Abstract
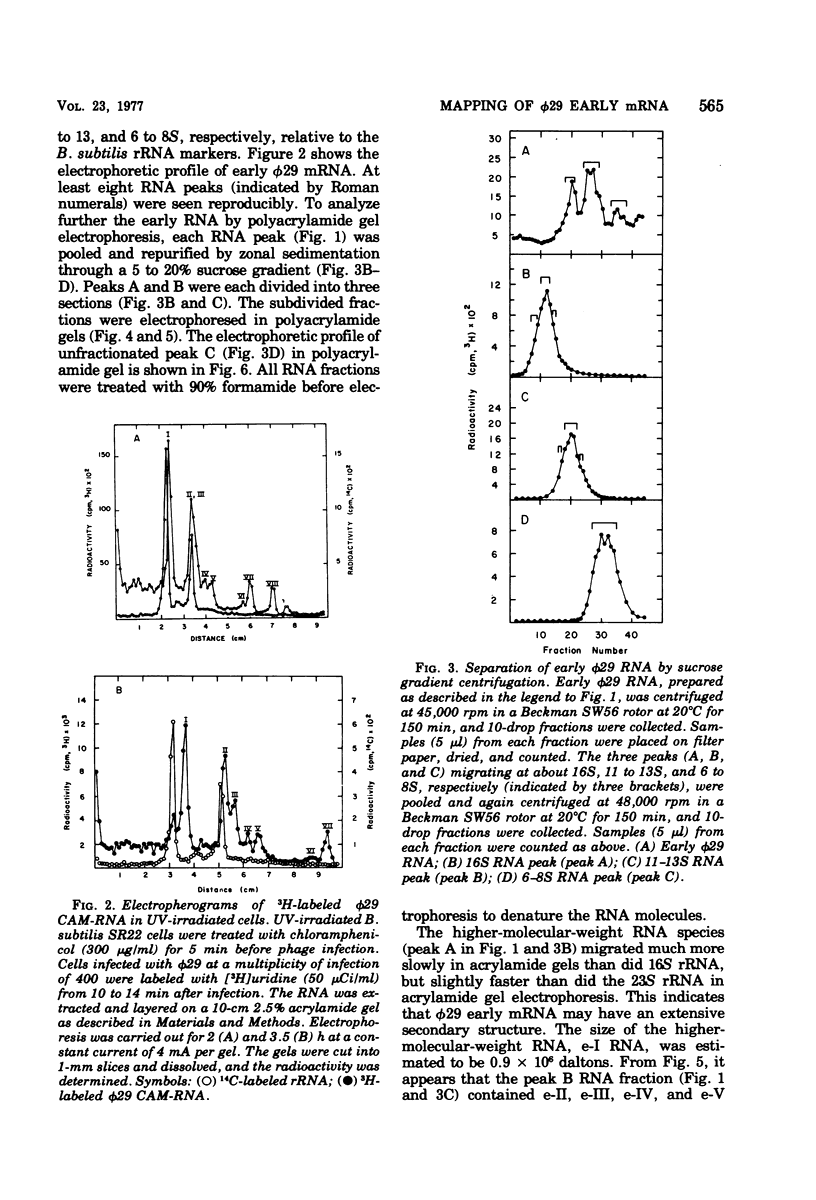
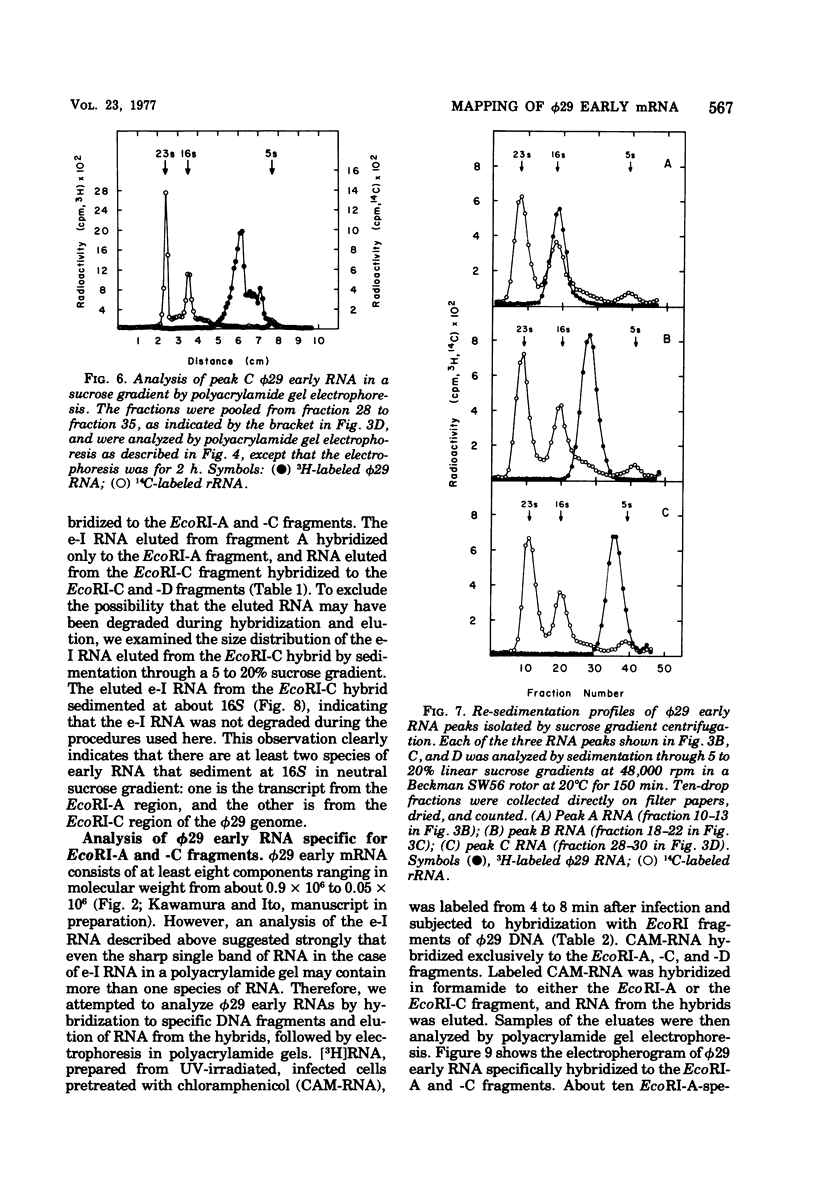
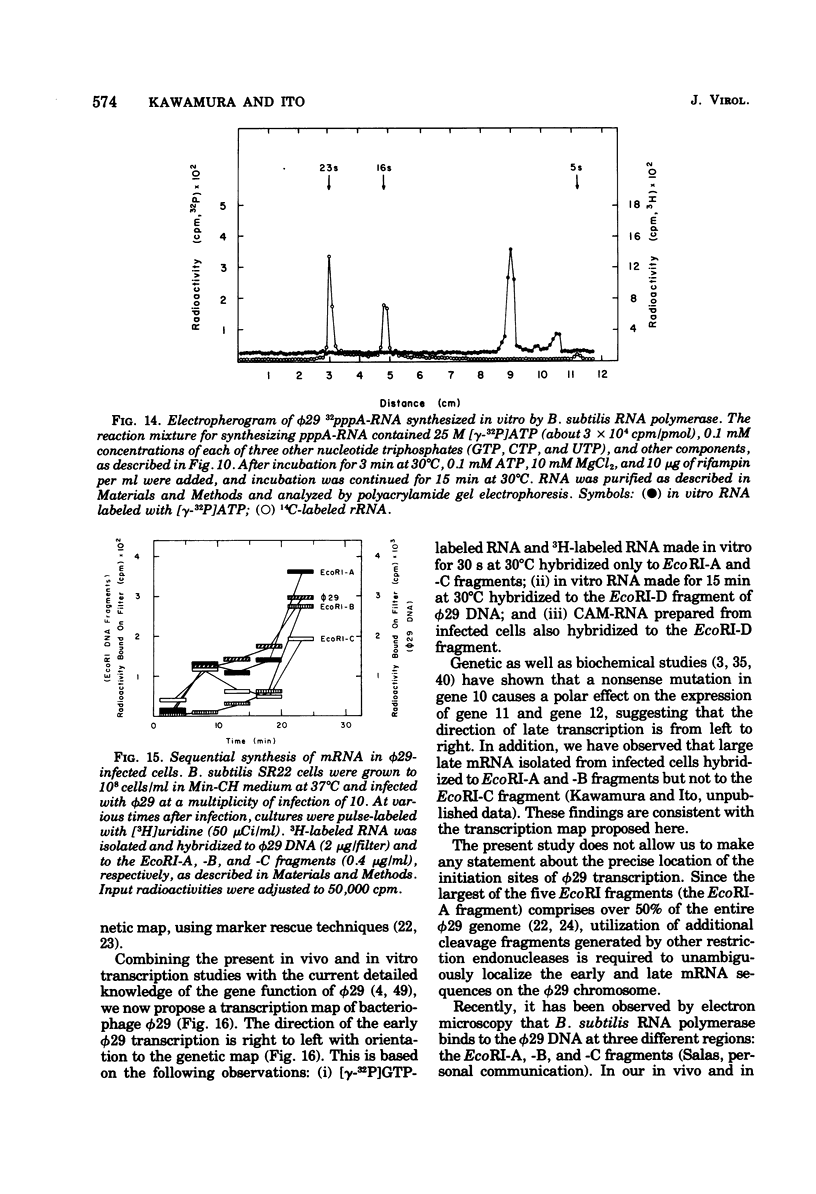
The φ29 early mRNA's synthesized in infected Bacillus subtilis were studied by using sedimentation velocity analysis, polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and hybridization of φ29 DNA fragments generated by the restriction endonuclease Eco RI. Viral RNAs synthesized in vivo in the resence of chloramphenicol were found to hybridize to Eco RI-A, -C, and -D fragments, but not to Eco RI-B and -E fragments, of the viral genome. Major early mRNA sedimenting as 16S material in neutral sucrose gradients was examined in detail. Radioactive φ29 RNA, purified by sucrose gradient centrifugation, was hybridized to either the Eco RI-A or Eco RI-C DNA fragment. The RNA was eluted from the hybrids and then tested for complementary hybrid formation with Eco RI-A and -C fragments. RNA eluted from the Eco RI-A fragment annealed only to the Eco RI-A fragment and not to the Eco RI-C fragment. Similarly, RNA eluted from the Eco RI-C fragment hybridized to the Eco RI-C and -D fragments. Viral RNAs synthesized in vitro using B. subtilis RNA polymerase hybridized to both Eco RI-A and -C DNA fragments. Furthermore, RNA initiated with [γ-32P]GTP also hybridized to both Eco RI-A and -C fragments. These results indicate that there are at least two efficient promotors for early transcription on the φ29 chromosome. In addition, a low-molecular-weight RNA initiated with [γ-32P]ATP was found to hybridize exclusively with the Eco RI-A fragment. Kinetic studies of φ29 mRNA synthesis during the lytic cycle have shown that viral RNAs hybridizable to the Eco RI-A and -C fragments are synthesized immediately after phage infection. On the other hand, mRNA specific for the Eco RI-B fragment was not synthesized for several minutes after phage infection. Based on the results of the in vivo and in vitro transcription studies, a transcription map of the φ29 chromosome is proposed.
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. L., Hickman D. D., Reilly B. E. Structure of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage phi 29 and the length of phi 29 deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):2081–2089. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.2081-2089.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. L., Mosharrafa E. T. Physical and biological properties of phage phi 29 deoxyribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1968 Oct;2(10):1185–1190. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.10.1185-1190.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. L., Reilly B. E. Analysis of bacteriophage phi 29 gene function: protein synthesis in suppressor-sensitive mutant infection of Bacillus subtilis. J Virol. 1974 Jan;13(1):211–221. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.1.211-221.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrascosa J. L., Camacho A., Moreno F., Jiménez F., Mellado R. P., Viñuela E., Salas M. Bacillus subtilis phage phi29. Characterization of gene products and functions. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jul 1;66(2):229–241. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10512.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrascosa J. L., Jiménez F., Viñuela E., Salas M. Synthesis in vitro of phi29-specific early proteins directed by phage DNA. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Feb 21;51(2):587–591. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb03960.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrascosa J. L., Viñuela E., Salas M. Proteins induced in Bacillus subtilis infected with bacteriophage phi 29. Virology. 1973 Nov;56(1):291–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy J. J., Geiduschek E. P. RNA polymerase from phage SP01-infected and uninfected Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4530–4541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy J. J., Geiduschek E. P. Transcription specificity of an RNA polymerase fraction from bacteriophage SP01-infected B. subtilis. FEBS Lett. 1973 Aug 15;34(2):172–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80786-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy J. J., Petrusek R. L., Geiduschek E. P. Conversion of Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase activity in vitro by a protein induced by phage SP01. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2366–2370. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. T7 early RNAs are generated by site-specific cleavages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1559–1563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox T. D. Identification of phage SP01 proteins coded by regulatory genes 33 and 34. Nature. 1976 Aug 26;262(5571):748–753. doi: 10.1038/262748a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox T. D., Pero J. New phage-SPO1-induced polypeptides associated with Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2761–2765. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita D. J., Ohlsson-Wilhelm B. M., Geiduschek E. P. Transcription during bacteriophage SPO1 development: mutations affecting the program of viral transcription. J Mol Biol. 1971 Apr 28;57(2):301–317. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90348-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie D., Spiegelman S. A quantitative assay for DNA-RNA hybrids with DNA immobilized on a membrane. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jul;12(3):829–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80331-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley L. A., Reilly B. E., Hagen E. W., Anderson D. L. Viral protein synthesis in bacteriophage phi 29-infected Bacillus subtilis. J Virol. 1973 Nov;12(5):1149–1159. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.5.1149-1159.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi M. N., Hayashi M. Isolation of phi X174 specific messenger ribonucleic acids in vivo and identification of their 5' terminal nucleotides. J Virol. 1972 Feb;9(2):207–215. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.2.207-215.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemphill H. E., Whiteley H. R. Bacteriophages of Bacillus subtilis. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Sep;39(3):257–315. doi: 10.1128/br.39.3.257-315.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hercules K., Schweiger M., Sauerbier W. Cleavage by RNase 3 converts T3 and T7 early precursor RNA into translatable message. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):840–844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland M., Whiteley H. R. RNA polymerase from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens infected with phi29 bacteriophage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2234–2237. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inciarte M. R., Lázaro J. M., Salas M., Vińuela E. Physical map of bacteriophage phi29 DNA. Virology. 1976 Oct 15;74(2):314–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito J., Kawamura F., Yanofsky S. Analysis of phi 29 and phi 15 genomes by bacterial restriction endonucleases, EcoR1 and Hpal. Virology. 1976 Mar;70(1):37–51. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90234-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito J., Spizizen J. Abortive infection of sporulating Bacillus subtilis 168 by phi 2 bacteriophage. J Virol. 1971 Apr;7(4):515–523. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.4.515-523.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez F., Avila J., Viñuela E., Salas M. Initiation of the transcription of phi29 DNA by Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 May 31;349(3):320–327. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(74)90119-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loening U. E. Molecular weights of ribosomal RNA in relation to evolution. J Mol Biol. 1968 Dec;38(3):355–365. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90391-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loskutoff D. J., Pène J. J., Andrews D. P. Gene expression during the development of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage phi 29. I. Analysis of viral-specific transcription by deoxyribonucleic acid-ribonucleic acid competition hybridization. J Virol. 1973 Jan;11(1):78–86. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.1.78-86.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loskutoff D. J., Pène J. J. Gene expression during the development of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage phi29. II. Resolution of viral-specific ribonucleic acid molecules. J Virol. 1973 Jan;11(1):87–97. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.1.87-97.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCorquodale D. J. The T-odd bacteriophages. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1975 Dec;4(2):101–159. doi: 10.3109/10408417509111574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire J. C., Pène J. J., Barrow-Carraway J. Gene expression during the development of bacteriophage phi 29. 3. Analysis of viral-specific protein synthesis with suppressible mutants. J Virol. 1974 Mar;13(3):690–698. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.3.690-698.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellado R. P., Moreno F., Viñuela E., Salas M., Reilly B. E., Anderson D. L. Genetic analysis of bacteriophage phi 29 of Bacillus subtilis: integration and mapping of reference mutants of two collections. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):495–500. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.495-500.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno F. Suppressor-sensitive mutants and genetic map of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage phi 29. Virology. 1974 Nov;62(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90298-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosharrafa E. T., Schachtele C. F., Reilly B. E., Anderson D. L. Complementary Strands of Bacteriophage phi29 Deoxyribonucleic Acid: Preparative Separation and Transcription Studies. J Virol. 1970 Dec;6(6):855–864. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.6.855-864.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachl C. A., Young E. T. Detection of polycistronic and overlapping bacteriophage T7 late transcripts by in vitro translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):312–316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Péne J. J., Barrow-Carraway J. Initiation of Bacillus subtilis ribonucleic acid polymerase on deoxyribonucleic acid from bacteriophages 2C, phi 29, T4, and lambda. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jul;111(1):15–23. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.1.15-23.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Péne J. J., Murr P. C., Barrow-Carraway J. Synthesis of bacteriophage phi 29 proteins in Bacillus subtilis. J Virol. 1973 Jul;12(1):61–67. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.1.61-67.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly B. E., Tosi M. E., Anderson D. L. Genetic analysis of bacteriophage phi29 of Bacillus subtilis: mapping of the cistrons coding for structural proteins. J Virol. 1975 Oct;16(4):1010–1016. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.4.1010-1016.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly B. E., Zeece V. M., Anderson D. L. Genetic study of suppressor-sensitive mutants of the Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage phi 29. J Virol. 1973 May;11(5):756–760. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.5.756-760.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachtele C. F., De Sain C. V., Anderson D. L. Transcription during the development of bacteriophage phi29: definition of "early" and "late" phi29 ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1973 Jan;11(1):9–16. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.1.9-16.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachtele C. F., De Sain C. V., Hawley L. A., Anderson D. L. Transcription during the development of bacteriophage phi 29: production of host- and phi 29-specific ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1972 Dec;10(6):1170–1178. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.6.1170-1178.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streeck R. E., Philippsen P., Zachau H. G. Cleavage of small bacteriophage and plasmid DNAs by restriction endonucleases. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jun 15;45(2):489–499. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03574.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Bacteriophage T7. Science. 1972 Apr 28;176(4033):367–376. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4033.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers W. C. A simple method for extraction of RNA from E. coli utilizing diethyl pyrocarbonate. Anal Biochem. 1970 Feb;33(2):459–463. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90316-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers W. C., Brunovskis I., Hyman R. W. The process of infection with coliphage T7. VII. Characterization and mapping of the major in vivo transcription products of the early region. J Mol Biol. 1973 Mar 5;74(3):291–300. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90374-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tijan R., Pero J. Bacteriophage SP01 regulatory proteins directing late gene transcription in vitro. Nature. 1976 Aug 26;262(5571):753–757. doi: 10.1038/262753a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y., Whitaker P. A., Nakada D. Early to late switch in bacteriophage T7 development: functional decay of T7 early messenger RNA. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 25;89(2):293–303. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90520-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- di Mauro E., Synder L., Marino P., Lamberti A., Coppo A., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Rifampicin sensitivity of the components of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Nature. 1969 May 10;222(5193):533–537. doi: 10.1038/222533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



