Abstract
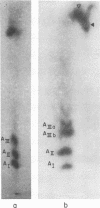
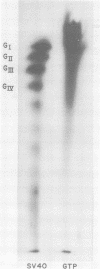
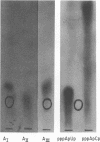
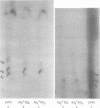
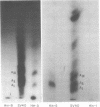
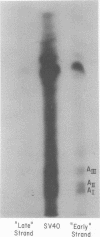
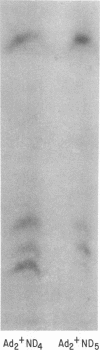
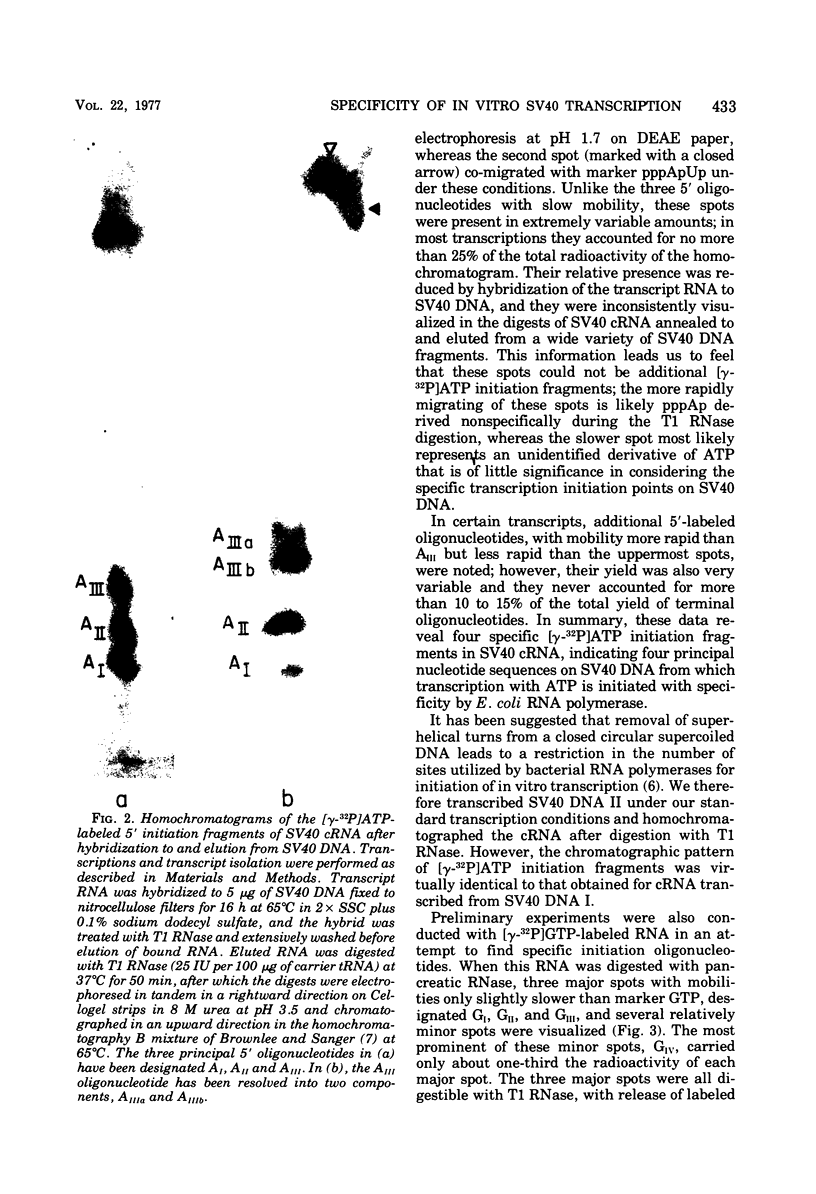
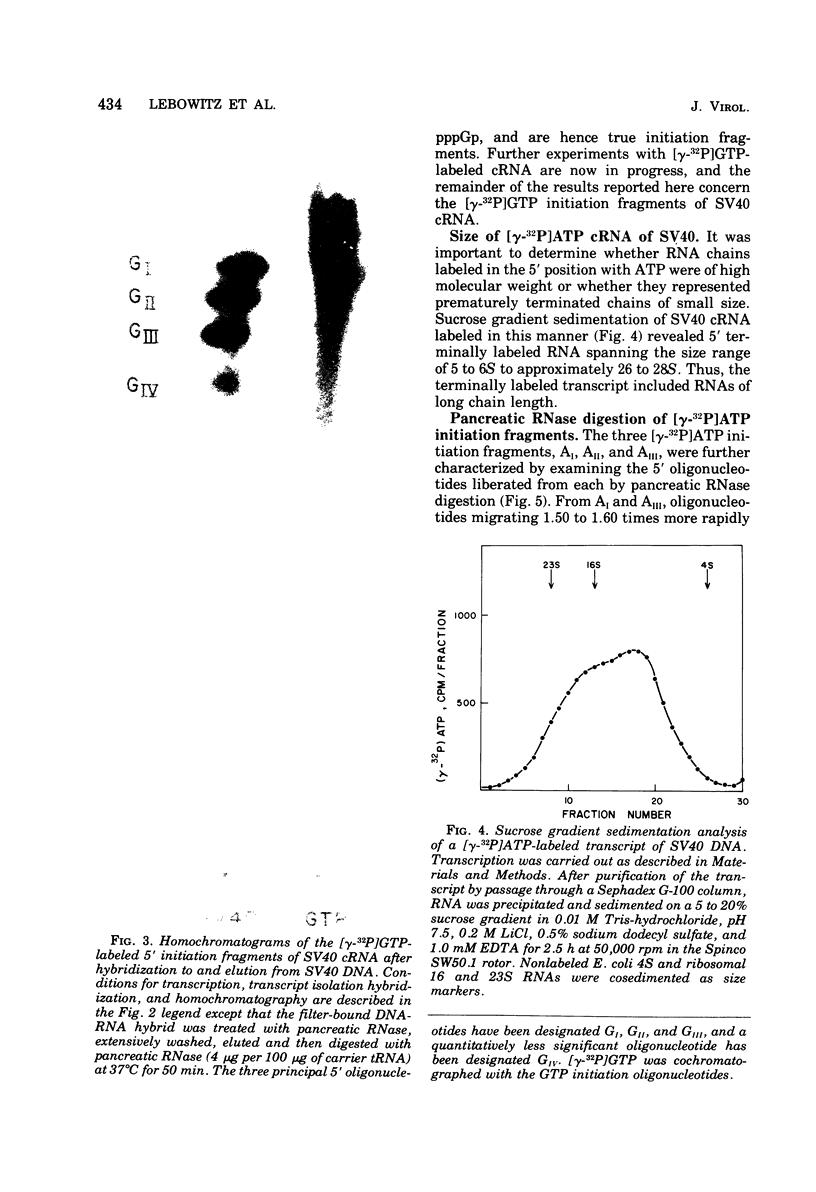
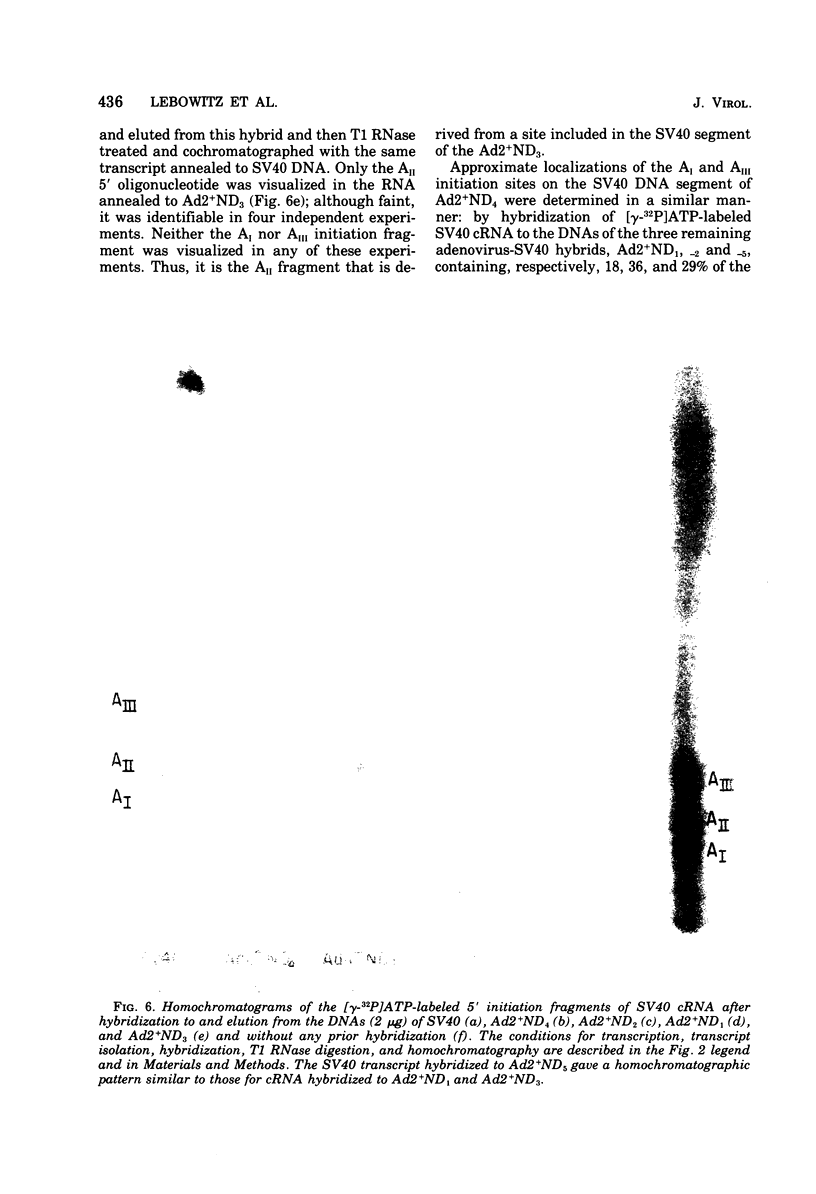
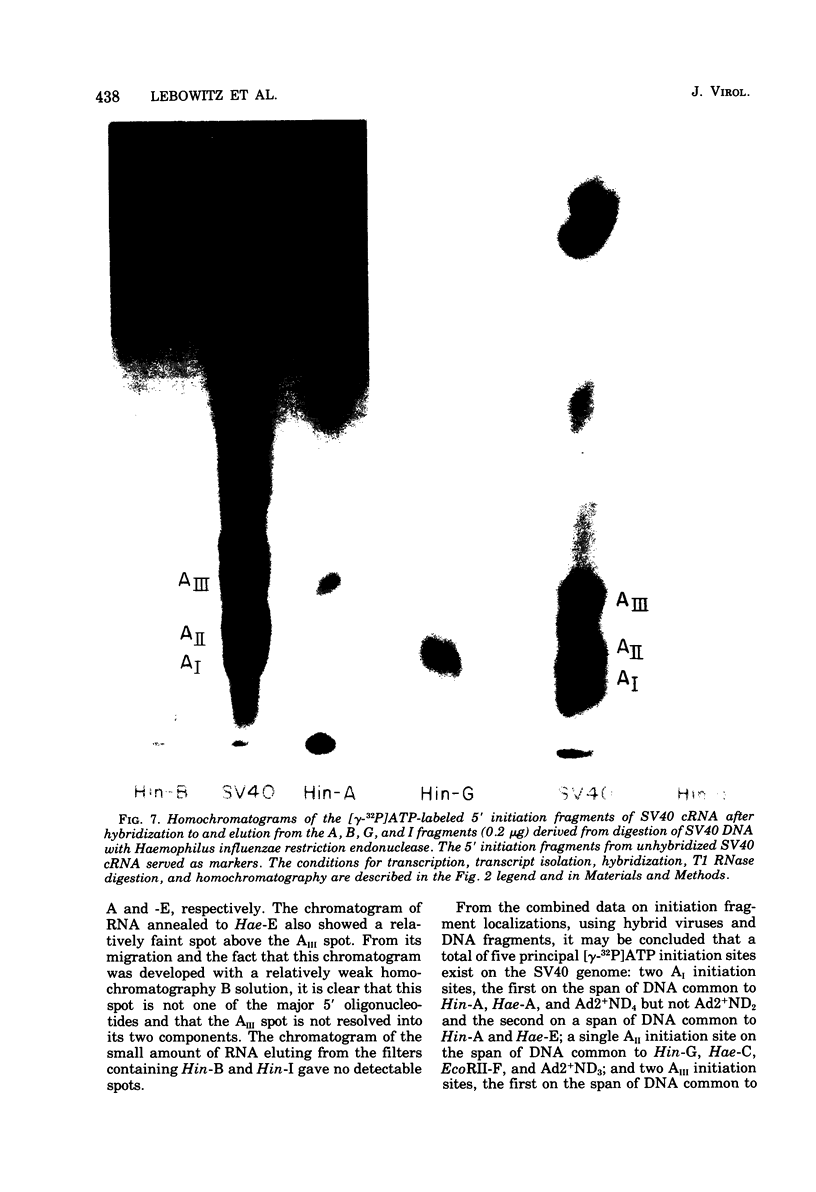
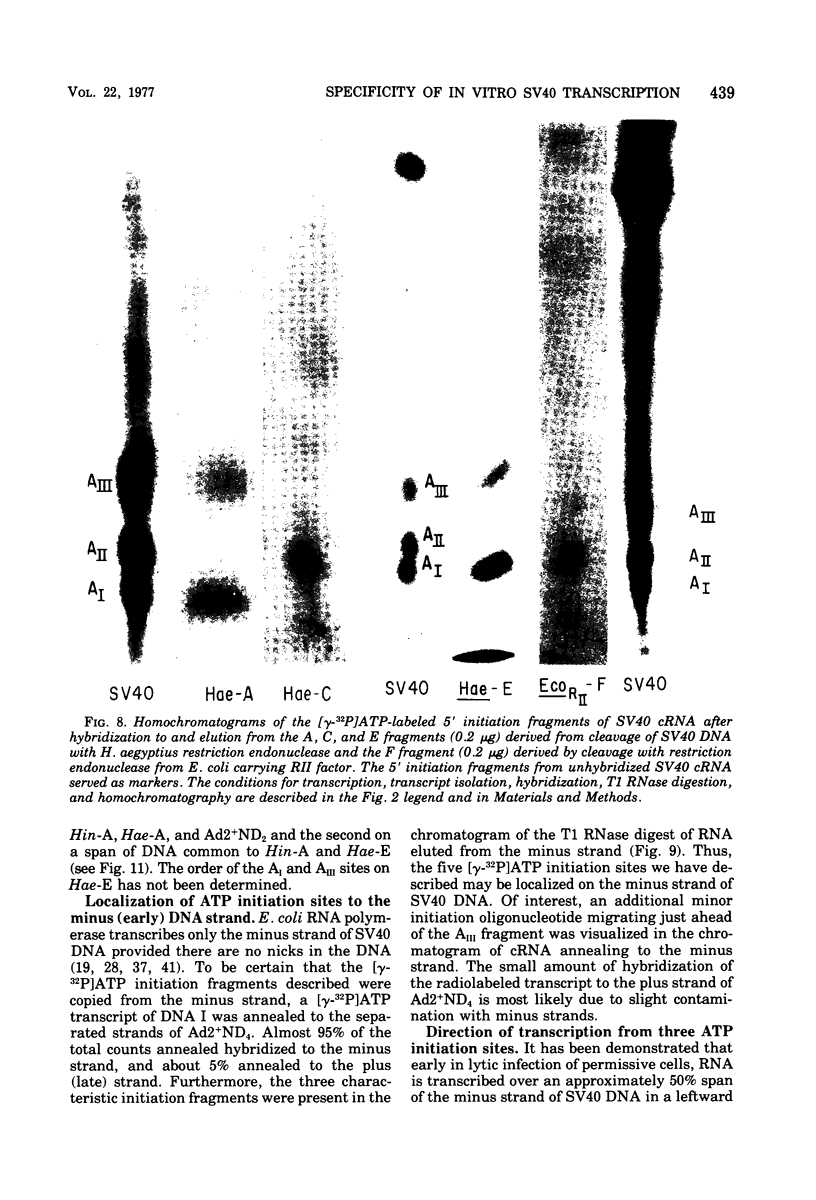
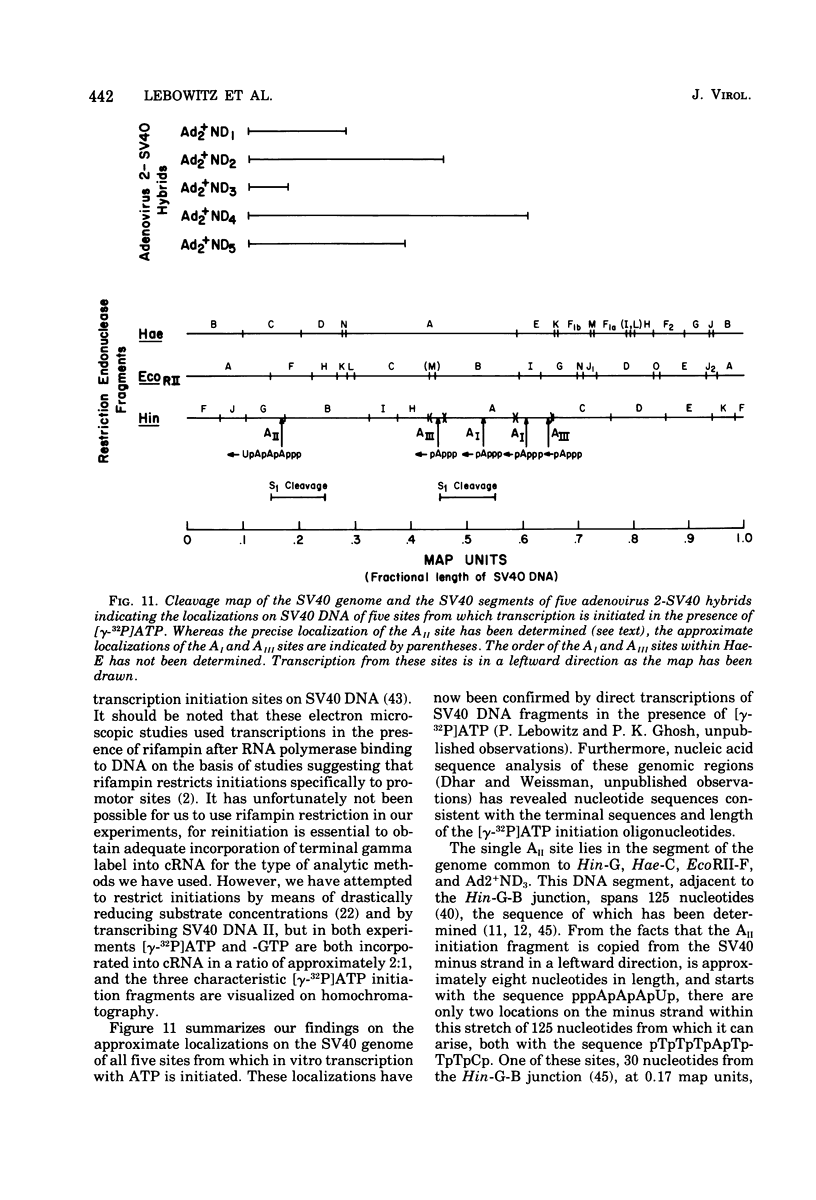
Simian virus 40 (SV40) DNA I was transcribed with Escherichia coli RNA polymerase in the presence of gamma-32P-labeled ribonucleoside triphosphates in order to investigate the specificity of initiation of in vitro transcription. ATP and GTP served as predominant initiating nucleotides, the former being incorporated about twice as much as the latter. Cleavage of [gamma-32P]ATP-labeled SV40 complementary RNA (cRNA) with T1 RNase followed by homochromatographic analysis of the resultant 5' initiation fragments revealed the presence of four specific initiation fragments 6 to 9 nucleotides in length, designated AI, AII, AIIIa, and AIIIb. By means of hybridization of [gamma-32P]ATP-labeled SV40 cRNA to DNA from specific adenovirus 2-SV40 hybrids and specific restriction endonuclease fragments of SV40 DNA before chromatographic analysis, it was possible to identify and determine approximate localizations of five [gamma-32P]ATP initiation sites on the SV40 genome: one in Hin-G close to the Hin-G-B junction, giving rise to the AII fragment, two in the overalpping fragment Hin-A-Hae-A,giving rise to AI and AIII fragments, and two in the fragment Hin-A-Hae-E, also giving rise to AI and AIII fragments. All five sites either fall within or lie near regions of the genome that are cleaved by S1 nuclease and subject to partial alkaline denaturation. These five sites lie on the minus strand of SV40 DNA and initiate RNAs that are copied in a leftward direction. Cleavage of [gamma-32P]GTP-labeled cRNA with pancreatic RNase liberated three major 5' initiation fragments of short length, GI, GII, and GIII, suggesting the presence of three principal GTP initiation sites.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allet B., Roberts R. J., Gesteland R. F., Solem R. Class of promotor sites for Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Nature. 1974 May 17;249(454):217–221. doi: 10.1038/249217a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bautz E. K., Bautz F. A. Initiation of RNA synthesis: the function of sigma in the binding of RNA polymerase to promoter sites. Nature. 1970 Jun 27;226(5252):1219–1222. doi: 10.1038/2261219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beard P., Morrow J. F., Berg P. Cleavage of circular, superhelical simian virus 40 DNA to a linear duplex by S1 nuclease. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1303–1313. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1303-1313.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Dahlberg J. E. RNA synthesis startpoints in bacteriophage lambda: are the promoter and operator transcribed? Nat New Biol. 1972 Jun 21;237(77):227–232. doi: 10.1038/newbio237227a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan M., Ozanne B., Sugden B., Sharp P. A., Sambrook J. Viral DNA in transformed cells. III. The amounts of different regions of the SV40 genome present in a line of transformed mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4183–4187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan P., Wang J. C., Echols H. Effect of circularity and superhelicity on transcription from bacteriophagelambda DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Nov;70(11):3077–3081. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.11.3077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee G. G., Sanger F. Chromatography of 32P-labelled oligonucleotides on thin layers of DEAE-cellulose. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Dec;11(2):395–399. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00786.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford L. V., Crawford E. M., Richardson J. P., Slayter H. S. The binding of RNA polymerase to polyoma and papilloma DNA. J Mol Biol. 1965 Dec;14(2):593–597. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80209-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danna K. J., Sack G. H., Jr, Nathans D. Studies of simian virus 40 DNA. VII. A cleavage map of the SV40 genome. J Mol Biol. 1973 Aug 5;78(2):363–376. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90122-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delius H., Westphal H., Axelrod N. Length measurements of RNA synthesized in vitro by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1973 Mar 15;74(4):677–687. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90056-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhar R., Subramanian K., Zain B. S., Pan J., Weissman S. M. Nucleotide sequence about the 3' terminus of SV40 DNA transcripts and the region where DNA synthesis is initiated. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):153–160. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhar R., Zain S., Weissman S. M., Pan J., Subramanian K. Nucleotide sequences of RNA transcribed in infected cells and by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase from a segment of simian virus 40 DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):371–375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie D., Spiegelman S. A quantitative assay for DNA-RNA hybrids with DNA immobilized on a membrane. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jul;12(3):829–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80331-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry P. H., Schnipper L. E., Samaha R. J., Crumpacker C. S., Lewis A. M., Jr, Levine A. S. Studies of nondefective adenovirus 2-simian virus 40 hybrid viruses. VI. Characterization of the DNA from five nondefective hybrid viruses. J Virol. 1973 May;11(5):665–671. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.5.665-671.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzberg M., Winocour E. Simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid transcription in vitro: binding and transcription patterns with a mammalian ribonucleic acid polymerase. J Virol. 1970 Nov;6(5):667–676. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.5.667-676.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hossenlopp P., Oudet P., Chambon P. Animal DNA-dependent RNA polymerases. Studies on the binding of mammalian RNA polymerases AI and B to Simian virus 40 DNA. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jan 16;41(2):397–411. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03281.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly T. J., Jr, Lewis A. M., Jr Use of nondefective adenovirus-simian virus 40 hybrids for mapping the simian virus 40 genome. J Virol. 1973 Sep;12(3):643–652. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.3.643-652.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., Byrne J. C., Martin M. A. Patterns of Simian Virus 40 DNA transcription after acute infection of permissive and nonpermissive cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1925–1928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., Martin M. A., Lee T. N., Danna K. J., Nathans D. A map of simian virus 40 transcription sites expressed in productively infected cells. J Mol Biol. 1973 Aug 5;78(2):377–389. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90123-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebowitz P., Bloodgood R. Transcription of simian virus 40 DNA by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase: synthesis of a DNA-RNA hybrid and discrete RNAs under restrictive transcription conditions. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 15;94(2):183–201. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90077-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebowitz P., Kelly T. J., Jr, Nathans D., Lee T. N., Lewis A. M., Jr A colinear map relating the simian virus 40 (SV40) DNA segments of six adenovirus-SV40 hybrids to the DNA fragments produced by restriction endonuclease cleavage of SV40 DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):441–445. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebowitz P., Siegel W., Sklar J. Hemophilus aegyptius restriction edonuclease cleavage map of the simian virus 40 genome and its colinear relation with the hemophilus influenzae cleavage map of SV40. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 5;88(1):105–123. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90297-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebowitz P., Weissman S. M., Radding C. M. Nucleotide sequence of a ribonucleic acid transcribed in vitro from lambda phage deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 25;246(16):5120–5139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. N., Nathans D. A transcriptional map of the SV40 genome in transformed cell lines. Virology. 1975 Jan;63(1):263–272. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90390-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis A. M., Jr, Levin M. J., Wiese W. H., Crumpacker C. S., Henry P. H. A nondefective (competent) adenovirus-SV40 hybrid isolated from the AD.2-SV40 hybrid population. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Aug;63(4):1128–1135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.4.1128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis A. M., Jr, Levine A. S., Crumpacker C. S., Levin M. J., Samaha R. J., Henry P. H. Studies of nondefective adenovirus 2-simian virus 40 hybrid viruses. V. Isolation of additional hybrids which differ in their simian virus 40-specific biological properties. J Virol. 1973 May;11(5):655–664. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.5.655-664.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom D. M., Dulbecco R. Strand orientation of simian virus 40 transcription in productively infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1517–1520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel J. L., Chambon P. Animal DNA-dependent RNA polymerases. Analysis of the RNAs synthesized on Simian virus 40 superhelical DNA by mammalian RNA polymerases AI and B. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jan 16;41(2):379–395. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03280.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel J. L., Chambon P. Animal DNA-dependent RNA polymerases. Studies on the reaction parameters of transcription in vitro of Simian virus 40 DNA by mammalian RNA polymerases AI and B. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jan 16;41(2):367–378. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03279.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow J. F., Berg P., Kelly T. J., Jr, Lewis A. M., Jr Mapping of simian virus 40 early functions on the viral chromosome. J Virol. 1973 Sep;12(3):653–658. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.3.653-658.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow J. F., Berg P. Location of the T4 gene 32 protein binding site on simian virus 40 DNA. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1631–1632. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1631-1632.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulder C., Delius H. Specificity of the break produced by restricting endonuclease R 1 in Simian virus 40 DNA, as revealed by partial denaturation mapping. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3215–3219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxman M. N., Levine A. S., Crumpacker C. S., Levin M. J., Henry P. H., Lewis A. M., Jr Studies of nondefective adenovirus 2-simian virus 40 hybrid viruses. IV. Characterization of the simian virus 40 ribonucleic acid species induced by wild-type simian virus 40 and by the nondefective hybrid virus, Ad2 + ND 1 . J Virol. 1971 Aug;8(2):215–224. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.2.215-224.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patch C. T., Lewis A. M., Jr, Levine A. S. Studies of nondefective adenovirus 2-simian virus 40 hybrid viruses. IX. Template topography in the early region of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1974 Mar;13(3):677–689. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.3.677-689.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J., Sharp P. A., Keller W. Transcription of Simian virus 40. I. Separation of the strands of SV40 DNA and hybridization of the separated strands to RNA extracted from lytically infected and transformed cells. J Mol Biol. 1972 Sep 14;70(1):57–71. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90163-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J., Sugden B., Keller W., Sharp P. A. Transcription of simian virus 40. 3. Mapping of "early" and "late" species of RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3711–3715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Wilcox K. W. A restriction enzyme from Hemophilus influenzae. I. Purification and general properties. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jul 28;51(2):379–391. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90149-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian K. N., Pan J., Zain S., Weissman S. M. The mapping and ordering of fragments of SV40 DNA produced by restriction endonucleases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Jun;1(6):727–752. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.6.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westphal H. SV40 DNA strand selection by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jun 14;50(2):407–420. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90201-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zain B. S., Dhar R., Weissman S. M., Lebowitz P., Lewis A. M., Jr Preferred site for initiation of RNA transcription by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase within the simian virus 40 DNA segment of the nondefective adenovirus-simian virus 40 hybrid viruses Ad2 + ND 1 and Ad2 + ND 3 . J Virol. 1973 May;11(5):682–693. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.5.682-693.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zain B. S., Weissman S. M., Dhar R., Pan J. The nucleotide sequence preceding an RNA polymerase initiation site on SV40 DNA. Part 1. The sequence of the late strand transcript. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Apr;1(4):577–594. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.4.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]