Abstract
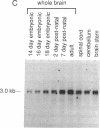
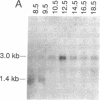
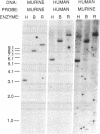
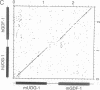
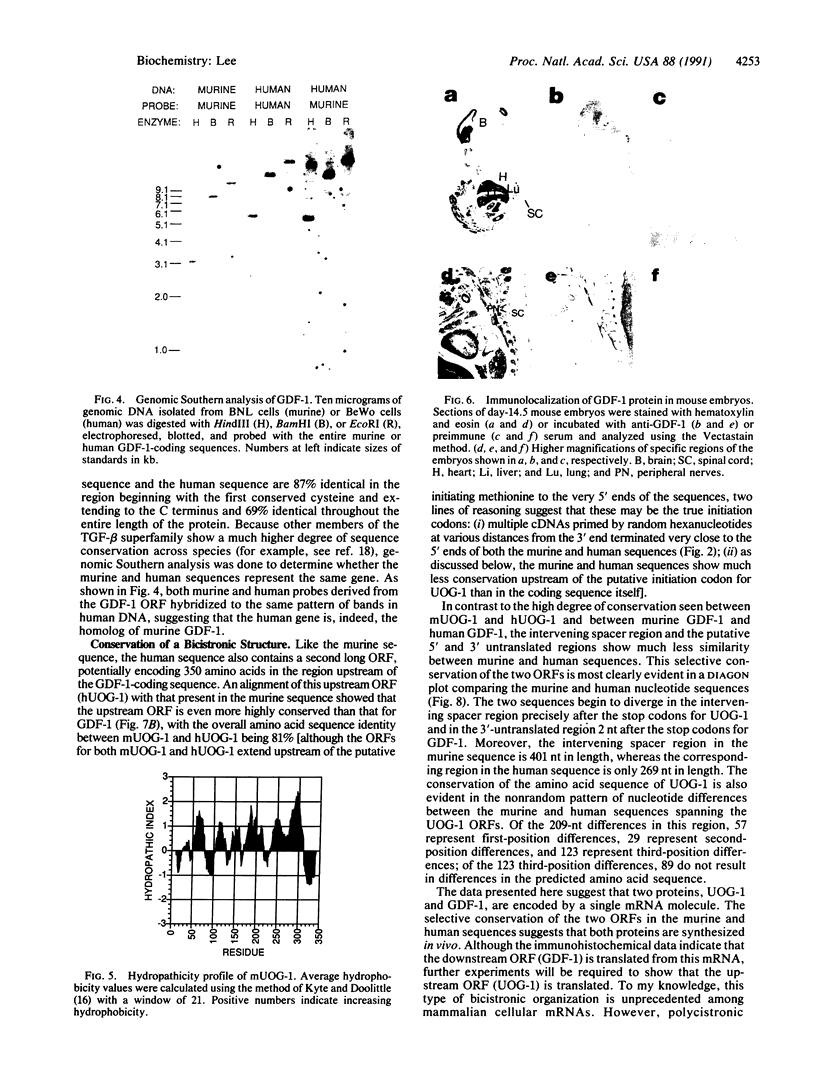
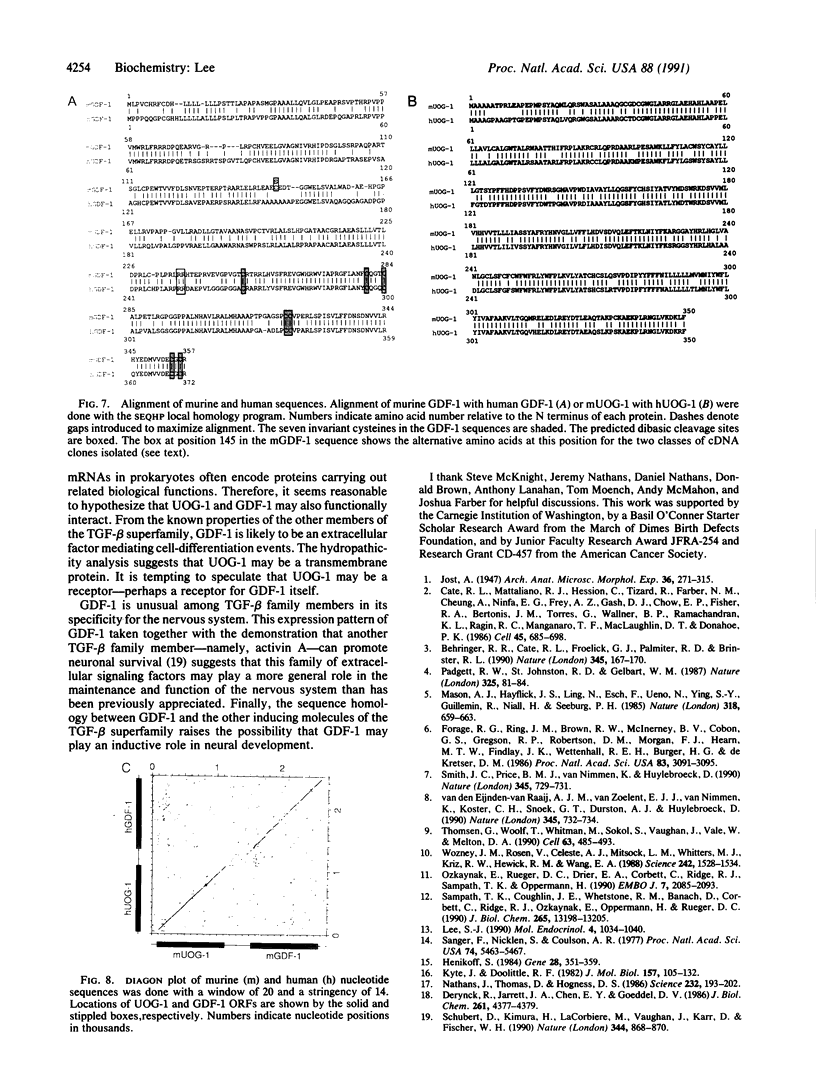
Growth/differentiation factor 1 (GDF-1) is a recently described member of the transforming growth factor beta superfamily isolated from a day-8.5 mouse embryo cDNA library. Northern (RNA) analysis of embryonic mRNA detected two GDF-1 transcripts [1.4 kilobases (kb) and 3.0 kb in length] displaying distinct temporal patterns of expression. Only the 3.0-kb transcript was detected in adult tissues, where its expression was restricted almost exclusively to the central nervous system. Comparison of murine and human brain cDNA sequences corresponding to the 3.0-kb transcript revealed high conservation of two nonoverlapping open reading frames with poor conservation of the intervening spacer region and the putative 5' and 3' untranslated sequences. By immunohistochemical analysis, the protein encoded by the downstream open reading frame (GDF-1) was detected exclusively in the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves in day-14.5 mouse embryos. The upstream open reading frame encodes a protein of unknown function containing multiple putative membrane-spanning domains. These findings raise the possibility that this mRNA may give rise to two different proteins.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behringer R. R., Cate R. L., Froelick G. J., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Abnormal sexual development in transgenic mice chronically expressing müllerian inhibiting substance. Nature. 1990 May 10;345(6271):167–170. doi: 10.1038/345167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cate R. L., Mattaliano R. J., Hession C., Tizard R., Farber N. M., Cheung A., Ninfa E. G., Frey A. Z., Gash D. J., Chow E. P. Isolation of the bovine and human genes for Müllerian inhibiting substance and expression of the human gene in animal cells. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):685–698. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90783-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Jarrett J. A., Chen E. Y., Goeddel D. V. The murine transforming growth factor-beta precursor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 5;261(10):4377–4379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forage R. G., Ring J. M., Brown R. W., McInerney B. V., Cobon G. S., Gregson R. P., Robertson D. M., Morgan F. J., Hearn M. T., Findlay J. K. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA species coding for the two subunits of inhibin from bovine follicular fluid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3091–3095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. J. Identification of a novel member (GDF-1) of the transforming growth factor-beta superfamily. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Jul;4(7):1034–1040. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-7-1034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason A. J., Hayflick J. S., Ling N., Esch F., Ueno N., Ying S. Y., Guillemin R., Niall H., Seeburg P. H. Complementary DNA sequences of ovarian follicular fluid inhibin show precursor structure and homology with transforming growth factor-beta. Nature. 1985 Dec 19;318(6047):659–663. doi: 10.1038/318659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathans J., Thomas D., Hogness D. S. Molecular genetics of human color vision: the genes encoding blue, green, and red pigments. Science. 1986 Apr 11;232(4747):193–202. doi: 10.1126/science.2937147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozkaynak E., Rueger D. C., Drier E. A., Corbett C., Ridge R. J., Sampath T. K., Oppermann H. OP-1 cDNA encodes an osteogenic protein in the TGF-beta family. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2085–2093. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07376.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. W., St Johnston R. D., Gelbart W. M. A transcript from a Drosophila pattern gene predicts a protein homologous to the transforming growth factor-beta family. Nature. 1987 Jan 1;325(6099):81–84. doi: 10.1038/325081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampath T. K., Coughlin J. E., Whetstone R. M., Banach D., Corbett C., Ridge R. J., Ozkaynak E., Oppermann H., Rueger D. C. Bovine osteogenic protein is composed of dimers of OP-1 and BMP-2A, two members of the transforming growth factor-beta superfamily. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):13198–13205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert D., Kimura H., LaCorbiere M., Vaughan J., Karr D., Fischer W. H. Activin is a nerve cell survival molecule. Nature. 1990 Apr 26;344(6269):868–870. doi: 10.1038/344868a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. C., Price B. M., Van Nimmen K., Huylebroeck D. Identification of a potent Xenopus mesoderm-inducing factor as a homologue of activin A. Nature. 1990 Jun 21;345(6277):729–731. doi: 10.1038/345729a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen G., Woolf T., Whitman M., Sokol S., Vaughan J., Vale W., Melton D. A. Activins are expressed early in Xenopus embryogenesis and can induce axial mesoderm and anterior structures. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):485–493. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90445-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozney J. M., Rosen V., Celeste A. J., Mitsock L. M., Whitters M. J., Kriz R. W., Hewick R. M., Wang E. A. Novel regulators of bone formation: molecular clones and activities. Science. 1988 Dec 16;242(4885):1528–1534. doi: 10.1126/science.3201241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Eijnden-Van Raaij A. J., van Zoelent E. J., van Nimmen K., Koster C. H., Snoek G. T., Durston A. J., Huylebroeck D. Activin-like factor from a Xenopus laevis cell line responsible for mesoderm induction. Nature. 1990 Jun 21;345(6277):732–734. doi: 10.1038/345732a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]