Abstract
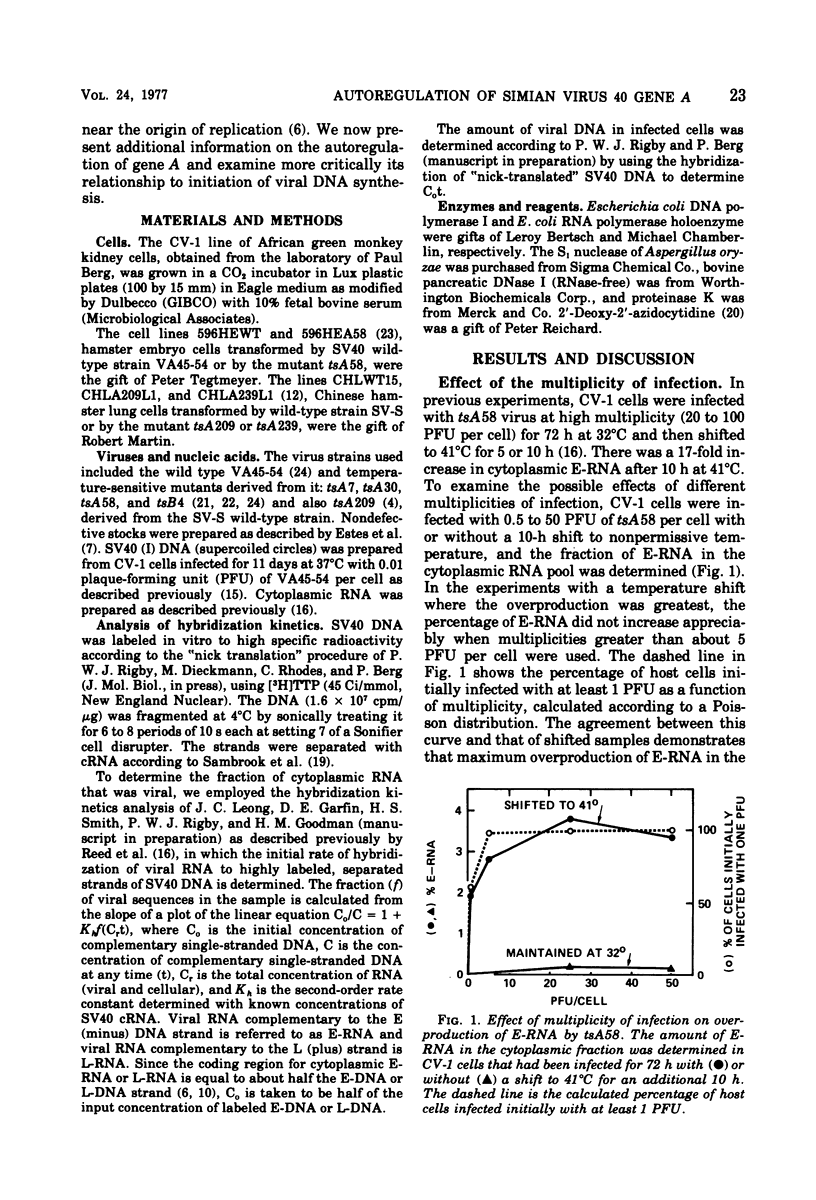
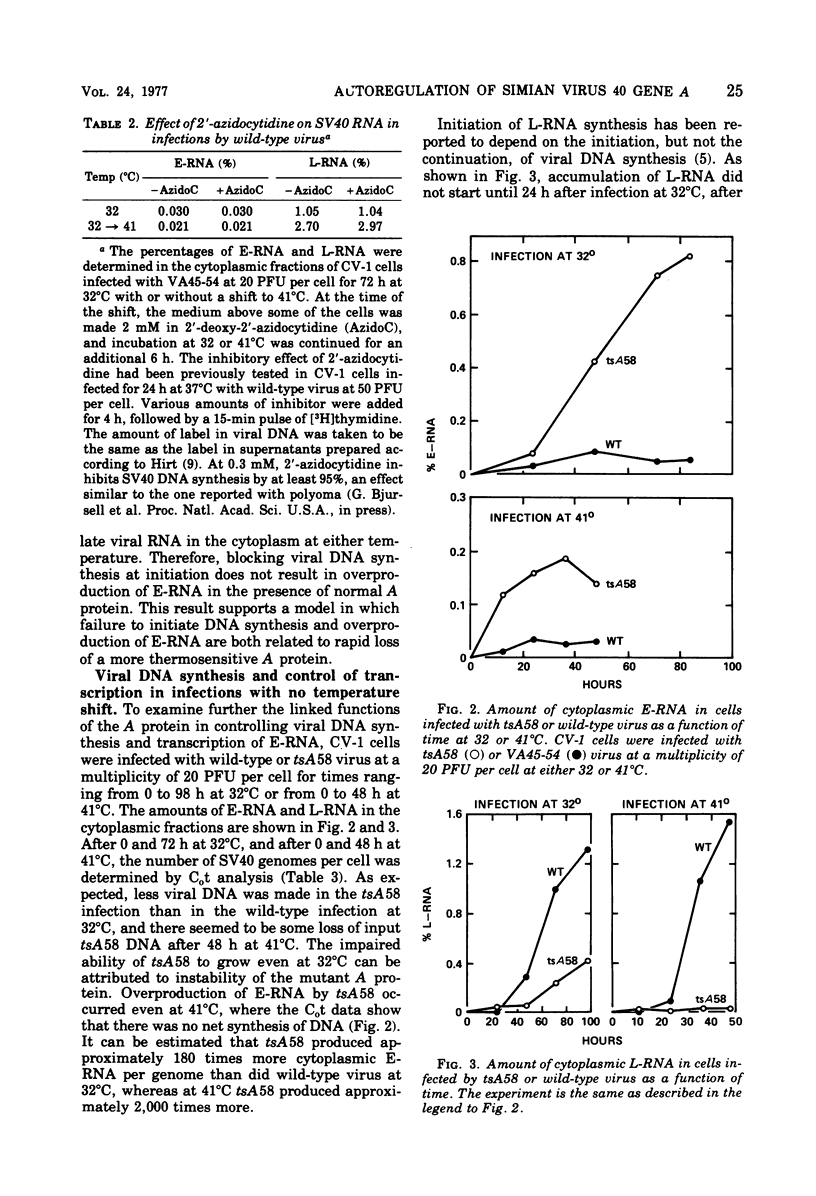
Cells infected by tsA mutants of simian virus 40 (SV40) overproduce early RNA. Overproduction results from failure of the temperature-sensitive A protein (T antigen) to inhibit early transcription. The amount of early RNA in the cytoplasm, determined quantitatively from the kinetics of hybridization to labeled complementary SV40 DNA, was elevated at both permissive (32°C) and nonpermissive (41°C) temperatures in all the early mutants tested (tsA7, -30, -58, and -209), but not in the late mutant tsB4. The amount of early RNA in a culture maintained at 32°C for 72 h and then shifted to 41°C was maximum when each cell was infected initially with at least one plaque-forming unit of tsA58. Azidocytidine (2′-deoxy-2′-azidocytidine), which inhibits initiation of DNA synthesis, did not cause overproduction of early RNA in cells infected with wild-type SV40, showing that the effect seen with tsA mutants is not due to interference with initiation of DNA synthesis per se. In parallel infections at 41°C, the amount of early RNA per copy of viral DNA was as much as 2,000 times greater with tsA58 than with wild-type SV40, even though there was no replication of the tsA58 DNA. Synthesis of late RNA could not be detected during the first 20 h of an infection by either virus at 32°C, indicating that late and early transcription are under different control. In three cell lines transformed by tsA mutants, the amount of early RNA increased moderately after a shift from 32 to 41°C, whereas with homologous cells transformed by wild-type virus, the amount of early RNA decreased, indicating that the A protein may be able to repress transcription of integrated SV40 DNA. All the observations are consistent with a simple model in which the binding of A protein at the origin of replication blocks either binding of RNA polymerase to the early promoter or its progress through the early gene(s).
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. L., Chang C., Mora P. T., Martin R. G. Expression and thermal stability of simian virus 40 tumor-specific transplantation antigen and tumor antigen in wild type- and tsA mutant-transformed cells. J Virol. 1977 Feb;21(2):459–467. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.2.459-467.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Butel J. S. Role of simian virus 40 gene A function in maintenance of transformation. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):619–635. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.619-635.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J. Y., Martin R. G. Complementation analysis of simian virus 40 mutants. J Virol. 1974 May;13(5):1101–1109. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.5.1101-1109.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhar R., Subramanian K. N., Pan J., Weissman S. M. Nucleotide sequence of a fragment of SV40 DNA that contains the origin of DNA replication and specifies the 5' ends of "early" and "late" viral RNA. IV. Localization of the SV40 DNA complementary to the 5' ends of viral mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 10;252(1):368–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Huang E. S., Pagano J. S. Structural polypeptides of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1971 May;7(5):635–641. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.5.635-641.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graessmann M., Graessman A. "Early" simian-virus-40-specific RNA contains information for tumor antigen formation and chromatin replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):366–370. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., Howley P., Nathans D., Martin M. Posttranscriptional selection of simian virus 40-specific RNA. J Virol. 1975 Feb;15(2):433–437. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.2.433-437.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. J., Nathans D. A map of temperature-sensitive mutants of simian virus 40. Virology. 1975 Jul;66(1):70–81. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90179-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. G., Chou J. Y. Simian virus 40 functions required for the establishment and maintenance of malignant transformation. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):599–612. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.599-612.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Weber K. Simian virus 40 gene A function and maintenance of transformation. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):636–644. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.636-644.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives C., Gilboa E., Revel M., Winocour E. Cell-free translation of simian virus 40 early messenger RNA coding for viral T-antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):457–461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I., Ferguson J., Davis R. W., Stark G. R. T antigen binds to simian virus 40 DNA at the origin of replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1605–1609. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I., Stark G. R., Alwine J. C. Autoregulation of simian virus 40 gene A by T antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3083–3087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. E., Gorecki M., Mulligan R. C., Danna K. J., Rozenblatt S., Rich A. Simian virus 40 DNA directs synthesis of authentic viral polypeptides in a linked transcription-translation cell-free system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1922–1926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rundell K., Collins J. K., Tegtmeyer P., Ozer H. L., Lai C. J., Nathans D. Identification of simian virus 40 protein A. J Virol. 1977 Feb;21(2):636–646. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.2.636-646.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J., Sharp P. A., Keller W. Transcription of Simian virus 40. I. Separation of the strands of SV40 DNA and hybridization of the separated strands to RNA extracted from lytically infected and transformed cells. J Mol Biol. 1972 Sep 14;70(1):57–71. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90163-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skoog L., Bjursell G., Thelander L., Hägerström T., Hobbs J., Eckstein F. 2'-Deoxy-2'-azidocytidine, a new inhibitor of DNA replication in mammalian cells. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jan;72(2):371–378. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P. Altered patterns of protein synthesis in infection by SV40 mutants. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):9–15. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P., Dohan C., Jr, Reznikoff C. Inactivating and mutagenic effects of nitrosoguanidine on simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):745–752. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P. Function of simian virus 40 gene A in transforming infection. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):613–618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.613-618.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P., Schwartz M., Collins J. K., Rundell K. Regulation of tumor antigen synthesis by simain virus 40 gene A. J Virol. 1975 Jul;16(1):168–178. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.1.168-178.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P. Simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis: the viral replicon. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):591–598. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.591-598.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenen D. G., Baygell P., Livingston D. M. Thermolabile T (tumor) antigen from cells transformed by a temperature-sensitive mutant of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4351–4355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



