Abstract
Enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis (ETBF), a human commensal and candidate pathogen in colorectal cancer (CRC), is a potent initiator of IL-17-dependent colon tumorigenesis in MinApc+/-mice. We examined the role of IL-17 and ETBF on the differentiation of myeloid cells into myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC) and tumor-associated macrophages (TAM), which are known to promote tumorigenesis. The myeloid compartment associated with ETBF-induced colon tumorigenesis in Min mice was defined using flow cytometry and gene expression profiling. Cell sorted immature myeloid cells were functionally assayed for inhibition of T cell proliferation and iNOS expression in order to delineate MDSC populations. A comparison of ETBF infection to that of other oncogenic bacteria (Fusobacterium nucleatum or pks+ E. coli) revealed a specific, ETBF-associated colonic immune infiltrate. ETBF-triggered colon tumorigenesis is associated with an IL-17-driven myeloid signature characterized by subversion of steady-state myelopoiesis in favor of the generation of protumoral monocytic (MO)-MDSCs. Combined action of the Bacteroides fragilis enterotoxin BFT and IL-17 on colonic epithelial cells promoted the differentiation of MO-MDSCs, which selectively upregulated Arg1 and Nos2, produced NO and suppressed T cell proliferation. Evidence of a pathogenic inflammatory signature in humans colonized with ETBF may allow for the identification of populations at risk for developing colon cancer.
Keywords: Enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis, myeloid derived suppressor cells, tumor microenvironment, tumor-promoting inflammation, Fusobacterium nucleatum, pks+E. coli
Introduction
Enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis (ETBF) is a human colonic symbiotic anaerobe prevalent in up to 50% of the general population. Emerging data suggests a link between ETBF and inflammatory bowel disease as well as colorectal cancer (CRC)(1-3). Consistent with these observations, we recently demonstrated that colonization of MinApc716/+ (Min) mice with ETBF triggered Th17-dependent colon tumorigenesis(4).
The murine ETBF Min model mirrors several critical features of human CRC including altered APC/β-catenin signaling, a predominant distal localization of colon tumors and accurate reproduction of the pathogenic role of overt Th17 responses in human CRC(5,6). Recently, IL-17 was shown to orchestrate the selective accumulation of CXCR2+ myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC) at inflammatory sites and the tumor microenvironment (TME) via promotion of CXCR2 ligand expression by epithelial and tumor cells under stress(7). He et al. described that tumor growth inhibition in IL-17R-deficient mice or via IL-17 neutralizing antibody treatment was due to reduced MDSC infiltration and increased numbers of intra-tumoral cytotoxic CD8+ T cells(8). In a model of carcinogen-induced de novo tumorigenesis, Wang et al. showed that IL-17 activated STAT3 through IL-6, and an IL-6-STAT3-dependent pathway regulated the expression of several inflammatory mediators (e.g. CXCL1, S100A8/9, Cox2 and IL-1β)(9). Notably, these cytokines have in common the ability to act specifically on immature myeloid cells (IMC) and may contribute to shifting steady-state myelopoiesis towards the generation of MDSC.
Together with regulatory T cells, MDSC mobilization to tissues in response to inflammatory stimuli represents a homeostatic mechanism designed to limit collateral damage(10). Cancer via its associated inflammatory microenvironment and cytokine milieu can alter the steady-state maturation and differentiation of mobilized IMCs, including monocytes (MO), macrophages (MΦ), dendritic cells (DC) and/or polymorphonuclear (PMN) cells, resulting instead in the generation of procarcinogenic myeloid cell populations, most importantly MDSCs(11,12).
Despite being phenotypically and functionally heterogeneous, MDSCs are derived from a common myeloid lineage and share a capacity for immune modulation(11). The two main subsets of MDSCs are defined as granulocytic (PMN; CD11bhiGr-1hiLy6CloLy6G+) and monocytic (MO; CD11bhiGr-1lowLy6ChiLy6G-) MDSCs(13). In contrast to IMCs, which are not immunosuppressive at steady state, MDSCs respond to inflammatory cytokines, i.e. IFN-γ, IL-4, IL-13, as well as various danger signals – including TLR ligands – with activation and deployment of immunosuppressive effector functions(14), including nitric oxide (NO), reactive oxygen species (ROS), and arginase 1 (ARG1)(15), a potent metabolic enzyme capable of inhibiting T cell responses. Several transcription factors critical to MDSC function have been identified, the most prominent are proteins of the STAT family as well NF-kB(11). Nonetheless, available data suggest the existence of other, as yet unrecognized, signaling pathways and transcriptional regulators critical to the immunosuppressive activity of MDSCs(16).
In light of these data, we hypothesized that ETBF inflammation and the ensuing high-levels of IL-17 production(4,7,17) act to disrupt normal myelopoiesis and result in the accumulation of procarcinogenic MDSCs in the TME. Our findings suggest that in contrast to the non-colitogenic Fusobacterium nucleatum (18) or the T cell-independent pks+ Escherichia coli(19), ETBF oncogenesis requires the coordinated action of its toxin, BFT and an IL-17-driven inflammatory response to orchestrate the recruitment of myeloid cells to the TME, as well as their differentiation and activation into immunosuppressive MDSCs, specifically, iNOShi MO-MDSCs. We propose herein that ETBF-triggered colon tumorigenesis is characterized by a specific immune signature combining IL-17-driven colitis and altered myeloid differentiation into MO-MDSC.
Results
ETBF specifically promotes the accumulation of immature monocytic cells in colon tumors of Min mice
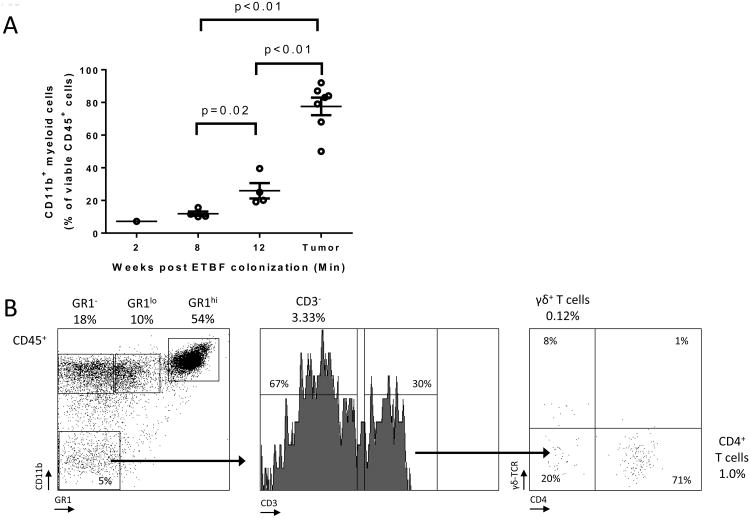
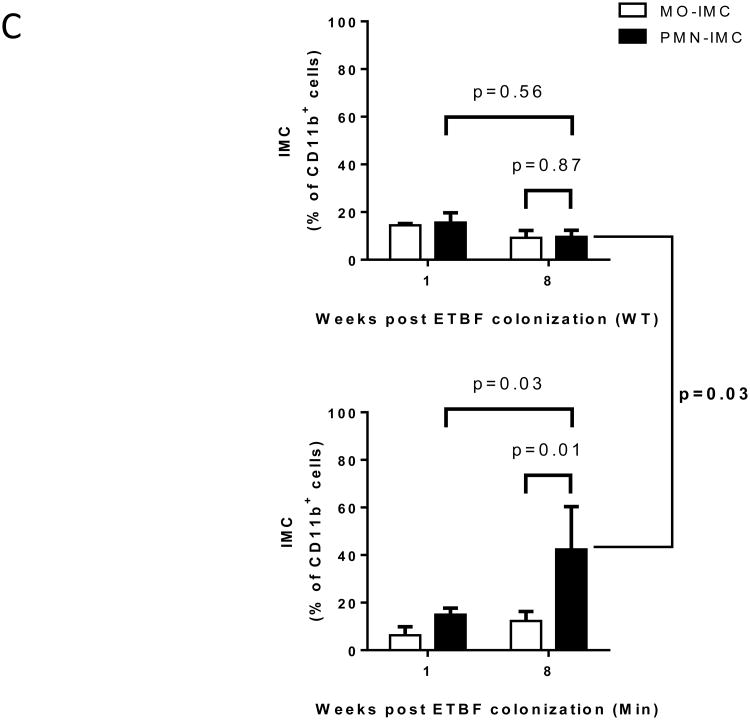
CD11b+ myeloid cells accumulated progressively over time in the distal colon of ETBF Min mice and at 3 months made up 77.6±5.4% (mean±SEM, n=3 experiments) of the tumor-infiltrating CD45+ leukocytes (Fig.1A) or 6.5±1.5% of all viable epithelial and hematopoietic cells. Thus, myeloid cells constituted the overwhelming majority of hematopoietic cells that infiltrated colon tumors in Min mice after 3 months of ETBF colonization. Among CD45+ leukocytes, three main groups of CD11b+ myeloid cells comprised the ETBF colon TME: macrophages (MΦ) (Gr-1-, 25±7.1%), monocytic (MO)-IMC (Gr-1low or Ly6ChiLy6G-, 11.8±1.7%) and granulocytic (PMN)-IMC (Gr-1hi or Ly6CloLy6G+, 45.3±7.9%) populations (all mean ± SEM, n=3 experiments, representative flow cytometry plots are shown in Fig.1B). CD4+ T cells and γδ+ T cells, the predominant sources of protumoral IL-17(4,20), made up only 1% and 0.1% of all CD45+ cells, respectively (Fig.1B). When comparing myeloid cell infiltration in the distal colon between C57BL/6 wildtype (WT) and Min mice, we noticed that IMCs were readily detectable in both strains at 1 week following infection (Fig.1C). However, with persistent ETBF colonization, IMCs – especially PMN-IMCs – accumulated in higher numbers in Min mice, while in WT, myeloid populations regressed by 8 weeks. To assess whether these observed differences were due to differential Apc function in Min versus WT mice, we addressed whether the Apc mutation affected the hematopoietic cell compartment in Min mice. For this purpose, lethally irradiated Min mice were reconstituted with WT or Min bone marrow (BM), challenged with ETBF and assessed for tumor numbers. As displayed in Fig.S1B, we found no significant difference between WT and Min BM-engrafted recipient Min mice, implying that Apc heterozygosity in the hematopoietic compartment does not impact tumorigenesis. This result suggests that the local myeloid environment is shaped by Apc loss of heterozygosity (LOH) in colonic epithelial cells (CEC) in conjunction with ETBF colonization of the colon.
Figure 1. Myeloid cells are the predominant leukocytic population infiltrating ETBF-induced colon tumors in Min mice.
A, Myeloid cells from enzymatically digested grossly normal distal colon tissue (weeks 2, 8 and 12 after ETBF colonization) and distal colon tumors (12 weeks post ETBF) were analyzed by CD45/CD11b staining and flow cytometry. Results are expressed as percent (%) of CD11b+ cells among viable CD45+ leukocytes. Aggregate data of n=7 independent experiments with pooled colon or tumors samples from 3-4 mice/experiment.
B, Flow cytometry of ETBF-triggered colon tumors in Min mice. Percent CD45+ cells are indicated. Representative plots of n=3 or more experiments with 3-4 mice/experiment.
C, Proportion of Ly6ChiLy6G- monocytic immature myeloid cells (MO-IMC) (white bars) and Ly6CloLy6G+ granulocytic (PMN)-IMC (black bars) as percent of CD11b+ isolated from distal colon of WT (top) or Min (bottom) mice at the time points indicated. Of note, IMC in distal colon tissue of sham Min mice were below the limit of detection. Aggregate data of n=4 independent experiments with pooled colon samples from 3 mice/group.
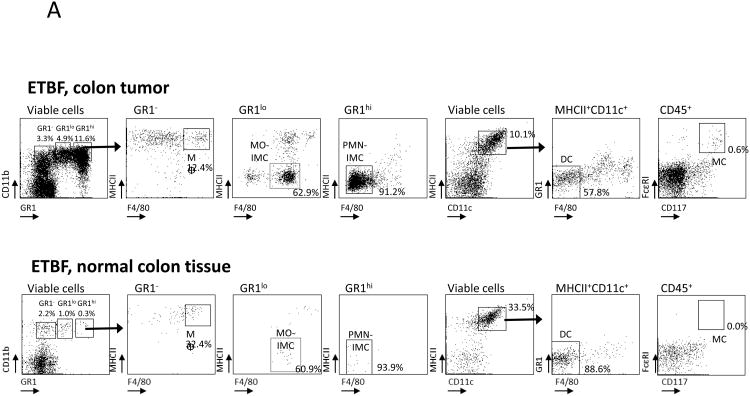
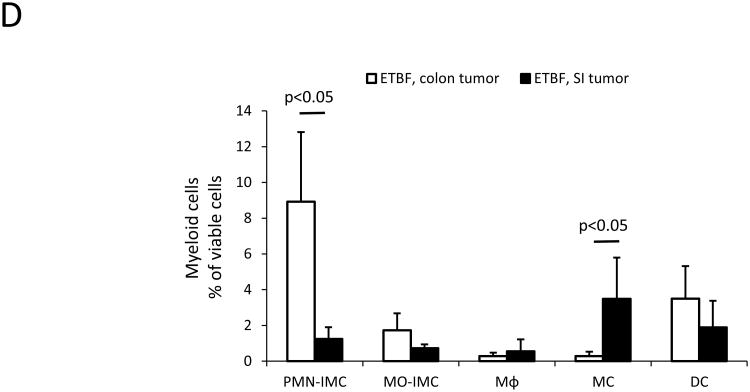
We previously demonstrated that ETBF stably colonizes the colon, but not the small intestine (SI), yielding markedly induced colon tumorigenesis in Min mice, localized predominantly to the distal colon (Fig.S1)(4). In contrast, SI tumorigenesis, a characteristic of parental Min mice, is unchanged upon ETBF colonization(4). We examined the myeloid compartment present in SI (ETBF-independent) and colon (ETBF-dependent) tumors as well as normal adjacent tissue by flow cytometry and microscopic analysis. We distinguished MΦ (CD11b+F4/80+MHC-II+Gr-1-CD11c-/lowSSCint), dendritic cells (DC, CD11chiMHC-IIhiSSClow), mast cells (MC, CD11b-FcεRI+CD117(c-kit)+), MO-IMCs (CD11b+Gr-1lowF4/80lowCD11c-/lowMHC-II-/+SSClow) and PMN-IMCs (CD11b+Gr-1hiF4/80-CD11c-MHC-II-SSChi) (Fig.2A-C). FSC/SSC analysis (Fig.2B) and Wright-Giemsa staining performed on PMN-IMC and MO-IMC sorted from ETBF-induced colon tumors confirmed their distinct morphologies (Fig.2C). Notably, although developing concomitantly in ETBF-colonized Min mice(4), the SI- and colon tumor-associated tumor microenvironment (TME) had distinct myeloid infiltrates (Fig.2D). MC were present in SI tumors but sparse in colon tumors (3.5±2.3% in SI versus 0.3±0.2% in colon, p<0.05, mean±SEM) and PMN-IMCs were significantly more common in colon than in SI tumors (8.9±3.9% in colon versus 1.2±0.6% in SI, p<0.05, mean±SEM). The normal tissue adjacent to colon tumors was characterized by a robust population of CD11chiMHC-IIhi DC (29.7% of viable cells in normal vs. 5.8% in ETBF tumors, Fig.2A).
Figure 2. Characterization of the myeloid compartment in ETBF-colonized Min mice.
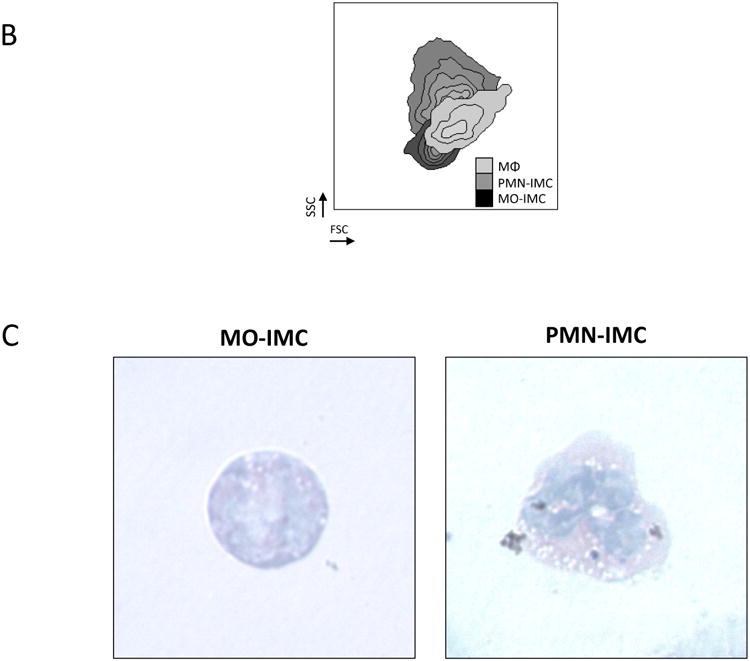
A, Flow cytometry of distal colon tumors (top) as well as adjacent grossly normal colon tissue (bottom) isolated from 3 month ETBF-colonized Min mice. CD11bhiGr-1lowMHC-IIloF4/80-/low MO-IMCs; CD11b+Gr-1hiMHC-IIloF4/80-/low PMN-IMCs; CD11b- FcRεI+CD117+ mast cells (MC); CD11b+Gr-1-F4/80+ macrophages (MΦ); CD11chiMHCIIhiGr-1-F4/80- dendritic cells (DC) are shown. In normal colon tissue, only MΦ and DC populations are readily detected since only few MO- and PMN-IMC are normally present in the lamina propria. Representative plots of n=3 or more experiments with 3-4 mice/experiment.
B, Representative forward scatter (FSC) and side scatter (SSC) of the predominant myeloid populations, i.e.: PMN-IMCs (CD11bhiGr-1hi), MO-IMCs (CD11bhiGr-1low) and MΦ (CD11bhiGr-1-F4/80+). Representative plot of n=3 or more experiments with 3-4 mice/experiment.
C, Wright-Giemsa staining of cytospin-fixed MO-IMC (left) and PMN-IMC (right), FACS-sorted as Ly6ChiLy6G- MO-IMC and Ly6CloLy6G+ PMN-IMC, respectively. Representative images of n=2 independent samples from one cell sorting experiment with tumor samples from 2-3 mice.
D, Proportions of myeloid cell subsets in ETBF-triggered distal colon tumors versus ETBF-independent small intestine (SI) tumors as defined by the gating strategy outlined in A. Bars represent mean±SEM of n=5 and n=3 independent experiments with 3-4 mice/experiment for colon and SI tumors, respectively.
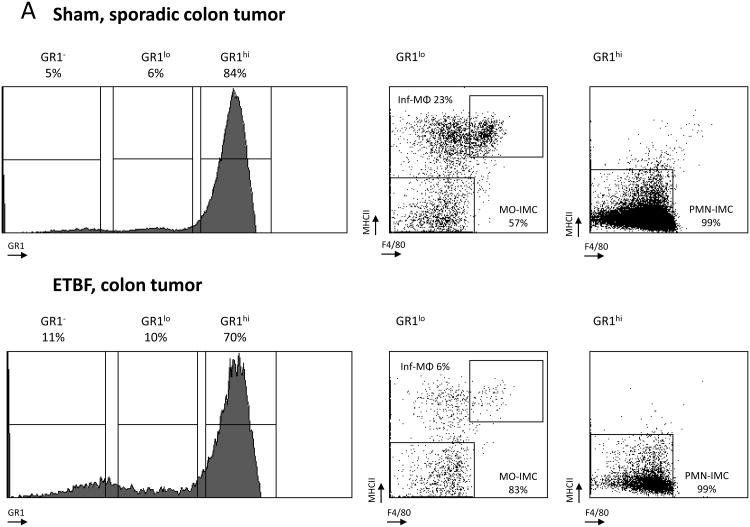
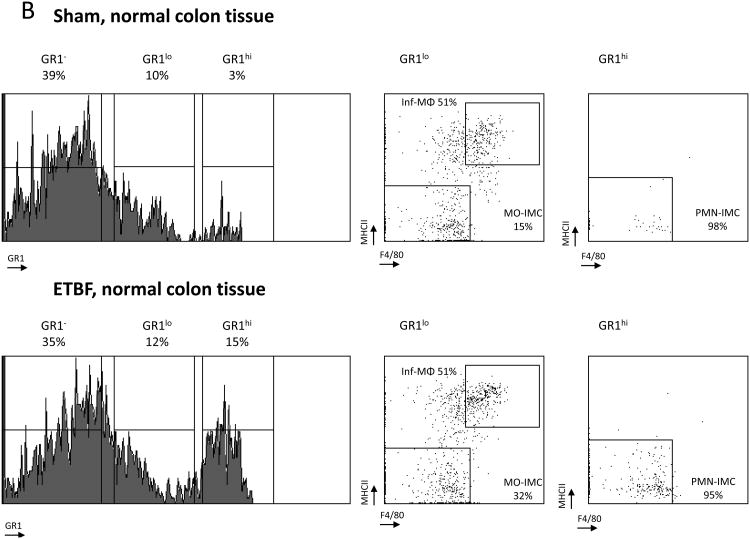
Subsequent comparison of the myeloid environment in colon tumors of ETBF-colonized versus sham Min mice provided evidence of altered myeloid differentiation in direct response to ETBF colonization (Fig.3A,B). Both the rare, sporadically-occurring colon tumors in sham Min mice and the abundant colon tumors in ETBF Min mice were highly infiltrated by PMN-IMCs (Gr-1hi; 84% versus 70% of CD11b+ cells in sham and ETBF tumors, respectively), which in grossly normal colon tissues constituted only a minor population (3% and 15% of CD11b+ cells in sham and ETBF-colonized Min mice, respectively) (Fig.3A,B). Combined with the time-dependent attrition of myeloid cells from the distal colon of WT mice colonized with ETBF (Fig.1C), this result suggests a likely ETBF-independent but Apc LOH dependent signal affecting myeloid cell differentiation in the TME of Min mice.
Figure 3. ETBF colonization promotes specific accumulation of MO-IMCs to the colon TME.
A, B, Flow cytometry analysis of myeloid cells in sporadic (sham) or ETBF-induced colon tumors (A) compared to normal colon tissue (B) in Min mice. Histograms represent Gr-1 expression on viable CD11b+ cells (% CD11b+ indicated). Dot plots represent F4/80 and MHC-II staining in CD11b+Gr-1low (left) and CD11b+Gr-1hi cells (right). Gr-1low encompasses inflammatory(inf) MΦ (MHC-IIhi F4/80hi) and MO-IMC (MHC-IIlow-int F4/80int) cell types whereas Grhi consists predominantly of PMN-IMCs (MHC-IIlow F4/80low). Representative plots of n=5 independent experiments with 2-4 mice/group. Additional representative flow cytometry plots are shown in Fig S8.
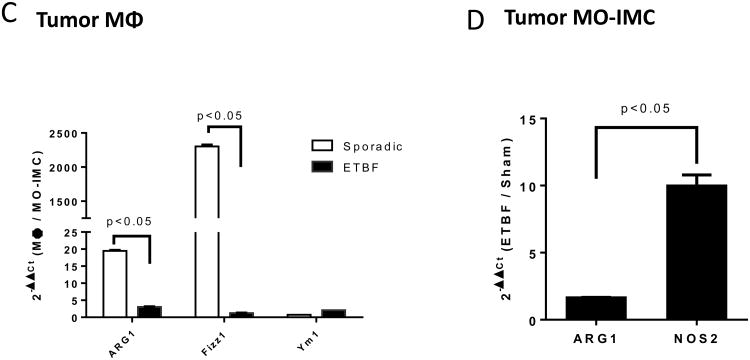
C, Arg1, Fizz1 and Ym1 expression in Inf-MΦ(1-3) versus MO-IMCs FACS-sorted from sporadic or ETBF tumors. Bars represent fold increase of gene expression in inflammatory MΦ compared to MO-IMCs, RQ (2-∆∆Ct(MΦ/MO-IMCs)). Aggregate data of n=2 independent samples from one cell sorting experiment with tumor samples from 2-3 mice/group.
D, Arg1 and Nos2 expression in MO-IMCs FACS-sorted from ETBF-induced colon tumor versus MO-IMCs from sporadic (sham) colon tumors. Bars represent fold increase of gene expression in ETBF compared to sham colon tumors, RQ (2-∆∆Ct(ETBF/Sham)). Aggregate data of independent samples from one cell sorting experiment with tumor samples from 2-3 mice/group.
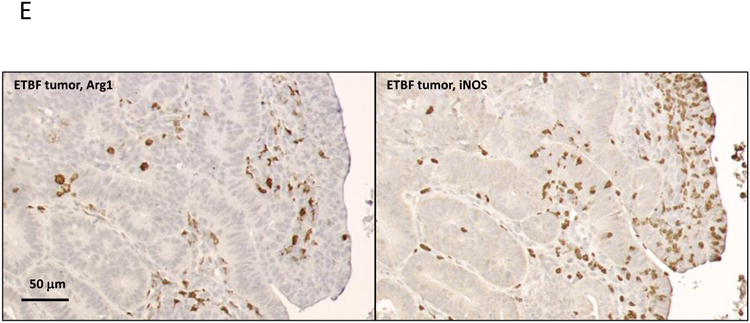
E, IHC expression of Arg1 (left) and iNOS (right) in ETBF-induced colon tumors. Scale bar: 50 μm. Representative images of n=3 or more independent experiments with 3-4 mice/experiment.
Sporadic, but not ETBF-induced tumors, were highly infiltrated by inflammatory MΦ (Inf-MΦ) expressing high levels of F4/80 and MHC-II (23% vs. 6% of CD11b+Gr-1low cells, respectively). MO-IMCs, on the other hand, accumulated markedly in ETBF but less so in sporadic colon tumors (83% vs. 57% of CD11b+Gr-1lowMHC-II-F4/80- cells, respectively, Fig.3A). Further, Inf-MΦ isolated from sporadic colon tumors over-expressed Arg1 and Fizz1 (though not Ym1), hallmarks of protumoral M2 MΦ (Fig.3C)(11), whereas ETBF tumor-derived MO-IMCs strongly upregulated Nos2 (encoding iNOS) but not Arg1 mRNA (×10 and <×2, respectively) compared to MO-IMCs isolated from sporadic colon tumors (Fig.3D). Gene expression profiling revealed that sparse Inf-MΦ (6%; Fig.3A) in ETBF-Min tumors expressed H2-ab1 (encoding MHC-II), Csf1r (encoding M-CSF), Il12b and Emr1 (encoding F4/80) (Fig.S2), indicating a terminally differentiated state but with lower expression of M2 markers compared to those in sporadic colon tumors (Fig.3C). Moreover, ETBF-associated MO-IMCs upregulated genes such as Ido1, Mmp9, S100a8/9, bearing resemblance to the transcriptional activity of MDSCs (Fig.S2). Lastly, IHC demonstrated that ARG1 and iNOS proteins did not co-localize in colon tumors of ETBF-colonized Min mice (Fig.3E) and therefore may delineate different myeloid effectors (M2-like MΦ versus MO-IMC). Taken together, these findings demonstrate that the specific accumulation of iNOS-expressing MO-IMC is a unique feature of the inflammatory microenvironment of colon tumors induced by ETBF. In SI tumors (ETBF-independent) (Fig.2D) as well as sporadic colon tumors (no ETBF colonization) (Fig.3A), levels of MO-IMCs are comparatively low.
Intratumoral but not peripheral MO-IMC are immunosuppressive in ETBF Min mice
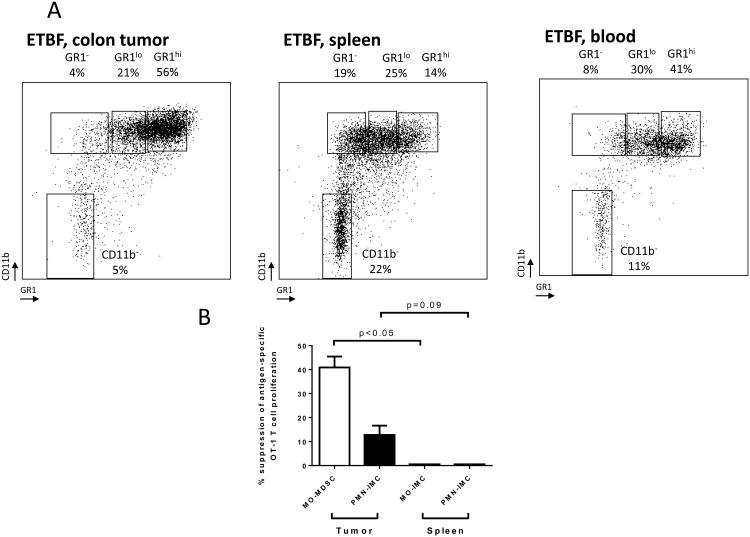
We sought to determine if the distinct population of ETBF colon tumor-associated iNOShi MO-IMCs displayed an immunosuppressive phenotype in accordance with their gene expression profile (Fig.3D). Although both MO- and PMN-IMCs were detected in the spleen, blood and colon tumors of ETBF tumor-bearing Min mice (Fig.4A), only colon tumor-associated MO-IMCs were immunosuppressive when assayed in vitro for inhibition of OVASIINFEKL-specific CD8+ T cell (OT-1) proliferation (40.9±4.5% of inhibition, mean±SEM, n=3 mice/group; Fig.4B). Comparatively, PMN-IMCs exhibited only very modest immunosuppressive activity on OT-1 cell proliferation (12.8±3.9%, as above). Thus, the distinct MO-IMC population associated with ETBF colon tumors resemble MO-MDSCs and will be so named henceforth.
Figure 4. Colon tumor-infiltrating myeloid cells are myeloid derived suppressor cells (MDSC).
A, Flow cytometry analysis of tumor, spleen and blood-derived myeloid cells in ETBF-colonized Min mice. Percent CD45 are indicated. Representative plots of n=3 or more experiments.
B, MO-MDSCs and PMN-IMCs (in tumors) and IMCs (in spleen) were cell-sorted from ETBF Min mice. Inhibition of proliferation of CFSE-labeled OVASIINFEKL-specific transgenic CD8+ T cells (OT-1) by MDSCs (T cell:IMC ratio 10:1) was measured by dilution of CFSE using flow cytometry. Independent samples from one cell sorting experiment with n=3 mice.
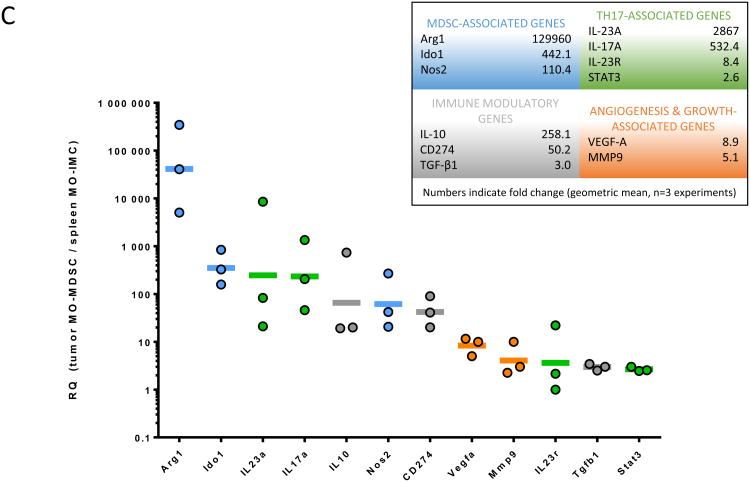
C, Gene expression array in MO-MDSCs (in tumors) or MO-IMCs (in spleen) of 3 month ETBF Min mice. Select genes are grouped according to biological function. Lines represent geometric mean of fold increase of gene expression (RQ) in tumor MDSCs versus spleen IMC. Dots represent RQ values from individual cell sorting experiments. Aggregate data of n=3 independent experiments with pooled tumor samples of 3-4 mice/experiment.
D, In vitro derived MO-IMC were adoptively transferred into Min mice with established colon tumors (2 months post ETBF colonization). 7 days after transfer, MO-IMC were harvested from spleen or colon tumors and Nos2 and Arg1 gene expression was analyzed. Ct values were normalized with CtGapdh (∆Ct=Ct-CtGapdh) and bars represent 2-∆Ct. Aggregate data of n=2 independent experiments with 2-3 mice/experiment. nd=not detected.
We next chose to compare the transcriptomes of splenic MO-IMCs and intratumoral MO-MDSCs (3 month post ETBF colonization) to probe the mechanism behind the CD8+ T cell suppression we observed. The expression of genes of interest was quantified using Taqman qPCR. As shown in Fig.4C, when compared to splenic MO-IMCs from ETBF-colonized mice, intratumoral ETBF MO-MDSCs exhibited a higher expression of Arg1 (×129,960) and Nos2 (×110), known to be central to arginine metabolism and Ido1 (×442), which mediates the degradation of tryptophan. These metabolic pathways are all well established as key players involved in the suppression of T cell responses(13,14,21). Il10 (×258), Cd274 (PD-L1, ×50) and Tgfb1 (×3) – known to contribute to inhibiting anti-tumor immunity in the TME(22) – were also highly expressed in ETBF tumor MO-MDSCs. Il23a, a promoter of Stat3 activation and Th17 differentiation, was strongly upregulated (×2,867). Finally, intratumoral ETBF MO-MDSCs overexpressed Stat3 (×3), Vegfa (×9) or Mmp9 (×5), genes involved in tumor growth and angiogenesis. Intratumoral PMN-IMC also displayed an immunosuppressive transcriptome (Fig.S3A). However, despite stark differences in their in vitro inhibitory capacities (Fig.4B), a direct comparison of TME-resident MO-MDSC and PMN-IMC showed no major differences in transcriptional programs (Fig.S3B), with the exception of the genes CCR2 (chemokine receptor mediating myeloid trafficking) and Il6 (protumoral cytokine via Stat3 activation), which were both upregulated only in MO-MDSC. Collectively, these results support the conclusion that ETBF induces a distinct population of immunosuppressive, protumoral MO-MDSCs in the colon TME, which are predicted to play a key role in ETBF-induced inflammatory carcinogenesis.
As recently reported, we found that Il17a was expressed in intratumoral ETBF MO-MDSCs but not splenic MO-IMCs (Fig.4C)(20). We ruled out contamination by Il17a derived from T cells (including CD4+, CD8+, γδ+, NKT cells) by flow cytometry (Fig.S4) and Cd3e qPCR (data not shown). However, although Il17a gene expression appeared to selectively delineate intratumoral MDSC (especially MO-MDSCs) (Fig.S5A), IL-17 protein was not detected by intracellular cytokine staining(20). Nonetheless, Il17a expression by MO-MDSCs correlates with their selective activation in the TME: when comparing gene expression 7 days after ETBF colonization in MO-MDSC and MO-IMC harvested from Min or WT mice respectively, we found IL-17 to be differentially regulated between groups, and highly expressed only in Min (×146, Fig.S5B). T cells isolated from Min versus WT mice displayed only modestly greater IL-17 expression (×5). Additional transcription factors that typically regulate Il17a transcription, such as Rorc, Il23r and Irf4, were detected in ETBF day 7 Min colon lamina propria-infiltrating MO-MDSCs at levels comparable to those found in infiltrating T cells (Fig.S5B), with the exception of Rorc, which was markedly increased only in MO-MDSCs isolated from Min distal colon (×596). IL-17 and Rorc expression, together with that of Nos2, may constitute activation markers specifically identifying ETBF-associated tumor MO-MDSCs.
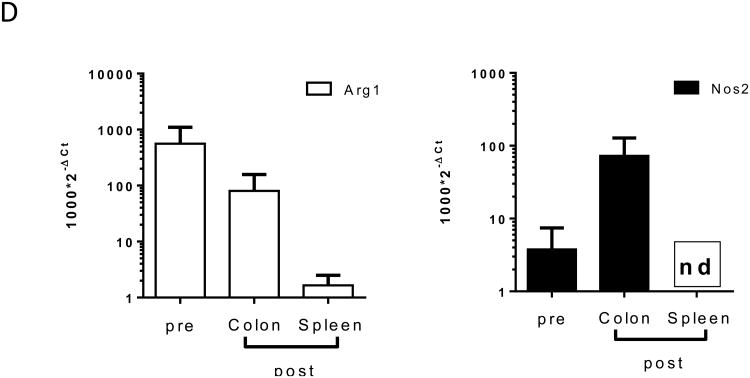
To further confirm the ability of the ETBF-associated TME to polarize IMCs towards MO-MDSCs, we adoptively transferred WT CD45.1+ BM-derived MO-IMCs into 2-month ETBF-colonized or sham-inoculated CD45.2+ Min mice. We compared the gene expression profile of CD45.1+ BM-derived MO-IMCs before and 7 days after transfer, when they were cell-sorted from spleen and colon tumors of the recipient mice. Nos2 was strongly upregulated in adoptively transferred cells isolated from colon tumors, but not spleen, of the ETBF Min recipients. Arg1 expression declined compared to pre-transfer BM-derived MO-IMCs (Fig.4D), consistent with data in Fig.3D.
In summary, our findings demonstrate that the ETBF-associated colon TME in Min mice uniquely promotes the differentiation to and recruitment of iNOShi MO-MDSCs (also marked by Il17a and Rorc expression), which are characterized by the capacity to suppress T cell responses as well as to provide tumor growth, pro-angiogenesis and pro-inflammatory factors.
Endogenous IL-17 mobilizes and activates MDSCs during de novo ETBF-induced colon tumorigenesis
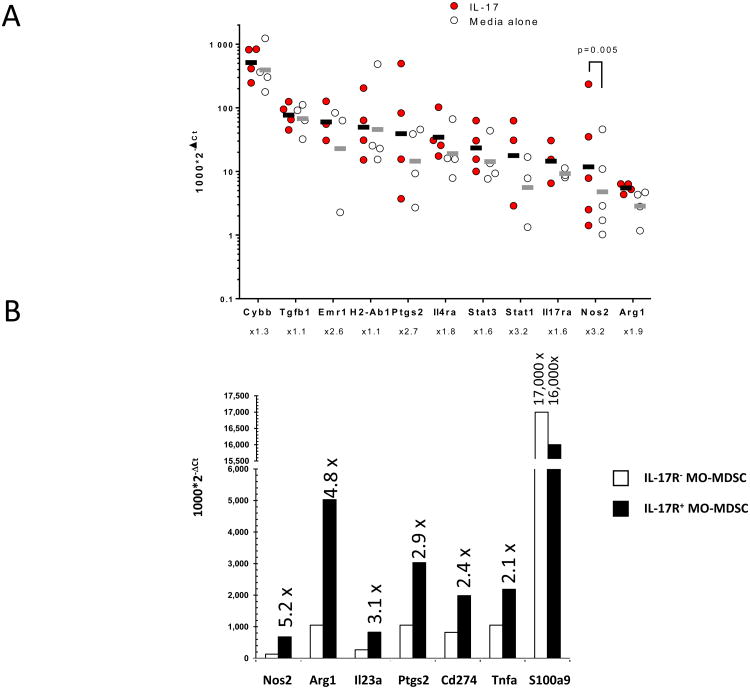
We next sought to identify tumor-associated signals accounting for MO-MDSC recruitment and their activation in ETBF-induced colon tumors. Since we previously demonstrated that IL-17 is critical to ETBF-triggered colon carcinogenesis and the accumulation of protumoral MDSCs in the TME was recently attributed to IL-17(4,7,17,23), we postulated that intratumoral IL-17 was, at least in part, responsible for the selective accumulation and activation of pro-carcinogenic iNOShi MO-MDSCs in the colon tumors of ETBF-colonized Min mice. To test this hypothesis, we demonstrated that IL-17R-expressing MO-MDSCs (Fig.4C) sorted from colon tumors of ETBF Min mice could be activated in response to recombinant IL-17 (rIL-17). Crucially, the ETBF TME is IL-17-rich and purified MO-MDSC are likely pre-conditioned, therefore the response to exogenous IL-17 may be suppressed. Notwithstanding, ex vivo treatment of purified MO-MDSCs with rIL-17 induced significant upregulation of Nos2 and modest upregulation of Arg1, genes involved in T cell immunosuppression (Fig.5A). In addition, we observed a trend to upregulate Stat3, which is strongly associated with protumoral activity, as well as proinflammatory genes such as Cybb (encoding NOX2), Ptgs2 (encoding COX2) or Stat1, in response to rIL-17 treatment. Notably, as shown in Fig.4C and Fig.S2, many of these genes were also overexpressed in vivo in ETBF tumor-derived MO-MDSCs. In contrast, splenic MO-IMCs isolated from ETBF-colonized Min mice were unable to upregulate Arg1 or Nos2 in response to rIL-17, despite comparable IL-17ra mRNA expression (data not shown), suggesting the notion that additional ETBF-driven mucosal (i.e. CEC or TME-derived) signals act in concert with IL-17 to promote protumoral and immunosuppressive MDSCs. Consistent with this idea, the upregulation of IL-10 and IL-23 gene transcription in vivo together with that of Stat3 underscored the likely contribution of paracrine feedback signaling on the expression of STAT3 (i.e. STAT3 activation is downstream of the IL-10 and IL-23 receptors), and suggests that STAT3 may serve as an important signal transducer of IL-17-mediated MDSC activation(9,24).
Figure 5. IL-17-induced protumoral transcriptomes in tumor-infiltrating MO-MDSC.
A, Tumor MO-MDSCs sorted from ETBF Min colon tumors were incubated overnight with rIL-17 (10 ng/ml) and gene expression was assessed by qPCR. Lines represent geometric mean of 2-∆Ct in MO-MDSCs cultured with IL-17 compared to medium alone. Dots represent 2-∆Ct values from individual cell sorting experiments. Fold increase of gene expression are indicated below gene labels. Increase of Nos2 expression in IL-17-treated cells was significant with p=0.0055 (ratio paired t test). Aggregate data of n=3-4 independent experiments with 2-3 mice/experiment.
B, Ex vivo gene expression in CD45.2+IL-17R- MO-MDSCs (white bars) and CD45.1+IL-17R+ MO-MDSCs (black bars) sorted from colon tumors of 2 month ETBF-colonized [CD45.2+IL-17R-/CD45.1+IL-17R+] mixed bone marrow (BM) chimera Min mice. Bars represent 2-∆Ct. Fold increase of gene expression between CD45.1+IL-17R+ vs. CD45.2+IL-17R- MDSCs are indicated above the black bars. Representative data of independent samples from one cell sorting experiment with n=2 mice.
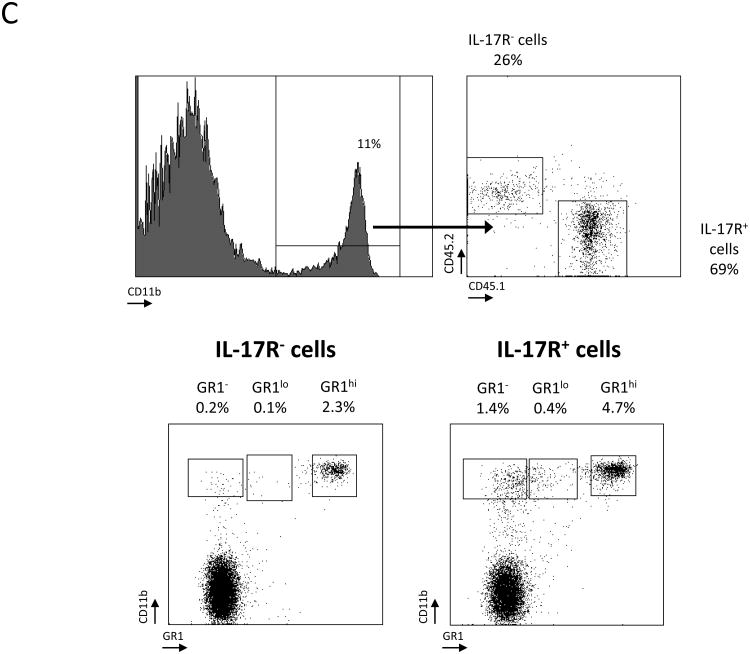
C, Flow cytometry of myeloid populations infiltrating colon tumors of 8 weeks ETBF-colonized mixed BM chimera [CD45.2+IL-17R-/CD45.1+IL-17R+] Min mice. Percentages and phenotype of CD45.2+ (IL-17R-/-) versus CD45.1+ (IL-17R+/+) myeloid populations were compared. CD11b and Gr-1 expression were analyzed in CD45.1+ and CD45.2+ cells independently. Representative plots of n=2 independent experiments with 3-4 mice/experiment.
Further, we found that the enhanced transcriptional activity of Nos2 correlated with increased nitric oxide protein expression: rIL-17 increased in vitro iNOS activity as measured by the production of nitric oxide (NO) in the culture supernatant of LPS-conditioned MO-MDSCs (Fig.S6). Spleen-derived MO-IMC were unable to produce NO upon in vitro stimulation.
Finally, using ETBF-colonized mixed BM chimeric Min mice – generated by reconstituting lethally irradiated Min mice with a 1:1 mixture of CD45.1+IL-17R+/+ and CD45.2+IL-17R-/- BM – we showed that CD45.1+IL-17R+ MO-MDSCs (i.e. sensitive to endogenous IL-17) sorted from colon tumors 10 weeks after ETBF inoculation exhibited a higher expression of Nos2, Arg1, Il23a, Ptgs2 (Cox2), Cd274 (PD-L1) and Tnfa (all IL-17 dependent genes) as compared to CD45.2+IL-17R-/- MO-MDSCs (Fig.5B). Together with our previous identification of many of the same transcripts in MO-MDSCs cultured in vitro with exogenous rIL-17 (Fig.5A), these results demonstrate direct involvement of IL-17 in establishing protumoral MO-MDSCs in the ETBF-induced TME. S100A9, a Stat3-dependent gene responsible for MDSC accumulation and activation(25), was not differentially regulated by IL-17, which signals predominantly through NF-κB, emphasizing that several regulatory pathways act in tandem to fully activate MDSCs.
Interestingly, although decreased in numbers compared to CD45.1+IL-17R+CD11b+ cells, CD45.2+IL-17R-CD11b+ cells were still present in the colon TME (69% CD45.1+ cells versus 26% CD45.2+ cells, respectively; Fig.5C), again implying that signals in addition to the direct action of IL-17 on IMCs coordinated MDSC recruitment to the ETBF colon TME. Nevertheless, the proportions of MO-MDSCs and other myeloid cells subsets (CD45.2+CD11bhiGr-1-), including MΦ and DC, were drastically decreased in IL-17R-deficient tumor-infiltrating CD45.2+ cells compared to cells derived from CD45.1+IL-17R+ hematopoietic progenitors. Notably, the proportion of PMN-MDSC in tumors decreased two fold in the IL-17R-deficient tumor-infiltrating CD45.2+ cells compared to CD45.1+IL-17R+ cells (2.3% to 4.7%, respectively), indicating a similar dependency on IL-17 (Fig.5C). These results highlight the ability of IL-17 to preferentially activate MO-MDSCs in vivo and drive their accumulation to the TME. However, other stimuli act in concert with IL-17 to mold the overall myeloid TME in ETBF-colonized Min mice.
Recruitment of IL-17-driven iNOShi-MO-MDSC constitutes an immune signature of ETBF colon tumorigenesis
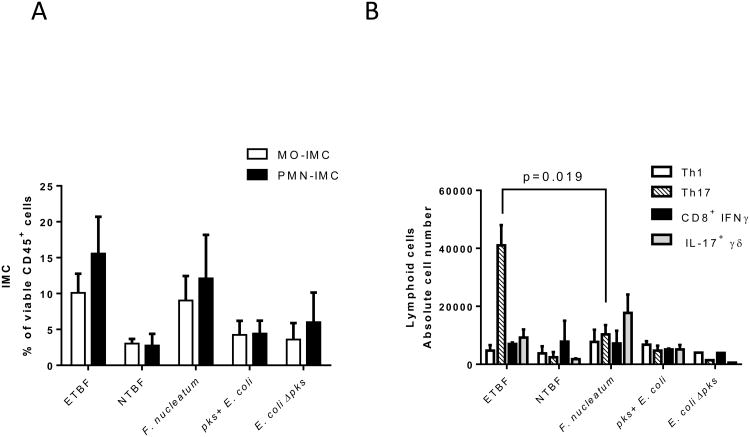
Our final aim was to address whether the myeloid environment that is established upon colonization with ETBF and is associated with ETBF-triggered colon tumorigenesis is specific to ETBF or common among oncogenic bacteria. To test for specificity, we compared ETBF colonization of WT mice with Fusobacterium nucleatum and pks+ E. coli, two bacteria strongly associated with CRC in humans(26) and shown to induce colon tumorigenesis in experimental murine models(18,19). As a control, we used the non-colitogenic Bacteroides fragilis 9349 pfd340 (NTBF) and E. coli lacking the genotoxic pks island (E. coli ∆pks).
Although mice were successfully colonized with each bacterium (Fig.S7), only ETBF and Fusobacterium induced a strong myeloid response upon colonization, which was characterized by an increased proportion of MO- and PMN-IMC in the distal colon by day 7 post-colonization (Fig.6A). This aligns with studies by Kostic et al., who showed an increase of myeloid subsets in small intestinal tumors following daily inoculation of Min mice with Fusobacterium for 8 weeks; colon tissues were not examined(18). It is worth pointing out that the authors used SI tumors as a surrogate for the TME in colon tumors. Per contra, in the context of ETBF infection, SI and colon tumors attract distinct myeloid populations (as shown in Fig.2D).
Figure 6. Mucosal immune response to Fusobacterium nucleatum, pks+ Escherichia coli, ETBF and NTBF colonization in WT mice.
A, Proportion of CD11b+Ly6ChiLy6G- MO-IMC (white bars) and CD11b+Ly6ClowLy6G+ PMN-IMC (black bars) as percent of viable CD45+ leukocytes isolated from distal colon of WT mice one week post-infection with oncogenic bacteria listed along the x-axis.
B, Absolute numbers of Th1 (CD3+CD4+IFNγ+), Th17 (CD3+CD4+IL-17+), cytotoxic T cells (CD3+CD8+IFNγ+) and γδ T cells (CD3+γδ+IL-17+) lymphoid populations isolated from distal colon as described in A.
A & B, Aggregate data of n=2 independent experiments with 3 mice per group.
Infection with pks+ E. coli had little impact on myeloid recruitment, consistent with published findings comparing oncogenic E. coli to control E. faecalis in which neither lymphoid (CD3) nor myeloid (as measured by Ly6B, F480 IHC) responses differed(19). However, and in stark contrast to ETBF(4), no other oncogenic bacterium triggered a predominant production of IL-17 (Fig.6B). Altogether, these results demonstrate that high IL-17 levels in combination with MO-MDSC accumulation may mark the pathogenic interaction of ETBF with colon CEC and be considered as the immune signature of tumorigenic ETBF infection.
Discussion
We show herein that ETBF-triggered de novo colon carcinogenesis in Min mice leads to the specific recruitment and activation of MO-MDSCs. We conclude that ETBF affects the myeloid compartment in two ways. First, ETBF-induced intratumoral IL-17 together with additional factors – likely epithelial-derived – orchestrate the recruitment of myeloid cells to the TME. Second, BFT-driven oncogenesis polarizes the differentiation of IMCs towards MDSCs. We identified an “immune signature” associated with ETBF-driven colon tumorigenesis, defined by high levels of IL-17 and an accumulation of iNOShi MO-MDSCs. This was radically different from the TME observed in ETBF-independent SI tumors, which were more infiltrated by MC and less by MDSCs, or sporadic colon tumors, which presented with a higher proportion of M2 MΦ and few MO-MDSC (Fig.2-3). Finally, among bacteria linked to the etiology of CRC, the immune landscape associated with ETBF infection was unique, affirming the distinct mechanisms via which these pathobionts can initiate and promote tumorigenesis.
Importantly, since ETBF accelerates the tumorigenesis process observed in the colons of Min mice, we cannot formally rule out that the differences in the proportions of MΦ and MO-MDSC between sham and ETBF-triggered tumors was not a consequence of rapid recruitment of IMCs to the ETBF-associated TME rather than of skewed myeloid differentiation related to the inflammatory and metabolic conditions within the ETBF-associated TME. However, the adoptive transfer of BM-derived IMCs demonstrated that they were (1) recruited to the ETBF-associated TME and (2) upregulated Nos2 (Fig.4D) and Il17 gene expression (Fig.S5), hallmarks of MO-MDSC activation in this study. This result supports a specific role of ETBF on altered myeloid differentiation in the TME rather than a kinetic effect. Namely, peripherally injected BM-derived IMCs (iNOSlow) differentiated into intratumoral MO-MDSC (iNOShi) within one week in ETBF-colonized Min mice.
In this study, IL-17 acted as a key inflammatory mediator for myeloid recruitment and polarization. Genetic ablation of IL-17R in the hematopoietic compartment profoundly affected proportions of MO-MDSC in the TME of ETBF Min mice, but did not abrogate myeloid recruitment. Recent studies in human CRC as well as numerous mouse models have proposed that IL-17 is critical for recruitment of MDSCs to the TME(7,8,23,27). However, sporadic colon tumors (that result from Apc deletion but not ETBF activity) are also infiltrated by Th17 cells (unpublished results), though without the accumulation of MO-MDSC, proof that additional ETBF-dependent epithelial signals, yet to be identified, shape local myelopoiesis.
The primary virulence determinant of ETBF is BFT(26). BFT is a metalloprotease that upon binding to a putative colonic epithelial cell receptor triggers cleavage of E-cadherin, thereby releasing E-cadherin-associated β-catenin and consequently activating Wnt (targeting c-Myc and resulting in epithelial proliferation)(28) and, separately, NF-κB (targeting proinflammatory mediators)(29) signaling pathways. BFT-induced production of IL-8 by human colonic epithelial cells, a NF-κB-dependent factor, and its murine homologue, CXCL1, can direct MDSC recruitment(23,30). Herein, we demonstrated that ETBF has the capacity to shape the inflammatory environment differently in CECApc+/- versus WT epithelia (no Apc deletion but intact BFT activity), resulting in a specific immune signature observable in Min colon tissue. In contrast, no sustained accumulation of MO-MDSC was evident in WT mice.
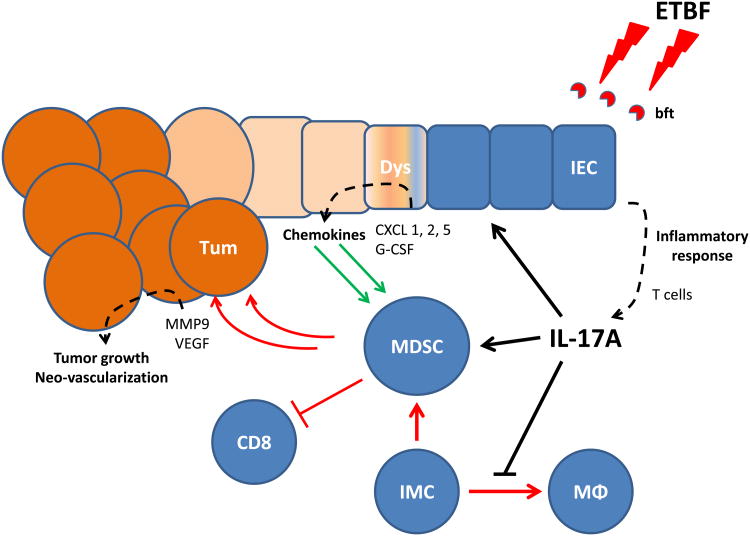
Select bacteria and their virulence factors can shape the colonic mucosal immune response, resulting in “immune signatures” defined by distinct proinflammatory gene expression profiles and the presence of specific immune cell subsets. Fusobacterium nucleatum which is enriched in a subset of colorectal carcinoma tissue samples was suggested to accelerate colon tumorigenesis in Min mice via the polarization of the myeloid compartment in absence of histologic colitis and Th17 activation(18). Similarly, pks+ E. coli strains were shown to promote colon tumorigenesis in the context of experimentally-induced colitis via colibactin, encoded in the pks island with the ability to trigger DNA-damage(19). Our findings herein, together with recently published data, collectively propose that the TME associated with ETBF colon tumors likely results from the combined action of BFT, IL-17 and a permissive genetic background (CECApc-/-)(4,20,31,32). It will be critical to investigate IL-17R-expressing tumor CEC under the influence of IL-17 and BFT, and identify mediators capable of polarizing the myeloid compartment towards protumoral MDSCs (Fig.7).
Figure 7. Proposed model for IL-17 recruitment of MDSCs into colon TME of ETBF-colonized Min mice.
ETBF induces submucosal IL-17 expression, which orchestrates the myeloid environment of ETBF-triggered colon tumors both directly by interacting with myeloid IL-17 receptors and indirectly by further inducing the ectopic production of chemokines and/or growth factors by dysplastic IL-17R+ colonic epithelial cells (CEC). The combined action of IL-17 and transformed CECs drives MDSCs to promote tumor growth via the suppression of immune effector cells, the activation of proliferative pathways (Stat3) as well as the production of proangiogenic mediators (i.e. MMP-9 and VEGF).
How and whether MDSCs, and in particular MO-MDSCs, contribute to ETBF-driven colon tumorigenesis remains unknown. We report here that colon tumor-infiltrating iNOShi MO-MDSCs suppressed antigen-specific CD8+ T cell responses in vitro, suggesting that the selective accumulation of immunosuppressive MO-MDSCs in ETBF-colonized Min mice may account, at least in part, for the development of gross colon tumors. While in vitro inhibition of T cell proliferation is considered a poor surrogate of in vivo immunosuppression, the concomitant gene expression profiling of MO-MDSCs, displaying a strong upregulation of inhibitory metabolic enzymes (Arg1, Nos2 and Ido), immune checkpoint ligands (PD-L1) and soluble mediators (Il10 and Tgfb1) – among other genes – supports our conclusion that tumor-infiltrating MO-MDSCs are potent suppressors of anti-tumor immunity. Furthermore, in the context of intestinal chronic inflammation, by inhibiting Th1 responses and producing high levels of IL-1β, IL-6 (not shown) and IL-23 (Fig.4C), MDSCs in the ETBF TME may contribute to the recruitment of Th17 and amplify IL-17-driven ETBF oncogenesis, while, simultaneously, contributing to the promotion of tumors by enabling an environment permissive for tumor growth and angiogenesis(23). This agrees with recent findings that IMCs are capable of promoting carcinogenesis via mechanisms other than T cell inhibition(33). Further, it supports our observation that ETBF-associated MO-MDSCs were immunosuppressive in vitro even though they did so at fairly modest levels (approximately 40% inhibition of proliferation) compared to suppression levels of 80-90% typically reported for MDSCs(34).
Human and murine observations suggest that long term carriage of ETBF with subclinical colon inflammation may have oncogenic consequences and support the notion that ETBF is novel candidate for initiation/promotion of human colon carcinogenesis. We show herein that a specific IL-17+ MO-MDSC-dominant immune signature was associated with ETBF tumorigenesis. In humans, we postulate that identification of similar immune signatures in ETBF-infected individuals may be predictive of malignant transformation. Longitudinal studies are required to assess if the use of cellular and molecular immune signatures as a biomarker holds promise of identifying individuals at risk for developing cancer, and for whom early eradication of ETBF could possibly prevent oncogenesis.
Methods
Mice and bacteria
C57BL/6 (wild-type, WT), CD45.1 C57BL/6 and MinApc716/+ (Min) mice were purchased from The Jackson Laboratories (Bar Harbor, ME) or obtained from Dr. David Huso (Johns Hopkins University) and bred in the vivarium. OT-1 T cell receptor transgenic RAG-/-mice were bred in-house. Mixed bone marrow (BM) chimeric mice were established by intravenous injection of 107 BM cells from donor mice into lethally irradiated (900 cGy) recipient mice. Unless otherwise stated, n=2-4 mice were used per experimental group, the colon of each mouse was processed independently and, thus, data reflects measurements in individual mice. Mice were maintained according to protocols approved by the Johns Hopkins University Animal Care and Use Committee.
ETBF strain 86-5443-2-2, NTBF strain 9343 pfd340 (4), Fusobacterium nucleatum strain 2432 (provided by Brandon Ellis, Johns Hopkins Medical Microbiology Laboratory), pks+ E. coli strain NC101 and E. coli strain NC101 ∆pks (provided by Dr. Christian Jobin, University of Florida) were used in this study. Mice were challenged at 4-6 weeks of age following per os antibiotic pre-treatment (clindamycin and streptomycin) and harvested at the time points described(4). BM chimeric mice were inoculated 6 weeks after BM engraftment. Fecal samples were cultured periodically post-inoculation to quantify and assure consistent ETBF colonization.
Leukocyte isolation from gut lamina propria, tumors and spleen
Small intestine and distal colon (Fig.S1A) were cut, washed and enzymatically digested (400 U/ml Liberase and 0.1 mg/ml DNAse1; Roche Diagnostics, Indianapolis, IN). Colon and blood leukocytes were isolated using Percoll gradient separation (GE Healthcare Life Science, Pittsburgh, PA). Splenocytes were isolated from Liberase-treated spleen samples using Lymphoprep density gradient (Accurate Chemical & Scientific Corporation, Westbury, NY).
Flow cytometry and cell sorting
Single cell suspensions were stained with Live/Dead Yellow (Life Technologies, Grand Island, NY), CD11b-PerCp/Cy5.5 (M1/70, Biolegend, San Diego, CA), I-A/I-E-AF488 (M5/114.15.2, Biolegend), Gr-1-Pacific Orange (RB6-8C5, Life Technologies), F4/80-PE-Cy7 (BM8, Biolegend), CD11c-APC-Cy7 (HL3, BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA), CD117-PE-Cy5 (2B8, Biolegend) and FcεRI (Mar-1, Biolegend). Ly6-C-Pacific Blue (HK1.4, Biolegend) and Ly6-G-AF647 (1A8, Biolegend) were used in adoptive transfer experiments. For intracellular cytokine staining, cells were stimulated for 4.5 h with 30 nM phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate and 1 μM ionomycin (both eBioscience) in presence of Golgistop (BD). Cells were subsequently stained against cell surface markers (CD4-PerCp/Cy5.5, GK1.5; CD3-AF700, 17A2; CD8-PE/CF594, 53-6.7; all Biolegend) followed by fixation/permeabilization (Cytofix/Cytoperm, BD) and staining using IL-17A-Pacific Blue (TC11-18H10.1, Biolegend). Flow cytometry was performed using a LSRII cytometer (BD) and data were analyzed with FACSDi-Va 6.1.3 software (BD). For cell sorting (FACS) experiments, myeloid populations were sorted using an AriaII cytometer (BD). MO-MDSCs were sorted as CD45+CD3-CD11bhiGr-1lowF4/80-/lowMHC-II-/low, PMN-MDSCs as CD45+CD3-CD11bhiGr-1hiF4/80-MHC-II-, and MΦ as CD45+CD3-CD11bhiGr-1-/lowF4/80hiMHC-II+ cells.
Suppression of antigen-specific proliferation
FACS-sorted IMC were co-incubated with CFSE-labelled OT-1 CD8+ T cells at T cell:IMC ratios of 10:1 or 1:1 in the presence of 1 μg/ml OVASIINFEKL peptide. Irradiated splenocytes were used as source of antigen-presenting cells. Proliferation was measured as dilution of CFSE and assessed by flow cytometry. Inhibition of proliferation was measured as 100 × [1-(%CFSElow OT-1 in co-culture with MDSC / %CFSElow OT-1 alone)].
Nitric oxide assay
FACS-sorted MO-MDSC were cultured for 16 hours in MEM medium alone or in the presence of recombinant mouse IL-17A (Biolegend) and LPS-B5 (Invivogen, San Diego, CA). Culture supernatants were screened for nitric oxide production using a NO detection kit (Enzo, Farmingdale, NY) as per the manufacturer's instructions.
Adoptive transfer of BM-derived IMCs
CD45.1+ BM cells were cultured for 5 days with G-CSF (100 ng/ml), GM-CSF (250 U/ml) and IL-13 (80 ng/ml) (Preprotech, Rocky Hill, NJ). MO-IMCs (CD11b+Ly6ChiLy6Gneg) were cell-sorted as described above and injected into sham Min or ETBF-colonized tumor-bearing Min mice. Cells were recovered from enzymatically digested colon tumors using FACS according to CD45.1, CD11b, Ly6C and Ly6G expression (Fig S9).
Taqman-based PCR array
Expression of 48 target genes by FACS-sorted myeloid populations was measured using Taqman technology-based custom-designed PCR array plates or individual assays following the manufacturer's instructions (Life Technologies). Expression of the genes of interest was normalized to Gapdh expression. Results were expressed as ∆Ct or ∆∆Ct (RQ, relative expression).
Immunohistochemistry
Serial FFPE tissue sections were deparaffinized and antigens retrieved by incubation in citrate buffer. Slides were stained with anti-iNOS (N-20, sc-651, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX) or anti-arginase 1 (LS-B4789, LifeSpan BioSciences, Seattle, WA). Poly-HRP conjugated anti-rabbit IgG (PV6119, Leica) was used as secondary. Sections were analyzed on an EcliPSE E800 microscope (Nikon Corporation).
Cytospin
MO- and PMN-IMC were cell-sorted as described above, fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde and annealed to slides via cytospin (800 rpm for 3 minutes). Slides were subsequently stained with Wright-Giemsa dye to visualize cells. Images were captured as described above.
Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed using the Student t, ratio-paired t, Mann-Whitney U or chi square tests. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. p values <0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Supplementary Material
Figure S1. ETBF Min mouse colons.
A, ETBF-triggered tumorigenesis is prominent in distal colons of Min mice.
B, Colon tumor counts from chimeric Min mice reconstituted with bone marrow from wildtype (C57BL/6) or Min donors. Tumor numbers were assessed at 12 weeks after inoculation with ETBF.
Representative image and graph of n=2 or more independent experiments.
Figure S2. Gene expression analysis in ETBF tumor-infiltrating myeloid cells.
MΦ and MO-IMCs were cell-sorted from 3 month ETBF Min colon tumors as CD11bhiGR1-MHC+F4/80+ and CD11bhiGR1loMHCloF4/80-, respectively. Bars represent fold increase of gene expression (RQ) in MΦ compared to MO-MDSCs. RQ>1, genes are overexpressed in tumor-associated macrophages; RQ<1, genes are overexpressed in MO-IMCs. Genes characterized by RQ>2 and RQ<0.5 are highlighted above and below the graph. Red boxes indicate genes characteristic of differentiated MΦ; green boxes indicate genes characteristic of MO-MDSCs. Representative graph of n=2 independent experiments.
Figure S3A. Gene expression array in PMN-IMCs sorted from colon tumors or spleen of 3 month ETBF Min mice.
Bars represent fold increase of gene expression (RQ) in IMCs sorted from tumors compared to those sorted from spleen. RQ>1 when genes are overexpressed in tumor IMCs; RQ<1 when genes are overexpressed in spleen. Genes characterized by RQ>2 are highlighted. Representative graph of n=2 independent experiments.
Figure S3B Same as in A, however comparing intratumoral MO-MDSCs to PMN-IMCs of 3 month ETBF Min mice. Representative graph of n=2 independent experiments.
Figure S4. Myeloid cell populations (CD11b+GR1hi and CD11b+GR1neg) cell-sorted from colon tumors for IL-17 qPCR were not contaminated by T cells.
Plots represent pre-sort CD3 and CD4 staining in CD11b+GR1hi, CD11b+GR1neg and CD11b- gates used for cell sorting and subsequent Il17a mRNA detection in myeloid cells associated with colon tumors, blood or spleen of 3 month ETBF-colonized Min mice. Representative staining of n=2 independent samples from one cell sorting experiment.
Figure S5. Tumor-infiltrating MDSCs express Il17a gene in colon tumors.
A, PMN-IMCs and MO-MDSCs or MO-IMCs were sorted from tumors, spleen or blood of 3 month ETBF-colonized Min mice. RNA extracted from each cell subset was assessed by qPCR for Il17a gene expression. Mean ± SEM is shown. Ct values were normalized with CtGapdh (ΔCt=Ct-CtGapdh) and bars represent 2-ΔCt. Aggregate data of n=2 independent experiments.
B, Myeloid and lymphoid populations were cell-sorted from C57BL/6 (WT) or Min distal colon lamina propria at day 7 post-ETBF colonization and assessed for Il17a, Rorc, Irf4 and Il23r expression by qPCR. Bars represent fold increased (RQ) between Min and wild type cell populations, RQ=2-ΔΔCt. Representative staining of n=2 independent samples from one cell sorting experiment.
Figure S6. Confirmation of Nos2 gene expression by detection of nitric oxide in culture supernatant of rIL-17-conditioned purified MO-MDSC.
MO-MDSCs cell-sorted from colon tumors or MO-IMCs sorted from spleen in ETBF Min mice were incubated overnight with IL-17 (10 ng/ml) in presence or absence of LPS (100ng/ml). Nitric oxide (NO) was measured in culture supernatants using a colorimetric assay. Lines represent geometric mean. Aggregate data from n=3-4 independent experiments.
Figure S7. Stool culture of oncogenic bacteria to confirm colonization.
Fresh stool samples were collected 7 days after inoculation with F. nucleatum, pks+ E. coli, E. coli ΔPKS, ETBF or NTBF. Samples were homogenized in PBS, serially diluted and cultured on Brucella (F. nucleatum), BHI (ETBF, NTBF) or MacConkey (E. coli) agar under optimal anaerobic or aerobic conditions. Colony forming units were manually counted within 24-48h of culturing.
Figure S8. Additional representative flow plots of MO-IMC, PMN-IMC and Mϕ subsets in sporadically occurring or ETBF-triggered colon tumors, as well as normal colon tissue. As described in Fig. 3A, 3B.
Figure S9. Gating strategy for the recovery of adoptively-transferred in vitro derived BM-MDSC.
A, CD45.1+ bone marrow cells were harvested and MDSCs were derived in vitro by culture with G-CSF, GM-CSF and IL-13 for 5 days. MO-MDSCs were cell-sorted and adoptively transferred to Min recipients previously infected with ETBF (ETBF 11 weeks) via tail-vein injection.
B, Colon tumors were harvested 1 week later (ETBF 12 weeks) and CD45.1+ were recovered and sorted by FACS for RNA extraction and Arg1/Nos2 qPCR analysis.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health through R01CA151325 (CLS), R01CA179440 (CLS), P30CA006973 (SKCCC core), P30DK089502 (GI Center).
Abbreviations
- BFT
Bacteroides fragilis toxin
- CEC
colonic epithelial cell
- CRC
colorectal cancer
- ETBF
Enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis
- IMC
immature myeloid cells
- Inf-MΦ
inflammatory macrophages
- MDSC
myeloid-derived suppressor cells
- MΦ
macrophages
- MO
monocytes
- PMN
polymorphonuclear cells
- TME
tumor microenvironment
Footnotes
Disclosures: The authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Supplementary Materials: Supplementary Materials is linked to the online version of this manuscript at http://www.nature.com/mi
Authorship Note: E.T.O. and F.H. performed the experimental work and drafted the manuscript; L.C., B.F. and H.F. provided technical assistance; C.D.-S. aided with tumor collection, J.F. assisted with Cytospin, A.T. assisted with flow cytometry and antibody panel design; S.W. contributed scientific expertise; X.W. performed the immunohistochemistry and ETBF microbiology; P.F. and C.D. conducted the microbiology for the other bacterial strains used, S.G. generated chimeric mice; D.M.P. and C.LS. provided scientific expertise, intellectual content and critical revision of the manuscript; F.H. coordinated and supervised all aspects of this work.
References
- 1.Prindiville TP, Sheikh RA, Cohen SH, Tang YJ, Cantrell MC, Silva J., Jr Bacteroides fragilis enterotoxin gene sequences in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Emerg Infect Dis. 2000;6:171–174. doi: 10.3201/eid0602.000210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Toprak NU, Yagci A, Gulluoglu BM, Akin ML, Demirkalem P, Celenk T, et al. A possible role of Bacteroides fragilis enterotoxin in the aetiology of colorectal cancer. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2006;12:782–786. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2006.01494.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Boleij A, Hechenbleikner EM, Goodwin AC, Badani R, Stein EM, Lazarev MG, et al. The Bacteroides fragilis toxin gene is prevalent in the colon mucosa of colorectal cancer patients. Clin Infect Dis. 2015;60:208–215. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciu787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Wu S, Rhee KJ, Albesiano E, Rabizadeh S, Wu X, Yen HR, et al. A human colonic commensal promotes colon tumorigenesis via activation of T helper type 17 T cell responses. Nature medicine. 2009;15:1016–22. doi: 10.1038/nm.2015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Tosolini M, Kirilovsky A, Mlecnik B, Fredriksen T, Mauger S, Bindea G, et al. Clinical impact of different classes of infiltrating T cytotoxic and helper cells (Th1, th2, treg, th17) in patients with colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2011;71:1263–1271. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-2907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sears CL, Garrett WS. Microbes, microbiota, and colon cancer. Cell Host Microbe. 2014;15:317–328. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2014.02.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ma S, Cheng Q, Cai Y, Gong H, Wu Y, Yu X, et al. IL-17A Produced by gammadelta T Cells Promotes Tumor Growth in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2014;74:1969–1982. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-2534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.He D, Li H, Yusuf N, Elmets CA, Li J, Mountz JD, et al. IL-17 promotes tumor development through the induction of tumor promoting microenvironments at tumor sites and myeloid-derived suppressor cells. J Immunol. 2010;184:2281–2288. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Wang L, Yi T, Zhang W, Pardoll DM, Yu H. IL-17 enhances tumor development in carcinogen-induced skin cancer. Cancer Res. 2010;70:10112–10120. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bronte V. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells in inflammation: uncovering cell subsets with enhanced immunosuppressive functions. Eur J Immunol. 2009;39:2670–2672. doi: 10.1002/eji.200939892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Gabrilovich DI, Ostrand-Rosenberg S, Bronte V. Coordinated regulation of myeloid cells by tumours. Nat Rev Immunol. 2012;12:253–268. doi: 10.1038/nri3175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Corzo CA, Condamine T, Lu L, Cotter MJ, Youn JI, Cheng P, et al. HIF-1alpha regulates function and differentiation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the tumor microenvironment. J Exp Med. 2010;207:2439–2453. doi: 10.1084/jem.20100587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Gabrilovich DI, Nagaraj S. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as regulators of the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009;9:162–174. doi: 10.1038/nri2506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ostrand-Rosenberg S, Sinha P. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells: linking inflammation and cancer. J Immunol. 2009;182:4499–4506. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0802740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gallina G, Dolcetti L, Serafini P, De Santo C, Marigo I, Colombo MP, et al. Tumors induce a subset of inflammatory monocytes with immunosuppressive activity on CD8+ T cells. J Clin Invest. 2006;116:2777–2790. doi: 10.1172/JCI28828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sinha P, Parker KH, Horn L, Ostrand-Rosenberg S. Tumor-induced myeloid-derived suppressor cell function is independent of IFN-gamma and IL-4Ralpha. Eur J Immunol. 2012;42:2052–2059. doi: 10.1002/eji.201142230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Chang SH, Mirabolfathinejad SG, Katta H, Cumpian AM, Gong L, Caetano MS, et al. T helper 17 cells play a critical pathogenic role in lung cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111:5664–5669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1319051111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kostic AD, Chun E, Robertson L, Glickman JN, Gallini CA, Michaud M, et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum potentiates intestinal tumorigenesis and modulates the tumor-immune microenvironment. Cell Host Microbe. 2013;14:207–215. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2013.07.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Arthur JC, Perez-Chanona E, Muhlbauer M, Tomkovich S, Uronis JM, Fan TJ, et al. Intestinal Inflammation Targets Cancer-Inducing Activity of the Microbiota. Science. 2012 doi: 10.1126/science.1224820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Housseau F, Wu S, Wick EC, Fan H, Wu X, Llosa NJ, et al. Redundant innate and adaptive sources of IL-17 production drive colon tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2016 doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-0749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Katz JB, Muller AJ, Prendergast GC. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in T-cell tolerance and tumoral immune escape. Immunol Rev. 2008;222:206–221. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00610.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Huang B, Pan PY, Li Q, Sato AI, Levy DE, Bromberg J, et al. Gr-1+CD115+ immature myeloid suppressor cells mediate the development of tumor-induced T regulatory cells and T-cell anergy in tumor-bearing host. Cancer Res. 2006;66:1123–1131. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wu P, Wu D, Ni C, Ye J, Chen W, Hu G, et al. gammadeltaT17 Cells Promote the Accumulation and Expansion of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in Human Colorectal Cancer. Immunity. 2014;40:785–800. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.03.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wang L, Yi T, Kortylewski M, Pardoll DM, Zeng D, Yu H. IL-17 can promote tumor growth through an IL-6-Stat3 signaling pathway. The Journal of experimental medicine. 2009;206:1457–64. doi: 10.1084/jem.20090207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Sinha P, Okoro C, Foell D, Freeze HH, Ostrand-Rosenberg S, Srikrishna G. Proinflammatory S100 proteins regulate the accumulation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. J Immunol. 2008;181:4666–4675. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.7.4666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Sears CL, Geis AL, Housseau F. Bacteroides fragilis subverts mucosal biology: from symbiont to colon carcinogenesis. J Clin Invest. 2014;124:4166–4172. doi: 10.1172/JCI72334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Chung AS, Wu X, Zhuang G, Ngu H, Kasman I, Zhang J, et al. An interleukin-17-mediated paracrine network promotes tumor resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy. Nat Med. 2013;19:1114–1123. doi: 10.1038/nm.3291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wu S, Morin PJ, Maouyo D, Sears CL. Bacteroides fragilis enterotoxin induces c-Myc expression and cellular proliferation. Gastroenterology. 2003;124:392–400. doi: 10.1053/gast.2003.50047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Wu S, Powell J, Mathioudakis N, Kane S, Fernandez E, Sears CL. Bacteroides fragilis enterotoxin induces intestinal epithelial cell secretion of interleukin-8 through mitogen-activated protein kinases and a tyrosine kinase-regulated nuclear factor-kappaB pathway. Infect Immun. 2004;72:5832–5839. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.10.5832-5839.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Highfill SL, Cui Y, Giles AJ, Smith JP, Zhang H, Morse E, et al. Disruption of CXCR2-mediated MDSC tumor trafficking enhances anti-PD1 efficacy. Sci Transl Med. 2014;6:237ra67. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3007974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.DeStefano Shields CE, Van Meerbeke SW, Housseau F, Wang H, Huso DL, Casero RA, Jr, et al. Reduction of murine colon tumorigenesis driven by enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis using cefoxitin treatment. J Infect Dis. 2016 doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiw069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Geis AL, Fan H, Wu X, Wu S, Huso DL, Wolfe JL, et al. Regulatory T cell response to enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis colonization triggers IL-17-dependent colon carcinogenesis. Cancer Discov. 2015 doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-15-0447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ortiz ML, Kumar V, Martner A, Mony S, Donthireddy L, Condamine T, et al. Immature myeloid cells directly contribute to skin tumor development by recruiting IL-17-producing CD4+ T cells. J Exp Med. 2015;212:351–367. doi: 10.1084/jem.20140835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kusmartsev SA, Li Y, Chen SH. Gr-1+ myeloid cells derived from tumor-bearing mice inhibit primary T cell activation induced through CD3/CD28 costimulation. J Immunol. 2000;165:779–785. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.2.779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Figure S1. ETBF Min mouse colons.
A, ETBF-triggered tumorigenesis is prominent in distal colons of Min mice.
B, Colon tumor counts from chimeric Min mice reconstituted with bone marrow from wildtype (C57BL/6) or Min donors. Tumor numbers were assessed at 12 weeks after inoculation with ETBF.
Representative image and graph of n=2 or more independent experiments.
Figure S2. Gene expression analysis in ETBF tumor-infiltrating myeloid cells.
MΦ and MO-IMCs were cell-sorted from 3 month ETBF Min colon tumors as CD11bhiGR1-MHC+F4/80+ and CD11bhiGR1loMHCloF4/80-, respectively. Bars represent fold increase of gene expression (RQ) in MΦ compared to MO-MDSCs. RQ>1, genes are overexpressed in tumor-associated macrophages; RQ<1, genes are overexpressed in MO-IMCs. Genes characterized by RQ>2 and RQ<0.5 are highlighted above and below the graph. Red boxes indicate genes characteristic of differentiated MΦ; green boxes indicate genes characteristic of MO-MDSCs. Representative graph of n=2 independent experiments.
Figure S3A. Gene expression array in PMN-IMCs sorted from colon tumors or spleen of 3 month ETBF Min mice.
Bars represent fold increase of gene expression (RQ) in IMCs sorted from tumors compared to those sorted from spleen. RQ>1 when genes are overexpressed in tumor IMCs; RQ<1 when genes are overexpressed in spleen. Genes characterized by RQ>2 are highlighted. Representative graph of n=2 independent experiments.
Figure S3B Same as in A, however comparing intratumoral MO-MDSCs to PMN-IMCs of 3 month ETBF Min mice. Representative graph of n=2 independent experiments.
Figure S4. Myeloid cell populations (CD11b+GR1hi and CD11b+GR1neg) cell-sorted from colon tumors for IL-17 qPCR were not contaminated by T cells.
Plots represent pre-sort CD3 and CD4 staining in CD11b+GR1hi, CD11b+GR1neg and CD11b- gates used for cell sorting and subsequent Il17a mRNA detection in myeloid cells associated with colon tumors, blood or spleen of 3 month ETBF-colonized Min mice. Representative staining of n=2 independent samples from one cell sorting experiment.
Figure S5. Tumor-infiltrating MDSCs express Il17a gene in colon tumors.
A, PMN-IMCs and MO-MDSCs or MO-IMCs were sorted from tumors, spleen or blood of 3 month ETBF-colonized Min mice. RNA extracted from each cell subset was assessed by qPCR for Il17a gene expression. Mean ± SEM is shown. Ct values were normalized with CtGapdh (ΔCt=Ct-CtGapdh) and bars represent 2-ΔCt. Aggregate data of n=2 independent experiments.
B, Myeloid and lymphoid populations were cell-sorted from C57BL/6 (WT) or Min distal colon lamina propria at day 7 post-ETBF colonization and assessed for Il17a, Rorc, Irf4 and Il23r expression by qPCR. Bars represent fold increased (RQ) between Min and wild type cell populations, RQ=2-ΔΔCt. Representative staining of n=2 independent samples from one cell sorting experiment.
Figure S6. Confirmation of Nos2 gene expression by detection of nitric oxide in culture supernatant of rIL-17-conditioned purified MO-MDSC.
MO-MDSCs cell-sorted from colon tumors or MO-IMCs sorted from spleen in ETBF Min mice were incubated overnight with IL-17 (10 ng/ml) in presence or absence of LPS (100ng/ml). Nitric oxide (NO) was measured in culture supernatants using a colorimetric assay. Lines represent geometric mean. Aggregate data from n=3-4 independent experiments.
Figure S7. Stool culture of oncogenic bacteria to confirm colonization.
Fresh stool samples were collected 7 days after inoculation with F. nucleatum, pks+ E. coli, E. coli ΔPKS, ETBF or NTBF. Samples were homogenized in PBS, serially diluted and cultured on Brucella (F. nucleatum), BHI (ETBF, NTBF) or MacConkey (E. coli) agar under optimal anaerobic or aerobic conditions. Colony forming units were manually counted within 24-48h of culturing.
Figure S8. Additional representative flow plots of MO-IMC, PMN-IMC and Mϕ subsets in sporadically occurring or ETBF-triggered colon tumors, as well as normal colon tissue. As described in Fig. 3A, 3B.
Figure S9. Gating strategy for the recovery of adoptively-transferred in vitro derived BM-MDSC.
A, CD45.1+ bone marrow cells were harvested and MDSCs were derived in vitro by culture with G-CSF, GM-CSF and IL-13 for 5 days. MO-MDSCs were cell-sorted and adoptively transferred to Min recipients previously infected with ETBF (ETBF 11 weeks) via tail-vein injection.
B, Colon tumors were harvested 1 week later (ETBF 12 weeks) and CD45.1+ were recovered and sorted by FACS for RNA extraction and Arg1/Nos2 qPCR analysis.