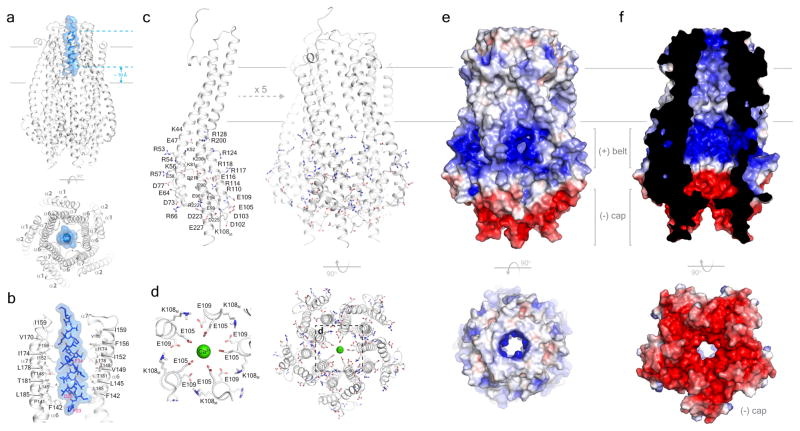
Figure 2. The structure of the ExbB/ExbDΔperi complex.
a. The ExbB/ExbDΔperi complex highlighting the TM helix of ExbD (blue) located within the TM pore of the ExbB pentamer (gray). b. Residues from helices α6 and α7 line the TM pore of ExbB (gray) and mediate interaction with the TM helix of ExbD (blue). For clarity, only two monomers of the ExbB pentamer are shown. c. The cytoplasmic domain of ExbB forms a large enclosed cavity that includes twelve arginines, six lysines, eleven glutamates, and seven aspartates from each monomer. d. Electronegatively charged residues E105 and E109 line the cytoplasmic pore and interact with a single calcium ion (green sphere). e. Electrostatic surface representation of ExbB showing the electropositive ‘belt’ and the electronegative ‘cap’. f. Cutaway view showing that the electrostatic surface properties of the inside cavity.