthesis in cells infected by Sindbis virus. J Virol. 1969 Aug;4(2):117–122. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.2.117-122.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger M. J., Schlesinger S., Burge B. W. Identification of a second glycoprotein in Sindbis virus. Virology. 1972 Feb;47(2):539–541. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90298-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger M. J., Schlesinger S. Large-molecular-weight precursors of sindbis virus proteins. J Virol. 1973 Jun;11(6):1013–1016. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.6.1013-1016.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. T., Strauss J. H. Replication of Sindbis virus. I. Relative size and genetic content of 26 s and 49 s RNA. J Mol Biol. 1972 Nov 28;71(3):599–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. T., Strauss J. H. Translation of Sindbis virus 26 S RNA and 49 S RNA in lysates of rabbit reticulocytes. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jun 25;86(2):397–409. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons K., Keränen S., Käriänen L. Identification of a precursor for one of the Semliki forest virus membrane proteins. FEBS Lett. 1973 Jan 15;29(2):87–91. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80532-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreevalsan T., Yin F. H. Sindbis virus-induced viral ribonucleic acid polymerase. J Virol. 1969 Jun;3(6):599–604. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.6.599-604.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Analysis of bacteriophage T7 early RNAs and proteins on slab gels. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Beato M., Hackemack B. A. Translation of 26 S virus-specific RNA from Semliki Forest virus-infected cells in vitro. Virology. 1974 Sep;61(1):120–128. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90247-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Wengler G. Localization of the 26-S RNA sequence on the viral genome type 42-S RNA isolated from SFV-infected cells. Virology. 1976 Aug;73(1):190–199. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]