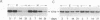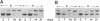Abstract
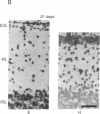
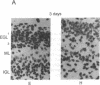
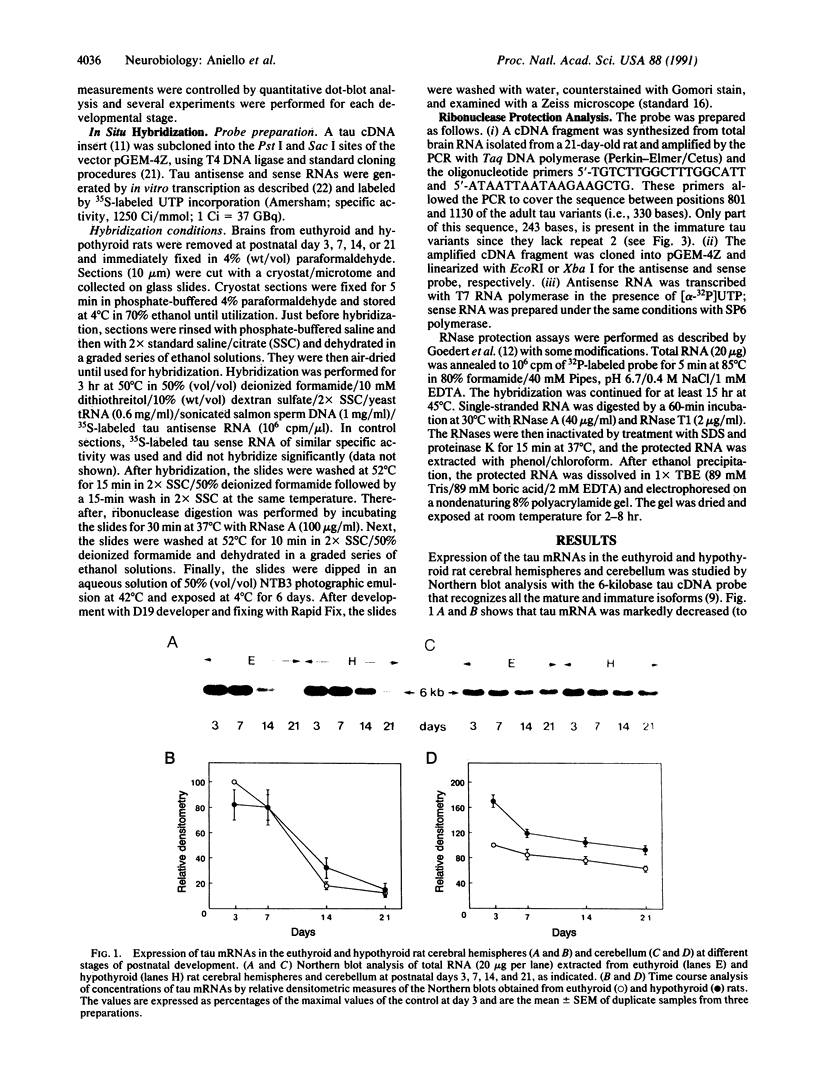
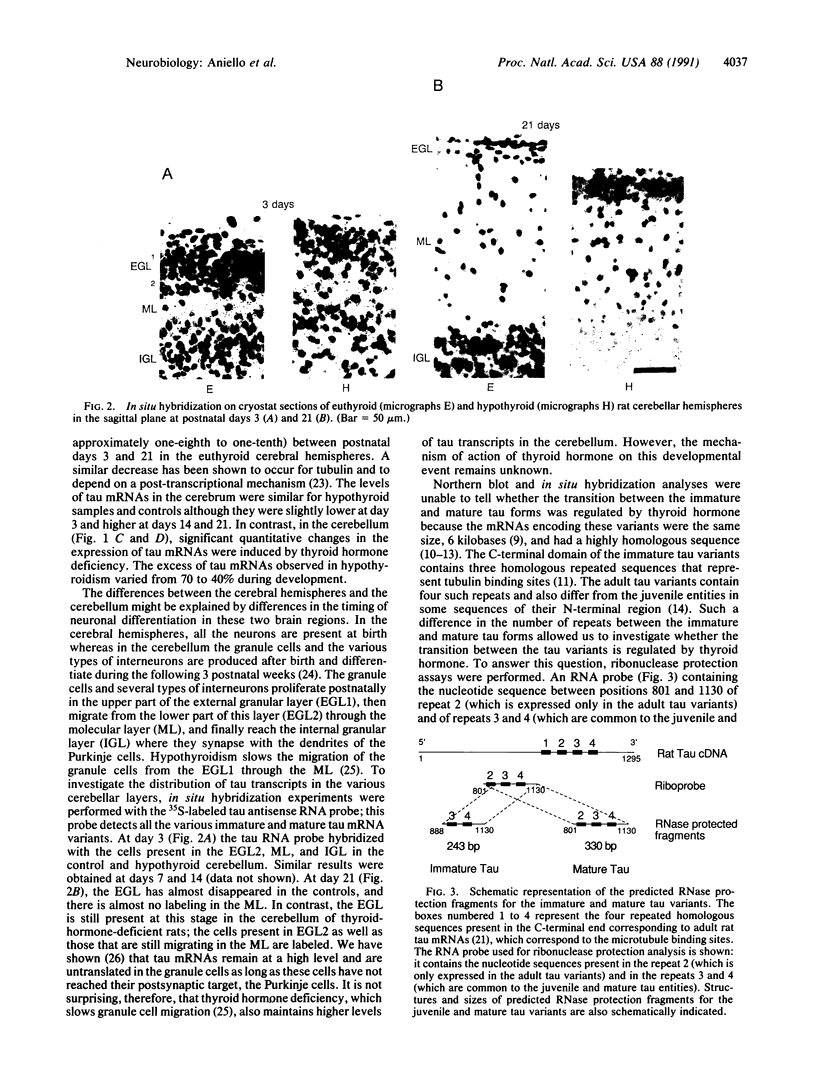
The effect of thyroid hormone on the expression of tau transcripts was studied during postnatal brain development. The level of tau mRNA was only slightly changed postnatally in the cerebral hemispheres of hypothyroid rats, whereas the level of tau mRNA in the cerebellum was maintained at a higher level than in the euthyroid controls. As shown by in situ hybridization studies, such an alteration in tau mRNA expression can be ascribed to an effect of thyroid hormone on the rate of migration of the granule cells in the cerebellum; that tau mRNAs remain high in the cerebellum as long as the granule cells are migrating correlates with the observation that hypothyroidism slows the rate of migration of granule cells. RNase protection assays also showed that thyroid hormone deficiency delays the transition between the immature and mature tau transcripts in both brain regions. Thus, one of the effects of thyroid hormone is to regulate the splicing mechanism that allows replacement of the juvenile tau variants by the adult entities during neuronal differentiation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altman J. Postnatal development of the cerebellar cortex in the rat. II. Phases in the maturation of Purkinje cells and of the molecular layer. J Comp Neurol. 1972 Aug;145(4):399–463. doi: 10.1002/cne.901450402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder L. I., Frankfurter A., Rebhun L. I. The distribution of tau in the mammalian central nervous system. J Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;101(4):1371–1378. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.4.1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitbart R. E., Andreadis A., Nadal-Ginard B. Alternative splicing: a ubiquitous mechanism for the generation of multiple protein isoforms from single genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:467–495. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brion J. P., Guilleminot J., Couchie D., Flament-Durand J., Nunez J. Both adult and juvenile tau microtubule-associated proteins are axon specific in the developing and adult rat cerebellum. Neuroscience. 1988 Apr;25(1):139–146. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caceres A., Kosik K. S. Inhibition of neurite polarity by tau antisense oligonucleotides in primary cerebellar neurons. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):461–463. doi: 10.1038/343461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Hwo S. Y., Kirschner M. W. Physical and chemical properties of purified tau factor and the role of tau in microtubule assembly. J Mol Biol. 1977 Oct 25;116(2):227–247. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90214-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couchie D., Charrière-Bertrand C., Nunez J. Expression of the mRNA for tau proteins during brain development and in cultured neurons and astroglial cells. J Neurochem. 1988 Jun;50(6):1894–1899. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb02494.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couchie D., Legay F., Guilleminot J., Lebargy F., Brion J. P., Nunez J. Expression of Tau protein and Tau mRNA in the cerebellum during axonal outgrowth. Exp Brain Res. 1990;82(3):589–596. doi: 10.1007/BF00228800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couchie D., Nunez J. Immunological characterization of microtubule-associated proteins specific for the immature brain. FEBS Lett. 1985 Sep 2;188(2):331–335. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80397-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drubin D. G., Caput D., Kirschner M. W. Studies on the expression of the microtubule-associated protein, tau, during mouse brain development, with newly isolated complementary DNA probes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):1090–1097. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.1090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellous A., Lennon A. M., Francon J., Nunez J. Thyroid hormones and neurotubule assembly in vitro during brain development. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Nov;101(2):365–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb19728.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francon J., Fellous A., Lennon A. M., Nunez J. Is thyroxine a regulatory signal for neurotubule assembly during brain development? Nature. 1977 Mar 10;266(5598):188–190. doi: 10.1038/266188a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francon J., Lennon A. M., Fellous A., Mareck A., Pierre M., Nunez J. Heterogeneity of microtubule-associated proteins and brain development. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Dec 15;129(2):465–471. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb07072.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Spillantini M. G., Potier M. C., Ulrich J., Crowther R. A. Cloning and sequencing of the cDNA encoding an isoform of microtubule-associated protein tau containing four tandem repeats: differential expression of tau protein mRNAs in human brain. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):393–399. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03390.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himmler A., Drechsel D., Kirschner M. W., Martin D. W., Jr Tau consists of a set of proteins with repeated C-terminal microtubule-binding domains and variable N-terminal domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1381–1388. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himmler A. Structure of the bovine tau gene: alternatively spliced transcripts generate a protein family. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1389–1396. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosik K. S., Orecchio L. D., Bakalis S., Neve R. L. Developmentally regulated expression of specific tau sequences. Neuron. 1989 Apr;2(4):1389–1397. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90077-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauder J. M. Effects of early hypo- and hyperthyroidism on development of rat cerebellar cortex. IV. The parallel fibers. Brain Res. 1978 Feb 17;142(1):25–39. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90174-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G., Cowan N., Kirschner M. The primary structure and heterogeneity of tau protein from mouse brain. Science. 1988 Jan 15;239(4837):285–288. doi: 10.1126/science.3122323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legrand J. Hormones thyroïdiennes et maturation du système nerveux. J Physiol (Paris) 1982;78(7):603–652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mareck A., Fellous A., Francon J., Nunez J. Changes in composition and activity of microtubule-associated proteins during brain development. Nature. 1980 Mar 27;284(5754):353–355. doi: 10.1038/284353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson J. L., Altman J. The effects of early hypo- and hyperthyroidism on the development of rat cerebellar cortex. I. Cell proliferation and differentiation. Brain Res. 1972 Sep 15;44(1):13–23. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90362-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunez J. Immature and mature variants of MAP2 and tau proteins and neuronal plasticity. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Nov;11(11):477–479. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H., Schwartz H. L., Mariash C. N., Kinlaw W. B., Wong N. C., Freake H. C. Advances in our understanding of thyroid hormone action at the cellular level. Endocr Rev. 1987 Aug;8(3):288–308. doi: 10.1210/edrv-8-3-288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels H. H., Forman B. M., Horowitz Z. D., Ye Z. S. Regulation of gene expression by thyroid hormone. J Clin Invest. 1988 Apr;81(4):957–967. doi: 10.1172/JCI113449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]