Abstract
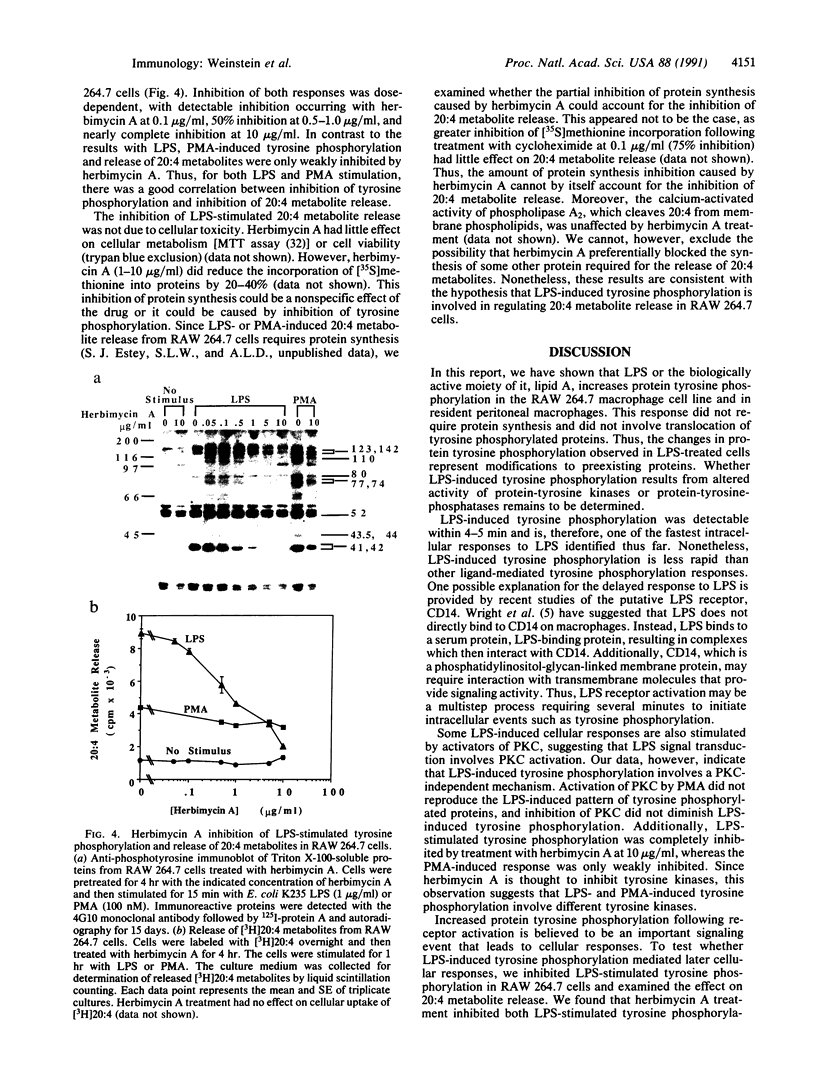
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a membrane component of Gram-negative bacteria, stimulates immune responses by activating macrophages, B lymphocytes, and other cells of the immune system. The mechanisms by which LPS activates these cells are poorly characterized. Since protein tyrosine phosphorylation appears to be a major intracellular signaling event that mediates cellular responses, we examined whether LPS alters tyrosine phosphorylation in macrophages. We found that Escherichia coli K235 LPS increased tyrosine phosphorylation of several proteins in the RAW 264.7 murine macrophage cell line and in resident peritoneal macrophages from C3H/HeSNJ mice. Changes in tyrosine phosphorylation were detectable by 4-5 min, reached a maximum by 15 min, and declined after 30-60 min. Protein tyrosine phosphorylation increased following stimulation with LPS at 100 pg/ml and was maximal with 10 ng/ml. Similar changes in tyrosine phosphorylation were induced by Salmonella minnesota R595 LPS and by the biologically active domain of LPS, lipid A, but not by the inactive lipid A derivative N2-monoacylglucosamine 1-phosphate. Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate also stimulated protein tyrosine phosphorylation, but some of the modulated proteins were different than those phosphorylated by LPS. Treatment of RAW 264.7 cells with a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, herbimycin A, inhibited both LPS-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation and LPS-stimulated release of arachidonic acid metabolites. Thus, increased protein tyrosine phosphorylation is a rapid LPS-activated signaling event that may mediate release of arachidonic acid metabolites in RAW 264.7 cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. O., Hamilton T. A. The cell biology of macrophage activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:283–318. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.001435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bijsterbosch M. K., Meade C. J., Turner G. A., Klaus G. G. B lymphocyte receptors and polyphosphoinositide degradation. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):999–1006. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80080-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brade H., Brade L., Rietschel E. T. Structure-activity relationships of bacterial lipopolysaccharides (endotoxins). Current and future aspects. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1988 Apr;268(2):151–179. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(88)80001-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bright S. W., Chen T. Y., Flebbe L. M., Lei M. G., Morrison D. C. Generation and characterization of hamster-mouse hybridomas secreting monoclonal antibodies with specificity for lipopolysaccharide receptor. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 1;145(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. A., Sefton B. M. Protein tyrosine phosphorylation is induced in murine B lymphocytes in response to stimulation with anti-immunoglobulin. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2125–2131. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07381.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel-Issakani S., Spiegel A. M., Strulovici B. Lipopolysaccharide response is linked to the GTP binding protein, Gi2, in the promonocytic cell line U937. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20240–20247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis P. D., Hill C. H., Keech E., Lawton G., Nixon J. S., Sedgwick A. D., Wadsworth J., Westmacott D., Wilkinson S. E. Potent selective inhibitors of protein kinase C. FEBS Lett. 1989 Dec 18;259(1):61–63. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81494-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding A. H., Sanchez E., Srimal S., Nathan C. F. Macrophages rapidly internalize their tumor necrosis factor receptors in response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):3924–3929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dziarski R. Correlation between ribosylation of pertussis toxin substrates and inhibition of peptidoglycan-, muramyl dipeptide- and lipopolysaccharide-induced mitogenic stimulation in B lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Jan;19(1):125–130. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forehand J. R., Pabst M. J., Phillips W. A., Johnston R. B., Jr Lipopolysaccharide priming of human neutrophils for an enhanced respiratory burst. Role of intracellular free calcium. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jan;83(1):74–83. doi: 10.1172/JCI113887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukazawa H., Mizuno S., Uehara Y. Effects of herbimycin A and various SH-reagents on p60v-src kinase activity in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Nov 30;173(1):276–282. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gessani S., Belardelli F., Pecorelli A., Puddu P., Baglioni C. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide and gamma interferon induce transcription of beta interferon mRNA and interferon secretion in murine macrophages. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2785–2789. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2785-2789.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser K. B., Asmis R., Dennis E. A. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide priming of P388D1 macrophage-like cells for enhanced arachidonic acid metabolism. Platelet-activating factor receptor activation and regulation of phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8658–8664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. R., Law D. A., DeFranco A. L. Stimulation of protein tyrosine phosphorylation by the B-lymphocyte antigen receptor. Nature. 1990 Jun 28;345(6278):810–813. doi: 10.1038/345810a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grupp S. A., Harmony J. A. Increased phosphatidylinositol metabolism is an important but not an obligatory early event in B lymphocyte activation. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):4087–4094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsi E. D., Siegel J. N., Minami Y., Luong E. T., Klausner R. D., Samelson L. E. T cell activation induces rapid tyrosine phosphorylation of a limited number of cellular substrates. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10836–10842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Introna M., Hamilton T. A., Kaufman R. E., Adams D. O., Bast R. C., Jr Treatment of murine peritoneal macrophages with bacterial lipopolysaccharide alters expression of c-fos and c-myc oncogenes. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 15;137(8):2711–2715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakway J. P., DeFranco A. L. Pertussis toxin inhibition of B cell and macrophage responses to bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Science. 1986 Nov 7;234(4777):743–746. doi: 10.1126/science.3095921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- June C. H., Fletcher M. C., Ledbetter J. A., Schieven G. L., Siegel J. N., Phillips A. F., Samelson L. E. Inhibition of tyrosine phosphorylation prevents T-cell receptor-mediated signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7722–7726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie C. C., Voelker D. R., Channon J. Y., Wall M. M., Zelarney P. T. Properties and purification of an arachidonoyl-hydrolyzing phospholipase A2 from a macrophage cell line, RAW 264.7. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Dec 16;963(3):476–492. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(88)90316-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Ryan J. L. Bacterial endotoxins and host immune responses. Adv Immunol. 1979;28:293–450. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60802-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Ryan J. L. Endotoxins and disease mechanisms. Annu Rev Med. 1987;38:417–432. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.38.020187.002221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. K., Kaplan D. R., Escobedo J. A., Rapp U. R., Roberts T. M., Williams L. T. Direct activation of the serine/threonine kinase activity of Raf-1 through tyrosine phosphorylation by the PDGF beta-receptor. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90100-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prpic V., Weiel J. E., Somers S. D., DiGuiseppi J., Gonias S. L., Pizzo S. V., Hamilton T. A., Herman B., Adams D. O. Effects of bacterial lipopolysaccharide on the hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate in murine peritoneal macrophages. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 15;139(2):526–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taffet S. M., Haddox M. K. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide induction of ornithine decarboxylase in the macrophage-like cell line RAW264: requirement of an inducible soluble factor. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Feb;122(2):215–220. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041220209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi H., Sakano T., Hamasaki T., Kashiwa H., Ueda K. Effect of protein kinase C inhibitor (H-7) and calmodulin antagonist (W-7) on pertussis toxin-induced IL-1 production by human adherent monocytes. Comparison with lipopolysaccharide as a stimulator of IL-1 production. Immunology. 1989 Jun;67(2):210–215. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uehara Y., Hori M., Takeuchi T., Umezawa H. Phenotypic change from transformed to normal induced by benzoquinonoid ansamycins accompanies inactivation of p60src in rat kidney cells infected with Rous sarcoma virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2198–2206. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virca G. D., Kim S. Y., Glaser K. B., Ulevitch R. J. Lipopolysaccharide induces hyporesponsiveness to its own action in RAW 264.7 cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21951–21956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J., Kester M., Dunn M. J. Involvement of a pertussis toxin-sensitive G-protein-coupled phospholipase A2 in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated prostaglandin E2 synthesis in cultured rat mesangial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Dec 16;963(3):429–435. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(88)90311-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wightman P. D., Raetz C. R. The activation of protein kinase C by biologically active lipid moieties of lipopolysaccharide. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10048–10052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Ramos R. A., Tobias P. S., Ulevitch R. J., Mathison J. C. CD14, a receptor for complexes of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and LPS binding protein. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1431–1433. doi: 10.1126/science.1698311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]