Abstract
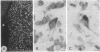
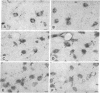
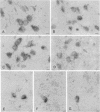
In situ hybridization experiments were performed in rat brain sections from normal and 6-hydroxydopamine-treated rats in order to map and identify the neurons expressing the D1 receptor gene in the striatum and the substantia nigra. Procedures of combined in situ hybridization, allowing the simultaneous detection of two mRNAs in the same section or in adjacent sections, were used to characterize the phenotypes of the neurons expressing the D1 receptor gene. D1 receptor mRNA was found in neurons all over the caudate-putamen, the accumbens nucleus, and the olfactory tubercle but not in the substantia nigra. In the caudate-putamen and accumbens nucleus, most of the neurons containing D1 receptor mRNA were characterized as medium-sized substance P neurons and distinct from those containing D2 receptor mRNA. Nevertheless, 15-20% of the substance P neurons did not contain D1 receptor mRNA. The neurons containing preproenkephalin A mRNA did not contain D1 receptor mRNA but contained D2 receptor mRNA. A small number of cholinergic and somatostatinergic neurons exhibited a weak reaction for D1 receptor mRNA. These results demonstrate that dopamine acts on efferent striatal neurons through expression of distinct receptors--namely, D1 and D2 in separate cell populations (substance P and preproenkephalin A neurons, respectively)--and can also act on nonprojecting neurons through D1 receptor expression.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen P. H., Gingrich J. A., Bates M. D., Dearry A., Falardeau P., Senogles S. E., Caron M. G. Dopamine receptor subtypes: beyond the D1/D2 classification. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Jun;11(6):231–236. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90249-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannon M. J., Elliott P. J., Bunney E. B. Striatal tachykinin biosynthesis: regulation of mRNA and peptide levels by dopamine agonists and antagonists. Brain Res. 1987 Dec;427(1):31–37. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(87)90041-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckstead R. M. Association of dopamine D1 and D2 receptors with specific cellular elements in the basal ganglia of the cat: the uneven topography of dopamine receptors in the striatum is determined by intrinsic striatal cells, not nigrostriatal axons. Neuroscience. 1988 Dec;27(3):851–863. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90188-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beninger R. J. The role of dopamine in locomotor activity and learning. Brain Res. 1983 Oct;287(2):173–196. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(83)90038-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertorello A. M., Hopfield J. F., Aperia A., Greengard P. Inhibition by dopamine of (Na(+)+K+)ATPase activity in neostriatal neurons through D1 and D2 dopamine receptor synergism. Nature. 1990 Sep 27;347(6291):386–388. doi: 10.1038/347386a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besson M. J., Graybiel A. M., Quinn B. Co-expression of neuropeptides in the cat's striatum: an immunohistochemical study of substance P, dynorphin B and enkephalin. Neuroscience. 1990;39(1):33–58. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90220-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloch B., Popovici T., Le Guellec D., Normand E., Chouham S., Guitteny A. F., Bohlen P. In situ hybridization histochemistry for the analysis of gene expression in the endocrine and central nervous system tissues: a 3-year experience. J Neurosci Res. 1986;16(1):183–200. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490160117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolam J. P., Wainer B. H., Smith A. D. Characterization of cholinergic neurons in the rat neostriatum. A combination of choline acetyltransferase immunocytochemistry, Golgi-impregnation and electron microscopy. Neuroscience. 1984 Jul;12(3):711–718. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90165-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouthenet M. L., Martres M. P., Sales N., Schwartz J. C. A detailed mapping of dopamine D-2 receptors in rat central nervous system by autoradiography with [125I]iodosulpride. Neuroscience. 1987 Jan;20(1):117–155. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunzow J. R., Van Tol H. H., Grandy D. K., Albert P., Salon J., Christie M., Machida C. A., Neve K. A., Civelli O. Cloning and expression of a rat D2 dopamine receptor cDNA. Nature. 1988 Dec 22;336(6201):783–787. doi: 10.1038/336783a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creese I., Sibley D. R., Hamblin M. W., Leff S. E. The classification of dopamine receptors: relationship to radioligand binding. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1983;6:43–71. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.06.030183.000355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dal Toso R., Sommer B., Ewert M., Herb A., Pritchett D. B., Bach A., Shivers B. D., Seeburg P. H. The dopamine D2 receptor: two molecular forms generated by alternative splicing. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4025–4034. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08585.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson V. L., Dawson T. M., Filloux F. M., Wamsley J. K. Evidence for dopamine D-2 receptors on cholinergic interneurons in the rat caudate-putamen. Life Sci. 1988;42(20):1933–1939. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(88)90492-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dearry A., Gingrich J. A., Falardeau P., Fremeau R. T., Jr, Bates M. D., Caron M. G. Molecular cloning and expression of the gene for a human D1 dopamine receptor. Nature. 1990 Sep 6;347(6288):72–76. doi: 10.1038/347072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois A., Savasta M., Curet O., Scatton B. Autoradiographic distribution of the D1 agonist [3H]SKF 38393, in the rat brain and spinal cord. Comparison with the distribution of D2 dopamine receptors. Neuroscience. 1986 Sep;19(1):125–137. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funckes C. L., Minth C. D., Deschenes R., Magazin M., Tavianini M. A., Sheets M., Collier K., Weith H. L., Aron D. C., Roos B. A. Cloning and characterization of a mRNA-encoding rat preprosomatostatin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):8781–8787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerfen C. R., Engber T. M., Mahan L. C., Susel Z., Chase T. N., Monsma F. J., Jr, Sibley D. R. D1 and D2 dopamine receptor-regulated gene expression of striatonigral and striatopallidal neurons. Science. 1990 Dec 7;250(4986):1429–1432. doi: 10.1126/science.2147780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerfen C. R. The neostriatal mosaic: striatal patch-matrix organization is related to cortical lamination. Science. 1989 Oct 20;246(4928):385–388. doi: 10.1126/science.2799392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glowinski J., Hervé D., Tassin J. P. Heterologous regulation of receptors on target cells of dopamine neurons in the prefrontal cortex, nucleus accumbens, and striatum. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;537:112–123. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb42100.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybiel A. M. Neurotransmitters and neuromodulators in the basal ganglia. Trends Neurosci. 1990 Jul;13(7):244–254. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90104-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guitteny A. F., Fouque B., Mougin C., Teoule R., Bloch B. Histological detection of messenger RNAs with biotinylated synthetic oligonucleotide probes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1988 Jun;36(6):563–571. doi: 10.1177/36.6.3259249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison M. B., Wiley R. G., Wooten G. F. Selective localization of striatal D1 receptors to striatonigral neurons. Brain Res. 1990 Oct 1;528(2):317–322. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91674-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haverstick D. M., Rubenstein A., Bannon M. J. Striatal tachykinin gene expression regulated by interaction of D-1 and D-2 dopamine receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Feb;248(2):858–862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosokawa S., Kato M. Physiology of peptides in basal ganglia. Prog Brain Res. 1986;66:73–89. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)64598-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez-Castellanos J., Graybiel A. M. Subdivisions of the dopamine-containing A8-A9-A10 complex identified by their differential mesostriatal innervation of striosomes and extrastriosomal matrix. Neuroscience. 1987 Oct;23(1):223–242. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90285-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kebabian J. W., Calne D. B. Multiple receptors for dopamine. Nature. 1979 Jan 11;277(5692):93–96. doi: 10.1038/277093a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubota Y., Inagaki S., Kito S. Innervation of substance P neurons by catecholaminergic terminals in the neostriatum. Brain Res. 1986 Jun 4;375(1):163–167. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90969-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Moine C., Normand E., Guitteny A. F., Fouque B., Teoule R., Bloch B. Dopamine receptor gene expression by enkephalin neurons in rat forebrain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):230–234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Moine C., Tison F., Bloch B. D2 dopamine receptor gene expression by cholinergic neurons in the rat striatum. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Sep 18;117(3):248–252. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90671-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monsma F. J., Jr, Mahan L. C., McVittie L. D., Gerfen C. R., Sibley D. R. Molecular cloning and expression of a D1 dopamine receptor linked to adenylyl cyclase activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6723–6727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawa H., Kotani H., Nakanishi S. Tissue-specific generation of two preprotachykinin mRNAs from one gene by alternative RNA splicing. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):729–734. doi: 10.1038/312729a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normand E., Popovici T., Fellmann D., Bloch B. Anatomical study of enkephalin gene expression in the rat forebrain following haloperidol treatment. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Dec 29;83(3):232–236. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90091-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normand E., Popovici T., Onteniente B., Fellmann D., Piatier-Tonneau D., Auffray C., Bloch B. Dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra modulate preproenkephalin A gene expression in rat striatal neurons. Brain Res. 1988 Jan 26;439(1-2):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91459-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oblin A., Zivkovic B., Bartholini G. Selective antagonists of dopamine receptor subtypes differentially affect substance P levels in the striatum and substantia nigra. Brain Res. 1987 Sep 22;421(1-2):387–390. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)91314-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner A., Anderson K. D. The patterns of neurotransmitter and neuropeptide co-occurrence among striatal projection neurons: conclusions based on recent findings. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1990 Sep-Dec;15(3):251–265. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(90)90003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson G. S., Vincent S. R., Fibiger H. C. Striatonigral projection neurons contain D1 dopamine receptor-activated c-fos. Brain Res. 1990 Jul 23;523(2):288–290. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91498-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salin P., Kerkerian-Le Goff L., Heidet V., Epelbaum J., Nieoullon A. Somatostatin-immunoreactive neurons in the rat striatum: effects of corticostriatal and nigrostriatal dopaminergic lesions. Brain Res. 1990 Jun 25;521(1-2):23–32. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91520-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salin P., Mercugliano M., Chesselet M. F. Differential effects of chronic treatment with haloperidol and clozapine on the level of preprosomatostatin mRNA in the striatum, nucleus accumbens, and frontal cortex of the rat. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 1990 Mar;10(1):127–144. doi: 10.1007/BF00733640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scatton B. Further evidence for the involvement of D2, but not D1 dopamine receptors in dopaminergic control of striatal cholinergic transmission. Life Sci. 1982 Dec 20;31(25):2883–2890. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90679-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P., Niznik H. B. Dopamine receptors and transporters in Parkinson's disease and schizophrenia. FASEB J. 1990 Jul;4(10):2737–2744. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.10.2197154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokoloff P., Giros B., Martres M. P., Bouthenet M. L., Schwartz J. C. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel dopamine receptor (D3) as a target for neuroleptics. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):146–151. doi: 10.1038/347146a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunahara R. K., Niznik H. B., Weiner D. M., Stormann T. M., Brann M. R., Kennedy J. L., Gelernter J. E., Rozmahel R., Yang Y. L., Israel Y. Human dopamine D1 receptor encoded by an intronless gene on chromosome 5. Nature. 1990 Sep 6;347(6288):80–83. doi: 10.1038/347080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa K., Williams C., Sabol S. L. Rat brain preproenkephalin mRNA. cDNA cloning, primary structure, and distribution in the central nervous system. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14301–14308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. S., 3rd, Bonner T. I., Brann M. R. Mesencephalic dopamine neurons regulate the expression of neuropeptide mRNAs in the rat forebrain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9827–9831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Q. Y., Grandy D. K., Thambi L., Kushner J. A., Van Tol H. H., Cone R., Pribnow D., Salon J., Bunzow J. R., Civelli O. Cloning and expression of human and rat D1 dopamine receptors. Nature. 1990 Sep 6;347(6288):76–80. doi: 10.1038/347076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]