Abstract
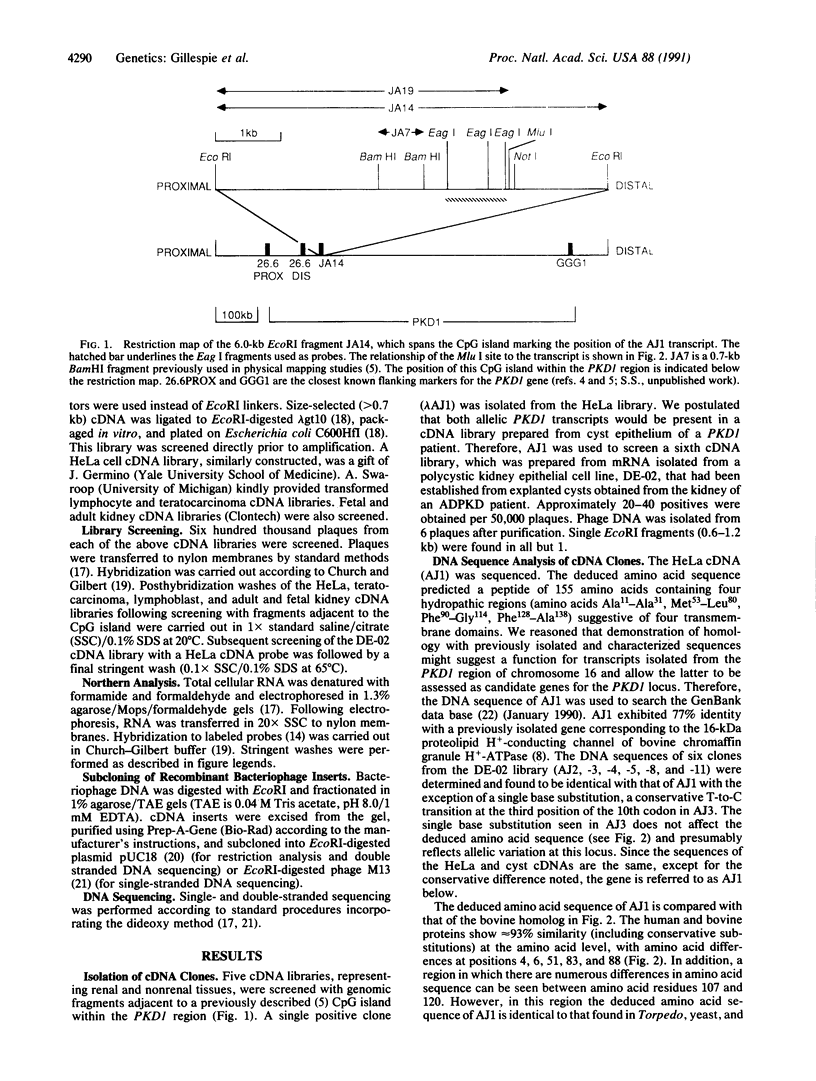
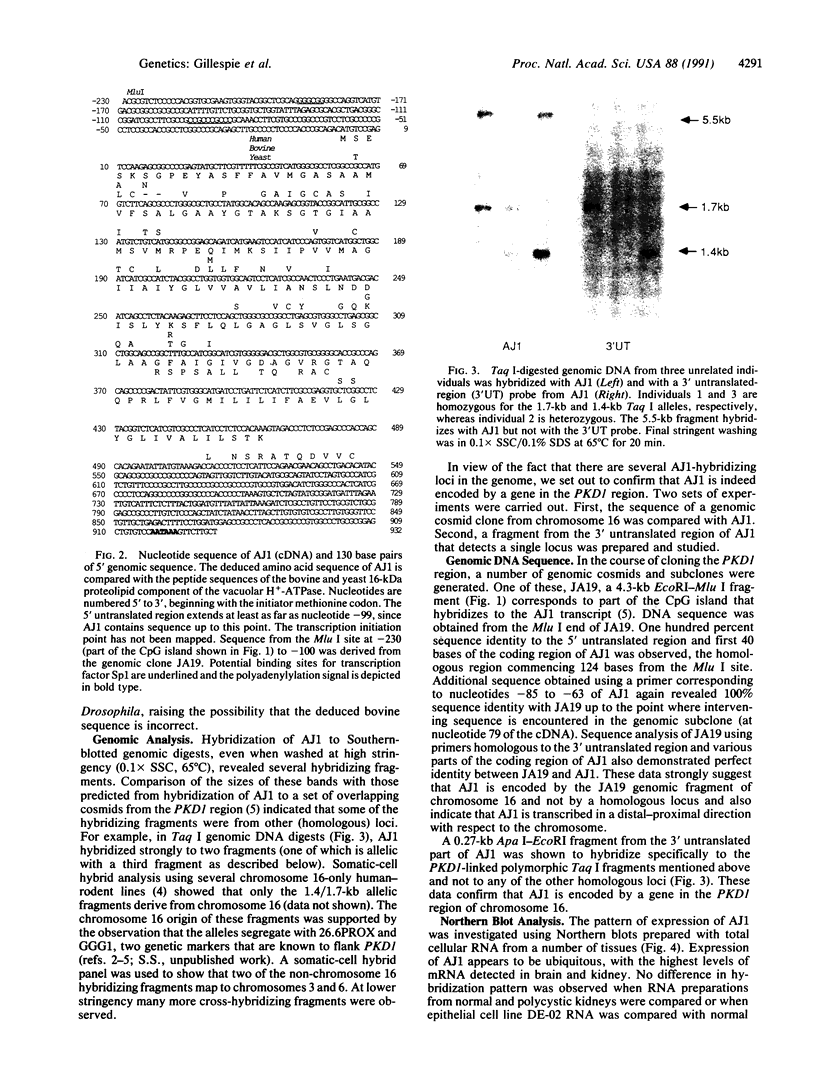
In an attempt to isolate candidate genes for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, a number of CpG-rich islands have been identified from a region defined genetically as the site of disease mutations. Genomic fragments adjacent to one of these islands were used to isolate cDNAs from both HeLa cells and cultured cystic epithelium that encode a 155-amino acid peptide having four putative transmembrane domains. The corresponding transcript was found in all tissues tested but was most abundant in brain and kidney. Potential control response elements were identified in the genomic region 5' to the initiation codon. The deduced amino acid sequence has 93% similarity to the 16-kDa proteolipid component that is believed to be part of the proton channel of the vacuolar H(+)-ATPase. Possible roles for a mutated proton channel in the pathogenesis of cystic disease were considered. However, sequencing of cDNAs corresponding to both alleles of an affected individual revealed no differences in the deduced amino acid sequence. Moreover, transcript size and abundance were not altered in cystic kidney.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alper S. L., Natale J., Gluck S., Lodish H. F., Brown D. Subtypes of intercalated cells in rat kidney collecting duct defined by antibodies against erythroid band 3 and renal vacuolar H+-ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5429–5433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilofsky H. S., Burks C. The GenBank genetic sequence data bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 11;16(5):1861–1863. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.1861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birman S., Meunier F. M., Lesbats B., Le Caer J. P., Rossier J., Israël M. A 15 kDa proteolipid found in mediatophore preparations from Torpedo electric organ presents high sequence homology with the bovine chromaffin granule protonophore. FEBS Lett. 1990 Feb 26;261(2):303–306. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80577-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplan M. J., Stow J. L., Newman A. P., Madri J., Anderson H. C., Farquhar M. G., Palade G. E., Jamieson J. D. Dependence on pH of polarized sorting of secreted proteins. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):632–635. doi: 10.1038/329632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carone F. A., Hollenberg P. F., Nakamura S., Punyarit P., Glogowski W., Flouret G. Tubular basement membrane change occurs pari passu with the development of cyst formation. Kidney Int. 1989 Apr;35(4):1034–1040. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dermietzel R., Völker M., Hwang T. K., Berzborn R. J., Meyer H. E. A 16 kDa protein co-isolating with gap junctions from brain tissue belonging to the class of proteolipids of the vacuolar H+-ATPases. FEBS Lett. 1989 Aug 14;253(1-2):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80917-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forgac M. Structure and function of vacuolar class of ATP-driven proton pumps. Physiol Rev. 1989 Jul;69(3):765–796. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1989.69.3.765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germino G. G., Barton N. J., Lamb J., Higgs D. R., Harris P., Xiao G. H., Scherer G., Nakamura Y., Reeders S. T. Identification of a locus which shows no genetic recombination with the autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease gene on chromosome 16. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 May;46(5):925–933. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie G. A., Germino G. G., Somlo S., Weinstat-Saslow D., Breuning M. H., Reeders S. T. Cosmid walking and chromosome jumping in the region of PKD1 reveal a locus duplication and three CpG islands. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):7071–7075. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.7071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch S., Strauss A., Masood K., Lee S., Sukhatme V., Gluck S. Isolation and sequence of a cDNA clone encoding the 31-kDa subunit of bovine kidney vacuolar H+-ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3004–3008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay S., Bird A. P. Use of restriction enzymes to detect potential gene sequences in mammalian DNA. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):336–338. doi: 10.1038/327336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Moriyama Y., Hulmes J. D., Pan Y. C., Nelson H., Nelson N. cDNA sequence encoding the 16-kDa proteolipid of chromaffin granules implies gene duplication in the evolution of H+-ATPases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5521–5524. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meagher L., McLean P., Finbow M. E. Sequence of a cDNA from Drosophila coding for the 16 kD proteolipid component of the vacuolar H(+)-ATPase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6712–6712. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I., Fuchs R., Helenius A. Acidification of the endocytic and exocytic pathways. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:663–700. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson H., Nelson N. The progenitor of ATP synthases was closely related to the current vacuolar H+-ATPase. FEBS Lett. 1989 Apr 10;247(1):147–153. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81259-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeders S. T., Breuning M. H., Davies K. E., Nicholls R. D., Jarman A. P., Higgs D. R., Pearson P. L., Weatherall D. J. A highly polymorphic DNA marker linked to adult polycystic kidney disease on chromosome 16. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):542–544. doi: 10.1038/317542a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeders S. T., Keith T., Green P., Germino G. G., Barton N. J., Lehmann O. J., Brown V. A., Phipps P., Morgan J., Bear J. C. Regional localization of the autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease locus. Genomics. 1988 Aug;3(2):150–155. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90146-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Hong G. F., Hill D. F., Petersen G. B. Nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage lambda DNA. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 25;162(4):729–773. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90546-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent C. A., Dunham I., Campbell R. D. Identification of multiple HTF-island associated genes in the human major histocompatibility complex class III region. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2305–2312. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08357.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull M. M., Pugh D. G., Lingrel J. B. The human Na, K-ATPase alpha 1 gene: characterization of the 5'-flanking region and identification of a restriction fragment length polymorphism. Genomics. 1990 Mar;6(3):451–460. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90475-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spies T., Bresnahan M., Strominger J. L. Human major histocompatibility complex contains a minimum of 19 genes between the complement cluster and HLA-B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8955–8958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson P. D., Sherwood A. C., Palla K., Du J., Watson R., Norman J. T. Reversed polarity of Na(+) -K(+) -ATPase: mislocation to apical plasma membranes in polycystic kidney disease epithelia. Am J Physiol. 1991 Mar;260(3 Pt 2):F420–F430. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.260.3.F420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]