Abstract
A recent publication by Mekonnen et al. demonstrated that among women with non-obstructive coronary artery disease, higher levels of circulating progenitor cells in the blood (CPC), were associated with impaired coronary flow reserve [1].
We performed a quality control assessment of the stability of circulating blood progenitor cells in blood samples stored at 4 °C, to determine the time period during which blood samples can be analyzed and yield consistent data for progenitor cell content. Healthy volunteers (n=6) were recruited and underwent phlebotomy, and blood was stored in EDTA tubes at 4 °C. Flow cytometry was performed to quantitate progenitor cell subsets at 0–4 h, 24 h, and 48 h post phlebotomy. All processed samples were fixed with 1% Paraformaldehyde and 1,000,000 total data events were collected. We found no significant differences in PC data for both CD34+ (P=0.68 for one-way ANOVA) and CD34+/CD133+ (P=0.74 for one-way ANOVA).
Specifications Table
| Subject area | Medicine |
| More specific subject area | Cardiology |
| Type of data | Tables, graphs |
| How data was acquired | Flow cytometry on BD FACS Canto II RUO |
| Data format | Analyzed |
| Experimental factors | EDTA preserved samples |
| Experimental features | A lyse-no wash procedure with the addition of fluorescent counting beads |
| Data source location | Atlanta, GA, USA. |
| Data accessibility | Data included in the article |
Value of the data
-
•
Increased confidence in data from rare progenitors in blood samples stored up to 48 h.
-
•
Increased opportunities for collaborations with distant institutions up to 48 h shipping samples to a central lab for analysis.
-
•
Multiple samples collected during one day can be analyzed in a batch the following day, thus increasing the efficiency of laboratory personnel analyzing samples.
1. Data
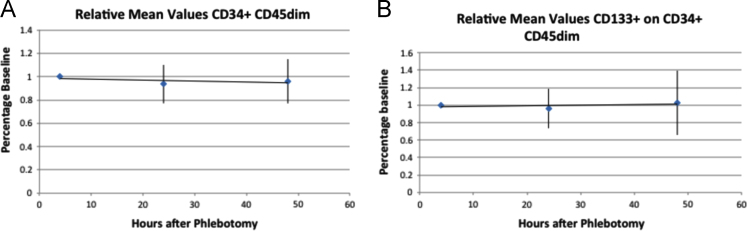
Progenitor cell content for CD34+/CD45dim, CD34+/CD133+/CD45dim, subsets in 300 uL aliquots of anticoagulated blood were measured by flow cytometry. Triplicate aliquots of blood from each sample were analyzed at each time point, and the mean values for each time point for every subject were calculated to determine the stability of the progenitor cell content during storage (Fig. 1). The standardized mean values for the 0–4 h time point was used as the baseline, and the relative change of mean values for the subsequent time points was calculated as a percentage of the baseline value. We found no significant differences in PC counts for both CD34+ (Fig. 1 Panel A, P=0.68) and CD34+/CD133+ (Fig. 1 Panel B, P=0.74).
Fig. 1.
Stability of progenitor cells over time during storage at 4 °C. A. Percentage change in mean values of CD34+/CD45dim cells from baseline values measured at 0–4 h and after 24 and 48 h storage. B. Percentage change of mean values of CD34+/CD45dim/CD133+ from baseline values measured at 0–4 h and after 24 and 48 h storage.
2. Experimental design, materials and methods
Gently mix by inversion and reverse pipet 300 ul blood sample to a 5 ml FACS tube. Add antibody cocktail to blood sample and vortex and incubate in the dark for 15 min. Add 1.2 ml Ammonium chloride lysis buffer, vortex and incubate in the dark for 10 min. Sample should become relatively transparent post lysis. Add 1.2 ml staining media the add 350 ul 1% paraformaldehyde to fix cells, seal the tubes with parafilm and mix gently by inverting several times. Store samples at 4 °C. Before acquisition on the FACS Canto II, reverse pipet 100 ul Invitrogen counting beads to the prepared samples, mixed gently and run. FCS files we a’re analyzed in FlowJo version 9.8.5.
3. Materials
| Item | Manufacturer | Catalog number |
| CD34 | Becton Dickson | 340430 |
| CD133 | Miltenyi Biotech | 130-090-826 |
| CD45 | Becton Dickson | 348805 |
| AccuCheck Counting beads | Fisher | PCB100_3654889900 |
| Tris Hydrochloride | Fisher | BP153 |
| Ammonium chloride | Sigma | A4514 |
| EDTA | Sigma | ED2SS |
| Ammonium hydroxide | Sigma | A6899 |
| Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) | Corning | 21–040-CV |
| Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) | Sigma | F4135 |
| Sodium Azide | Sigma | S8032 |
| Paraformaldehyde | Fisher | 04042 |
Tris Buffered Ammonium chloride Lysis solution-
2.06 g Tris Hydrochloride.
8.26 g Ammonium chloride.
0.037 g EDTA.
QS to 1 L DI H2O and pH to 7.2–7.5 using ammonium Hydroxide. Store at RT.
Staining Media-
1X PBS 485 mL.
15 mL FBS.
0.5 g of Sodium azide (NaN3).
Combine and store at 4 °C.
Footnotes
Transparency data associated with this article can be found in the online version at doi:10.1016/j.dib.2016.11.050.
Transparency document. Supplementary material
Supplementary material
.
Reference
- 1.Mekonnen G., Hayek S.S., Mehta P.K., Li Q., Mahar E., Mou L., Kenkre T.S., Petersen J.W., Azarbal B., Samuels B., Anderson R.D. Circulating progenitor cells and coronary microvascular dysfunction: results from the NHLBI-sponsored Women׳s Ischemia Syndrome Evaluation–Coronary Vascular Dysfunction Study (WISE-CVD) Atherosclerosis. 2016;253:111–117. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2016.08.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary material