Abstract
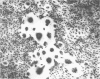
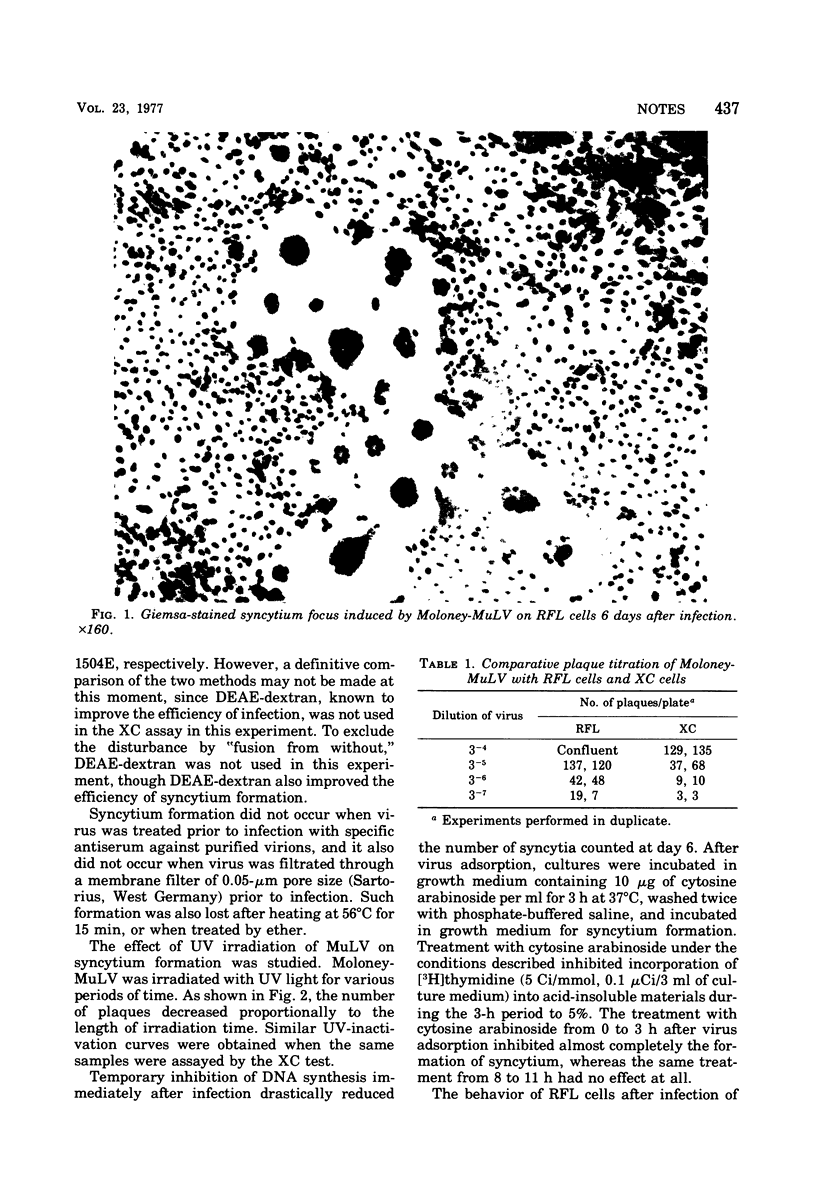
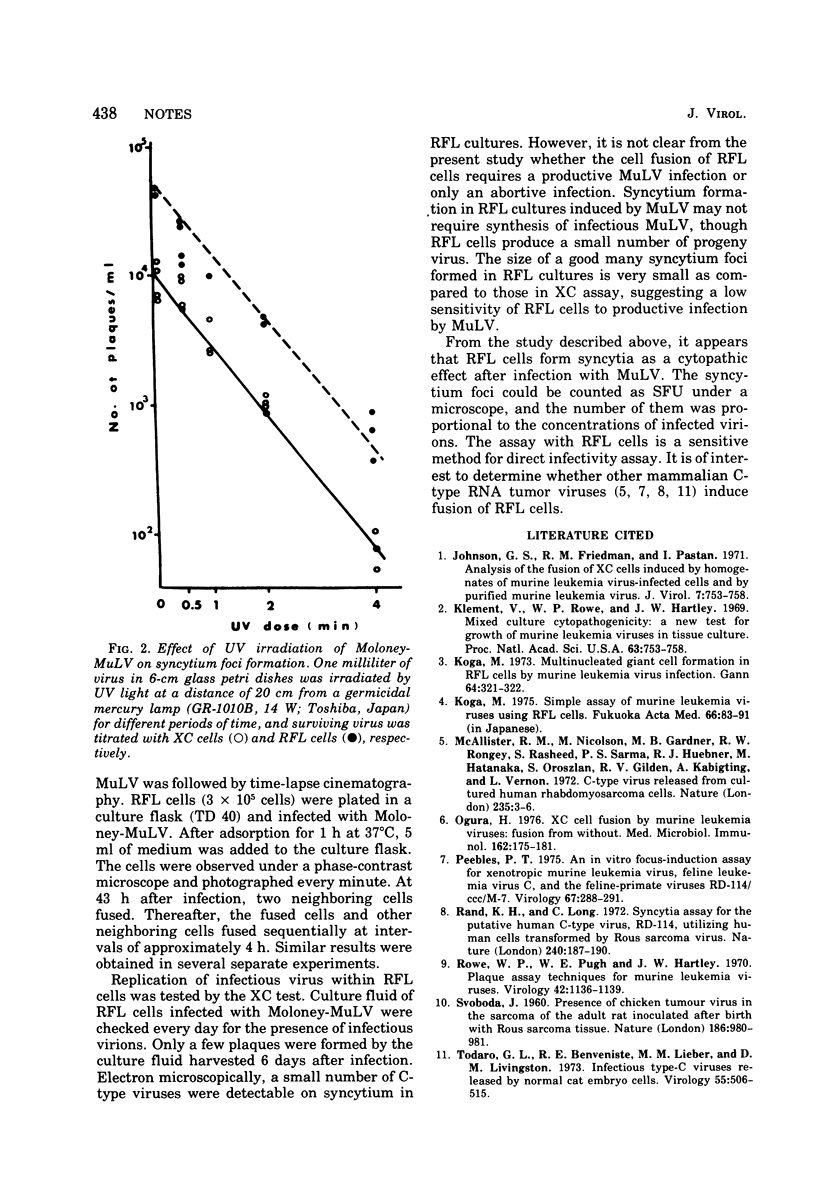
Normal rat embryo cell (RFL) from syncytia after infection with murine leukemia virus. The assay for counting the number of syncytium foci produced in RFL cells is a sensitive method for a direct infectivity assay of murine leukemia virus.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Johnson G. S., Friedman R. M., Pastan I. Analysis of the fusion of XC cells induced by homogenates of murine leukemia virus-infected cells and by purified murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1971 Jun;7(6):753–758. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.6.753-758.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klement V., Rowe W. P., Hartley J. W., Pugh W. E. Mixed culture cytopathogenicity: a new test for growth of murine leukemia viruses in tissue culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jul;63(3):753–758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.3.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga M. Multinucleated giant cell formation in cultured cells by murine leukemia virus infection. Gan. 1973 Jun;64(3):321–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga M. [Simple assay of murine leukemia viruses using RFL-cells (author's transl)]. Fukuoka Igaku Zasshi. 1975 Feb;66(2):83–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister R. M., Nicolson M., Gardner M. B., Rongey R. W., Rasheed S., Sarma P. S., Huebner R. J., Hatanaka M., Oroszlan S., Gilden R. V. C-type virus released from cultured human rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jan 5;235(53):3–6. doi: 10.1038/newbio235003a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogura H. XC cell fusion by murine leukemia viruses: fusion from without. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1976 Dec 1;162(3-4):175–181. doi: 10.1007/BF02120995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peebles P. T. An in vitro focus-induction assay for xenotropic murine leukemia virus, feline leukemia virus C, and the feline--primate viruses RD-114/CCC/M-7. Virology. 1975 Sep;67(1):288–291. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90427-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand K. H., Long C. Syncytial assay for the putative human C-type virus, RD-114, utilizing human cells transformed by Rous sarcoma virus. Nat New Biol. 1972 Dec 6;240(101):187–190. doi: 10.1038/newbio240187a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Pugh W. E., Hartley J. W. Plaque assay techniques for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):1136–1139. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90362-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVOBODA J. Presence of chicken tumour virus in the sarcoma of the adult rat inoculated after birth with Rous sarcoma tissue. Nature. 1960 Jun 18;186:980–981. doi: 10.1038/186980b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., Benveniste R. E., Lieber M. M., Livingston D. M. Infectious type C viruses released by normal cat embryo cells. Virology. 1973 Oct;55(2):506–515. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90192-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]