Abstract
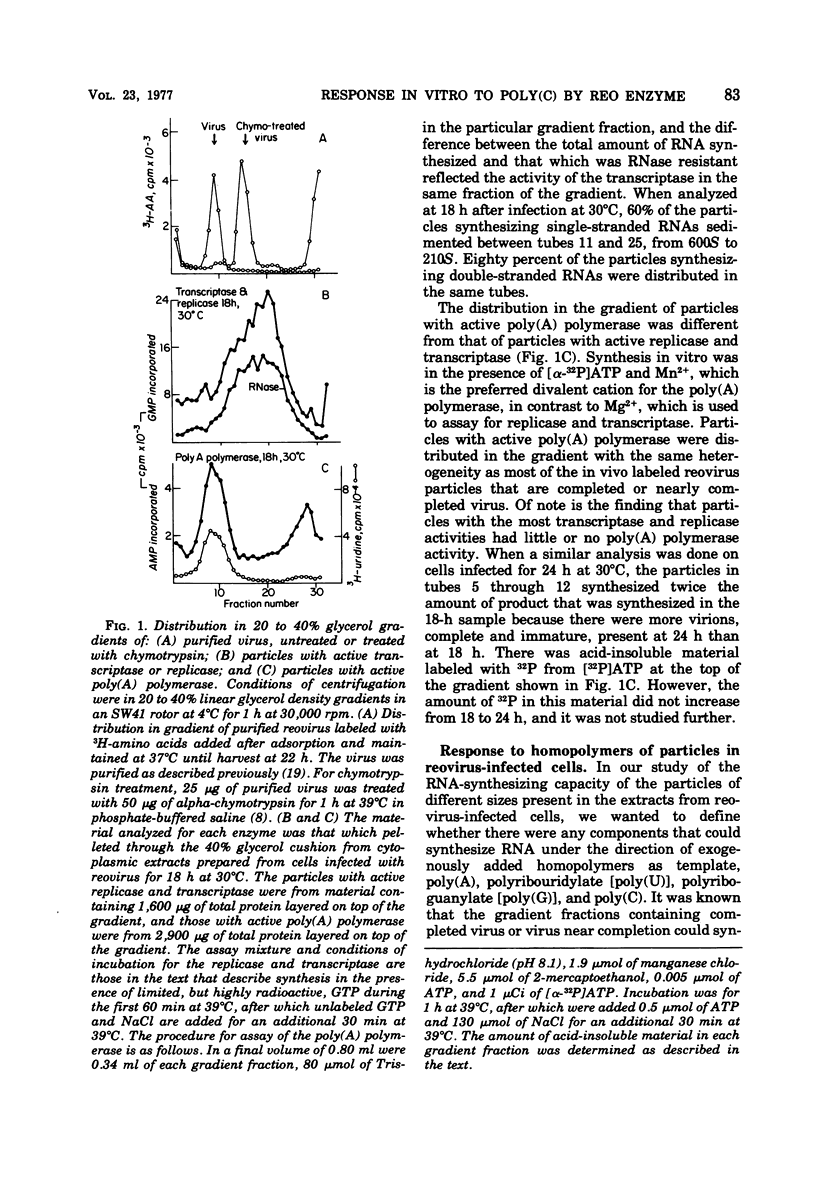
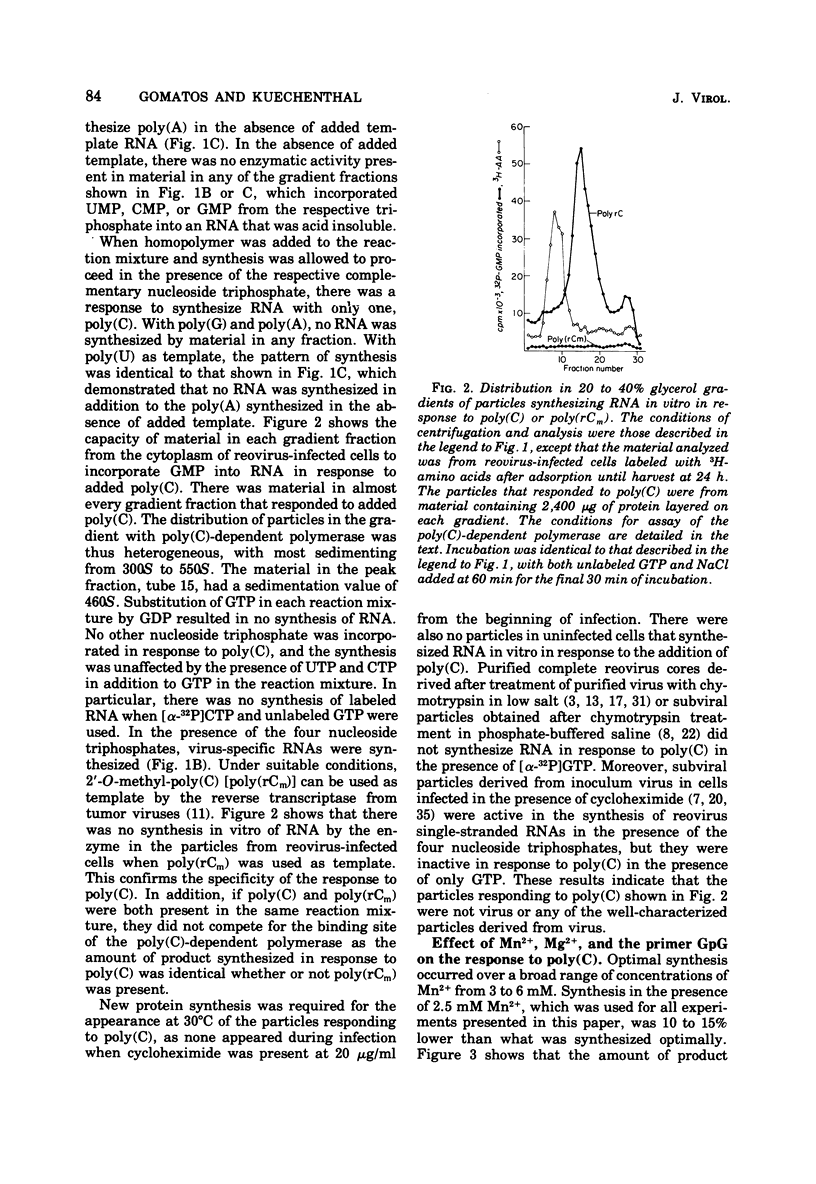
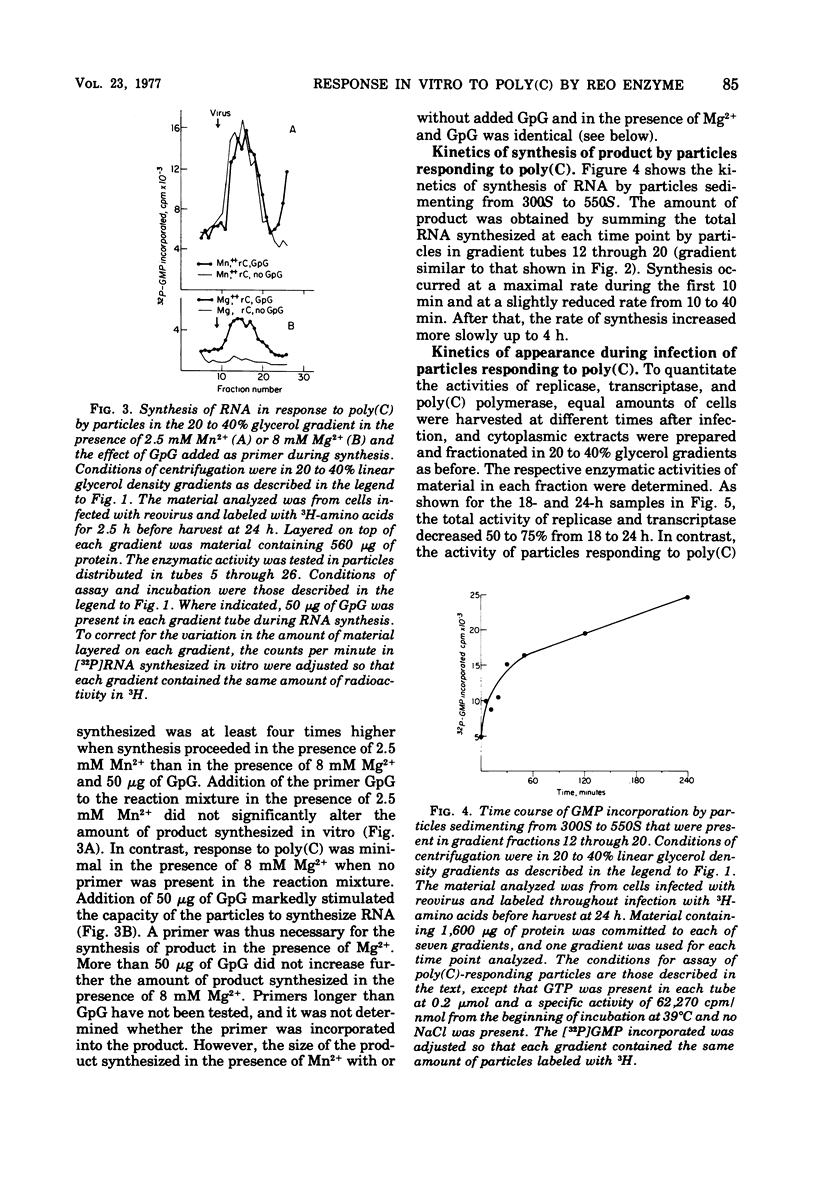
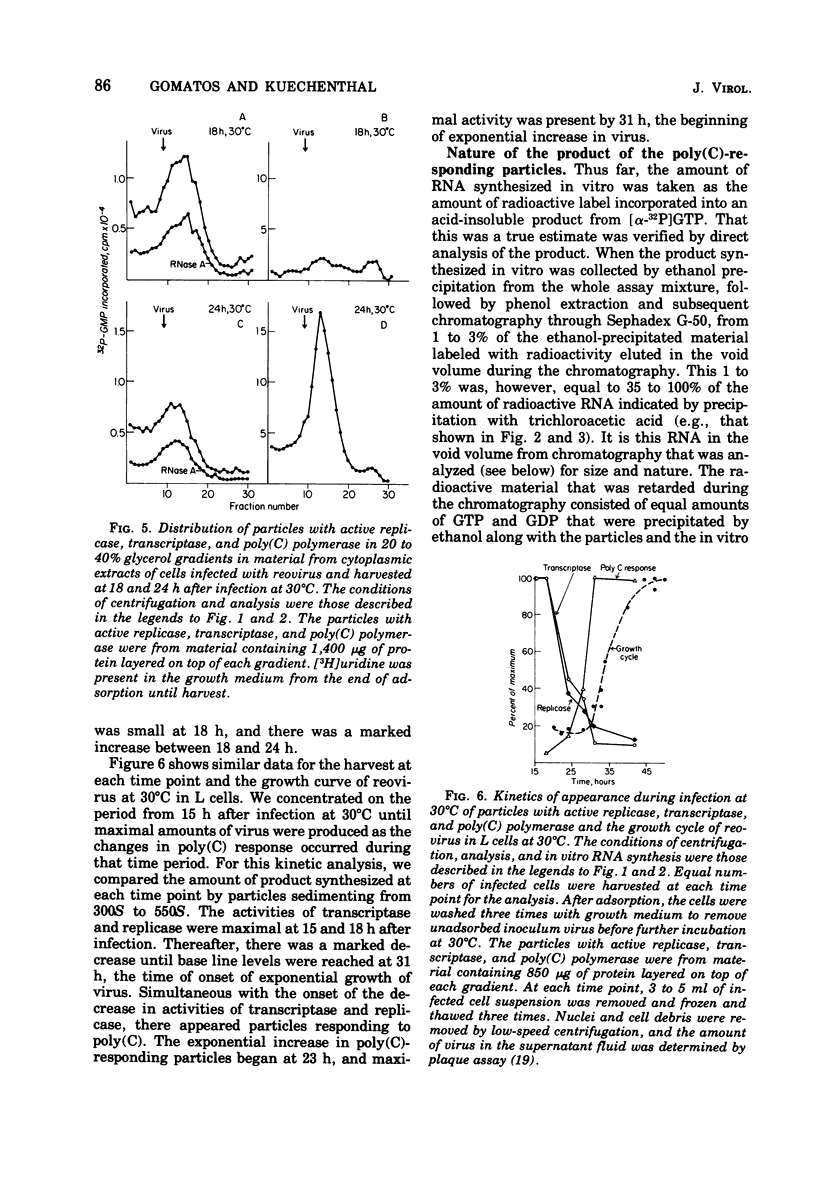
In reovirus-infected cells, virus-specific particles accumulate that have associated with them a polyribocytidylate [poly(C)]-dependent polymerase. This enzyme copies in vitro poly(C) to yield the double-stranded poly(C)·polyriboguanylate [poly(G)]. The particles with poly(C)-dependent polymerase were heterogeneous in size, with most sedimenting from 300S to 550S. Exponential increase in these particles began at 23 h, and maximal amounts were present by 31 h, the time of onset of exponential growth of virus at 30°C. Maximal amounts of particles with active transcriptase and replicase were present at 15 and 18 h after infection. Thereafter, there was a marked decrease in particles with active transcriptase and replicase until base line levels were reached at 31 h. Thus, the increase in poly(C)-responding particles occurred coincident with the decrease in particles with active transcriptase and replicase. The requirement for poly(C) as template was specific because no RNA was synthesized in vitro in response to any other homopolymer, including 2′-O-methyl-poly(C). Synthesis was optimal in the presence of Mn2+ as the divalent cation, and no primer was necessary for synthesis. In contrast, the dinucleotide GpG markedly stimulated synthesis in the presence of 8 mM Mg2+. The size of the poly(C)·poly(G) synthesized in vitro was dependent on the size of the poly(C) used as template. This suggested that the whole template was copied into a complementary strand of similar size. The Tm of the product was between 100 and 130°C. Hydrolysis of the product labeled in [32P]GMP with alkali or RNase T2 yielded GMP as the only labeled mononucleotide. This does indicate that the synthesis of the poly(G) strand in vitro did not proceed by end addition to the poly(C) template, but proceeded on a separate strand.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acs G., Klett H., Schonberg M., Christman J., Levin D. H., Silverstein S. C. Mechanism of reovirus double-stranded ribonucleic acid synthesis in vivo and in vitro. J Virol. 1971 Nov;8(5):684–689. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.5.684-689.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellamy A. R., Shapiro L., August J. T., Joklik W. K. Studies on reovirus RNA. I. Characterization of reovirus genome RNA. J Mol Biol. 1967 Oct 14;29(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsa J., Copps T. P., Sargent M. D., Long D. G., Chapman J. D. New intermediate subviral particles in the in vitro uncoating of reovirus virions by chymotrypsin. J Virol. 1973 Apr;11(4):552–564. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.4.552-564.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsa J., Graham A. F. Reovirus: RNA polymerase activity in purified virions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Dec 30;33(6):895–901. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90396-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsa J., Grover J., Chapman J. D. Presence of nucleoside triphosphate phosphohydrolase activity in purified virions of reovirus. J Virol. 1970 Sep;6(3):295–302. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.3.295-302.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Both G. W., Lavi S., Shatkin A. J. Synthesis of all the gene products of the reovirus genome in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1975 Feb;4(2):173–180. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90124-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. T., Zweerink H. J. Fate of parental reovirus in infected cell. Virology. 1971 Dec;46(3):544–555. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90058-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M. Plaque formation and isolation of pure lines with poliomyelitis viruses. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):167–182. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi Y., Morgan M., Muthukrishnan S., Shatkin A. J. Reovirus messenger RNA contains a methylated, blocked 5'-terminal structure: m-7G(5')ppp(5')G-MpCp-. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):362–366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOMATOS P. J., TAMM I., DALES S., FRANKLIN R. M. Reovirus type 3: physical characteristics and interaction with L cells. Virology. 1962 Jul;17:441–454. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90139-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard G. F., Rottman F., Green M. Poly(2'-O-methylcytidylate)-oligodeoxyguanylate as a template for the ribonucleic acid directed deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase in ribonucleic acid tumor virus particles and a specific probe for the ribonucleic acid directed enzyme in transformed murine cells. Biochemistry. 1974 Apr 9;13(8):1632–1641. doi: 10.1021/bi00705a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomatos P. J. Comparison of the virion polymerase of reovirus with the enzyme purified from reovirus-infected cells. J Virol. 1970 Nov;6(5):610–620. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.5.610-620.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomatos P. J. Reovirus-specific, single-stranded RNA's synthesized in vitro with enzyme purified from reovirus-infected cells. J Mol Biol. 1968 Nov 14;37(3):423–439. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90112-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomatos P. J., Tamm I. THE SECONDARY STRUCTURE OF REOVIRUS RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 May;49(5):707–714. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.5.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay A. J., Joklik W. K. Demonstration that the same strand of reovirus genome RNA is transcribed in vitro and in vivo. Virology. 1971 May;44(2):450–453. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90276-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joklik W. K. Studies on the effect of chymotrypsin on reovirions. Virology. 1972 Sep;49(3):700–715. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90527-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapuler A. M., Mendelsohn N., Klett H., Acs G. Four base-specific nucleoside 5'-triphosphatases in the subviral core of reovirus. Nature. 1970 Mar 28;225(5239):1209–1213. doi: 10.1038/2251209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krug R. M., Gomatos P. J. Absence of adenine-rich ribonucleic acid from purified infectious reovirus 3. J Virol. 1969 Nov;4(5):642–650. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.5.642-650.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau R. Y., Van Alstyne D., Berckmans R., Graham A. F. Synthesis of reovirus-specific polypeptides in cells pretreated with cycloheximide. J Virol. 1975 Sep;16(3):470–478. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.3.470-478.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDEL B. THE EXTRACTION OF RIBONUCLEIC ACID FROM POLIOVIRUS BY TREATMENT WITH SODIUM DODECYL SULFATE. Virology. 1964 Mar;22:360–367. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90026-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDowell M. J., Joklik W. K., Villa-Komaroff L., Lodish H. F. Translation of reovirus messenger RNAs synthetesized in vitro into reovirus polypeptides by several mammalian cell-free extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2649–2653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan E. M., Zweerink H. J. Characterization of transcriptase and replicase particles isolated from reovirus-infected cells. Virology. 1975 Dec;68(2):455–466. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90286-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan E. M., Zweerink H. J. Reovirus morphogenesis. Corelike particles in cells infected at 39 degrees with wild-type reovirus and temperature-sensitive mutants of groups B and G. Virology. 1974 Jun;59(2):556–565. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90465-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakuma S., Watanabe Y. Incorporation of in vitro synthesized reovirus double-stranded ribonucleic acid into virus corelike particles. J Virol. 1972 Nov;10(5):943–950. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.5.943-950.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakuma S., Watanabe Y. Unilateral synthesis of reovirus double-stranded ribonucleic acid by a cell-free replicase system. J Virol. 1971 Aug;8(2):190–196. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.2.190-196.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawicki D. L., Gomatos P. J. Replication of semliki forest virus: polyadenylate in plus-strand RNA and polyuridylate in minus-strand RNA. J Virol. 1976 Nov;20(2):446–464. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.2.446-464.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonberg M., Silverstein S. C., Levin D. H., Acs G. Asynchronous synthesis of the complementary strands of the reovirus genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):505–508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J., LaFiandra A. J. Transcription by infectious subviral particles of reovirus. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):698–706. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.698-706.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J., Sipe J. D., Loh P. Separation of ten reovirus genome segments by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Virol. 1968 Oct;2(10):986–991. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.10.986-991.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J., Sipe J. D. RNA polymerase activity in purified reoviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Dec;61(4):1462–1469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.4.1462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein S. C., Astell C., Christman J., Klett H., Acs G. Shythesis of reovirus oligo adenylic acid in vivo and in vitro. J Virol. 1974 Mar;13(3):740–752. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.3.740-752.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein S. C., Astell C., Levin D. H., Schonberg M., Acs G. The mechanisms of reovirus uncoating and gene activation in vivo. Virology. 1972 Mar;47(3):797–806. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90571-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein S. C., Christman J. K., Acs G. The reovirus replicative cycle. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:375–408. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.002111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skehel J. J., Joklik W. K. Studies on the in vitro transcription of reovirus RNA catalyzed by reovirus cores. Virology. 1969 Dec;39(4):822–831. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoltzfus C. M., Morgan M., Banerjee A. K., Shatkin A. J. Poly(A) polymerase activity in reovirus. J Virol. 1974 Jun;13(6):1338–1345. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.6.1338-1345.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachsman J. T., Levin D. H., Acs G. Ribonucleoside triphosphate-dependent pyrophosphate exchange of Reovirus cores. J Virol. 1970 Oct;6(4):563–565. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.4.563-565.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweerink H. J., Ito Y., Matsuhisa T. Synthesis of reovirus double-stranded RNA within virionlike particles. Virology. 1972 Nov;50(2):349–358. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90386-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweerink H. J., Joklik W. K. Studies on the intracellular synthesis of reovirus-specified proteins. Virology. 1970 Jul;41(3):501–518. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90171-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweerink H. J., Morgan E. M., Skyler J. S. Reovirus morphogenesis: characterization of subviral particles in infected cells. Virology. 1976 Sep;73(2):442–453. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90405-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweerink H. J. Multiple forms of SS leads to DS RNA polymerase activity in reovirus-infected cells. Nature. 1974 Feb 1;247(5439):313–315. doi: 10.1038/247313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



