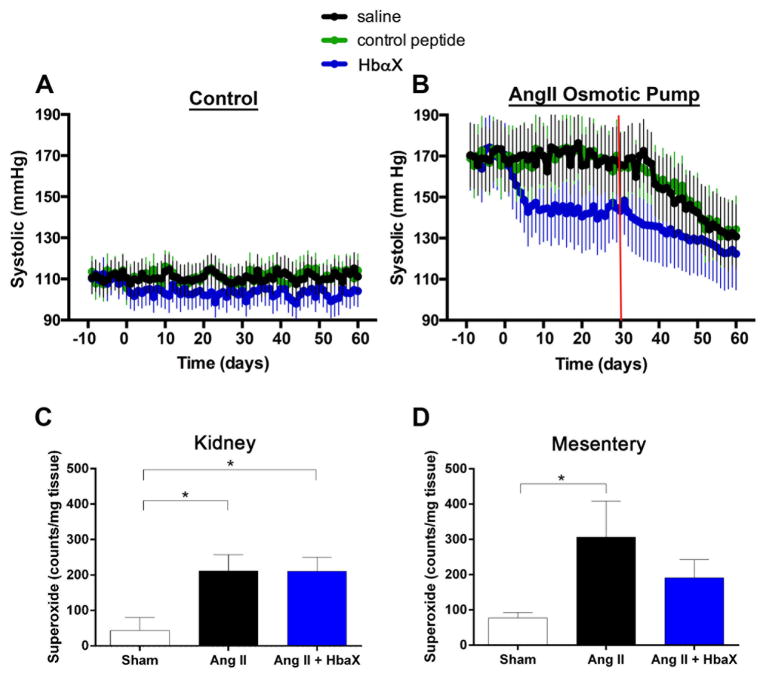
Figure 2. Sustained decrease in systolic blood pressure with HbαX.
Either normotensive mice (A: N=4) or mice with osmotic pumps loaded with AngII (B: N=4) were injected every other day starting at day 0 with saline (black), a scrambled control peptide (green; 5 mg/kg) or HbαX (blue; 5 mg/kg) and systolic blood pressure via radiotelemetery was obtained daily. A baseline was measured for 10 days prior to the start of injections. Red line in B denotes approximate end of AngII infusion due osmotic pump lifetime. Superoxide production from kidney (C) and mesenteric (D) tissues was assayed from mice with AngII pumps and HbαX injections (n=3) or saline injections (n=3), or receiving sham surgery (n=4).