Abstract
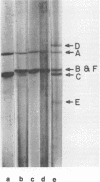
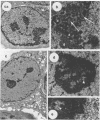
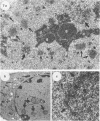
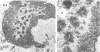
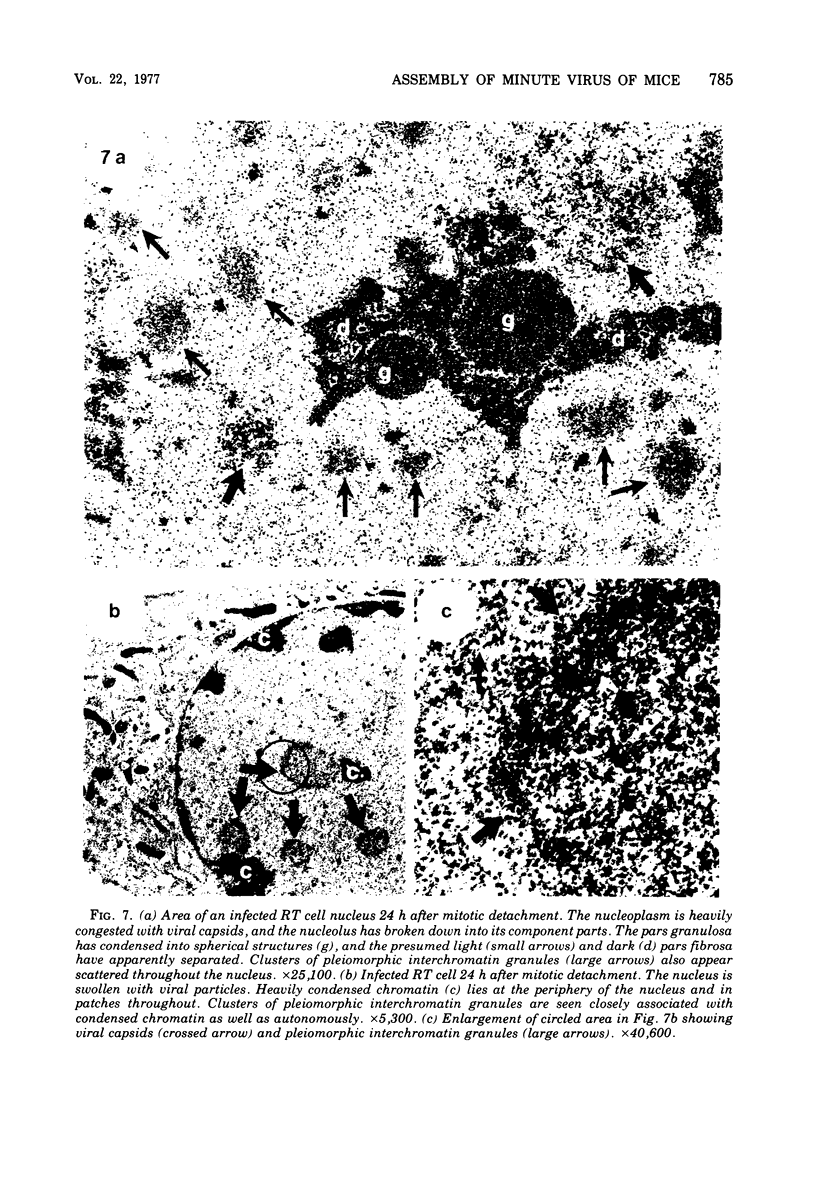
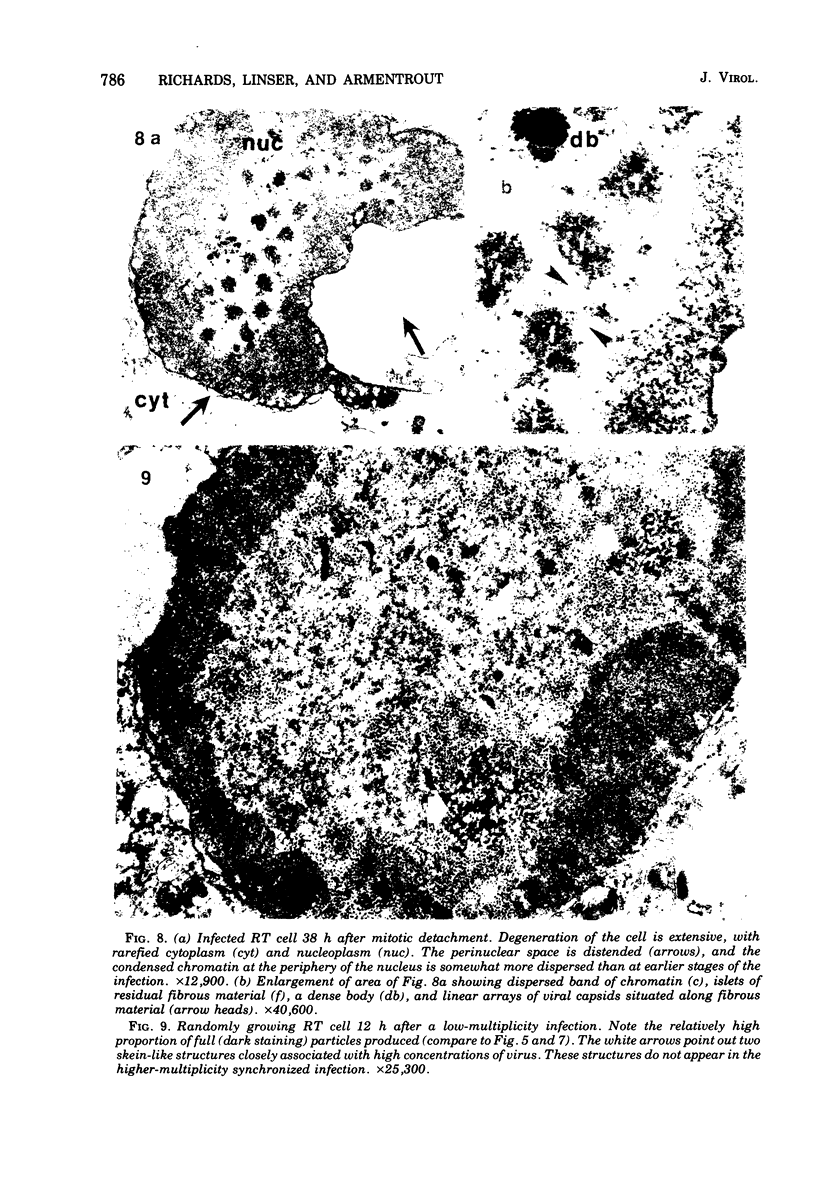
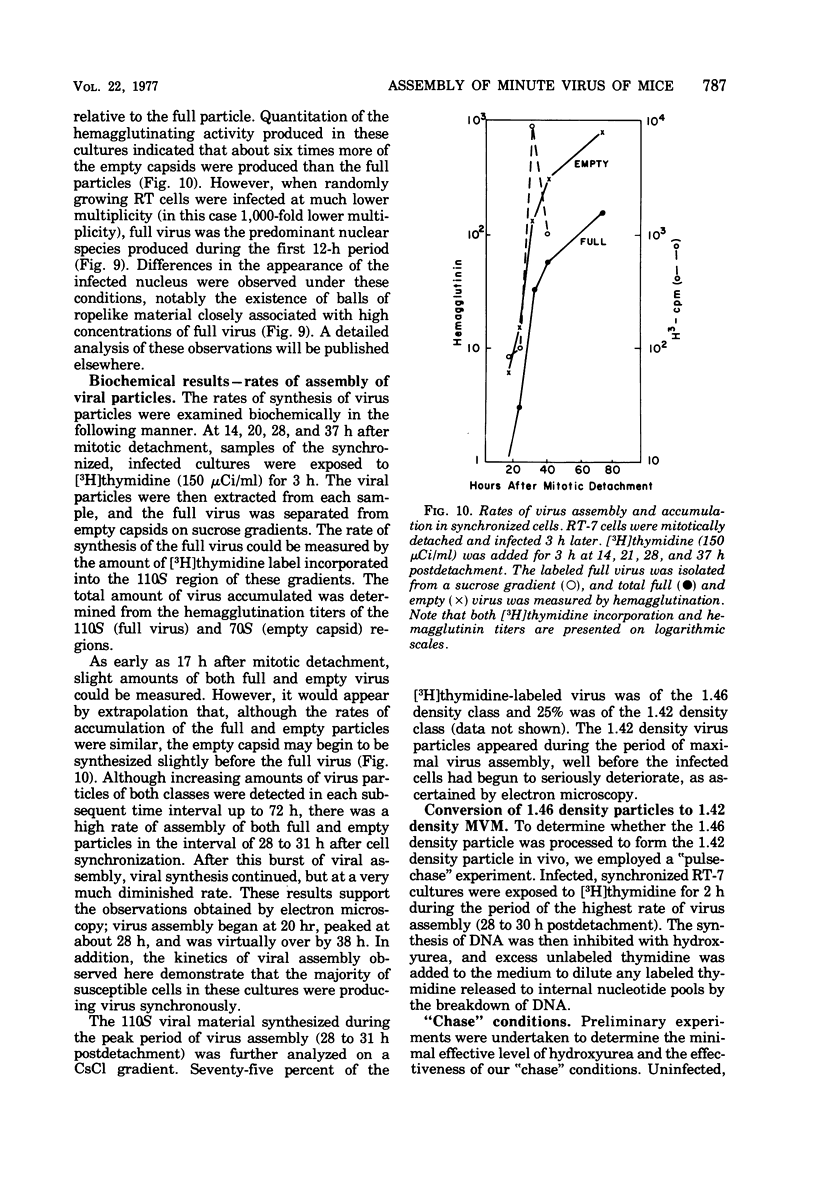
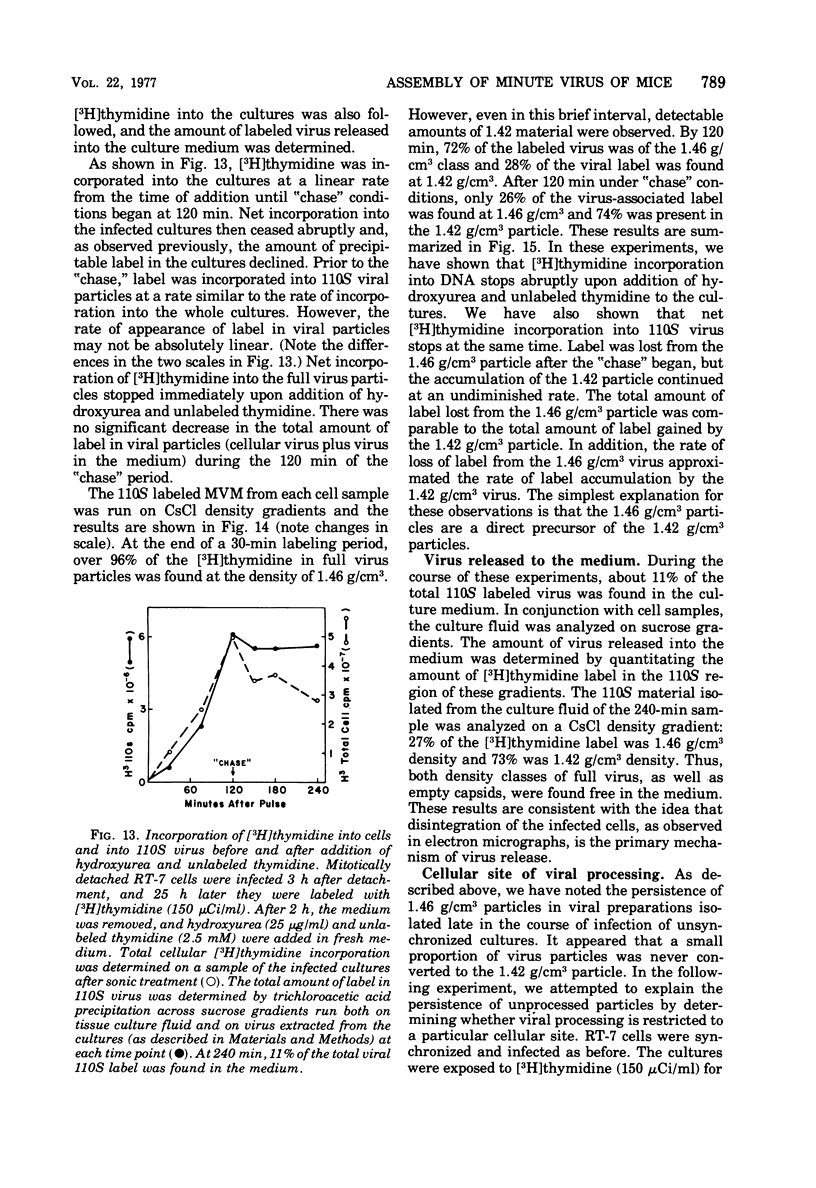
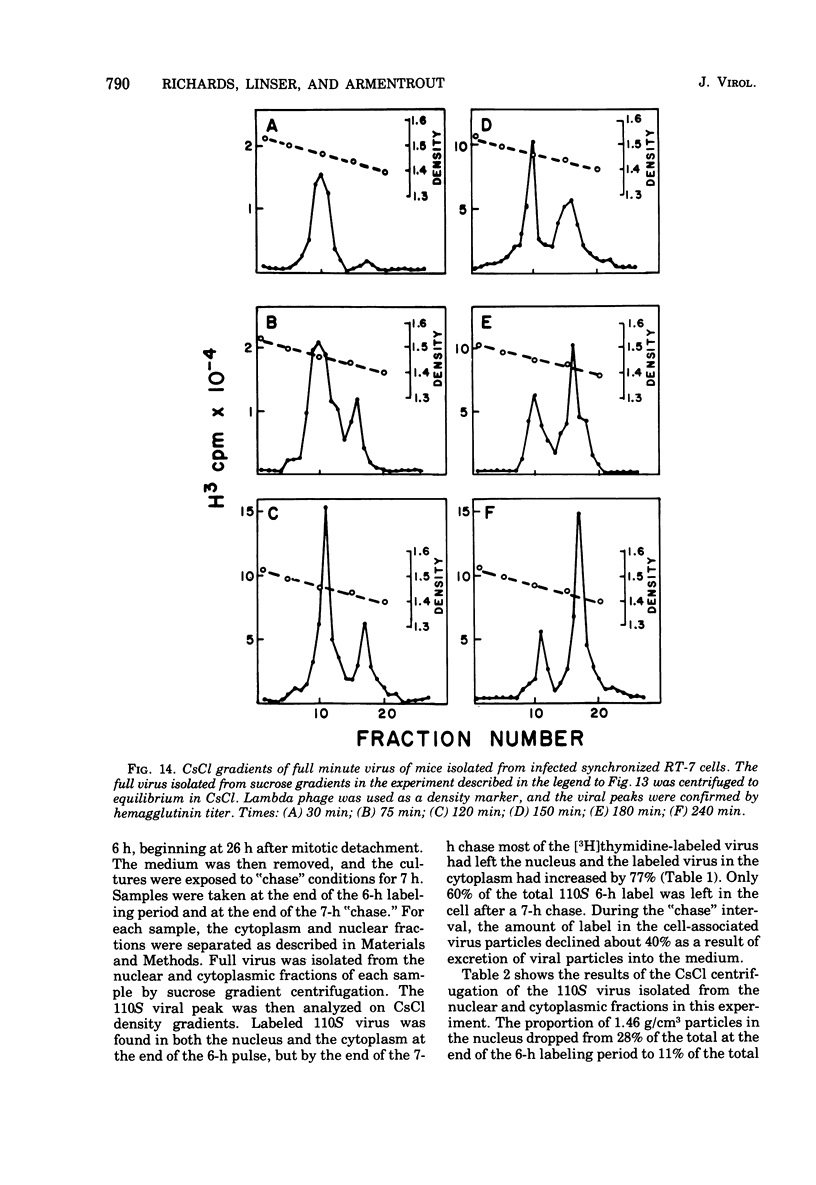
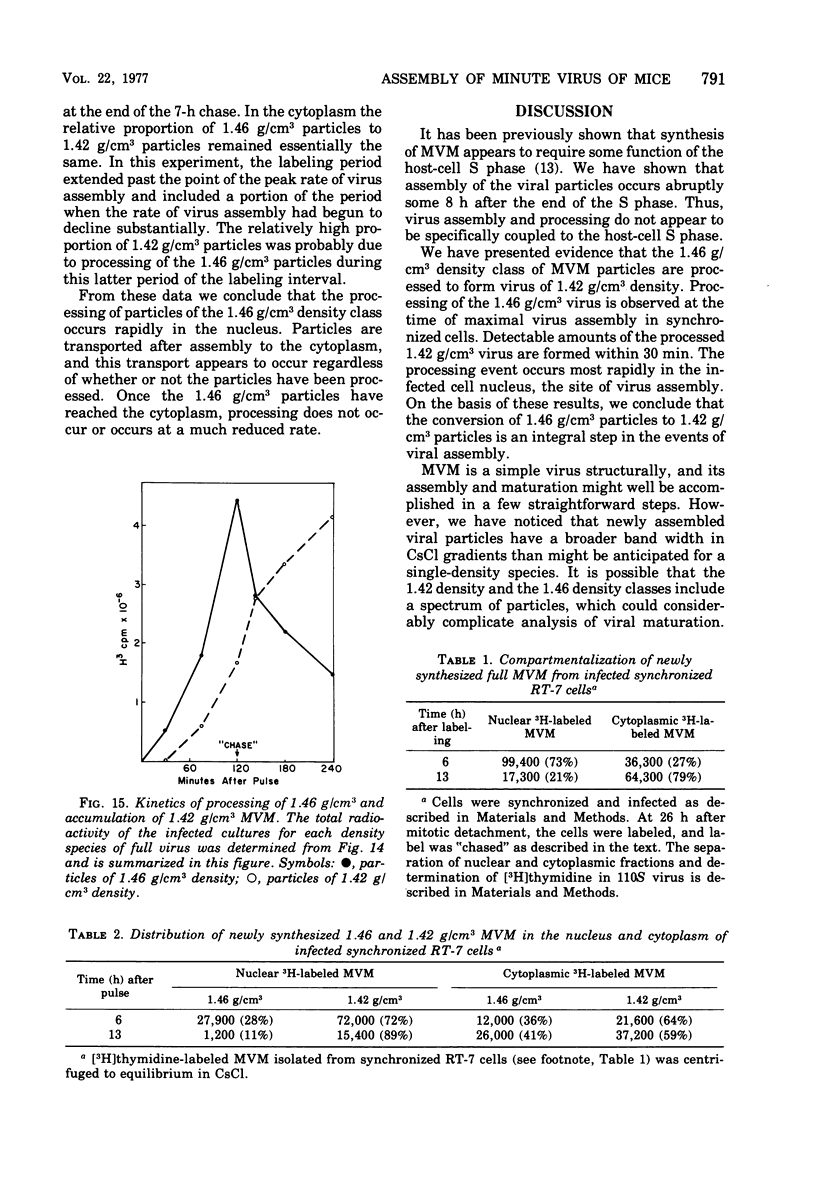
The rates of assembly of the three classes of particles of minute virus of mice were examined in synchronized rat brain cells by a combination of electron microscopy and biochemical techniques. We observed a burst of virus assembly beginning about 8 h after the end of cellular S phase. Labeled thymidine incorporated into the 1.46 g/cm3 class of full virus particles was transferred almost quantitatively to the 1.42 g/cm3 class. The 1.46 g/cm3 virus appeared to be an immediate precursor to the 1.42 g/cm3 class. Conversion of the 1.46 density virus to the 1.42 density particles was observed at the time of virus assembly. The processing was rapid and occurred primarily in the nucleus. Infected cells did not contain significant pools of viral DNA in a form that could be encapsulated in the absence of DNA synthesis. The role of the empty virus capsids in the assembly process is discussed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann P. A., Hoggan M. D., Melnick J. L., Pereira H. G., Vago C. Parvoviridae. Intervirology. 1975;5(1-2):83–92. doi: 10.1159/000149884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinton G. M., Hayashi M. The parovivirus MVM: particles with altered structural proteins. Virology. 1975 Jul;66(1):261–261. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90196-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinton G. M., Hayashi M. The parvovirus MVM: a comparison of heavy and light particle infectivity and their density conversion in vitro. Virology. 1976 Oct 1;74(1):57–63. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90127-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Tomas C. B., Baltimore D. Morphogenesis of poliovirus. II. Demonstration of a new intermediate, the proviron. J Virol. 1973 Nov;12(5):1122–1130. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.5.1122-1130.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampton E. G. H-1 virus growth in synchronized rat embryo cells. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Apr;16(4):266–268. doi: 10.1139/m70-049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegl G., Gautschi M. Multiplication of parvovirus LuIII in a synchronized culture system. III. Replication of viral DNA. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):841–853. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.841-853.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegl G., Gautschi M. The multiplication of parvovirus Lu3 in a synchronized culture system. I. Optimum conditions for virus replication. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1973;40(1):105–118. doi: 10.1007/BF01242642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer I. I., Toolan H. W. Ultrastructural studies of H-1 parvovirus replication. I. Cytopathology produced in human NB epithelial cells and hamster embryo fibroblasts. Virology. 1975 May;65(1):40–54. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer I. I. Ultrastructural studies of H-1 parvovirus replication. II. Induced changes in the deoxyribonucleoprotein and ribonucleoprotein components of human NB cell nuclei. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Oct 1;95(1):205–217. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90625-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tattersall P., Cawte P. J., Shatkin A. J., Ward D. C. Three structural polypeptides coded for by minite virus of mice, a parvovirus. J Virol. 1976 Oct;20(1):273–289. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.1.273-289.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tattersall P. Replication of the parvovirus MVM. I. Dependence of virus multiplication and plaque formation on cell growth. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):586–590. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.586-590.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tattersall P., Ward D. C. Rolling hairpin model for replication of parvovirus and linear chromosomal DNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 9;263(5573):106–109. doi: 10.1038/263106a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W. Parallel isolation procedures for metaphase chromosomes, mitotic apparatus, and nuclei. Methods Enzymol. 1975;40:75–89. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(75)40008-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]