Abstract
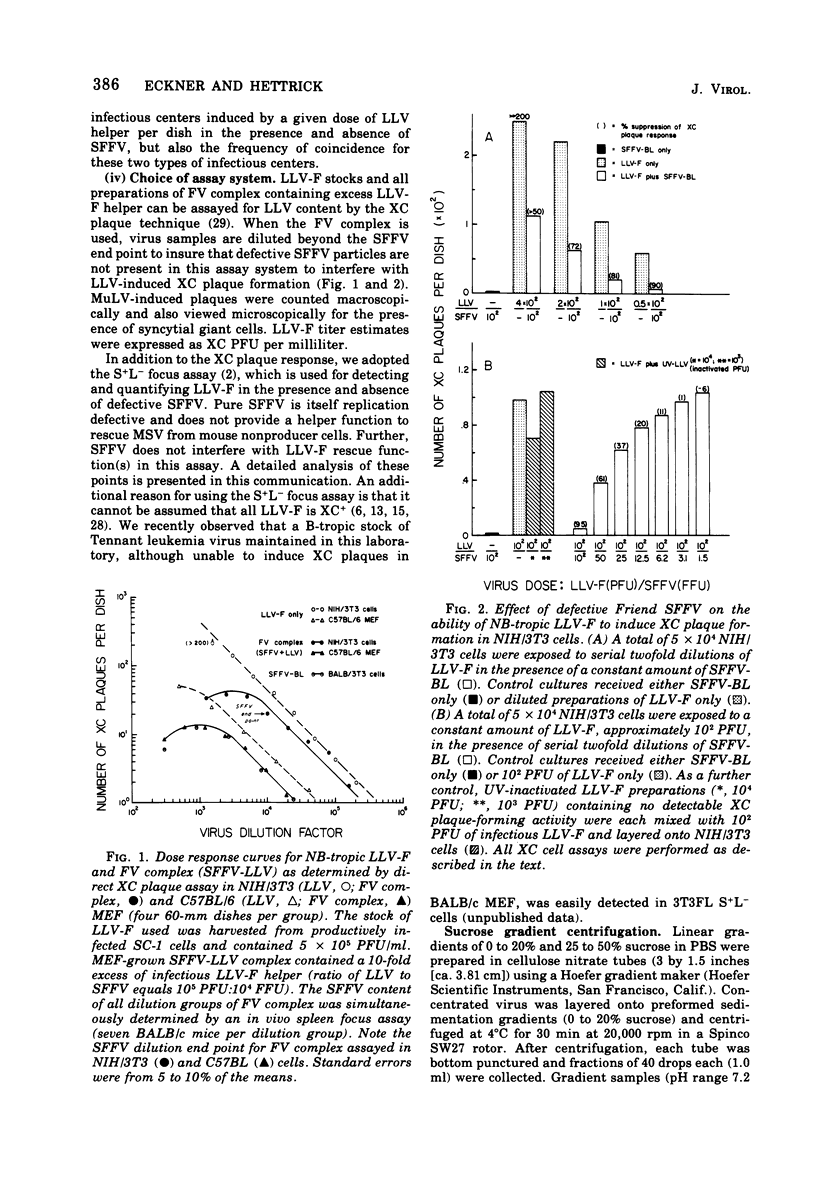
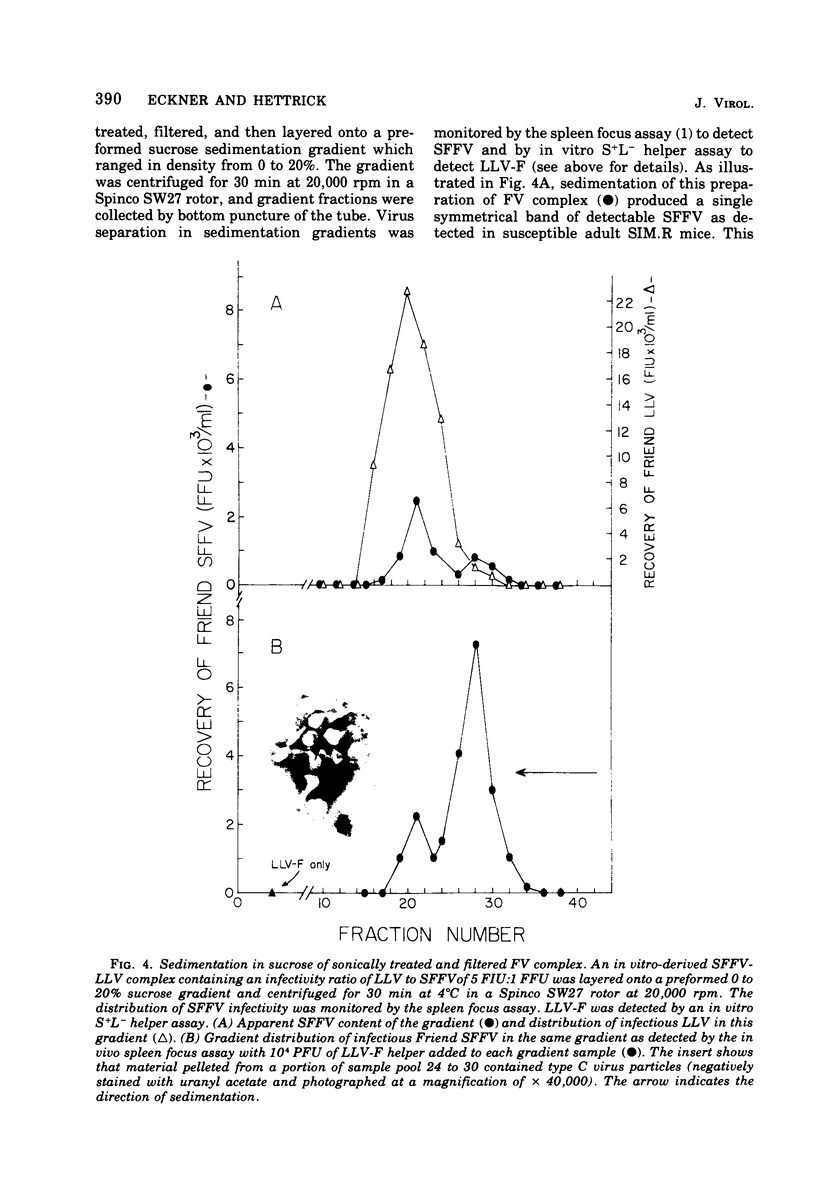
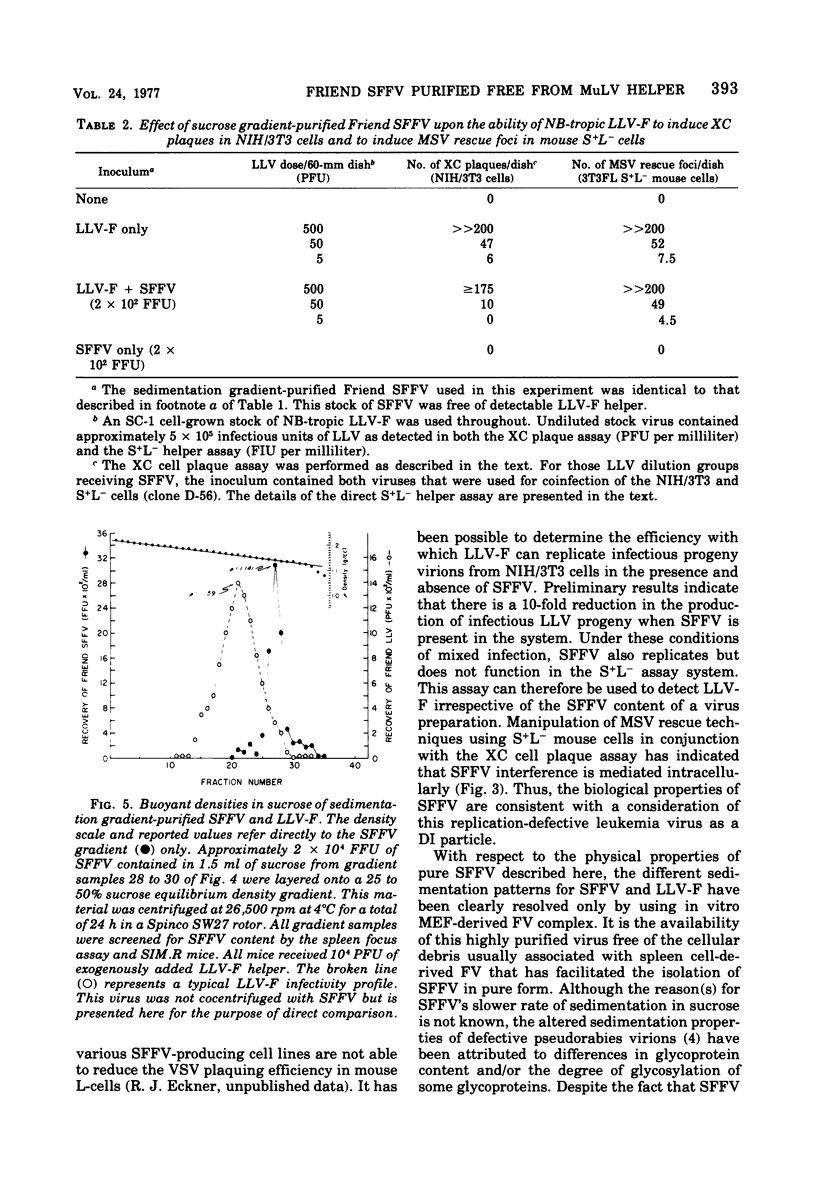
Defective Friend spleen focus-forming virus (SFFV) is able to interfere with the ability of its naturally occurring leukemia-inducing helper virus (LLV-F) to induce XC plaque formation in several different strains of mouse embryo cells. This interference has been observed by using two different SFFV preparations, one contained in an NB-tropic stock of Friend virus (FV) complex, and the second present in a C57BL-adapted strain of FV complex containing an associated B-tropic LLV-F helper. The LLV-F in NB-tropic FV complex effectively induced XC plaques in C57BL/6 (Fv-1bb; Fv-2rr) mouse embryo fibroblasts (MEF) only in the absence of coinfecting SFFV, indicating that Fv-2-associated resistance to SFFV-induced focus formation in vivo does not necessarily extend to the restriction of SFFV function(s) in vitro (i.e., in Fv-2rr C57BL MEF). SFFV interference appears to be an intracellular event since LLV-F can adsorb onto, penetrate, and rescue defective murine sarcoma virus (MSV) from transformed 3T3FL S+L− cells with equal efficiency in the presence and absence of SFFV. However, significantly fewer LLV-infected S+L− cells released LLV-F progeny if SFFV was present. These observations suggest that Friend SFFV may be classified as a defective, interfering (DI) particle. Further support for this conclusion has come from studies designed to investigate two physical properties of defective SFFV particles. SFFV layered onto a 0 to 20% sucrose sedimentation gradient was recovered as a symmetrical band of virus that sedimented more slowly than standard LLV-F particles. Pooled SFFV-containing gradient samples contained visualizable type C virus particles and occasionally small amounts of detectable LLV-F. In an attempt to determine the buoyant density of sedimentation gradient-purified SFFV, pooled SFFV samples were layered onto a 25 to 50% sucrose equilibrium density gradient and were centrifuged to equilibrium. Greater than 50% of the infectious SFFV originally layered onto this gradient was recovered and seen as a narrow symmetrical band with peak SFFV infectivity at a sucrose density of 1.14 g/ml. The observed difference between SFFV and LLV-F buoyant densities appears to be related to an inherent physical property of each virus. Mixtures of these two viruses express the buoyant density of that virus population which is in excess in fabricated FV complexes probably due to the formation of SFFV-LLV aggregates. Finally, gradient-purified SFFV failed to induce XC plaques in MEF and did not function to rescue MSV as expected since SFFV itself is replication defective.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AXELRAD A. A., STEEVES R. A. ASSAY FOR FRIEND LEUKEMIA VIRUS: RAPID QUANTITATIVE METHOD BASED ON ENUMERATION OF MACROSCOPIC SPLEEN FOCI IN MICE. Virology. 1964 Nov;24:513–518. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90199-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassin R. H., Tuttle N., Fischinger P. J. Isolation of murine sarcoma virus-transformed mouse cells which are negative for leukemia virus from agar suspension cultures. Int J Cancer. 1970 Jul 15;6(1):95–107. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910060114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassin R. H., Tuttle N., Fischinger P. J. Rapid cell culture assay technic for murine leukaemia viruses. Nature. 1971 Feb 19;229(5286):564–566. doi: 10.1038/229564b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Porat T., Lonis B., Kaplan A. S. Further characterization of A population of defective, interfering pseudorabies virions. Virology. 1975 May;65(1):179–186. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90018-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besmer P., Baltimore D. Mechanism of restriction of ecotropic and xenotropic murine leukemia viruses and formation of pseudotypes between the two viruses. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):965–973. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.965-973.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole C. N., Smoler D., Wimmer E., Baltimore D. Defective interfering particles of poliovirus. I. Isolation and physical properties. J Virol. 1971 Apr;7(4):478–485. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.4.478-485.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLarco J., Todaro G. J. Membrane receptors for murine leukemia viruses: characterization using the purified viral envelope glycoprotein, gp71. Cell. 1976 Jul;8(3):365–371. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90148-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckner R. J. Continuous replication of Friend virus complex (spleen focus-forming virus-lymphatic leukemia-inducing virus) in mouse embryo fibroblasts. Retention of leukemogenicity and loss of immunosuppressive properties. J Exp Med. 1975 Oct 1;142(4):936–948. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.4.936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckner R. J. Helper-dependent properties of Friend spleen focus-forming virus: effect of the Fv-1 gene on the late stages in virus synthesis. J Virol. 1973 Sep;12(3):523–533. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.3.523-533.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckner R. J., Kumar V., Bennett M. Immunogenetic analysis of the mechanism of induction of Friend virus leukemia. Transplant Proc. 1975 Jun;7(2):173–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckner R. J., Steeves R. A. A classification of the murine leukemia viruses. Neutralization of pseudotypes of Friend spleen focus-forming virus by type-specific murine antisera. J Exp Med. 1972 Oct 1;136(4):832–850. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.4.832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenyö E. M., Grundner G. Characteristics of murine C-type viruses. I. Independent assortment of infectivity in one in vivo and four in vitro assays. Int J Cancer. 1973 Sep 15;12(2):452–462. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910120216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gisselbrecht S., Bassin R. H., Gerwin B. I., Rein A. Dual susceptibility of A 3T3 mouse cell line to infection by N- and B-tropic murine leukemia virus: apparent lack of expression of the FV-1 gene. Int J Cancer. 1974 Jul 15;14(1):106–113. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910140113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Clonal cells lines from a feral mouse embryo which lack host-range restrictions for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1975 May;65(1):128–134. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Huebner R. J. Host-range restrictions of murine leukemia viruses in mouse embryo cell cultures. J Virol. 1970 Feb;5(2):221–225. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.2.221-225.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson I. C., Lieber M. M., Todaro G. J. Mink cell line Mv 1 Lu (CCL 64). Focus formation and the generation of "nonproducer" transformed cell lines with murine and feline sarcoma viruses. Virology. 1974 Jul;60(1):282–287. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90386-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins N., Jolicoeur P. Variants of N-tropic leukemia virus derived from BALB/c mice. J Virol. 1975 Oct;16(4):991–999. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.4.991-999.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S. Defective interfering viruses. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1973;27:101–117. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.27.100173.000533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Greenawalt J. W., Wagner R. R. Defective T particles of vesicular stomatitis virus. I. Preparation, morphology, and some biologic properties. Virology. 1966 Oct;30(2):161–172. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90092-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunsmann G., Moennig V., Pister L., Seifert E., Schäfer W. Properties of mouse leukemia viruses. VIII. The major viral glycoprotein of Friend leukemia virus. Seroimmunological, interfering and hemagglutinating capacities. Virology. 1974 Dec;62(2):307–318. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90394-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolicoeur P., Baltimore D. Effect of Fv-1 gene product on proviral DNA formation and integration in cells infected with murine leukemia viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2236–2240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J. G., Grimley P. M., Ramseur J. M., Berezesky I. K. Deficiency of 60 to 70S RNA in murine leukemia virus particles assembled in cells treated with actinomycin D. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):152–161. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.152-161.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilly F. Fv-2: identification and location of a second gene governing the spleen focus response to Friend leukemia virus in mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1970 Jul;45(1):163–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisel J., Klement V., Lai M. M., Ostertag W., Duesberg P. Ribonucleic acid components of murine sarcoma and leukemia viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3536–3540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning J. S., Schaffer F. L., Soergel M. E. Correlation between murine sarcoma virus buoyant density, infectivity, and viral RNA electrophoretic mobility. Virology. 1972 Sep;49(3):804–807. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90537-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moennig V., Frank H., Hunsmann G., Schneider I., Schafer W. Properties of mouse leukemia viruses. VII. The major viral glycoprotein of friend leukemia virus. Isolation and physicochemical properties. Virology. 1974 Sep;61(1):100–111. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90245-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp U. R., Nowinski R. C. Endogenous ecotropic mouse type C viruses deficient in replication and production of XC plaques. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):411–417. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.411-417.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Pugh W. E., Hartley J. W. Plaque assay techniques for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):1136–1139. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90362-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar N. H., Moore D. H. Separation of B and C type virions by centrifugation in gentle density gradients. J Virol. 1974 May;13(5):1143–1147. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.5.1143-1147.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarma P. S., Cheong M. P., Hartley J. W., Huebner R. J. A viral interference test for mouse leukemia viruses. Virology. 1967 Sep;33(1):180–184. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90111-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuh V., Blackstein M. E., Axelrad A. A. Inherited resistance to N- and B-tropic murine leukemia viruses in vitro: titration patterns in strains SIM and SIM.R congenic at the Fv-1 locus. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):473–480. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.473-480.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steeves R. A., Eckner R. J., Bennett M., Mirand E. A., Trudel P. J. Isolation and characterization of a lymphatic leukemia virus in the Friend virus complex. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1971 Jun;46(6):1209–1217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steeves R. A., Mirand E. A., Bulba A., Trudel P. J. Spleen foci and polycythemia in C57B1 mice infected with host-adapted Friend leukemia virus. Int J Cancer. 1970 May 15;5(3):346–356. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910050307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steeves R. A., Strand M., August J. T. Structural proteins of mammalian oncogenic RNA viruses: murine leukemia virus neutralization by antisera prepared against purified envelope glycoprotein. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):187–189. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.187-189.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M. L., Maizel J. V., Jr Friend leukemia and endogenous viruses. I. Production of friend and endogenous C-type particles by mouse cells cultured in vitro. Virology. 1975 May;65(1):55–66. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90006-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M. L., Maizel J. V., Jr Friend leukemia and mouse endogenous viruses. II. Proteins of Friend leukemia and mouse endogenous C-type particles produced by BALB/c mouse cell cultures. Virology. 1975 May;65(1):67–67. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sveda M. M., Fields B. N., Soeiro R. Host restriction of friend leukemia virus; fate of input virion RNA. Cell. 1974 Aug;2(4):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90021-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troxler D. H., Boyars J. K., Parks W. P., Scolnick E. M. Friend strain of spleen focus-forming virus: a recombinant between mouse type C ecotropic viral sequences and sequences related to xenotropic virus. J Virol. 1977 May;22(2):361–372. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.2.361-372.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi M. J., Hamamoto S. T., Duafala J. G., Pitelka D. R. Atypical C particles in adenocarcinomas induced by implantation of FUKU cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Dec;53(6):1835–1837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




