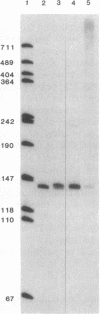
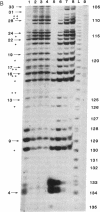
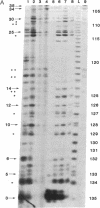
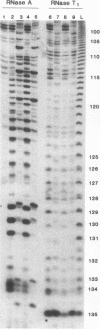
Abstract
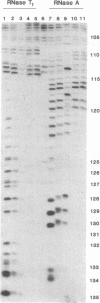
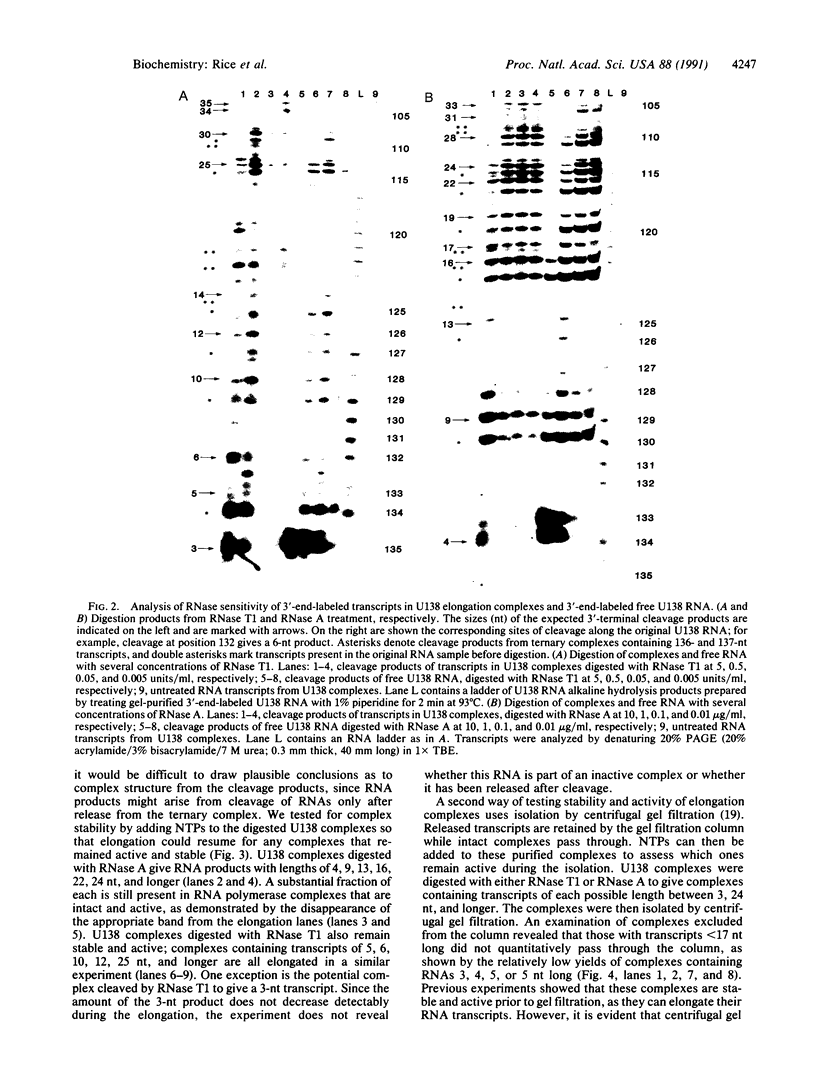
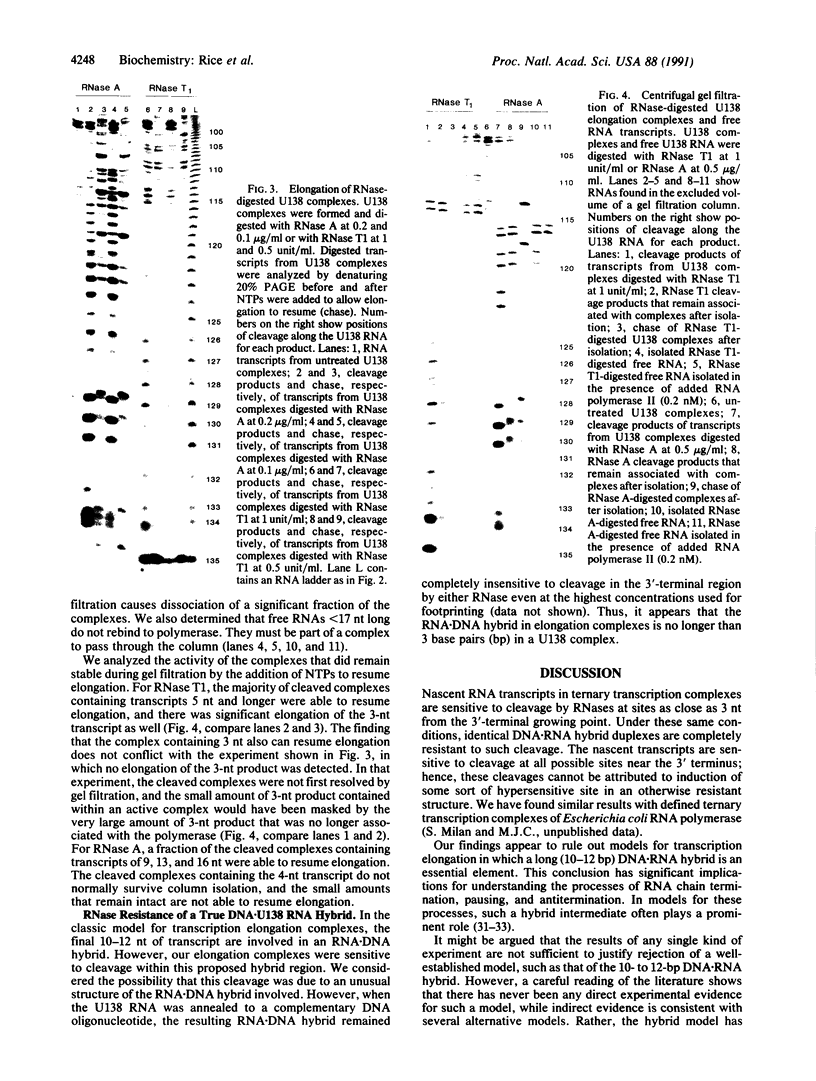
Ternary complexes of RNA polymerase II, bearing the nascent RNA transcript, are intermediates in the synthesis of all eukaryotic mRNAs and are implicated as regulatory targets of factors that control RNA chain elongation and termination. Information as to the structure of such complexes is essential in understanding the catalytic and regulatory properties of the RNA polymerase. We have prepared complexes of purified RNA polymerase II halted at defined positions along a DNA template and used RNase footprinting to map interactions of the polymerase with the nascent RNA. Unexpectedly, the transcript is sensitive to cleavage by RNases A and T1 at positions as close as 3 nucleotides from the 3'-terminal growing point. Ternary complexes in which the transcript has been cleaved to give a short fragment can retain that fragment and remain active and able to continue elongation. Since DNA.RNA hybrid structures are completely resistant to cleavage under our reaction conditions, the results suggest that any DNA.RNA hybrid intermediate can extend for no more than 3 base pairs, in dramatic contrast to recent models for transcription elongation. At lower RNase concentrations, the transcript is protected from cleavage out to about 24 nucleotides from the 3' terminus. We interpret this partial protection as due to the presence of an RNA binding site on the polymerase that binds the nascent transcript during elongation, a model proposed earlier by several workers in preference to the hybrid model. The properties of this RNA binding site are likely to play a central role in the process of transcription elongation and termination and in their regulation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S., Miller W. Modulation of the two promoters of the galactose operon of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1979 Jun 7;279(5713):492–494. doi: 10.1038/279492a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arndt K. M., Chamberlin M. J. RNA chain elongation by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Factors affecting the stability of elongating ternary complexes. J Mol Biol. 1990 May 5;213(1):79–108. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80123-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. L., Koren R., Mildvan A. S. Magnetic resonance studies of the conformation of enzyme-bound adenylyl(3' leads to 5')uridine and adenosine 5'-triphosphate on RNA polymerase from Esherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1977 Jul 26;16(15):3322–3333. doi: 10.1021/bi00634a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley D. L., Groudine M. A block to elongation is largely responsible for decreased transcription of c-myc in differentiated HL60 cells. Nature. 1986 Jun 12;321(6071):702–706. doi: 10.1038/321702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Hahn S., Guarente L., Sharp P. A. Five intermediate complexes in transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):549–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90578-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busby S., Spassky A., Buc H. On the binding of tRNA to Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Interactions between the core enzyme, DNA and tRNA. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Sep 1;118(3):443–451. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05540.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai H., Luse D. S. Transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in vitro. Properties of preinitiation, initiation, and elongation complexes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):298–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai H., Luse D. S. Variations in template protection by the RNA polymerase II transcription complex during the initiation process. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3371–3379. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiLauro R., Taniguchi T., Musso R., de Crombrugghe B. Unusual location and function of the operator in the Escherichia coli galactose operon. Nature. 1979 Jun 7;279(5713):494–500. doi: 10.1038/279494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOX C. F., GUMPORT R. I., WEISS S. B. THE ENZYMATIC SYNTHESIS OF RIBONUCLEIC ACID. V. THE INTERACTION OF RIBONUCLEIC ACID POLYMERASE WITH NUCLEIC ACIDS. J Biol Chem. 1965 May;240:2101–2109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnham P. J., Platt T. A model for transcription termination suggested by studies on the trp attenuator in vitro using base analogs. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):739–748. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90320-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R., Blumenthal T. Analysis of RNA polymerase by trypsin cleavage. Different structural changes produced by heparin and DNA. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1702–1704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamper H. B., Hearst J. E. A topological model for transcription based on unwinding angle analysis of E. coli RNA polymerase binary, initiation and ternary complexes. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):81–90. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90092-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour D. S., Lis J. T. RNA polymerase II interacts with the promoter region of the noninduced hsp70 gene in Drosophila melanogaster cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3984–3989. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodo H. G., 3rd, Blatti S. P. Purification using polyethylenimine precipitation and low molecular weight subunit analyses of calf thymus and wheat germ DNA-dependent RNA polymerase II. Biochemistry. 1977 May 31;16(11):2334–2343. doi: 10.1021/bi00630a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huaifeng M., Hartmann G. R. RNA polymerase: interaction of RNA and rifampicin with the subassembly alpha 2 beta. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Mar 1;131(1):113–118. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07237.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen D. E., von Hippel P. H. DNA "melting" proteins. I. Effects of bovine pancreatic ribonuclease binding on the conformation and stability of DNA. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 25;251(22):7198–7214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadesch T. R., Chamberlin M. J. Studies of in vitro transcription by calf thymus RNA polymerase II using a novel duplex DNA template. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5286–5295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao S. Y., Calman A. F., Luciw P. A., Peterlin B. M. Anti-termination of transcription within the long terminal repeat of HIV-1 by tat gene product. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):489–493. doi: 10.1038/330489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola T. K., Kane C. M. Intrinsic sites of transcription termination and pausing in the c-myc gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4389–4394. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler C., Mi H., Hartman G. R. Competition of rifampicin with binding of substrate and RNA to RNA polymerase. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Mar 1;122(3):515–518. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06467.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krummel B., Chamberlin M. J. RNA chain initiation by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Structural transitions of the enzyme in early ternary complexes. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 19;28(19):7829–7842. doi: 10.1021/bi00445a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S. A., Krakow J. S. Studies on the product binding sites of the Azotobacter vinelandii ribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 25;250(8):2878–2884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S. A. The structure and mechanism of action of bacterial DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1981;38(3):165–210. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(81)90013-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J. R., Krummel B., Chamberlin M. J. Isolation and properties of transcribing ternary complexes of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase positioned at a single template base. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 5;196(1):85–100. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90512-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maderious A., Chen-Kiang S. Pausing and premature termination of human RNA polymerase II during transcription of adenovirus in vivo and in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5931–5935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mather E. L., Nelson K. J., Haimovich J., Perry R. P. Mode of regulation of immunoglobulin mu- and delta-chain expression varies during B-lymphocyte maturation. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):329–338. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90226-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui T., Segall J., Weil P. A., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors required for accurate initiation of transcription by purified RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11992–11996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melnikova A. F., Beabealashvilli R., Mirzabekov A. D. A study of unwinding of DNA and shielding of the DNA grooves by RNA polymerase by using methylation with dimethylsulphate. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Mar;84(1):301–309. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12169.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menendez M., Kolb A., Buc H. A new target for CRP action at the malT promoter. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4227–4234. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02771.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger W., Schickor P., Heumann H. A cinematographic view of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase translocation. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2745–2754. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08416.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappaport J., Reinberg D., Zandomeni R., Weinmann R. Purification and functional characterization of transcription factor SII from calf thymus. Role in RNA polymerase II elongation. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5227–5232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinberg D., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Purification and functional analysis of initiation factors IIB and IIE. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3310–3321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinberg D., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Transcription factor IIS stimulates elongation of RNA chains. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3331–3337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reines D., Chamberlin M. J., Kane C. M. Transcription elongation factor SII (TFIIS) enables RNA polymerase II to elongate through a block to transcription in a human gene in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10799–10809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reines D., Wells D., Chamberlin M. J., Kane C. M. Identification of intrinsic termination sites in vitro for RNA polymerase II within eukaryotic gene sequences. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 20;196(2):299–312. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90691-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. P. Attachment of nascent RNA molecules to superhelical DNA. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):565–579. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80087-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrer H., Zillig W. Studies on the transcription complex of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Oct 3;79(2):401–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11822.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels M., Fire A., Sharp P. A. Separation and characterization of factors mediating accurate transcription by RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14419–14427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SivaRaman L., Reines D., Kane C. M. Purified elongation factor SII is sufficient to promote read-through by purified RNA polymerase II at specific termination sites in the human histone H3.3 gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14554–14560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein P. J., Mildvan A. S. Magnetic resonance and kinetic studies of initiator-substrate distances on RNA polymerase from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 27;17(13):2675–2684. doi: 10.1021/bi00606a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A., Emery A. J., Jr, Sternberger N. Sedimentation properties of E. coli RNA polymerase and its complexes with polyuridylic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Sep 22;24(6):929–936. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90339-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A. Studies of the ribonucleic acid polymerase from Escherichia coli. V. Studies of its complexes with polyribonucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jan 25;244(2):425–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straney D. C., Crothers D. M. Intermediates in transcription initiation from the E. coli lac UV5 promoter. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):449–459. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90175-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straney S. B., Crothers D. M. Lac repressor is a transient gene-activating protein. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):699–707. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90093-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TISSIERES A., BOURGEOIS S., GROS F. Inhibition of RNA polymerase by RNA. J Mol Biol. 1963 Jul;7:100–103. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. W., Roeder R. G., Sawadogo M. Physical analysis of transcription preinitiation complex assembly on a class II gene promoter. Science. 1988 Sep 9;241(4871):1335–1338. doi: 10.1126/science.3413495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Hippel P. H., Bear D. G., Morgan W. D., McSwiggen J. A. Protein-nucleic acid interactions in transcription: a molecular analysis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:389–446. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.002133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]