Abstract
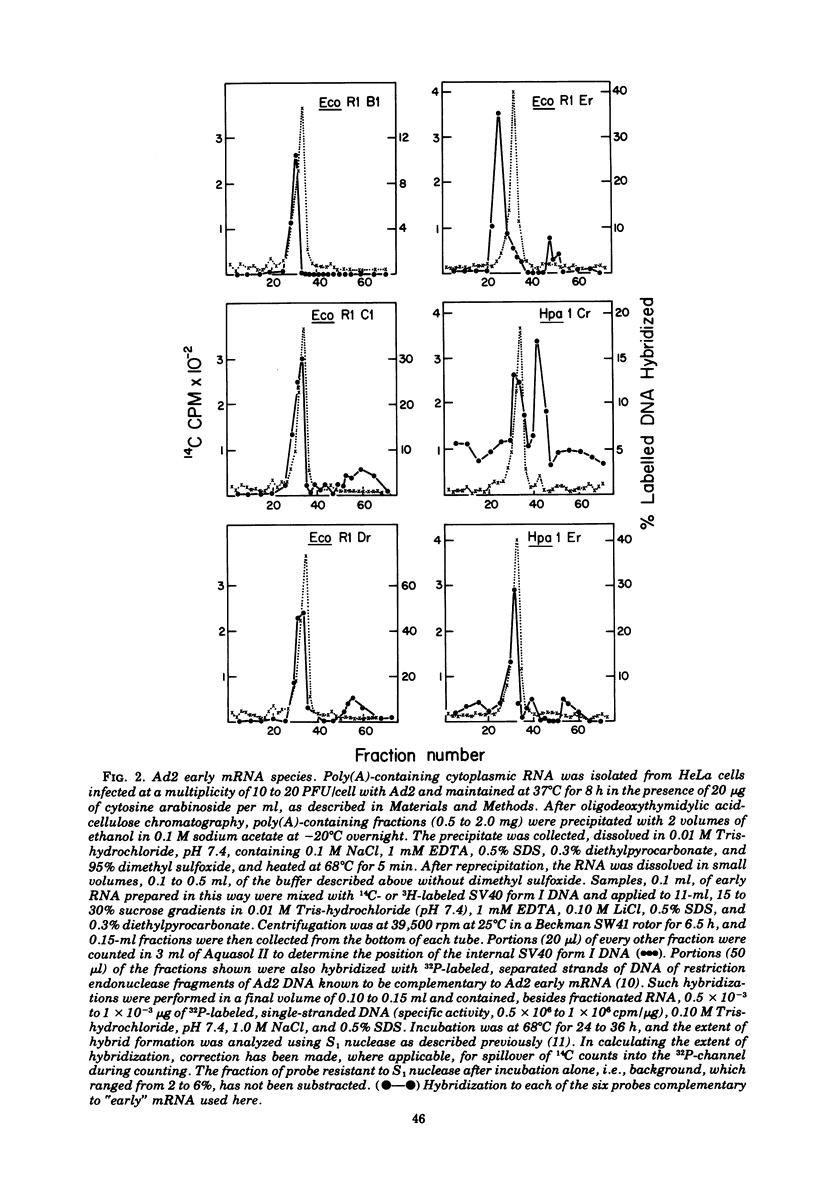
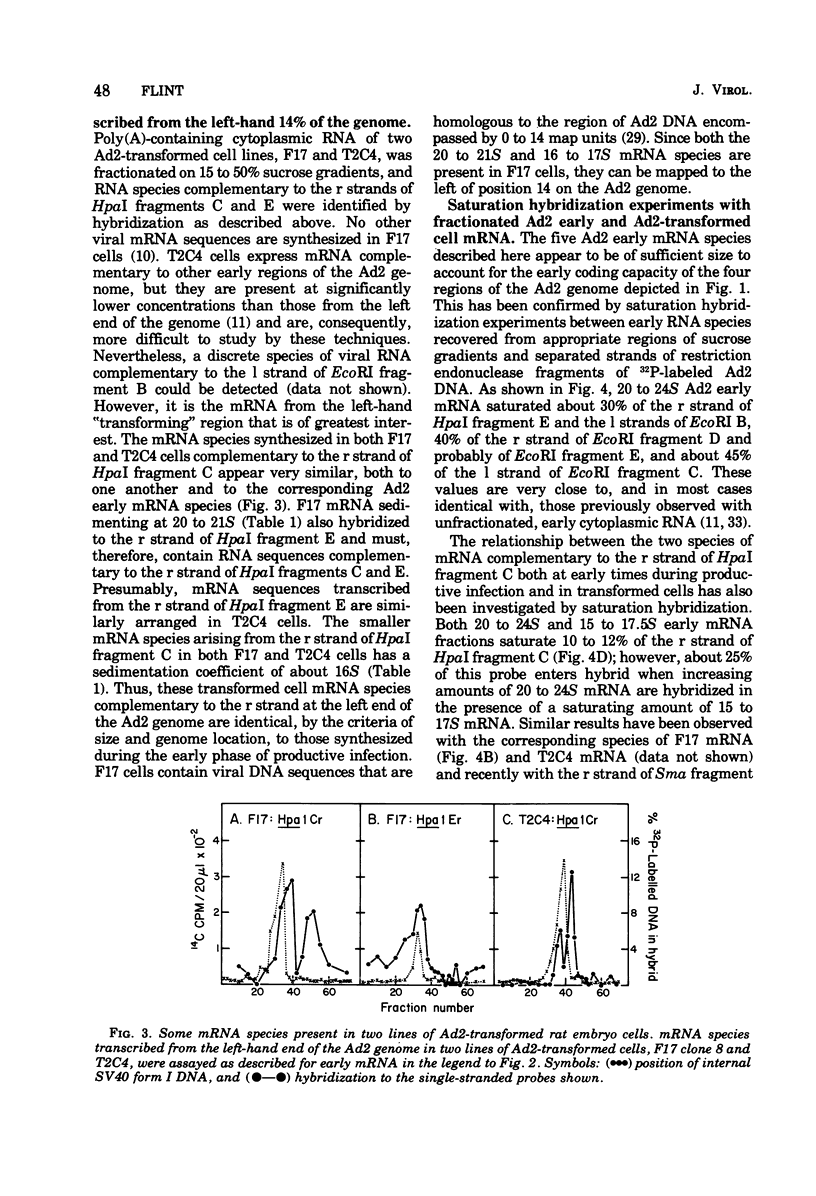
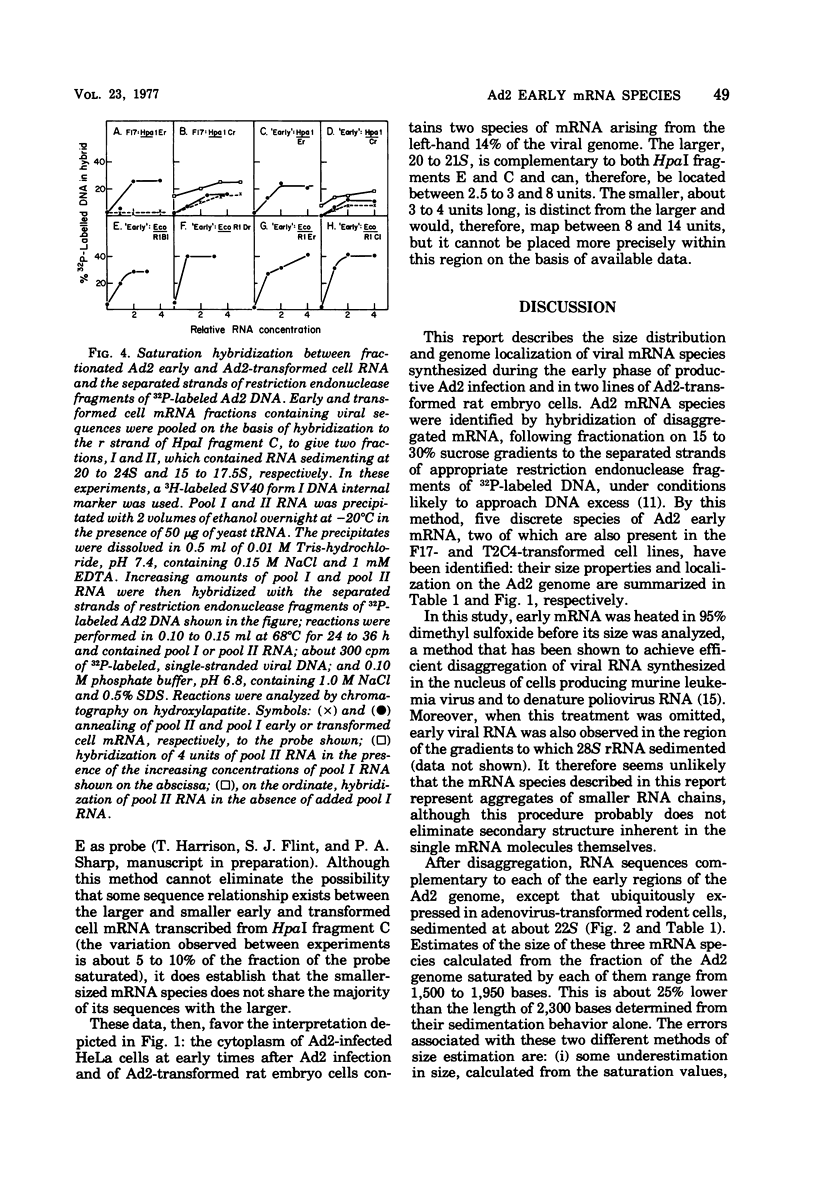
mRNA isolated from adenovirus 2-infected HeLa cells at early times during the productive cycle and from two lines of adenovirus 2-transformed rat embryo cells (F17 and T2C4) was fractionated on sucrose gradients after disaggregation. Viral mRNA species were identified by hybridization across such gradients with the separated strands of restriction endonuclease fragments of 32P-labeled DNA known to be complementary to adeovirus 2 "early" and adenovirus 2-transformed cell mRNA. mRNA transcribed from the left-hand 14% of the adenovirus 2 genome was found to comprise two species, 16 to 17S and 20 to 21S: the same sized mRNA's were present both at early times during productive infection and in the two transformed rat cell lines. Direct comparison of the sequences present in these two mRNA species by additional saturation hybridizations suggests that they are not related to one another. Three additional regions of the adenovirus 2 genome, all of which are located in the right-hand 40% of the adenovirus 2 genome, are complementary to early mRNA sequences: each of these appears to specify one major mRNA species of about 22S. Thus, five major species of adenovirus type 2 early mRNA have been identified. Two of these, copied from the left-hand 14% of the viral genome, are also present in adenovirus 2-transformed rat cells.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachenheimer S., Darnell J. E. Hybridization of mRNA from adenovirus-transformed cells to segments of the adenovirus genome. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):286–289. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.286-289.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büttner W., Veres-Molnár Z., Green M. Isolation of DNA Strand-specific early messenger RNA species in cells infected by human adenovirus 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):2951–2955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.2951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büttner W., Veres-Molnár Z., Green M. Preparative isolation and mapping of adenovirus 2 early messenger RNA species. J Mol Biol. 1976 Oct 25;107(2):93–114. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin W. W., Maizel J. V., Jr The polypeptides of adenovirus. VII. Further studies of early polypeptides in vivo and localization of E2 and E2A to the cell plasma membrane. Virology. 1976 Jun;71(2):518–530. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90378-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinnadurai G., Rho H. M., Horton R. B., Green M. mRNA from the transforming segment of the adenovirus 2 genome in productively infected and transformed cells. J Virol. 1976 Oct;20(1):255–263. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.1.255-263.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A., McGrogan M., Mulder C., Raskas H. J. Identification of early adenovirus type 2 RNA species transcribed from the left-hand end of the genome. J Virol. 1975 Oct;16(4):905–912. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.4.905-912.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A., Raskas H. J. Effect of cycloheximide on RNA metabolism early in productive infection with adenovirus 2. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):26–32. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.26-32.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A., Raskas H. J. Nuclear transcripts larger than the cytoplasmic mRNAs are specified by segments of the adenovirus genome coding for early functions. Cell. 1976 Jun;8(2):205–213. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint S. J., Berget S. M., Sharp P. A. Adenovirus transcription. III. Mapping of viral RNA sequences in cells productively infected by adenovirus type 5. Virology. 1976 Jul 15;72(2):443–455. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90173-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint S. J., Gallimore P. H., Sharp P. A. Comparison of viral RNA sequences in adenovirus 2-transformed and lytically infected cells. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jul 25;96(1):47–68. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90181-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman A. E., Black P. H., Vanderpool E. A., Henry P. H., Austin J. B., Huebner R. J. Transformation of primary rat embryo cells by adenovirus type 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):1205–1212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.1205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgieff M., Bachenheimer S., Darnell J. E. An examination of the nuclear RNA of adenovirus-transformed cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):475–482. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granboulan N., Girard M. Molecular weight of poliovirus ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1969 Oct;4(4):475–479. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.4.475-479.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harter M. L., Shanmugam G., Wold W. S., Green M. Detection of adenovirus type 2-induced early polypeptides using cycloheximide pretreatment to enhance viral protein synthesis. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):232–242. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.232-242.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseltine W. A., Baltimore D. Size of murine RNA tumor virus-specific nuclear RNA molecules. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):331–337. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.331-337.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Baltimore D., Stampfer M. Ribonucleic acid synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus. 3. Multiple complementary messenger RNA molecules. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):946–957. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90343-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar A., Lindberg U. Characterization of messenger ribonucleoprotein and messenger RNA from KB cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):681–685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landgraf-Leurs M., Green M. DNA strand selection during the transcription of the adenovirus 2 genome in infected and transformed cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jul 27;312(4):667–673. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90070-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. B., Atkins J. F., Baum P. R., Solem R., Gesteland R. F., Anderson C. W. Location and identification of the genes for adenovirus type 2 early polypeptides. Cell. 1976 Jan;7(1):141–151. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90264-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg U., Persson T., Philipson L. Isolation and characterization of adenovirus messenger ribonucleic acid in productive infection. J Virol. 1972 Nov;10(5):909–919. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.5.909-919.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons J. T., Green M. Biochemical studies on adenovirus multiplication. 18. Resolution of early virus-specific RNA species in Ad 2 infected and transformed cells. Virology. 1971 Jul;45(1):154–162. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90122-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson U., Sambrook J. Amount of viral DNA in the genome of cells transformed by adenovirus type 2. J Mol Biol. 1973 Jan;73(1):125–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90164-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson U., Tibbetts C., Philipson L. Hybridization maps of early and late messenger RNA sequences on the adenovirus type 2 genome. J Mol Biol. 1976 Mar 15;101(4):479–501. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90241-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipson L., Pettersson U., Lindberg U., Tibbetts C., Vennström B., Persson T. RNA synthesis and processing in adenovirus-infected cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):447–456. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Knipe D. Nucleotide sequence complexities, molecular weights, and poly(A) content of the vesicular stomatitis virus mRNA species. J Virol. 1975 Apr;15(4):994–1003. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.4.994-1003.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saborio J. L., Oberg B. In vivo and in vitro synthesis of adenovirus type 2 early proteins. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):865–875. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.865-875.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J., Botchan M., Gallimore P., Ozanne B., Pettersson U., Williams J., Sharp P. A. Viral DNA sequences in cells transformed by simian virus 40, adenovirus type 2 and adenovirus type 5. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):615–632. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J., Williams J., Sharp P. A., Grodzicker T. Physical mapping of temperature-sensitive mutations of adenoviruses. J Mol Biol. 1975 Sep 25;97(3):369–390. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schincariol A. L., Howatson A. F. Replication of vesicular stomatitis virus. II. Separation and characterization of virus-specific RNA species. Virology. 1972 Sep;49(3):766–783. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90533-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Gallimore P. H., Flint S. J. Mapping of adenovirus 2 RNA sequences in lytically infected cells and transformed cell lines. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):457–474. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Pettersson U., Sambrook J. Viral DNA in transformed cells. I. A study of the sequences of adenovirus 2 DNA in a line of transformed rat cells using specific fragments of the viral genome. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jul 15;86(4):709–726. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90348-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada K., Fujinaga K., Hama S., Sekikawa K., Ito Y. Virus-specific ribonucleic acid in the nucleus and cytoplasm of rat embryo cells transformed by adenovirus type 2. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):648–652. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.648-652.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tal J., Craig E. A., Zimmer S., Raskas H. J. Localization of adenovirus 2 messenger RNA's to segments of the viral genome defined by endonuclease R-R1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4057–4061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannock G. A., Gibbs A. J., Cooper P. D. A re-examination of the molecular weight of poliovirus RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jan 23;38(2):298–304. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90712-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuei D., Fujinaga K., Green M. The mechanism of viral carcinogenesis by DNA mammalian viruses: RNA transcripts containing viral and highly reiterated cellular base sequences in adenovirus-transformed cells (DNA-RNA hybridization-viral-cell mRNA). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):427–430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Vliet P. C., Levine A. J., Ensinger M. J., Ginsberg H. S. Thermolabile DNA binding proteins from cells infected with a temperature-sensitive mutant of adenovrius defective in viral DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1975 Feb;15(2):348–354. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.2.348-354.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall R., Philipson L., Darnell J. E. Processing of adenovirus specific nuclear RNA during virus replication. Virology. 1972 Oct;50(1):27–34. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90342-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall R., Weber J., Gage Z., Darnell J. E. Production of viral mRNA in adenovirus- transformed cells by the post- transcriptional processing of heterogeneous nuclear RNA containing viral and cell sequences. J Virol. 1973 Jun;11(6):953–960. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.6.953-960.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Dawid I. B. Secondary structure maps of RNA: processing of HeLa ribosomal RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2827–2831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. F. Enhancement of adenovirus plaque formation on HeLa cells by magnesium chloride. J Gen Virol. 1970 Dec;9(3):251–255. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-9-3-251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



