Abstract
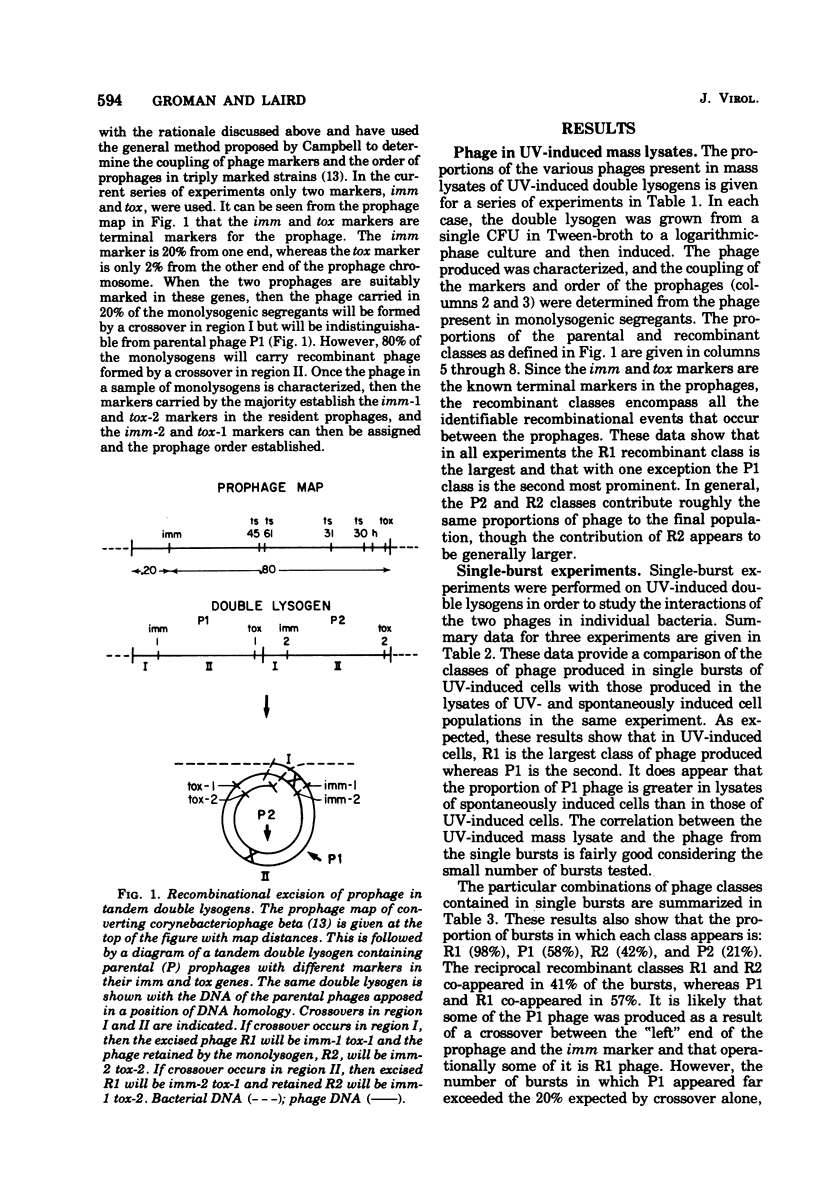
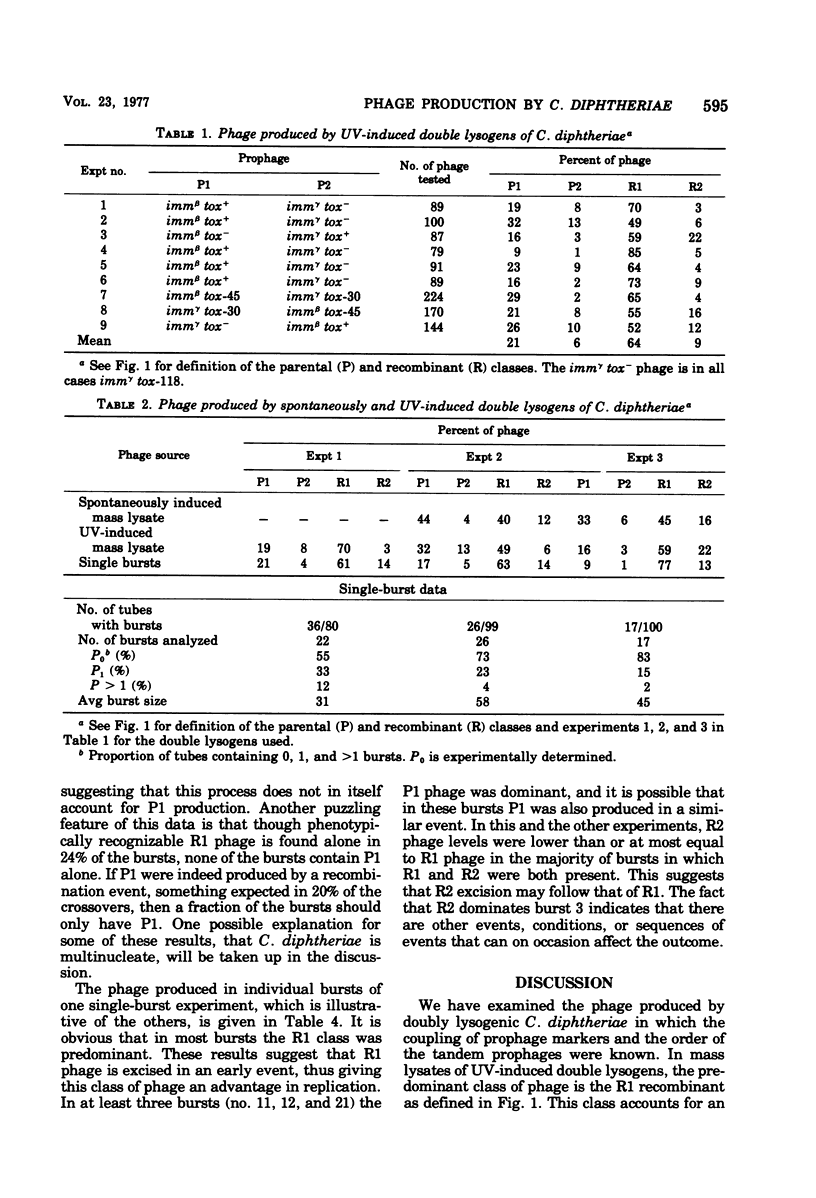
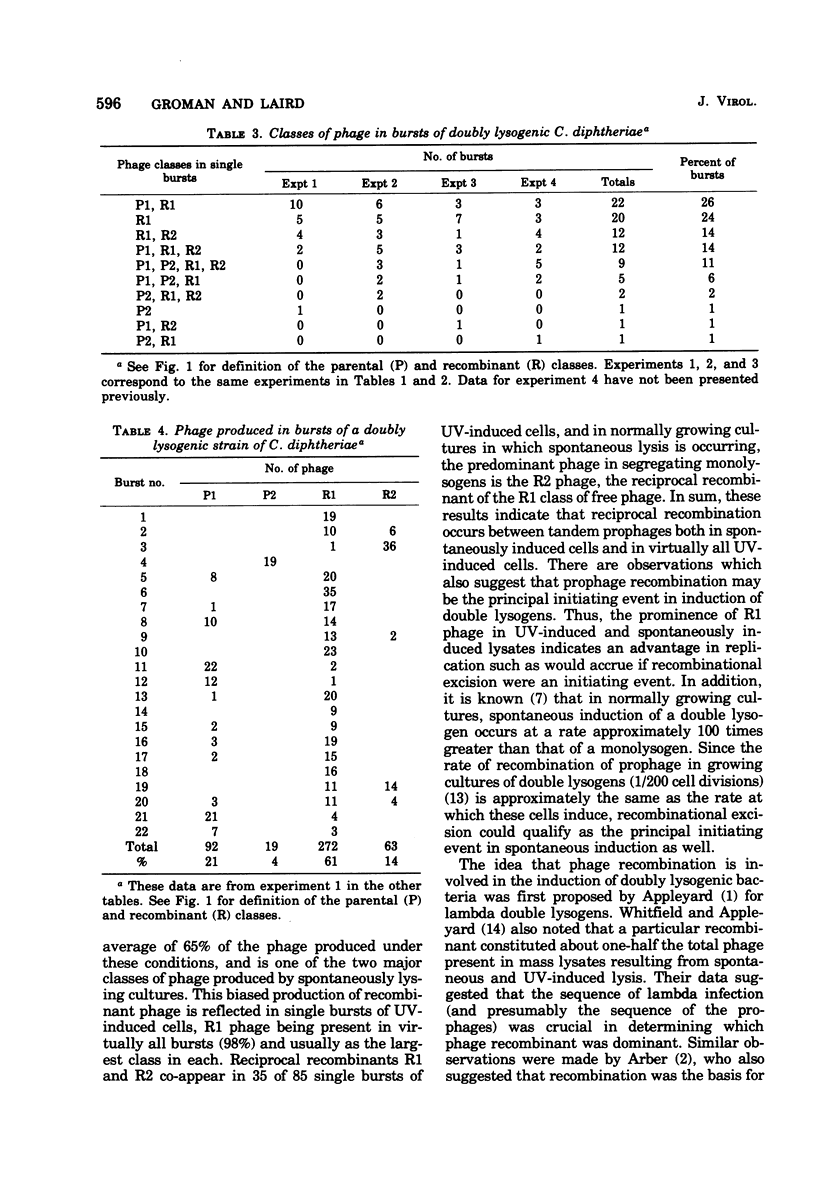
Parental and recombinant phage production by tandem, double lysogens of Corynebacterium diphtheriae was studied in strains in which the coupling of prophage markers and the order of prophage was established. The results from studies of mass lysates and single bursts showed that the recombinant class of phage, designated R1, was predominant in UV-induced lysates followed by the parental, P1 class and to a lesser extent the P2 and R2 classes. Single bursts of UV-treated cells contained phage from one to all four of the phage classes, and this appeared to reflect the action of two excision processes. The data indicate that recombinant phages R1 and R2 are formed by a process of general recombinational excision and that this is the primary event leading to phage production in both UV-irradiated and spontaneously induced double lysogens. This process, which depends on exchange between homologous genes and is reciprocal, accounts for the excision of R1 phage from the host chromosome. A second excision process, probably site-specific excision, also occurs in many of the same cells and accounts for the excision of P1, P2, and R2 phages. The significance of these results for the spread of toxinogenicity in strains of C. diphtheriae is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appleyard R K. Segregation of New Lysogenic Types during Growth of a Doubly Lysogenic Strain Derived from Escherichia Coli K12. Genetics. 1954 Jul;39(4):440–452. doi: 10.1093/genetics/39.4.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calef E. Mapping of integration and excision crossovers in superinfection double lysogens for phage lambda in Escherichia coli. Genetics. 1967 Mar;55(3):547–556. doi: 10.1093/genetics/55.3.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROMAN N. B., EATON M., BOOHER Z. K. Studies of mono- and polylysogenic Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J Bacteriol. 1958 Mar;75(3):320–325. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.3.320-325.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman M. E., Yarmolinsky M. B. The integration and excision of the bacteriophage lambda genome. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:735–747. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes R. K., Barksdale L. Comparative studies with tox plus and tox minus corynebacteriophages. J Virol. 1970 Jun;5(6):783–784. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.6.783-794.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes R. K., Barksdale L. Genetic analysis of tox+ and tox- bacteriophages of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J Virol. 1969 Jun;3(6):586–598. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.6.586-598.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes R. K. Characterization and genetic mapping of nontoxinogenic (tox) mutants of corynebacteriophage beta. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):195–207. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.195-207.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird W., Groman N. Isolation and characterization of tox mutants of corynebacteriophage beta. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):220–227. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.220-227.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird W., Groman N. Orientation of the tox gene in the prophage of corynebacteriophage beta. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):228–231. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.228-231.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird W., Groman N. Prophage map of converting corynebacteriophage beta. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):208–219. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.208-219.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITFIELD J. F., APPLEYARD R. K. Recombination and phenotypic mixing during phage growth in strains of Escherichia coli doubly lysogenic for coliphage lambda. Virology. 1958 Apr;5(2):275–290. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(58)90024-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


